Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Jsa Sample
Hochgeladen von
Achmad Djadjang0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
179 Ansichten4 SeitenJSA No. JSABuilder Sample Library - 4 (short) Job / Operation Title: Electric Arc Welding Date: Department / Division / Section: Facility Maintenance Analysis Reviewed By: Name Person 3 Person(s) Performing This Job: Name Person 1 Name Person 2 Supervisor: Name Person 1 Task / Step Potential Hazards Recommended Safe Job Procedures 1. Sign in and inspect arc welding equipment cables and connections; look for loose connections, frayed insulation on electrode holders and cables (see photo)
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenJSA No. JSABuilder Sample Library - 4 (short) Job / Operation Title: Electric Arc Welding Date: Department / Division / Section: Facility Maintenance Analysis Reviewed By: Name Person 3 Person(s) Performing This Job: Name Person 1 Name Person 2 Supervisor: Name Person 1 Task / Step Potential Hazards Recommended Safe Job Procedures 1. Sign in and inspect arc welding equipment cables and connections; look for loose connections, frayed insulation on electrode holders and cables (see photo)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
179 Ansichten4 SeitenJsa Sample
Hochgeladen von
Achmad DjadjangJSA No. JSABuilder Sample Library - 4 (short) Job / Operation Title: Electric Arc Welding Date: Department / Division / Section: Facility Maintenance Analysis Reviewed By: Name Person 3 Person(s) Performing This Job: Name Person 1 Name Person 2 Supervisor: Name Person 1 Task / Step Potential Hazards Recommended Safe Job Procedures 1. Sign in and inspect arc welding equipment cables and connections; look for loose connections, frayed insulation on electrode holders and cables (see photo)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS
JSA No. JSABuilder Sample Library - 4 (short)
Job/Operation Title:
Electric Arc Welding
Date:
Department/Division/Section:
Facility Maintenance
Analysis Developed By:
Name Person 2
Location(s):
Welding Shop
Analysis Reviewed By:
Name Person 3
Person(s) Performing This Job:
Name Person 1
Name Person 2
Supervisor:
Name Person 1
Job Start Date: Duration:
2 hours
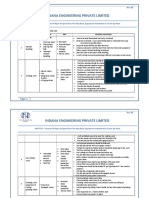
Task/Step Potential Hazards Recommended Safe Job Procedures
1. Sign in and inspect (Step 1) - Welding/Cutting/Burning
Equipment
- Wires, cables, hoses
- Before setting up the welding shop, visit the Admin desk
to sign in.
- Inspect arc welding equipment cables and connections;
look for loose connections, frayed insulation on electrode
holders and cables (see photo), make sure electrical
cables are dry (complete safety checklist).
Step 1 Image:
2. Steps 2 - 6 - x--- NA ---x Steps 2 - 6 have been removed to keep this sample to a
reasonable length.
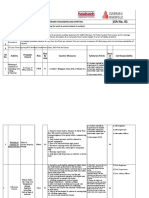
3. Perform the weld (Step 7) - Arc rays
- Combustible materials
- Electrical equipment
(transformers, switching gear,
breakers, high voltage lines)
- Ignitable materials and liquids
- Infrared (IR)
- Light (optical) radiation (i.e.
- User proper PPE (see photo).
- Follow manufacturer recommended procedures, lessons
learned and experience.
- If possible, position shelf so that head is not in fumes
while welding.
- If possible use sub arc process to minmimize light and
fumes, and/or minimize the production of welding fumes
by using the lowest acceptable amperage and holding the
JSA No: JSABuilder Sample Library - 4 (short) | Electric Arc Welding 1 of 4
welding operations, etc.).
- Repetitive motion or other
ergonomic concerns
- Rolling or pinching objects
- Sharp objects
- Slag splatter
- Sparks
- Ultraviolet (UV)
- WELDING FUMES AND GASES
- Welding/Cutting/Burning
Equipment
- Wires, cables, hoses
electrode perpendicular and as close to the
work surface and possible.
- Keep electrode moving. Tack as appropriate for project
and metal type.
- Finish the weld.
Step 3 Image:
4. Steps 8 - 9 - x--- NA ---x Steps 8 - 9 have been removed to keep this sample to a
reasonable length.
