Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Syllabus - IInd Sem Power Electronics
Hochgeladen von
Umashankar VermaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Syllabus - IInd Sem Power Electronics
Hochgeladen von
Umashankar VermaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
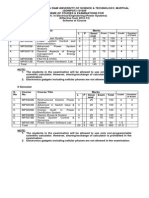
Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai
SCHEME OF EXAMINATION
M.E. (POWER ELECTRONICS) in the Department of Electrical Engg.
IInd SEMESTER
S
N
Board of
study
Subject
code
Subject Name
Periods per
week
Scheme of exam
Total
Marks
Credit
L+(T+P)
2
L T P
Theory/Practical
ESE CT TA
1 Electrical Engg. 562211(24)
Switched mode Power
Conversion
3 1 - 100 20 20 140 4
2 Electrical Engg. 562212(24) Power Electronics Drives 3 1 - 100 20 20 140 4
3 Electrical Engg. 562213(24)
PWM Converters &
Applications
3 1 - 100 20 20 140 4
4 Electrical Engg. 559211(24) EHV AC & DC 3 1 - 100 20 20 140 4
5 Refer table 2 Elective 2 3 1 - 100 20 20 140 4
6 Electrical Engg. 562221(24) Power Modules Lab - - 3 75 - 75 150 2
7 Electrical Engg. 562222(24)
Power Electronics
Simulation Lab
- - 3 75 - 75 150 2
TOTAL 15 5 6 650 100 250 1000 24
L- Lecture, T- Tutorial, P- Practical, ESE- End Semester Examination,
CT - Class Test, TA- Teacher's Assessment.
Note : Duration of all theory papers will be of Three Hours.
Table 2
Elective 2
Board of Study Code Subject
Electrical Engg. 562231(24) Fuzzy Systems
Electrical Engg. 562232(24)
Optimization Techniques
Note (1) 1/4th of total strength of students subject to minimum of twenty students is required to offer an
elective in the college in a Particular academic session .
Note (2) Choice of elective course once made for an examination cannot be changed in future
examinations.
Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai
Semester: M. E. II Branch: Electrical Engg.
Subject: Switched Mode Power Conversion Code: 562211 (24)
Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Tutorial Periods: 12
Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100
Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02
Unit :I
Reactive Elements in Power Electronic Systems, Design of inductor, Design of transformer, Capacitors for
power electronic applications.
Unit :II
Basic concepts of Switched Mode power converters, DC-DC converters Characteristics, constituent
elements, operating principles.
Unit : III
Steady state analysis, stress and sizing of elements, control methods, duty ratio, current programmed,
frequency programmed and sliding mode control, Dynamic analysis and frequency domain models.
Unit :IV
Classification of resonant converters, Basic resonant circuit concepts, Load resonant converters, Resonant
switch converters, Zero voltage switching.
Unit :V
Design of feed back compensators, unity power factor rectifiers, resistor emulation principle and
applications to rectifiers.
Reference Book
1. Switched Mode Power Conversion, Course Notes, CCE, IISc, 2004.
2. Issa Batarseh, Power Electronic Circuits, John Wiley, 2004.
3. Philip T Krein, Elements of Power Electronics ,Oxford Press,1997.
Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai
Semester: M. E. II Branch: Electrical Engg.
Subject: Power Electronics Drives Code: 562212 (24)
Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Tutorial Periods: 12
Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100
Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02
Unit :I
Basic power electronic drive system, components. Different types of loads, shaft-load coupling systems.
Stability of power electronic drive.
Unit :II
Conventional methods of D.C.motor speed control, single phase and three phase converter fed D.C motor
drive. Power factor improvement techniques, four quadrant operation.
Unit :III
Chopper fed drives, input filter design. Step-up chopper for photovoltaic systems. Braking and speed
reversal of DC motor drives using choppers, multiphase choppers.
Unit :IV
Conventional methods of induction motor speed control.. Solid state controllers for Stator voltage control,
soft starting of induction motors, Rotor side speed control of wound rotor induction motors. Voltage source
and Current source inverter fed induction motor drives.
Unit :V
Speed control of synchronous motors, field oriented control, load commutated inverter drives, switched
reluctance motors and permanent magnet motor drives.
