Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cam Profile Analysis
Hochgeladen von
PremjeetSingh100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
155 Ansichten4 SeitenThis document will guide you through the analysis of simple cam profiles.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document will guide you through the analysis of simple cam profiles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
155 Ansichten4 SeitenCam Profile Analysis
Hochgeladen von
PremjeetSinghThis document will guide you through the analysis of simple cam profiles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
EXPERIMENT
AIM- Cam Profile Analysis (Graphical Method)
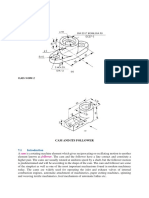
APPARATUS REQUIRED- Cam-Follower Mechanism
THEORY- A cam is a rotating machine element which gives reciprocating or
oscillating motion to another element known as follower. The cam and the follower
have a line contact and constitute a higher pair. The cams are usually rotated at
uniform speed by a shaft, but the follower motion is pre-determined and will be
according to the shape of the cam.
A cam profile is drawn to visualize the motion of the follower along the revolution
of cam.
In order to draw the cam profile for a radial cam, first of all the displacement
diagram for the given motion of the follower is drawn. Then by constructing the
follower in its proper position at each angular position, the profile of the working
surface of the cam is drawn. In constructing the cam profile, the principle of
kinematic inversion is used, i.e.the cam is imagined to be stationary and the
follower is allowed to rotate in the opposite direction to the cam rotation.
PROCEDURE-
The displacement diagram, as shown in Fig is drawn as discussed in the
following steps :
1. Draw a horizontal line AX= 360 to some suitable scale. On this line, mark AS=
60 to represent outstroke of the follower, ST= 30 to represent dwell, TP= 60 to
represent return stroke and PX= 210 to represent dwell.
2. Draw vertical line AY equal to the stroke of the follower (i.e.40 mm) and
complete the rectangle as shown in fig.
3. Divide the angular displacement during outstroke and return stroke into any
equal number of even parts (say six) and draw vertical lines through each point.
4. Since the follower moves with uniform velocity during outstroke and return
stroke, there-fore the displacement diagram consists of straight lines. Join AG and
HP.
5. The complete displacement diagram is shown by AGHPX in Fig.
DISPLACEMENT DIAGRAM
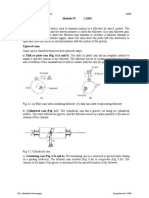
(a) Profile of the cam when the axis of follower passes through the axis of cam
shaft
The profile of the cam when the axis of the follower passes through the axis of
the cam shaft, as shown in Fig, is drawn as discussed in the following steps :
1. Draw a base circle with radius equal to the minimum radius of the cam (i.e.50
mm) with O as centre.
2. Since the axis of the follower passes through the axis of the cam shaft, therefore
mark trace point A, as shown in Fig.
3. From OA, mark angle AOS= 60 to represent outstroke, angle SOT= 30 to
represent dwell and angle TOP= 60 to represent return stroke.
4. Divide the angular displacements during outstroke and return stroke (i.e. angle
AOS and angle TOP) into the same number of equal even parts as in displacement
diagram.
5. Join the points 1, 2, 3 ...etc. and 0 , 1 , 2, 3 , ... etc. with centre O and
produce beyond the base circle as shown in Fig.
6. Now set off 1B, 2C, 3D... etc. and 0 H, 1 J... etc. from the displacement
diagram.
7. Join the points A, B, C,... M, N, P with a smooth curve. The curve AGHPA is
the complete profile of the cam.
CAM PROFILE
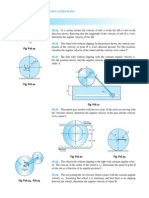
(b) Profile of the cam when the axis of the follower is offset by 20 mm from the
axis of the cam shaft
The profile of the cam when the axis of the follower is offset from the axis of
the cam shaft, as shown in Fig. 20.12, is drawn as discussed in the following
steps :
1. Draw a base circle with radius equal to the minimum radius of the cam (i.e.50
mm) with O as centre.
2. Draw the axis of the follower at a distance of 20 mm from the axis of the cam,
which intersects the base circle at A.
3. Join AO and draw an offset circle of radius 20 mm with centre O.
4. From OA, mark angle AOS= 60 to represent outstroke, angle SOT= 30 to
represent dwell and angle TOP= 60 to represent return stroke.
5. Divide the angular displacement during outstroke and return stroke (i.e.angle
AOS and angle TOP) into the same number of equal even parts as in displacement
diagram.
6. Now from the points 1, 2, 3 ... etc. and 0,1,2,3 ... etc. on the base circle,
draw tangents to the offset circle and produce these tangents beyond the base circle
as shown in Fig.
7. Now set off 1B, 2C, 3D... etc. and 0 H, 1 J... etc. from the displacement
diagram.
8. Join the points A, B, C...M, N, P with a smooth curve. The curve AGHPA is the
complete profile of the cam.