5. Remove excess slag from
welded material (Step 10)
- Electrical equipment
(transformers, switching gear,
breakers, high voltage lines)
- Hand tools
- metal chips
- Repetitive motion or other
ergonomic concerns
- Sharp objects
- Sparks
- Wires, cables, hoses
When welded material has cooled, use chipping hammer
or grinder to remove excess slag from weld (see photo).
Secure material to workbench with clamps as necessary,
before chipping. FACE SHIELD IS REQUIRED FOR THIS
ACTIVITY TO PROTECT FROM FLYING DEBRIS. Be
alert to fingers and pinch points and struck-by potential.
Step 5 Image:
JSA No: JSABuilder Sample Library - 4 (short) | Electric Arc Welding 2 of 4
6. Steps 11 - 12 - x--- NA ---x Steps 11 - 12 have been removed to keep this sample to
a reasonable length.
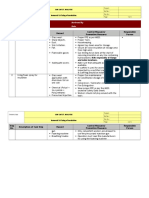
POTENTIAL HAZARDS OF THIS JOB
Physical Hazards Consequences
Combustible materials
Electrical equipment (transformers, switching gear,
breakers, high voltage lines)
Hand tools
hot electrodes
Ignitable materials and liquids
Inadequate lighting
Light (optical) radiation (i.e. welding operations,
etc.).
metal chips
Poor Housekeeping
Repetitive motion or other ergonomic concerns
Rolling or pinching objects
Sharp objects
Slag splatter
Sparks
Welding/Cutting/Burning Equipment
Wires, cables, hoses
x--- NA ---x
Awkward or static position
Cuts and abrasions
Electrocution or shock
Excessive lifting, twisting, pushing, pulling, reaching, or bending
Exposure (inhaling, swallowing, or absorbing) to harmful levels of gases,
vapors, aerosols, liquids, fumes, or dust)
Exposure to excessive light (welding)
Falling ( < 6 feet), tripping, or slipping
Injury caused by slip, trip or fall
Pinches
Slag splatter
Sparks
Struck by falling or flying object
Struck by uncontrolled pressure release
Thermal burns
Chemical Hazards Description/Health Hazards
WELDING FUMES AND GASES
()
Welding smoke is a mixture of very fine particles (fumes) and gases. Many of
the substances in welding smoke, such as chromium, nickel, arsenic,
asbestos, manganese, silica, beryllium, cadmium, nitrogen oxides,phosgene,
acrolein, fluorine compounds, carbon monoxide, cobalt, copper, lead, ozone,
selenium, and zinc can be extremely toxic.
Generally, welding fumes and gases come from:
- base material being welded or the fi ller material that is used;
JSA No: JSABuilder Sample Library - 4 (short) | Electric Arc Welding 3 of 4
- coatings and paints on the metal being welded, or coatings covering the
electrode;
- shielding gases supplied from cylinders;
The health effects of welding exposures are difficult to list, because the
fumes may contain so many different substances that are known to be
harmful (depending on the factors listed above). The individual components
of welding smoke can affect just about any part
of the body, including the lungs, heart, kidneys, and central nervous system.
(Welding Hazard Safety Program, TX Dept of Insurance)
Radiological Hazards Description/Health Hazards
Arc rays
Infrared (IR)
Ultraviolet (UV)
Visible light
Effect on the Eyes - Welder's flash (feeling of sand or grit in eyes, blurred
vision, intense pain, burning, and headache)
Effects on the Eyes - Cataracts
Effects on the Skin - Burns
momentary blinding
HAZARD CONTROL MEASURES USED FOR THIS JOB
Administrative Controls:
Certified operators
Competent person
Drug and alcohol policy
Emergency procedures
Equipment maintenance and servicing manual
Ergonomic procedure
Hot work procedure
Housekeeping practices
Inspections (ongoing) work areas, equipment, tools,
etc.
Inspections (pre-job) - work areas, equipment, tools,
etc.
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
Monitoring (hazardous atmospheres)
Operating instructions (equipment)
Operating procedures (process)
Radiological safety program
Safety checklists (use to document inspections)
Required Training:
Ergonomics
Fire protection (extinguishers)
General Safety
Hazard Communication (HAZCOM)
Orientation (site or job)
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Respiratory protection
Welding, cutting, and brazing
Engineering Controls:
Ventilation and exhausting.
