Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
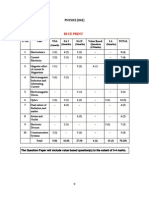
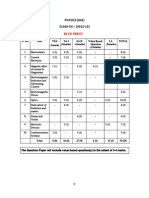
Upper Six 2013 STPM Physics 2 Trial Exam
Hochgeladen von
Ow Yu ZenOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Upper Six 2013 STPM Physics 2 Trial Exam
Hochgeladen von
Ow Yu ZenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Instructions to candidates:
DO NOT OPEN THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
Answer all questions in Section A. Marks will not be deducted for wrong answers. For each
question, four suggested answers are given. Choose the most suitable answer and mark the answer
on the obfective Answer Sheet provided.
Answer all questions in Section B. Write vour answers in the spaces provided.
Answer any two questions in Section C. All essential working should be shown. For numerical
answers, unit should be quoted wherever appropriate. Begin each answer on a fresh sheet of paper
and arrange vour answers in numerical order.Use the data from the data sheet in page 10 .
Jalues of constants are provided on page 10 in this question paper.
PAPER 2 (KERTAS 2)
960/2
One and a half hours (Satu jam sete ngah)
Name : Class :
confidential
960/1
Physics
1 hours 30 minutes
SEK. MEN. KEB. TINGGI MELAKA
(Malacca High School. Estd.1826)
Ke Arah Kecemerlangan Pendidikan
STPM 2013 TRIAL EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2
PHYSICS
Prepared by : Verified by :
Wee Choi Chiang Julie Yap Azmi Bin Sakmis
Guru Eizik PK Tingkatan 6
This question paper consists of 10 printed pages.
2
3
4
5
6
7
Section B 15 marks]
Answer all questions in this section in the space provided.
16. (a) Define capacitance of a capacitor. |1]
(b) Explain the effect of dielectric on the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitors. |2]
(c) An isolated charged parallel plates capacitor of capacitance 20.0 E is filled with a
dielectric of dielectric constant 10.0 and is charged by a battery of e.m.f. 12.0V as shown
in Eigure 1 below. The dielectric is then pulled out from the capacito r until half only half
of the space is filled with the dielectric as shown in Eigure 2.
(i) Calculate the new capacitance of the capacitor. |2]
(ii) Calculate the final potential difference across the capacitor. |2]
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Eigure 1
Eigure 2
8
17. (a) A sinusoidal voltage V 200 sin(100a t) is supplied to a pure resistance of 100 O.
(i) Calculate the root mean square current through the resistor. |2]
(ii) Calculate the average rate of heat dissipated in the resistor. |2]
(b) If the same voltage is supplied to a pure capacitor of capacitance 40.0 E,
(i) calculate the reactance of the capacitor. |2]
(ii) calculate the root mean square current through the capacitor. |2]
9
Section C 30 marks]
Answer ANY TWO QUESTION ONLY from this section in your own answer sheets.
18. (a) Explain what is meant by drift velocity of free electrons in a metal conductor. |1]
(b) (i) A potential difference of 2.00V is supplied to a constantan wire of l ength 60.0 cm and
diameter 0.400 mm. If the resistivity of constantan is 5.00x10
-7
Om and the density of free
electrons in constantan is 4.00x10
28
m
-3
, calculate the drift velocity of free electrons in the
constantan wire. |4]
(ii) Owing to heating effect, the temperature of the constantan wire increases, explain the
effect on the drift velocity of the free electrons. |2]
(c) In the circuit below, E
1
6.0 V, E
2
5.0 V, E
3
4.0 V, R
1
100 O and R
2
50 O
(i) Eind the current in each resistor. |6]
(ii) Calculate the potential difference between a and b. |2]
10
19. (a) Define magnetic flux density. |2]
(b) A charged particle travelling with a speed of 1.00x10
6
m/sec enters a magnetic field of 0.0500
T. The particle is deflected as shown in the diagram below, and travels in a circular path of
radius 20.0 cm.