Reference Book
1. P.C Sen, Thyristor DC Drives, John wiely and sons, New York, 1981.
2. R.Krishnan, Electric Motor Drives Modeling, Analysis and Control, Prentice-Hall of India Pvt Ltd., New
Delhi, 2003.
3. Bimal K.Bose, Modern Power Electronics and AC Drives, Pearson Education (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.,
New Delhi, 2003.
Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai
Semester: M. E. II Branch: Electrical Engg.
Subject: PWM Converters And Applications Code: 562213 (24)
Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Tutorial Periods: 12
Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100
Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02
Unit :I
AC/DC and DC/AC power conversion, overview of applications of voltage source converters, pulse
modulation techniques for bridge converters.
Unit :II
Bus clamping PWM, space vector based PWM, advanced PWM techniques, practical devices in converter;
calculation of switching and conduction losses.
Unit :III
Compensation for dead time and DC voltage regulation; dynamic model of a PWM converter, multilevel
converters; constant V/F induction motor drives.
Unit :IV
Estimation of current ripple and torque ripple in inverter fed drives; line side converters with power factor
compensation.
Unit :V
Active power filtering, reactive power compensation; harmonic current compensation.
Reference Book
1. Mohan, Undeland and Robbins, Power Electronics; Converters, Applications and Design,John Wiley
and Sons,2nd edition , 1995.
2. Erickson R W, Fundamentals of Power Electronics, Chapman and Hall, 2001.
3. Vithyathil J,Power Electronics: Principles and Applications , McGraw Hill, 1995.
Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai
Semester: M. E. II Branch: Electrical Engg.
Subject: EHV-AC&DC Code: 559211 (24)
Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Tutorial Periods: 12
Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100
Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02
UNIT-1
Sequential impedances of AC systems EHVAC transmission over voltages, insulation design of lightning
and switching over voltages, High voltage testing of AC equipments, Reactive Power compensation of
EHV AC lines.
UNIT-2
DC Power Transmission Technology: Application of DC Transmission, Description of DC Transmission
System, Planning for HVDC Transmission, Modern Trends in DC Transmission, Thyristor Device, Thyristor
Valve, Valve Tests, Recent Trends in valves. Comparison of EHV AC & DC transmission.
UNIT-3
HVDC Converters: Pulse Number, Choice of Converter Configuration, Simplified Analysis of Graetz
Circuit, Converter Bridge Characteristics. Characteristics of a Twelve Pulse Converter, Detailed Analysis of
Converters
HVDC System Control: Principal of DC Link Control, Converter Control Characteristics, System Control
Hierarchy, Firing Angle Control, Current and Extinction Angle Control, Starting and Stopping of DC Link,
Power Control, Higher Level Controllers, Telecommunication Requirements
UNIT-4
Converter Faults and Protection: Converter Faults , Protection Against Overcurrents, Over voltages in a
Converter Station , Surge Arresters, Protection Against Over voltages.
Smoothing Reactor and DC Line: Smoothing Reactors, DC Line, Transient over Voltages In DC Line,
Protection of DC Line, DC Breakers, Monopolar Operation, Effects of Proximity of AC and DC
Transmission Lines
UNIT-5
Reactive Power Control: Reactive Power Requirements in Steady State, Sources of Reactive Power,
Static Var Systems, Reactive Power Control during Transients
Harmonics and Filters: Generation of Harmonics, Design of AC Filters, DC Filters, Carrier Frequency and
RI Noise
Text:
1. HVDC Power Transmission System: K.R. Padiyar , Wiley Eastern Limited.
Reference:
1. Power System Stability and Control by Prabha Kundur- EPRI. Mc Graw Hill Inc.
Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai
Semester: M. E. II Branch: Electrical Engg.
Subject: Fuzzy System Code: 562231 (24)
Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Tutorial Periods: 12
Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100
Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02
Unit :I
Different faces of imprecision inexactness, Ambiguity, Undecidability, Fuzziness and certainty,
Probability and fuzzy logic, Intelligent systems.
Unit :II
Fuzzy sets and crisp sets - Intersections of Fuzzy sets, Union of Fuzzy sets, the complement of Fuzzy
sets.
Unit :III
Fuzzy reasoning - Linguistic variables, Fuzzy propositions, Fuzzy compositional rules of inference-
Methods of decompositions, Defuzzification.