Required PPE:
Boots - compatible for OSHA electrical protection requirements
Clothing - fire resistant
Clothing - long pants
Clothing - long sleeve shirt
Fire resistant gauntlet glove
Safety glasses: see manual for lens shade requirements for welder & spotter
Side shield
Welding hood
Welding jacket & apron
Required Permit(s):
No permit required - verify no LOTO is in progress
on chosen equipment
Welding shop - space reservation (see Admin desk
for list of welding operations & times)
Other Information:
A 2A20B:C fire extinguisher must be readily available and within arm's reach
at all times. Fire alarm operability must be confirmed prior to start of work.
Follow manufacturer instructions to test fire alarm. Also, follow all
manufacturer instructions for operation of the electic arc welder. STOP
WORK immediately if an unsafe or potentially unsafe condition exists.
JSABuilder chemical Description/Health Hazards is from the CAMEO database maintained by the U.S. EPA, NOAA, and the U.S. Coast Guard
(www.cameochemicals.noaa.gov). The creator of this JSA is responsible for any edits to this information.
JSA No: JSABuilder Sample Library - 4 (short) | Electric Arc Welding 4 of 4
This sample created at www.JSABuilder.com.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Jsa Welding Diesel PipelineDokument3 SeitenJsa Welding Diesel PipelineHow Chin Engineering Sdn BhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Tig Welding (RRC) - Job ProcedureDokument3 SeitenManual Tig Welding (RRC) - Job Proceduretitto84886100% (1)
- Rohan Builders (i) Pvt.Ltd. - Job Safety Analysis for Compound Wall PaintingDokument2 SeitenRohan Builders (i) Pvt.Ltd. - Job Safety Analysis for Compound Wall PaintingEka100% (1)
- Radiography JSADokument2 SeitenRadiography JSAVipul ShankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jsa For Ut TestDokument2 SeitenJsa For Ut Testnasar_mahsood50% (2)
- 9 Use of Hand Roller Compactor SafetyDokument2 Seiten9 Use of Hand Roller Compactor SafetyarchieNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSA-020-Safety Watch-Hot WorkDokument2 SeitenJSA-020-Safety Watch-Hot WorkNishad MuhammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jsa PaintDokument2 SeitenJsa PaintKhalid NaseemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily JSADokument4 SeitenDaily JSAumn_mlkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building De-Dusting JSADokument3 SeitenBuilding De-Dusting JSAJayesh J PillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSA - Dismantling CM ShedDokument4 SeitenJSA - Dismantling CM ShedvivekaramanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSA Erection of Gathering TentDokument12 SeitenJSA Erection of Gathering TentMuhammad Tariq100% (2)
- JSA Machinal PipingDokument7 SeitenJSA Machinal PipingNaitik Desai48100% (1)
- EF 1931-STCC-JSA-33 Fire Proofing of The Steel Structure and Vessel Foun...Dokument5 SeitenEF 1931-STCC-JSA-33 Fire Proofing of The Steel Structure and Vessel Foun...Anis Uddin100% (2)
- NEBOSH GC3 Observations Sheet SampleDokument12 SeitenNEBOSH GC3 Observations Sheet SampleShezi Bhatti100% (3)
- Kaztec Fabrication Yard, Snake Island: Job Safety Analysis (JSA)Dokument3 SeitenKaztec Fabrication Yard, Snake Island: Job Safety Analysis (JSA)Ogunwa EmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rt-J.s.a Star Int'l NDT ServicesDokument2 SeitenRt-J.s.a Star Int'l NDT ServicesأحمدآلزهوNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISC-JSA Grouting Works For Shared FenceDokument4 SeitenISC-JSA Grouting Works For Shared FenceSameer AlmahboubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) : Contractor: Date: Doc. No. & Rev. No.: 00Dokument6 SeitenJob Hazard Analysis (Jha) : Contractor: Date: Doc. No. & Rev. No.: 00poovazhaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jsa For The Installation of I EamDokument5 SeitenJsa For The Installation of I EamMohammed MinhajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excavation JSADokument4 SeitenExcavation JSASalah Abd EldayemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Safety Analysis: Trench Preparation & Thrust Boring Activity Required References Jsa ReviewDokument4 SeitenJob Safety Analysis: Trench Preparation & Thrust Boring Activity Required References Jsa ReviewMoaatazz Nouisri100% (1)