CAM PROFILE
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cams SynthesisDokument36 SeitenCams SynthesisShinchanus Monyetus GeblekusNoch keine Bewertungen
- CamDokument38 SeitenCamEbrahim HanashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Row-Column Designs: January 2001Dokument10 SeitenRow-Column Designs: January 2001Nanmita SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study On The Cam Profile Used in Various Manufacturing MachinesDokument15 SeitenStudy On The Cam Profile Used in Various Manufacturing MachinesHazrat BelalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cam ViceDokument50 SeitenCam ViceAakash Dindigul100% (1)
- Upsp A Decade AfterDokument11 SeitenUpsp A Decade AfterTheus LineusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction Paper "Advanced Water Treatment"Dokument1 SeiteReaction Paper "Advanced Water Treatment"CharisseElaineDionisioNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Read A Vernier CaliperDokument4 SeitenHow To Read A Vernier CaliperKarl Pepon AyalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of Globoidal Cam Index DriveDokument6 SeitenDesign and Analysis of Globoidal Cam Index DriveijsretNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wells O&M ManualDokument80 SeitenWells O&M Manualpatitay036817100% (1)
- TOR Only-East Indonesia Water SupplyDokument60 SeitenTOR Only-East Indonesia Water SupplyAgus NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asws Reverse Osmosis PlantDokument7 SeitenAsws Reverse Osmosis PlantEngenharia MecânicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Design For Microbial Treatment of Waste Water With Advanced Oxidation ProcessDokument46 SeitenPlant Design For Microbial Treatment of Waste Water With Advanced Oxidation ProcessFaisal MumtazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loading S Calculations by Dr. Ghaida Abu Rumman enDokument36 SeitenLoading S Calculations by Dr. Ghaida Abu Rumman ensauroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - Hydraulic StructureDokument60 SeitenChapter 5 - Hydraulic Structureummi surayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Manual For Small Wastewater Works 2009-2Dokument52 SeitenDesign Manual For Small Wastewater Works 2009-2VichekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Digestion Water TreatmentDokument2 SeitenAdvance Digestion Water TreatmentRashesh ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Water TreatmentDokument12 SeitenChemical Water TreatmentEderango JackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belts and RopesDokument43 SeitenBelts and RopesharishankarnadarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Measurement ManualDokument10 SeitenFlow Measurement ManualSHANKARNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnswersDokument5 SeitenAnswersDivyam ShreevatsalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressed Air JournalDokument12 SeitenCompressed Air JournalMark Centeno100% (1)
- High-Rate Wastewater Treatment by A Shaft-TypeDokument6 SeitenHigh-Rate Wastewater Treatment by A Shaft-TypeFabio NascimentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAD CAM Laboratory ManualDokument227 SeitenCAD CAM Laboratory ManualGopinath B L NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Exercise Problems CamsDokument36 Seiten3 Exercise Problems Camsparth raizadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vandayar Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument15 SeitenVandayar Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringJeeevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Work 1: SectioningDokument6 SeitenClass Work 1: Sectioningjoseph olojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GearsDokument37 SeitenGearsذوالفقار علي حسينNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cams Design & Kinematic Analysis: According To The Surface in ContactDokument13 SeitenCams Design & Kinematic Analysis: According To The Surface in ContactFaisal MaqsoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cam-And-Follower ppt-40-48Dokument9 SeitenCam-And-Follower ppt-40-48Lakshmi Narayana SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cam ProfileDokument7 SeitenCam ProfileAllen Generis0% (1)
- Tom-Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenTom-Assignment 1jamunaa83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cam DrawingDokument12 SeitenCam DrawingПараг ТамбеNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of CamsDokument18 SeitenClassification of CamsabasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME352 Lecture 4 CamsDokument43 SeitenME352 Lecture 4 CamsRaghav GaneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-4 CamsDokument37 SeitenUnit-4 CamsgauthamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caed ProblemsDokument20 SeitenCaed ProblemsPardeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME360 Chapter 5 CamsDokument44 SeitenME360 Chapter 5 CamsmangyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isometric DrawingDokument20 SeitenIsometric DrawingRamesh KomiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cam and Follower Part 1Dokument7 SeitenCam and Follower Part 1Safdar Ali NiaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Drawing: Construction of Ellipse ProcedureDokument11 SeitenEngineering Drawing: Construction of Ellipse Proceduredoss186Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit6 CAMSDokument27 SeitenUnit6 CAMSGokulraju RangasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Dokument6 SeitenME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Kumar RajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angles, Bearings and AzimuthDokument10 SeitenAngles, Bearings and AzimuthMarc Dared CagaoanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drawing Cam Displacement DiagramDokument2 SeitenDrawing Cam Displacement DiagramcisnarFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics of Machinery (EME 202) CamsDokument25 SeitenKinematics of Machinery (EME 202) Camshitaishi5599Noch keine Bewertungen