Unit :IV
Methodology of fuzzy design - Direct & Indirect methods with single and multiple experts, Adaptive fuzzy
control, Rule base design using dynamic response.
Unit :V
Fuzzy logic applications to engineering, Fuzzy decision making, Neuro-Fuzzy systems, Fuzzy Genetic
Algorithms.
Reference Book
1. Zimmermann, H.J., Fuzzy set theory and its applications, Allied publishers limited, Madras,2001
2. Klir, G.J., and Folge., T., Fuzzy sets, uncertainty and information, PHI, New Delhi,1997.
3. EarlCox,,The Fuzzy Systems Handbook, AP professional Cambridge, MA 02139, 1998.
Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai
Semester: M. E. II Branch: Electrical Engg.
Subject: Optimization Techniques Code: 562232 (24)
Total Theory Periods: 40 Total Tutorial Periods: 12
Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 100
Minimum number of class test to be conducted: 02
Unit :I
Linear programming formulation-Graphical and simplex methods-Big-M method-Two phase method-Dual
simplex method-Primal Dual problems.
Unit :II
Unconstrained one dimensional optimization techniques -Necessary and sufficient conditions Unrestricted
search methods-Fibonacci and golden section method- Quadratic Interpolation methods, cubic
interpolation and direct root methods.
Unit :III
Unconstrained n dimensional optimization techniques direct search methods Random search pattern
search and Rosen broochs hill claiming method- Descent methods- Steepest descent, conjugate gradient,
quasi -Newton method.
Unit :IV
Constrained optimization Techniques- Necessary and sufficient conditions Equality and inequality
constraints-Kuhn-Tucker conditions-Gradient projection method-cutting plane method- penalty function
method.
Unit :V
Dynamic programming- principle of optimality- recursive equation approach- application to shortest route,
cargo-loading, allocation and production schedule problems.
Reference Book
1. Rao,S.S.,Optimization :Theory and Application Wiley Eastern Press, 2nd edition, 1984.
2. Taha,H.A., Operations Research An Introduction, Prentice Hall of India,2003.
3. Fox, R.L.,Optimization methods for Engineering Design, Addition Welsey, 1971.
Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai
POWER MODULES LABORATORY
Semester: M. E. II Branch: Electrical Engineering
Subject: Power Modules Laboratory Code: 562221 (24)
Total Practical Periods: 40
Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 75
Development of various configurations of power modules using SCRs, IGBTs, power transistors
and power MOSFETs. Practical converter design considerations- Snubber design, gate and base
drive circuits.
DC to DC converters of various configurations using SCRs, IGBTs, power transistors and power
MOSFETs.
DC to AC converters of various configurations using SCRs, IGBTs, power transistors and power
MOSFETs.
AC to AC converters of various configurations using SCRs, IGBTs, power transistors and power
MOSFETs..
Practical implementation of control techniques for voltage control, speed control and harmonic
minimization.
Reference Book
1. Ned Mohan, Undeland and Robbin, Power Electronics: converters, Application and design, John
Wileyand sons.Inc, Newyork, 2002.
2. M.H. Rashid, Power Electronics Handbook, Elseiver Press, 2003.
3. John D. Lenk ,Simplified Design of Switching Power Supplies, Butterworth-Heinemann, 1996.
Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai
Semester: M. E. I Branch: Electrical Engineering
Subject: Power Electronics Simulation Lab Code: 562222 (24)
Total Practical Periods: 40
Total Marks in End Semester Exam. : 75
1. Solution of transcendental equation by numerical techniques.
2. Computing the conduction angle for selective reduction of harmonics by Newton Raphson method.
3. Solution of Matrices using Runge Kutta method.
4. Simulation of Solid State Circuits by PSPICE / MATLAB & SIMULINK.
5. Simulation of Controlled rectifiers by PSPICE / MATLAB & SIMULINK.
6. Simulation of Diode rectifiers, using PSPICE / MATLAB & SIMULINK.
7. Simulation of AC voltage controllers using PSPICE / MATLAB & SIMULINK.
8. Simulation of DC voltage controllers using PSPICE / MATLAB & SIMULINK.
9. Simulation of speed control schemes for DC and AC motors.
10. Mathematical modeling of Power Electronic Systems.
References
1. Rashid, M.H.,"SPICE for Power Electronics and Electric Power". Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 1993.