- JSA For Painting Works-Hazards ControlDokument4 SeitenJSA For Painting Works-Hazards Controlkaleem0% (2)
- Rigging JSA RiggerDokument12 SeitenRigging JSA RiggeraQiLGunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSRP Project: Confined Space Entry CertificateDokument1 SeiteNSRP Project: Confined Space Entry CertificateThanh Tung DongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Safety Analysis MDC Cylinder ReplacementDokument2 SeitenJob Safety Analysis MDC Cylinder ReplacementMaxi Pro100% (2)
- 02.JSA WeldingDokument2 Seiten02.JSA Weldingr0sh0% (1)
- Refueling JSA 4 08 2019 Rev.03 Near WaterDokument9 SeitenRefueling JSA 4 08 2019 Rev.03 Near Waterrisky indra antariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qatar Liquefied Gas Company Limited JSA for Cutting, Grinding and WeldingDokument5 SeitenQatar Liquefied Gas Company Limited JSA for Cutting, Grinding and WeldingMohammad Fazal KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area Hard Barrication JsaDokument4 SeitenArea Hard Barrication JsanishantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mig Welding JSADokument2 SeitenMig Welding JSANoval Febri100% (1)
- Jsa For RadiographyDokument3 SeitenJsa For Radiographyjithin shankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Injury & Illness Prevention Program: Job Safety Analysis FormDokument2 SeitenInjury & Illness Prevention Program: Job Safety Analysis FormArif RachmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Safety Analysis (Rolling For MS Plates)Dokument1 SeiteJob Safety Analysis (Rolling For MS Plates)Muhammad Ali100% (2)
- Job Safety Analysis: Night Work at SiteDokument2 SeitenJob Safety Analysis: Night Work at SiteSaiyad RiyazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jsa Removal Fixing InsulationDokument2 SeitenJsa Removal Fixing InsulationAprilia Rizki Ardila63% (8)
- JSA-For Lifting Activity by CraneDokument3 SeitenJSA-For Lifting Activity by CraneEman MantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil JSA Form Application of Protective Coating On Sump PitsDokument1 SeiteCivil JSA Form Application of Protective Coating On Sump PitsdrmuhsinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jsa No-01 Container UnloadingDokument4 SeitenJsa No-01 Container Unloadingsumith s100% (1)
- Job Safety Analysis Pre-Task Briefing: MASAR Project Makkah KSADokument2 SeitenJob Safety Analysis Pre-Task Briefing: MASAR Project Makkah KSAmahammed saleem100% (2)
- Pipe Lowering JHADokument6 SeitenPipe Lowering JHASalam AlkataluniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jsa Grinding Welding Gas CuttingDokument3 SeitenJsa Grinding Welding Gas CuttingRyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sarawak JSA for Concrete CuttingDokument4 SeitenSarawak JSA for Concrete CuttingMohammad Irfan Kiki IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jsa Non Destructive TestingDokument2 SeitenJsa Non Destructive Testingghulammohyuddin100% (1)
- # 20 Installation of Cable Tray Trunking (SWP)Dokument5 Seiten# 20 Installation of Cable Tray Trunking (SWP)Anonymous kWfNFbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Welding and Cutting Safety PDFDokument55 SeitenGas Welding and Cutting Safety PDFGnanasekaran MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Extingisher Inspection ProcedureDokument2 SeitenFire Extingisher Inspection ProcedurewaheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSA NO 2 Piling WorkDokument6 SeitenJSA NO 2 Piling WorkfadliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Safety Analysis Worksheet: Short Descriptive Title of Task: New Revised ReviewedDokument2 SeitenJob Safety Analysis Worksheet: Short Descriptive Title of Task: New Revised ReviewedZulfokar FahdawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- JS A Excavation Work For Electrical CableDokument3 SeitenJS A Excavation Work For Electrical CableMohammed MinhajNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSA - Suface Preparationand Brush PaintingDokument5 SeitenJSA - Suface Preparationand Brush PaintingAzad pravesh khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Safety Harness Inspection SheetDokument4 Seiten03 Safety Harness Inspection Sheetxiangjintao100% (1)
- JHA PlumberDokument3 SeitenJHA PlumberEko Susanto100% (1)