(i) State whether the particle carries positive charge or negative charge. |1]
(ii) Determine the specific charge (ratio of q/m) for the particle. |3]
(ii) If an electric field is applied to the same region with the magnetic field, the charged
particle will travel through the region without any deflection. Determine the direction and
magnitude of the electric field. |3]
(c) (i) Account for the production of a Hall voltage when a thin strip of a metal conductor,
carrying a current, is placed in a magnetic field. |3]
(ii) A flat copper ribbon 0.330 mm thick carries a steady current of 50.0 A and is located in a
uniform magnetic field of 1.30 T directed perpendicular to the plane of the ribbon. If a Hall
voltage of 9.60 nV is measured across the ribbon, what is the charge density of the free
electrons? |3]
20. (a) Define magnetic flux linkage. |1]
(b) State the laws of electromagnetic induction. |2]
(c) A square coil of side 5.00 cm lies perpendicular to a magnetic field of magnetic flux density 4.0 T as
shown in the diagram below. The coil consists of 200 turns of wire and total resistance of 5.00 O.
(i) What is the magnetic flux linkage cutting the coil? |1]
If the coil is rotated about its axis of rotation through an angle of 90o in 0.200 seconds.
(ii) Calculate the magnitude of the average e.m.f. induced in the coil while i t is being rotated.
|2]
(iii) Calculate the magnitude of the induced current flowing in the coil. |1]
(iv) What is the direction of the induced current in the coil. Explain your answer qualitatively.
|3]
(v) Calculate the amount of heat dissipated in the coil. |1]
(vi) If the coil is rotated continuously with a frequency of 50 Hz, determine the root mean square
current produced in the coil. |4]
x x x x x x
x x x x x x
x x x x x x
x x x x x x
x x x
x x x
Axis of rotation
11
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Dovidovits - Geopolymer Chemistry and Applications PDFDokument33 SeitenDovidovits - Geopolymer Chemistry and Applications PDFdimas dibiantara0% (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Bewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (4)
- Unit 2 ReviewDokument3 SeitenUnit 2 ReviewGaurnett FlowersNoch keine Bewertungen
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Astm F 1140-07Dokument5 SeitenAstm F 1140-07jsiddh30100% (2)
- Physics Class 12th Board Question Bank PDFDokument743 SeitenPhysics Class 12th Board Question Bank PDFVineet sharma100% (1)
- Sspc-Pa Guide 3 PDFDokument16 SeitenSspc-Pa Guide 3 PDFvricardol100% (1)
- Physics Exam IdeaDokument419 SeitenPhysics Exam IdeaAditya50% (2)
- Xam Idea Previous Years Question Papers 2008-2012Dokument419 SeitenXam Idea Previous Years Question Papers 2008-2012Mohammed Farhad77% (13)
- Trial STPM Physics Term 2 - Module 1Dokument12 SeitenTrial STPM Physics Term 2 - Module 1annahiaz0% (1)
- Intro To Chem Short For NursingDokument22 SeitenIntro To Chem Short For Nursingakisah malinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 26 CombineDokument24 SeitenWorksheet 26 CombineCleo Poulos0% (1)
- PSPM 2 2015-16Dokument8 SeitenPSPM 2 2015-16Iain Choong WK100% (1)
- G-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2Dokument12 SeitenG-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2annahiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xtut2 2017 Solutions PDFDokument15 SeitenXtut2 2017 Solutions PDFadahrenelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Cbse Physics Sample Paper 2013 Model 1Dokument6 SeitenClass 12 Cbse Physics Sample Paper 2013 Model 1Sunaina RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics2015 16Dokument6 SeitenPhysics2015 16tranquil_452889939Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 5028461218105393490 PDFDokument596 Seiten1 5028461218105393490 PDFShailesh DholaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1ST Term Xii Physics 2021Dokument12 Seiten1ST Term Xii Physics 2021RiyazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Paper Physics PDFDokument4 Seiten12th Paper Physics PDFchopadetanushreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFDokument14 SeitenSpty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFyeateshwarriorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Without This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFDokument4 SeitenWithout This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFAmit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13122023013802physics Practice Paper 1Dokument8 Seiten13122023013802physics Practice Paper 1Srushti ChouguleNoch keine Bewertungen