2. Rashid,M.H.,"SPICE for circuits and electronics using PSPICE", Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 1995.
3. Ned Mohan, "Power Electronics, Computer Simulation Analysis and Education using PSPICE",
Minnesota Power Electronics Research and Education, USA, 1992
4. Giuseppa Mossobreio, "Semiconductor Device Modelling with SPICE", McGraw Hill Inc, New York, 1993
5. Bimal K.Bose, "Power Electronics and Variable Frequency Drives", IEEE Press, New Jersey, 1996.
6. Chee-Mun-Ong,"Dynamic simulation of Electric Machinery using MATLAB/SIMULINK", Prentice Hall
PTR, New Jersey, 1998.
7. "The PSPICE User's Guide", Math works Inc, 1994.
8. "The SIMULINK User's Guide", Math works Inc, 1994.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiDokument10 SeitenChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiShoaib KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Sem ElectricalDokument15 Seiten6th Sem Electricalaki007guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6THDokument19 Seiten6THPiyush KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- M Tech EEE IInd Sem - SyllabusDokument10 SeitenM Tech EEE IInd Sem - SyllabusAbhishek GahirwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus - B Tech 7th Semester For WebsiteDokument20 SeitenSyllabus - B Tech 7th Semester For WebsiteSurya ElectronicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7th Sem ElectricalDokument15 Seiten7th Sem ElectricalSourabh TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peca Course Policy PDFDokument9 SeitenPeca Course Policy PDFAayush NandolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Sem ME Elect PowerDokument10 Seiten2 Sem ME Elect PowerAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- SyllabusDokument8 SeitenSyllabusPrasanna Kumar VilluriNoch keine Bewertungen
- BE VII Sem Electrical Engg JEC JabalpurDokument13 SeitenBE VII Sem Electrical Engg JEC JabalpursvmgrgNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTech EE Power Common Syllabus 10.04.14!2!2Dokument22 SeitenMTech EE Power Common Syllabus 10.04.14!2!2alfred_googleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semester 2 SyllabusDokument9 SeitenSemester 2 SyllabusMohammed KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.tech (PE) Syllabus2014Dokument52 SeitenM.tech (PE) Syllabus2014shashi_2384Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai: M.E. in Power Systems EngineeringDokument10 SeitenChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai: M.E. in Power Systems EngineeringVishal DibyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IV EEE Final 5 Units COURSE - OVERVIEWDokument81 SeitenIV EEE Final 5 Units COURSE - OVERVIEWVinamra GovilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3RDDokument14 Seiten3RDPiyush KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To PE L1Dokument29 SeitenIntroduction To PE L1Subhash MurkuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8THDokument11 Seiten8THPiyush KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE593Dokument4 SeitenEE593hassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electri Sem 8Dokument4 SeitenElectri Sem 8Ajeet KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 27 ML839 Power ElectronicsDokument2 Seiten27 ML839 Power Electronicsjimmy jimenez barriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10ec73 Power Electronics Vtu SyllabusDokument2 Seiten10ec73 Power Electronics Vtu SyllabusYaichenbaPebamNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE Power Generation Systems DesignDokument32 SeitenEE Power Generation Systems DesignPARTH DAVENoch keine Bewertungen
- B.tech (EE) 5th & 6th SemDokument23 SeitenB.tech (EE) 5th & 6th SemAdan HoodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.Tech PE&D Oct8 2013 PDFDokument16 SeitenM.Tech PE&D Oct8 2013 PDFamn04febNoch keine Bewertungen
- EA6210 Protection and Switchgear Lab GuideDokument5 SeitenEA6210 Protection and Switchgear Lab GuideAvi PokiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Code-Subject Name - Power Quality Improvement Programme: B.Tech - EEDokument2 SeitenSubject Code-Subject Name - Power Quality Improvement Programme: B.Tech - EEDharmdasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUE ML839 Power ElectronicsDokument2 SeitenNUE ML839 Power Electronicsjimmy jimenez barriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE001 SyllabusDokument2 SeitenEE001 SyllabusAditya YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical New SyallabusDokument65 SeitenElectrical New SyallabusSuraj KanojiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE-368 Power Electronics CourseDokument2 SeitenEE-368 Power Electronics Coursebilal nagoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.Tech Course Structure and Syllabus for Power EngineeringDokument14 SeitenM.Tech Course Structure and Syllabus for Power EngineeringcharinathrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 FullDokument8 Seiten2 FullDhaval MerNoch keine Bewertungen