- DRG ch6 PDFDokument35 SeitenDRG ch6 PDFRamim AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAM Design: Cycloidal MotionDokument1 SeiteCAM Design: Cycloidal MotionallovidNoch keine Bewertungen
- TVKBPDokument13 SeitenTVKBPTommyVercettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- January 2013 An KeyDokument10 SeitenJanuary 2013 An KeysnvijayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1 EvolutesandinvolutesDokument15 SeitenPresentation 1 EvolutesandinvolutesPrajwal P Churi100% (1)
- OrbitDokument5 SeitenOrbitimranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parametric Spur GearDokument11 SeitenParametric Spur GearGoutam AcharjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDokument8 Seiten9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precalculo2 6Dokument77 SeitenPrecalculo2 6Javier Palomino GarateNoch keine Bewertungen
- SurveyingDokument63 SeitenSurveyingShazrin Yusof100% (1)
- Section of SolidsDokument12 SeitenSection of SolidsSriram JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question BankDokument7 SeitenQuestion BankmunirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Synthesis of Elliptical Gears Generated by Shaper-CuttersDokument9 SeitenThe Synthesis of Elliptical Gears Generated by Shaper-CuttersBen TearleNoch keine Bewertungen
- ES Parent Bulletin Vol#19 2012 May 25Dokument13 SeitenES Parent Bulletin Vol#19 2012 May 25International School ManilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affidavit of Co OwnershipDokument2 SeitenAffidavit of Co OwnershipEmer MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating A Research Space (C.A.R.S.) ModelDokument5 SeitenCreating A Research Space (C.A.R.S.) ModelNazwa MustikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABHA Coil ProportionsDokument5 SeitenABHA Coil ProportionsOctav OctavianNoch keine Bewertungen
- B-GL-385-009 Short Range Anti-Armour Weapon (Medium)Dokument171 SeitenB-GL-385-009 Short Range Anti-Armour Weapon (Medium)Jared A. Lang100% (1)
- Thermal Physics Lecture 1Dokument53 SeitenThermal Physics Lecture 1Swee Boon OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil List: Audi Front Axle DriveDokument35 SeitenOil List: Audi Front Axle DriveAska QianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linux ProgramDokument131 SeitenLinux ProgramsivashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ty Baf TaxationDokument4 SeitenTy Baf TaxationAkki GalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Sample 2 - Eoc and CrucibleDokument35 SeitenWork Sample 2 - Eoc and Crucibleapi-259791703Noch keine Bewertungen
- E-CRM Analytics The Role of Data Integra PDFDokument310 SeitenE-CRM Analytics The Role of Data Integra PDFJohn JiménezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LU 5.1 ElectrochemistryDokument32 SeitenLU 5.1 ElectrochemistryNurAkila Mohd YasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics 11 02566Dokument13 SeitenElectronics 11 02566卓七越Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The PCB Shelf Life Extending The Life of PCBsDokument9 SeitenWhat Is The PCB Shelf Life Extending The Life of PCBsjackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joomag 2020 06 12 27485398153Dokument2 SeitenJoomag 2020 06 12 27485398153Vincent Deodath Bang'araNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bagian AwalDokument17 SeitenBagian AwalCitra Monalisa LaoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSRM Ultima BrochureDokument2 SeitenBSRM Ultima BrochuresaifuzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB and Attendance PolicyDokument2 SeitenOB and Attendance PolicyAshna MeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scoring Rucric Lecture Eassess2.docx NewDokument6 SeitenScoring Rucric Lecture Eassess2.docx NewMaica Ann Joy SimbulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP Week 8Dokument4 SeitenLP Week 8WIBER ChapterLampungNoch keine Bewertungen
- EP07 Measuring Coefficient of Viscosity of Castor OilDokument2 SeitenEP07 Measuring Coefficient of Viscosity of Castor OilKw ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Doing Business in Grenada & OECSDokument14 SeitenGuidelines For Doing Business in Grenada & OECSCharcoals Caribbean GrillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Index: © Christopher Pitt 2018 C. Pitt, The Definitive Guide To AdonisjsDokument5 SeitenIndex: © Christopher Pitt 2018 C. Pitt, The Definitive Guide To AdonisjsZidi BoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- WSD M1a283 B50Dokument9 SeitenWSD M1a283 B50'Lampa'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Competency PDFDokument1 SeiteLearning Competency PDFLEOMAR PEUGALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ships Near A Rocky Coast With Awaiting Landing PartyDokument2 SeitenShips Near A Rocky Coast With Awaiting Landing PartyFouaAj1 FouaAj1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Education Deteriorating - EditedDokument3 SeitenPhilippine Education Deteriorating - EditedRukimi Yamato100% (1)
- Retail Branding and Store Loyalty - Analysis in The Context of Reciprocity, Store Accessibility, and Retail Formats (PDFDrive)Dokument197 SeitenRetail Branding and Store Loyalty - Analysis in The Context of Reciprocity, Store Accessibility, and Retail Formats (PDFDrive)Refu Se ShitNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB 60 Repair Parts PDFDokument282 SeitenTB 60 Repair Parts PDFvatasa100% (2)
- Pantone PDFDokument53 SeitenPantone PDF2dlmediaNoch keine Bewertungen