- E2T2 PracticeDokument12 SeitenE2T2 PracticeAatishImrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- r5210205 Electromagnetic FieldsDokument1 Seiter5210205 Electromagnetic FieldsMicro EmissionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compact 1168571Dokument2 SeitenCompact 1168571deepak bamelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 BPT (12th) Physics Ashish Ranjan in Proofing 04-09-2015Dokument4 Seiten2 BPT (12th) Physics Ashish Ranjan in Proofing 04-09-2015RanveerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Q Paper HSC Apr 2021 Kubal AcademyDokument4 SeitenPhysics Q Paper HSC Apr 2021 Kubal AcademyRAVINDRA WAYKOLENoch keine Bewertungen
- Half Yearly Examination 2020 - Physics (Subjective Question Paper) XiiDokument2 SeitenHalf Yearly Examination 2020 - Physics (Subjective Question Paper) XiiAlok RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 'Sri Krishna Public School, Bistupur: This Question Paper Consists of 4 PagesDokument5 Seiten'Sri Krishna Public School, Bistupur: This Question Paper Consists of 4 Pagesdeua2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Physics FinalDokument2 SeitenApplied Physics FinalSabeeh HasnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- VII Phys 205 Final Winter2012 SolutionsDokument9 SeitenVII Phys 205 Final Winter2012 SolutionsJashan ThindNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC203-C Image Marked Image MarkedDokument2 SeitenEC203-C Image Marked Image MarkedManjunath BadigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 12Dokument6 SeitenPhysics 12satishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physic 12 Sample PaperDokument5 SeitenPhysic 12 Sample PaperDeep ChovatiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emf 3Dokument6 SeitenEmf 329viswa12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guess Paper Class - Xii Subject - PhysicsDokument5 SeitenGuess Paper Class - Xii Subject - PhysicsTanmay KarmakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys102 182 Final Exam Zero VersionDokument12 SeitenPhys102 182 Final Exam Zero VersionNano SuyatnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEET101 Basic Electrical Engg.-1Dokument2 SeitenBEET101 Basic Electrical Engg.-1mr.prashant.cseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emf 7Dokument8 SeitenEmf 729viswa12Noch keine Bewertungen
- BP&QP 1Dokument6 SeitenBP&QP 1Akash AchuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Set 10Dokument10 SeitenPhysics Set 10bijayakumal819Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2010 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Dokument30 SeitenCBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2010 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4zelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Test - Half Test - I: Topic: - NCERT BOOK-1Dokument4 SeitenPhysics Test - Half Test - I: Topic: - NCERT BOOK-1ChetanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Assignment 1Dokument3 SeitenClass Assignment 1chiragNoch keine Bewertungen
- ModelPapers MODELPAPER10 Physics12Dokument1 SeiteModelPapers MODELPAPER10 Physics12Maulik KarasaliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMK Mantin 2014Dokument10 SeitenSMK Mantin 2014LIM YANG SHIAN MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field TheoryDokument2 SeitenField TheoryPratyush DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Zimbabwe Department of Physics BSC Part I: PH103Dec 2010Dokument3 SeitenUniversity of Zimbabwe Department of Physics BSC Part I: PH103Dec 2010Shawn MoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 Electromagnetism Exam SolutionsDokument12 Seiten2020 Electromagnetism Exam SolutionsReacher ElliotNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS 12th Sci Prelim Question PaperDokument4 SeitenPHYSICS 12th Sci Prelim Question PaperAditya Deshmukh0% (1)
- 9397physics Paper 2 (2012) With SolutionsDokument5 Seiten9397physics Paper 2 (2012) With SolutionsdannycbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 6 Q.1. A Rectangular Coil, With Corners LabeledDokument2 SeitenTutorial 6 Q.1. A Rectangular Coil, With Corners LabeledJohn LionelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topper Sample Paper 2 Class XII-PhysicsDokument5 SeitenTopper Sample Paper 2 Class XII-PhysicsAbhishek RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Three Hours) : Sample Paper - 2011 Class - XII Subject - PhysicsDokument5 Seiten(Three Hours) : Sample Paper - 2011 Class - XII Subject - PhysicsValay DaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Most Imp Derivation and Long Answer Questions in Physics 1Dokument23 SeitenList of Most Imp Derivation and Long Answer Questions in Physics 1Aham GtyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS (Theory) : General InstructionsDokument5 SeitenPHYSICS (Theory) : General InstructionsKapil BakshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Con - LAbDokument1 SeiteModel Con - LAbOw Yu ZenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primavera P6Dokument29 SeitenPrimavera P6Ow Yu ZenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task Force Value Engineering: Section 1Dokument36 SeitenTask Force Value Engineering: Section 1Ow Yu ZenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task Force Value Engineering: Section 1Dokument36 SeitenTask Force Value Engineering: Section 1Ow Yu ZenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Guideline PDFDokument92 SeitenThesis Guideline PDFNadira NadieyraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP16 MasmaDokument28 SeitenHP16 MasmaAsyraf MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSMADokument100 SeitenMSMADante Lau Jing TeckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of Malaysia: Suruhanjaya Perkhidmatan Air NegaraDokument27 SeitenLaws of Malaysia: Suruhanjaya Perkhidmatan Air NegaraOw Yu ZenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class License Group Members:-: SHA Fatin OW RONDokument12 SeitenClass License Group Members:-: SHA Fatin OW RONOw Yu ZenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urban Drainage Hydraulic CalculationsDokument1 SeiteUrban Drainage Hydraulic CalculationsImran AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESB 2018 Abstract Proceedings 4Dokument1.099 SeitenESB 2018 Abstract Proceedings 4Alan PolancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wear in ChutesDokument17 SeitenWear in ChutesJDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective StressDokument25 SeitenEffective StressGungah SaileshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Porous Plates With Varying ViscosityDokument12 SeitenPorous Plates With Varying ViscosityMajid KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Heat Capacity Lab Report2Dokument6 SeitenSpecific Heat Capacity Lab Report2milayosores100% (2)
- Semiconductor - Experiment PDFDokument116 SeitenSemiconductor - Experiment PDFMuthu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiopenDokument4 SeitenDiopenademar john ZamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Number 2Dokument9 SeitenActivity Number 2Mariella SingsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDFDSEFDokument3 SeitenSDFDSEFpppppp5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sensitometry: Describing Photographic PerformanceDokument55 SeitenSensitometry: Describing Photographic PerformanceilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminium Etching MicroChemicals PDFDokument3 SeitenAluminium Etching MicroChemicals PDFDaniela Silva MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 43 1571743442 MethylRedIndicatorSolution-MSDSDokument6 Seiten43 1571743442 MethylRedIndicatorSolution-MSDSisyie jrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodictrendsinre ActivityDokument5 SeitenPeriodictrendsinre Activityapi-2441793080% (1)
- Laboratory Measurement of Capillary PressureDokument17 SeitenLaboratory Measurement of Capillary Pressureel hadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3102 Shade Matching in Aesthetic Dentistry From Past To Recent Advances PDFDokument9 Seiten3102 Shade Matching in Aesthetic Dentistry From Past To Recent Advances PDFsapnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- P-ToLUENESULFONIC ANHYDRIDE Ts2O From TsOH P2O5 Kieselguhr Then DCE Extraction EtcDokument3 SeitenP-ToLUENESULFONIC ANHYDRIDE Ts2O From TsOH P2O5 Kieselguhr Then DCE Extraction Etcfchem11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrothermal Synthesis of Hydroxy Sodalite Zeolite Membrane SeparationDokument8 SeitenHydrothermal Synthesis of Hydroxy Sodalite Zeolite Membrane Separationcelcenu100% (1)
- Optical Based Non Invasive Glucometer With IoTDokument3 SeitenOptical Based Non Invasive Glucometer With IoTSuwetha I GNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT 140Dokument13 SeitenRT 140Dmitrii Pustoshkin100% (1)
- N-Containing Secondary CompoundsDokument16 SeitenN-Containing Secondary CompoundsNasiha el KarimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zangar C Water Percolation 5 Water OcrDokument86 SeitenZangar C Water Percolation 5 Water Ocrreem.ranoom.moonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Skill NotesDokument46 SeitenPractical Skill NotesAli Ghasemi Koohi KheiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-6 ThermodynamicsDokument11 SeitenChapter-6 ThermodynamicsDaksh ChothaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch182 PDFDokument4 Seitench182 PDFabualamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM-4143 Slide Metoda EOR (Week IX)Dokument51 SeitenTM-4143 Slide Metoda EOR (Week IX)AwabNoch keine Bewertungen