- BE Electrical Sem 7-8 SyllabusDokument37 SeitenBE Electrical Sem 7-8 SyllabusManish Kumar BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVDC Transmission SystemsDokument2 SeitenHVDC Transmission Systemskmd_venkatsubbu0% (1)
- Elec 4614Dokument5 SeitenElec 4614ahmad16_ftua6999Noch keine Bewertungen
- BSC Electronics Syllabus Kerala UniversityDokument64 SeitenBSC Electronics Syllabus Kerala UniversityVarunRaj67% (3)
- M Tech EEE Ist Sem - SyllabusDokument10 SeitenM Tech EEE Ist Sem - SyllabusAbhishek GahirwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mehran University Power Systems CourseDokument7 SeitenMehran University Power Systems CourseHabiba AzeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be EeeDokument38 SeitenBe EeeGopinathblNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE May 04 2011Dokument40 SeitenEE May 04 2011ChandanUpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aps, PS, Pse, PSC, E&pe, Eps, Psc&a, Psc&ae PDFDokument16 SeitenAps, PS, Pse, PSC, E&pe, Eps, Psc&a, Psc&ae PDFKVSR SEKHARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsDokument2 SeitenSyllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsKalum ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Year BTech Electronics Syllabus 2022-23Dokument48 SeitenFinal Year BTech Electronics Syllabus 2022-23SiddhantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power SystemDokument22 SeitenPower SystemVenkat RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sem6 SyllabusDokument5 SeitenSem6 SyllabusSamsung TabletNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Tech Electrical Engineering 5th Sem CurriculumDokument19 SeitenB. Tech Electrical Engineering 5th Sem CurriculumBijayKumarDasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DTU..Power Electronics and Srives CurculemDokument2 SeitenDTU..Power Electronics and Srives Curculemsatish reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus For ElectDokument30 SeitenSyllabus For Elects MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE809 Course PlanDokument2 SeitenEE809 Course PlanAbhay JangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- SYLLABUSDokument2 SeitenSYLLABUSNithin KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBGS 7 Sem 20-21290521110137Dokument18 SeitenCBGS 7 Sem 20-21290521110137kushagra vashishthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M Tech Power System SyllabusDokument28 SeitenM Tech Power System Syllabusvaibhav_yadav798Noch keine Bewertungen
- Converter-Based Dynamics and Control of Modern Power SystemsVon EverandConverter-Based Dynamics and Control of Modern Power SystemsBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Computer Methods in Power Systems Analysis with MATLABVon EverandComputer Methods in Power Systems Analysis with MATLABNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control of Power Electronic Converters and Systems: Volume 1Von EverandControl of Power Electronic Converters and Systems: Volume 1Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlVon EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Lali SciDokument12 SeitenLali SciUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To SociologyDokument10 SeitenAn Introduction To SociologyDrjKmrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument1 SeitePresentation 1Umashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Lab ManualDokument49 SeitenAnalog Lab ManualUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro and Small Enterprises PolicyDokument11 SeitenMicro and Small Enterprises PolicyUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BastarDokument4 SeitenBastarUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Lab ManualDokument60 SeitenAnalog Lab ManualUmashankar Verma100% (1)
- Basic Electronics CseDokument2 SeitenBasic Electronics CseUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - SCILAB WorkshopDokument8 Seiten1 - SCILAB WorkshopUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agroand Food Processing Policy 2012 ChhattisgarhDokument12 SeitenAgroand Food Processing Policy 2012 ChhattisgarhUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Model QuestionsDokument10 SeitenElectronics Model QuestionsUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn Matl 1MATLAB BASICSDokument3 SeitenLearn Matl 1MATLAB BASICSUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - SCILAB WorkshopDokument8 Seiten1 - SCILAB WorkshopUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and Digital Simulation of DPFC