- Activity Hazard AnalysisDokument4 SeitenActivity Hazard AnalysisGerrard Singh100% (1)
- Jsa Sample PDFDokument4 SeitenJsa Sample PDFKaoru AmaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railroad American Welding Society CompressDokument27 SeitenRailroad American Welding Society CompressM Lazuardi Imani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smaw Facilitator GuideDokument62 SeitenSmaw Facilitator Guidekhairy2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- GMAW Facilitator GuideDokument42 SeitenGMAW Facilitator GuideEng trk100% (1)
- 3.jsa - Arc Welding-NDokument5 Seiten3.jsa - Arc Welding-NVivek NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rci Technological Education: To: Subject: Re: (Junkyardprojects) Welding InformationDokument8 SeitenRci Technological Education: To: Subject: Re: (Junkyardprojects) Welding Informationأحمد دعبسNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tool Function QuestionnaireDokument9 SeitenTool Function QuestionnairerongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1008-OAJ-MS-R0 1017 - HDPE Pipes InstallationDokument9 Seiten1008-OAJ-MS-R0 1017 - HDPE Pipes InstallationrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beast Jersey Sizing ChartDokument1 SeiteBeast Jersey Sizing ChartrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installing GFM903 - 905 - 925 Onto The Gate PDFDokument8 SeitenInstalling GFM903 - 905 - 925 Onto The Gate PDFLokman Toolib50% (2)
- Nondestructive Tests Are Tests That Determine The Usefulness, Serviceability, or Quality of A Part or Material Without Limiting Its Usefulness. Is Important For QualityDokument19 SeitenNondestructive Tests Are Tests That Determine The Usefulness, Serviceability, or Quality of A Part or Material Without Limiting Its Usefulness. Is Important For QualityrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSWIP-WI-6-92 15th Edition April 2017Dokument17 SeitenCSWIP-WI-6-92 15th Edition April 2017NarendrasinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Ebook - PDF) - Programming - C and C++ in Five DaysDokument67 Seiten(Ebook - PDF) - Programming - C and C++ in Five Daystinkerer212Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1008-OAJ-MS-R0 1017 - HDPE Pipes InstallationDokument9 Seiten1008-OAJ-MS-R0 1017 - HDPE Pipes InstallationrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unconventional Oil RushDokument20 SeitenUnconventional Oil RushrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personaliti Dagangan: Semakan Keseluruhan PedagangDokument27 SeitenPersonaliti Dagangan: Semakan Keseluruhan PedagangrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black and Decker Waterjet Manual gl200 - UkDokument16 SeitenBlack and Decker Waterjet Manual gl200 - UkrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- pw1300td pw1300tdw b5Dokument40 Seitenpw1300td pw1300tdw b5rongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA/QC Requirements On FabricationDokument10 SeitenQA/QC Requirements On Fabricationhash117Noch keine Bewertungen
- VISION TEST RECORDDokument1 SeiteVISION TEST RECORDRafiqKuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Fat Burning WorkoutDokument19 SeitenSample Fat Burning Workoutifoxmedia100% (8)
- CSWIP-WI-6-92 15th Edition April 2017Dokument17 SeitenCSWIP-WI-6-92 15th Edition April 2017NarendrasinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabrication FlowchartDokument1 SeiteFabrication FlowchartrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Price List: Inspector (CAWI, CWI, SCWI) Certified Welding Educator (CWE)Dokument1 Seite2019 Price List: Inspector (CAWI, CWI, SCWI) Certified Welding Educator (CWE)rongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TPoints Redemption 1 PDFDokument22 SeitenTPoints Redemption 1 PDFrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TPoints Redemption 2Dokument22 SeitenTPoints Redemption 2rongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3new Rigging AwarenessDokument36 Seiten3new Rigging AwarenessrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form Inspection Over Head CraneDokument1 SeiteForm Inspection Over Head CraneputumomoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Price List For Peninsular Malaysia: Peugeot 207Dokument2 SeitenPrice List For Peninsular Malaysia: Peugeot 207rongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Art of War in The Middle Ages A DDokument162 SeitenThe Art of War in The Middle Ages A DrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peugeot 3008 SpecDokument2 SeitenPeugeot 3008 SpecamuihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Areas ClasificadasDokument8 SeitenAreas Clasificadasedin64Noch keine Bewertungen
