Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ELG4139: Rectifiers and Controlled Rectifiers: AC To DC Converters
Hochgeladen von
El ZapaterOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ELG4139: Rectifiers and Controlled Rectifiers: AC To DC Converters
Hochgeladen von
El ZapaterCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
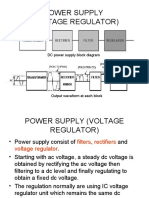
ELG4139: Rectifiers and Controlled Rectifiers
AC to DC Converters
Linear Rectifier
Consist of:
Transformer: steps ac voltage up or down.
Rectifier Diodes: change ac to bumpy dc.
Filter Network: includes capacitors and inductors,
smooths out the bumps.
Voltage Regulator: keeps the voltage constant.
Protection: usually a zener diode circuit.
Example: Computer Power Supply
Example: Adjustable Motor Speed Drive
Power Supply Specifics: Half Wave Rectifier
Source: ARRL
Half-Wave Rectifier
High ripple factor.
Low rectification
efficiency.
Low transformer
utilization factor.
Power Supply Specifics
Full Wave Center-Tapped Rectifier
Source: ARRL
Power Supply: Full Wave Bridge Rectifier
Source: ARRL
Filtering
Capacitors are used in power supply filter networks. The
capacitors smooth out the rippled AC to DC.
Source: ARRL
Rectifier Performance Parameters
2 2
dc rms ac
V V V =
ac dc
P P / = q Rectification Efficiency
dc rms
V V FF / =
1 1
2
2
2
2 2
= =
= = FF
V
V
V
V V
V
V
RF
dc
rms
dc
dc rms
dc
ac
Form Factor
Ripple factor
Example 1: A half-wave rectifier has a pure resistive load of R
Determine (a) The efficiency, (b) Form factor (c) Ripple factor.
t
t
t
e e
t
t
m m
m dc
V V
t d t V V = = =
}
)) 0 cos( cos (
2
) sin(
2
1
0
R
V
R
V
I
m dc
dc
t
= =
2
) sin (
2
1
0
2 m
m rms
V
t V V = =
}
t
e
t
R
V
I
m
rms
2
=
% 53 . 40
2
*
2
*
*
*
= = = =
R
V V
R
V V
I V
I V
P
P
m m
m m
rms rms
dc dc
ac
dc
t t
q
57 . 1
2
2
= = = =
t
t
m
m
dc
rms
V
V
V
V
FF
211 . 1 1 57 . 1 1
2 2
= = = = FF
V
V
RF
dc
ac
.
Three-Phase Diode Bridge Rectifier
Waveforms and Conduction Times of Three-Phase Bridge Rectifier
Three-Phase Full-Wave Rectifier
Example 2: A single-phase diode bridge rectifier has a purely resistive load of
R=15 ohms and, VS=300 sin 314 t and unity transformer ratio. Determine (a) The
efficiency, (b) Form factor, (c) Ripple factor, (d) and, (d) Input power factor.
V
V
t d t V V
m
m dc
956 . 190
2
sin
1
0
= = =
}
t
e e
t
t
A
R
V
I
m
dc
7324 . 12
2
= =
t
( ) V
V
t d t V V
m
m rms
132 . 212
2
sin
1
2 / 1
0
2
= =
(
(
=
}
t
e e
t
% 06 . 81 = = =
rms rms
dc dc
ac
dc
I V
I V
P
P
q
11 . 1 = =
dc
rms
V
V
FF
482 . 0 1 1
2
2
2
2 2
= = =
= = FF
V
V
V
V V
V
V
RF
dc
rms
dc
dc rms
dc
ac
Input power factor =
1
cos Power Real
= =
S S
S S
I V
I V
Power Apperant
|
Alternative! Controlled Switching Mode
By using linear regulator, the AC to DC converter is not efficient and
of large size and weight!
Using Switching-Mode
High efficiency
Small size and light weight
For high power (density) applications.
Use Power Electronics!
Thyristors and Controlled Rectifiers
Controlled Rectifier Circuit
=
1
2
1 +
=
1
2
1/2
=
2
1
+
2
2
1/2
Example: Consider the following SCR-based variable voltage supply. For RL=240 Ohm, derive the
RMS value of the load voltage as a function of the firing angle, and then calculate the load power
when the firing angle o is 0, t/2, and t.