System using Matlab SimulinkDokument5 SeitenModeling and Digital Simulation of DPFC System using Matlab SimulinkUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic ElexDokument160 SeitenBasic ElexUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Zone ConversionDokument3 SeitenTime Zone ConversionUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important TreatysDokument2 SeitenImportant TreatysUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Dates of World HistoryDokument7 SeitenImportant Dates of World HistoryUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokument593 SeitenHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- MadhviDokument73 SeitenMadhviUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Details of AdvertisementDokument4 SeitenDetails of AdvertisementUmashankar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Theory of MatterDokument9 SeitenElectric Theory of Matteralefs42296Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2ED Advanced Math William Guo ToC RefDokument11 Seiten2ED Advanced Math William Guo ToC RefOliver Henry CamonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- US Army Radio Wave Propagation and AntennasDokument186 SeitenUS Army Radio Wave Propagation and Antennaswa4gvt5044100% (1)
- Activated Carbon ASTM Test PackageDokument3 SeitenActivated Carbon ASTM Test PackageHarizal HamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5A: Term Distribution of Course: ST STDokument3 SeitenForm 5A: Term Distribution of Course: ST STFrances TangubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Craig Vaughan CHPTR 08Dokument45 SeitenCraig Vaughan CHPTR 08Alionk GaaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- FBC Boiler and Auxiliary EquipmentDokument17 SeitenFBC Boiler and Auxiliary EquipmentyogacruiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychrometric Charts (Humidity Chart)Dokument7 SeitenPsychrometric Charts (Humidity Chart)ccami709Noch keine Bewertungen
- Do You Supply Similar Materials?: SAE J1392 Grade 070ZL Hot-RolledDokument4 SeitenDo You Supply Similar Materials?: SAE J1392 Grade 070ZL Hot-RolledALEX MURPHYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw Jack Mechanism and Types in 40 CharactersDokument14 SeitenScrew Jack Mechanism and Types in 40 CharactersfadyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improvements in The Design of Winch: A ReviewDokument5 SeitenImprovements in The Design of Winch: A ReviewIJARTETNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid-base equilibria conceptsDokument2 SeitenAcid-base equilibria conceptsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasonic Testing of Materials 133Dokument1 SeiteUltrasonic Testing of Materials 133joNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics I Lab #3 Wheatstone Bridge CircuitDokument4 SeitenElectronics I Lab #3 Wheatstone Bridge Circuitmlj8753Noch keine Bewertungen
- CapsuleDokument7 SeitenCapsuleNouman Khan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ULAS Sci8Q3 WK 5 6Dokument10 SeitenULAS Sci8Q3 WK 5 6Joan MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tips and Tricks HPLC TroubleshootingDokument7 SeitenTips and Tricks HPLC TroubleshootingFelipe MonteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGS Annual 2019 Form V Mathematics Advanced Multiple ChoiceDokument36 SeitenSGS Annual 2019 Form V Mathematics Advanced Multiple ChoiceDog DogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics7c Fa00 mt1 Packard ExamDokument2 SeitenPhysics7c Fa00 mt1 Packard ExamfrankongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retainingwall bs8110Dokument11 SeitenRetainingwall bs8110unionewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab de Mosfet PDFDokument24 SeitenLab de Mosfet PDFLeslye Flores SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHA6113 Lab Group 8 Activity 3Dokument6 SeitenPHA6113 Lab Group 8 Activity 3Ray Stephen SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph of ProjectileDokument9 SeitenGraph of ProjectileMd AzharuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protective TextilesDokument6 SeitenProtective TextilesKhubab ShakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeigerDokument7 SeitenGeigerHyamy Julian Evliro100% (1)
- Royal College Term Test Papers 2020 Maths English MediumDokument12 SeitenRoyal College Term Test Papers 2020 Maths English MediumSithmi HerathNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0521138175Dokument191 Seiten0521138175Mohamed Arbi Ben Younes100% (4)
- Earth Air Heat Exchanger PerformanceDokument4 SeitenEarth Air Heat Exchanger Performanceviraj shettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridgmanita PDFDokument2 SeitenBridgmanita PDFAnibal Urango AlcantaraNoch keine Bewertungen