- Asb Calculator v11Dokument2 SeitenAsb Calculator v11rongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASNT Level IIIDokument1 SeiteASNT Level IIIrongohcolemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chalcopyrite Leaching in Alchoholic Acid MediaDokument19 SeitenChalcopyrite Leaching in Alchoholic Acid MediamtanaydinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heliflex GC Capillary ColumnsDokument2 SeitenHeliflex GC Capillary Columnsjjxcz2hfzhNoch keine Bewertungen
- UniplanxDokument12 SeitenUniplanxbiik0076153Noch keine Bewertungen
- Zio Ciro Catalogue 2020Dokument21 SeitenZio Ciro Catalogue 2020ronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog Profilitec2010Dokument202 SeitenCatalog Profilitec2010nasuemilNoch keine Bewertungen
- BC Brochure Redura Piston 2 Auflage RGB WEBDokument16 SeitenBC Brochure Redura Piston 2 Auflage RGB WEBJoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement Treatment GIT 1Dokument12 SeitenCement Treatment GIT 1Sparsh ShukalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Wiring On Insulators PDFDokument1 SeiteOpen Wiring On Insulators PDFlouieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler and Aux Maintenance ManualDokument248 SeitenBoiler and Aux Maintenance Manualkeerthi dayarathnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 1 Chapter 4Dokument26 SeitenScience Form 1 Chapter 4Beevy GB73% (11)
- Fibrsep Fiberglass Depth CartridgeDokument2 SeitenFibrsep Fiberglass Depth Cartridgeakamalapuri388100% (1)
- Corrosion Failure Analysis of Galvanized Steel Pipes in A Water Irrigation SystemDokument6 SeitenCorrosion Failure Analysis of Galvanized Steel Pipes in A Water Irrigation SystemC_rovere100% (1)
- Explosive Management PlanDokument28 SeitenExplosive Management Planbruktawit100% (1)
- Chemistry Final Exam PracticeDokument22 SeitenChemistry Final Exam PracticeRida Muhammad RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-3 Additive ManufacturingDokument45 SeitenModule-3 Additive Manufacturingprajapati21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete WorksDokument16 SeitenConcrete WorksKristine Ericka May CozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tendernotice 3Dokument4 SeitenTendernotice 3Balvir ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CQM SMCDokument15 SeitenCQM SMCGabriel CantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDokument24 SeitenDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationJitender Singh Tomar100% (1)
- Ethoxylated Nonylphenol - ChemistryDokument15 SeitenEthoxylated Nonylphenol - Chemistrysimbua720% (1)
- Clean Electronics CatalogueDokument36 SeitenClean Electronics CatalogueAbe KobNoch keine Bewertungen
- MX 400 PDFDokument1 SeiteMX 400 PDFtanbqtb03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog EncoreDokument71 SeitenCatalog EncoreGabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Screw Design Guide: Myticon Timber ConnectorsDokument52 SeitenStructural Screw Design Guide: Myticon Timber ConnectorsciviliiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Industrial Ground Floor Slab Desig1Dokument3 SeitenConcrete Industrial Ground Floor Slab Desig1Mahata PriyabrataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fine Chemicals - CatalystsDokument46 SeitenFine Chemicals - CatalystsSiddharth chandan dasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suzlon - S - PR - 444 - REV01 - 1Dokument4 SeitenSuzlon - S - PR - 444 - REV01 - 1Shubham BaderiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UHV Chambers - BirnbaumDokument16 SeitenUHV Chambers - Birnbaumpique86Noch keine Bewertungen
- N (G) - 2Nh (G) : StoichiometryDokument5 SeitenN (G) - 2Nh (G) : StoichiometryJaidenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christmas Doll Eva PatternDokument12 SeitenChristmas Doll Eva PatternDiana Triviño91% (11)