Full-Wave Rectifiers Using SCR
=
2
2
=
2
=
2
2
1/2
=
2
=
With a purely resistive load, SCRs S
1
and S
2
can conduct from o to t, and SCRs S
3
and S
4
can conduct from o+t to 2t.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Subaru Impreza Wiring Diagram PDFDokument66 SeitenSubaru Impreza Wiring Diagram PDFlostris23462% (13)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- PBM Power PointDokument32 SeitenPBM Power PointCarlos Quispe100% (1)
- The Valve Wizard - Valve TesterDokument3 SeitenThe Valve Wizard - Valve TestermarcosscaratoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Dokument69 SeitenPower Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Sankaran Nampoothiri KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Report About HVDC TECHNOLOGYDokument21 SeitenFinal Report About HVDC TECHNOLOGYSefu BikorimanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lighting in Interior DesignDokument18 SeitenLighting in Interior DesignVidhisha BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annexure On New Parts Developed Status JSRDokument426 SeitenAnnexure On New Parts Developed Status JSRD Chandrawati100% (1)
- Chapter 2 FinalDokument83 SeitenChapter 2 FinalSana SaleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES)Dokument8 SeitenInternational Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES)www.irjes.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- S6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFDokument27 SeitenS6 PE Lab Manual 2018 MATLAB PDFhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectifiers and Switched Mode Power Supply UnitDokument85 SeitenRectifiers and Switched Mode Power Supply UnitVignesh MeyyappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connection Box - Electric, 05-19Dokument8 SeitenConnection Box - Electric, 05-19nacho006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1 Power SupplyDokument7 SeitenLab 1 Power SupplyKatherine YenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mit Aec Labmanula 10esl37Dokument45 SeitenMit Aec Labmanula 10esl37anon_70724250Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Two: Ac-Dc Conversion: Uncontroled RectificationsDokument53 SeitenChapter Two: Ac-Dc Conversion: Uncontroled Rectificationsfor life100% (3)
- Esq.+E.+FPS+CCM CHI LWBDokument103 SeitenEsq.+E.+FPS+CCM CHI LWBVictor PinedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinamics DCM Emergency StopDokument13 SeitenSinamics DCM Emergency StopAbez FiveNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPS Toyota BackgroundDokument8 SeitenEPS Toyota BackgroundDilan Senarathne100% (1)
- Villa Construction Program Gantt ChartDokument3 SeitenVilla Construction Program Gantt ChartHarshalNoch keine Bewertungen
- RectifierDokument37 SeitenRectifierMahendra Mandalapu MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topology Review DC DC ConvertersDokument54 SeitenTopology Review DC DC ConvertersaknuslNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec6 - Diode RectifiersDokument47 SeitenLec6 - Diode RectifiersMA KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switched Mode Power Conversion: Devices For Efficient Power Conversion Switches Inductors TransformersDokument47 SeitenSwitched Mode Power Conversion: Devices For Efficient Power Conversion Switches Inductors TransformersmsraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 442 Power Electronics I Controlled Rectifiers (AC-DC ConvertersDokument36 SeitenEE 442 Power Electronics I Controlled Rectifiers (AC-DC Convertershamza malikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variable DC Power Using Full Bridge ConverterDokument6 SeitenVariable DC Power Using Full Bridge Convertergoten10daNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Trans VRDokument32 Seiten15 Trans VRAkbarDwiSyahputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Circuit II Chap 3 Power Electronics: DC DC ConvertersDokument17 SeitenElectronic Circuit II Chap 3 Power Electronics: DC DC ConvertersSauravAbidRahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 1: Halfwave and Fullwave RectifiersDokument5 SeitenExperiment No. 1: Halfwave and Fullwave RectifiersTonmoy RafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machine K-NotesDokument38 SeitenElectrical Machine K-NotesAkashGauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec5 - Diode RectifiersDokument28 SeitenLec5 - Diode RectifiersMA KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.-Electrotecnia Unit2 PDFDokument12 Seiten2.-Electrotecnia Unit2 PDFJayaraj LathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Half-Wave Rectifier With R LoadDokument18 Seiten1 Half-Wave Rectifier With R LoadKARMUGHILLAAN MANIMARAN STUDENTNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESD Lab Manual PDFDokument67 SeitenESD Lab Manual PDFAnonymous mg0FcO1xjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics 1-2015bjrDokument80 SeitenPower Electronics 1-2015bjrNurAdiFirawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omega Type ETB-29 Lab Manual (CURAJ)Dokument18 SeitenOmega Type ETB-29 Lab Manual (CURAJ)McMillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 (A) : Controlled RectifiersDokument22 SeitenModule 4 (A) : Controlled RectifiersAishwarya PKamatagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simultaneous Transmission of Ac and DC PowerDokument6 SeitenSimultaneous Transmission of Ac and DC PowermdayyubNoch keine Bewertungen
- YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING FACULTY POWER ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LABDokument9 SeitenYEDITEPE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING FACULTY POWER ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LABDhananjay LimayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report About HVDCDokument21 SeitenReport About HVDCSefu BikorimanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual 2Dokument92 SeitenLab Manual 2Joyce GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- L08 Power Amplifier (Class A)Dokument24 SeitenL08 Power Amplifier (Class A)mkrasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 DC Drives Part2Dokument75 SeitenChapter 1 DC Drives Part2Mohammad MunzirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Supply DesignDokument8 SeitenPower Supply DesignMario Plinio CrivelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ManualDokument146 SeitenLab Manualranjith krishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No 14-1Dokument4 SeitenExperiment No 14-1afrahakbar3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rectifier Circuits: 2.1 Experiments in Rectifiers 2.1.1 Aim of The ExperimentDokument12 SeitenRectifier Circuits: 2.1 Experiments in Rectifiers 2.1.1 Aim of The ExperimentrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peak Reading Voltmeter: +Vp +Vp +Vp Vp π 2 π ωt Vp π 2 π ωt ωt +VpDokument30 SeitenPeak Reading Voltmeter: +Vp +Vp +Vp Vp π 2 π ωt Vp π 2 π ωt ωt +VpAbhinav GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flyback ConvertorDokument6 SeitenFlyback ConvertorEysha qureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase Half Wave Rectifier SimulationDokument15 SeitenSingle Phase Half Wave Rectifier SimulationShailendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Power Supply Block DiagramDokument15 SeitenDC Power Supply Block DiagramKuAdenan KuSyakranNoch keine Bewertungen
- L6 Diodes and Applications(New2024)Dokument44 SeitenL6 Diodes and Applications(New2024)Aron DionisiusNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Filter and Power SupplyDokument27 Seiten2 - Filter and Power Supplyangelo rodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AimDokument12 SeitenAimkarakeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 17 - ACACDokument19 SeitenLecture 17 - ACACĐạt Nguyễn XuânNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 328 Lecture 4Dokument33 SeitenEe 328 Lecture 4Eric KerrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2c Power Supply (Voltage Regulator)Dokument14 Seiten2c Power Supply (Voltage Regulator)Love StrikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2c Power Supply (Voltage Regulator)Dokument14 Seiten2c Power Supply (Voltage Regulator)Dzul HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2c Power Supply (Voltage Regulator)Dokument14 Seiten2c Power Supply (Voltage Regulator)Dzul HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Power Supply FundamentalsDokument30 SeitenDC Power Supply FundamentalsMuizz ZainolNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 027 Fundamentals of Electronics - Rectifier Circuit AnalysisDokument39 SeitenECE 027 Fundamentals of Electronics - Rectifier Circuit AnalysisMiyuki NakiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Power Supply (Voltage Regulator) - 2Dokument78 Seiten2 Power Supply (Voltage Regulator) - 2Winter NaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Fault DerivationDokument89 SeitenAnalog Fault DerivationSachidananda SwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics 1: ENEL371S2Dokument30 SeitenPower Electronics 1: ENEL371S2bpd21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Line or Naturally Commutated ConvertersDokument32 SeitenLine or Naturally Commutated ConvertersMichael Adu-boahenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Analog MetersDokument25 SeitenElectronic Analog MetersAbhinav GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEEN40197 Lecture Notes AJF PDFDokument46 SeitenEEEN40197 Lecture Notes AJF PDFAnonymous gVhwdk9ui9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rectifier Meters: Binoy B NairDokument20 SeitenRectifier Meters: Binoy B NairSailes SenthilNoch keine Bewertungen
- M12 Actuator/Sensor Distribution Boxes: 6-PortsDokument2 SeitenM12 Actuator/Sensor Distribution Boxes: 6-PortsJose Gregorio Lira SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Delta and Open Delta Configurations ExplainedDokument3 SeitenTransformer Delta and Open Delta Configurations ExplainedtangouzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts Catalog: Browning .50 M2 Machine Gun, AssemblyDokument32 SeitenParts Catalog: Browning .50 M2 Machine Gun, AssemblyJay Mason100% (1)
- Zelio Relay Rumc3ab1bdDokument5 SeitenZelio Relay Rumc3ab1bdVania ArbulúNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3RF29500KA16 Datasheet en PDFDokument5 Seiten3RF29500KA16 Datasheet en PDFkarthick UNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classé CA-400 Service Manual GuideDokument20 SeitenClassé CA-400 Service Manual GuideVictor TettehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osti Ia G Interlocks Noncontact v032113Dokument56 SeitenOsti Ia G Interlocks Noncontact v032113EvaldoGualbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uf 1002 FDokument3 SeitenUf 1002 FJose M PeresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staircase Section Aa''Dokument1 SeiteStaircase Section Aa''Manvi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3TL CatalogDokument44 Seiten3TL CatalogEduardo Castañares VillarroelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Speed AdjustmentDokument1 SeiteEngine Speed Adjustmentsixin93551Noch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Operation - Autotransformer Starter PDFDokument3 SeitenTheory of Operation - Autotransformer Starter PDFDiago100% (1)
- Listening: Listen and NumberDokument4 SeitenListening: Listen and NumberMaríaVisiedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP1472 r1.0 PDFDokument13 SeitenMP1472 r1.0 PDFAdyel PujolNoch keine Bewertungen
- MASSSDokument4 SeitenMASSSvijaycrismaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeutraDokument6 SeitenNeutraKinga KokovicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bosch Motronic Mp3 2-Multipoint-Xu10j2cte RGX 406 Peugeot Fan ClubDokument7 SeitenBosch Motronic Mp3 2-Multipoint-Xu10j2cte RGX 406 Peugeot Fan ClubMohamed TarekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuse and Types of Fuses - Constructio, Operation & ApplicationsDokument9 SeitenFuse and Types of Fuses - Constructio, Operation & ApplicationsKhaled RabeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bypass Switch PDFDokument1 SeiteBypass Switch PDFAdhyartha KerafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metric: Dwgb001 Dwg. Tol. and InterpDokument26 SeitenMetric: Dwgb001 Dwg. Tol. and InterpAndré MariaNoch keine Bewertungen