Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
MRCPCH Guide Neonate
Hochgeladen von
Rajiv Kabad100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
279 Ansichten4 Seiten1) The document provides guidelines for treating different types of neonatal seizures, listing first, second, third, and fourth line treatment options.
2) It also discusses lung development in utero, describing how the airways begin forming at 24 days and are almost completely formed by 16 weeks, and how alveoli continue developing after birth.
3) Additionally, it mentions some infectious causes of hydrops fetalis, a condition of fluid accumulation in tissues, including cytomegalovirus, syphilis, and others.
Originalbeschreibung:
Mrcpch Guide part 2
Originaltitel
Mrcpch Guide Neonate
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1) The document provides guidelines for treating different types of neonatal seizures, listing first, second, third, and fourth line treatment options.
2) It also discusses lung development in utero, describing how the airways begin forming at 24 days and are almost completely formed by 16 weeks, and how alveoli continue developing after birth.
3) Additionally, it mentions some infectious causes of hydrops fetalis, a condition of fluid accumulation in tissues, including cytomegalovirus, syphilis, and others.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
279 Ansichten4 SeitenMRCPCH Guide Neonate
Hochgeladen von
Rajiv Kabad1) The document provides guidelines for treating different types of neonatal seizures, listing first, second, third, and fourth line treatment options.
2) It also discusses lung development in utero, describing how the airways begin forming at 24 days and are almost completely formed by 16 weeks, and how alveoli continue developing after birth.
3) Additionally, it mentions some infectious causes of hydrops fetalis, a condition of fluid accumulation in tissues, including cytomegalovirus, syphilis, and others.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
MRCPCH GUIDE NEONATE
Medical treatment of seizures
Seizure Type Generalised Partial
Symptomatic
Partial- Benign Infantile spasms
1
st
Line Sodium Valproate Carbamazepine
Nothing
Vigabatrin
2
nd
Line Lamotrogine/
carbamazepine
Lamotrogine
Carbemezepine
ACTH
3
rd
Line Gabapentin/
Topiramate/
Clonazepam
Topiramate
4
th
Line Phenytoin
The airways begin as an outpouching from the primitive gut at 24 days and by 26 days two
primary branches, which will go to form the major bronchi, can be discerned. For the next 3
months growth consists of branching of the endodermal tube into the surrounding
mesenchyme. By 10 weeks cartilage is deposited in the bronchi and by 16 weeks formation of
new bronchi is almost complete. The terminal air sacs or alveoli appear as outpouchings of the
bronchioles after 28 weeks and increase in number to form multiple pouches of a common
chamber called the alveolar duct. After birth alveolar stability is dependent upon the release
of pulmonary surfactant into the lumen. Synthesis and release of surfactant rely more on
humoral control mechanisms than mechanical factors. Alveolar type II cells, which synthesize
surfactant, have microvilli on the luminal surface and contain lamellar bodies. The lamellar
bodies (storage sites for surfactant) are first recognized at about 22 weeks. The terminal air
sacs are shallow and wide mouthed in the newborn baby; several months later they assume a
cup shape. Growth of the lung occurs by increasing the number of bronchiolar divisions,
alveoli, alveolar diameters and surface area for gas exchange. Alveoli may continue to form as
long as body length increases.
Hydrops Fetalis
The importance of infection with B19V is increasingly recognised. Use of diagnostic tests has
demonstrated that perhaps 20% of fetal hydrops is associated with this maternal/fetal
infection. Other infectious causes include Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Syphilis, herpes simplex,
Toxoplasmosis, hepatitis B, Adenovirus, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Coxsackievirus type B,
Listeria monocytogenes.
The pH of a healthy newborn is between 7.35 and 7.4. The systolic blood pressure at term is
normally 60mmHg rising to 90mmHg by 1 year. The survival of infants at 23 weeks is in the
order of 30% and rises to around 85% by 28 weeks. The average OFC at term is about 35cm
while the PNMR is 7-8/1000 of all births (i.e. live births & still births).
ROP is a disease of premature infants. All babies less than 1500 g birth weight or younger than
32 weeks' GA at birt h are at risk of developing ROP. However, higher oxygen saturation levels
were not found to worsen the disease in prethreshold babies. Laser surgery (xenon, argon,
diode) has been shown to be as effective as cryotherapy for ROP and is used in more advanced
cases. Complications include: Loss of vision, amblyopia due to high refractive errors,
Strabismus, Glaucoma, Retinal detachment.
IUGR has a prevalence of 10% among all pregnancies. However, the figure varies in different
patient populations, with rates of 3-5% among healthy mothers, and rates of 25% or higher in
some high risk groups, such as, hypertensive mothers. The cause is often not known.
Growth-restricted pregnancies are often complicated by a high rate of antepartum and
intrapartum fetal distress and the need for caesarean delivery. Infants born who are small for
their gestational dates are predisposed to higher rates of low APGAR scores, low cord pH,
intraventricular haemorrhage, necrotising enterocolitis, hypoglycaemia, hypocalcaemia, and
polycythaemia.
The sonographic criteria for IUGR include (1) an elevated ratio of femoral length to abdominal
circumference (AC), (2) an elevated ratio of head circumference (HC) to AC, and (3)
unexplained oligohydramnios .
In most cases of IUGR, especially those due to primary placental insufficiency (the most
common cause), the fetal abdomen is small, while the head and extremities are normal or near
normal. This finding is known as the head-sparing effect. In cases of severe, early-onset IUGR
(those due to chromosomal anomalies), the fetus tends to be more symmetrically small.
Many syndromes representing problems in the morphogenesis of branchial arches [5], [8] have
been reported including Goldenhaar syndrome, Pierre Robin and Treacher Collins syndrome.
Ectopic thyroid tissue may be present anywhere along the path of descent of the thyroid gland.
A pilonidal sinus is in the natal cleft.
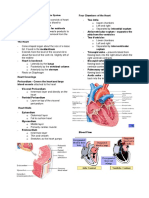
In the first week of life in utero (1/40), the embryo derives its nutrients and discards its waste
by a simple process of diffusion. Development of the uteroplacental circulation commences
at 9 days and is fully established within the third week after fertilisation (3/40). The
cytotrophoblast proliferates, and processes form the primary stem villi. Further differentiation
of the mesoderm forms the blood vessels, which subsequently connect with the vessels
forming in the embryo. These differentiated structures are called the tertiary stem villi. Gases,
nutrients and wastes diffuse between maternal and fetal blood between four established
layers: (1) the endothelium of the villus capillaries; (2) the villus connective tissue; (3) a layer
of cytotrophoblast; and (4) a layer of syncytiotrophoblast. The placenta contains 150 ml of
maternal blood and is replaced 34 times per minute. Carbon dioxide, urea and uric acid pass
from the fetal to the maternal blood as waste.
Trophoblastic lacunae develop within the syncytiotrophoblast. Maternal capillaries within
this area expand to form maternal sinusoids. Extra-embryonic mesoderm grows and extends
into the primary stem villi to become secondary villi. The placenta produces steroid
hormones and prostaglandins.
The pharyngeal pouches consist of bars of mesenchymal tissue separated from each other by
pharyngeal pouches and clefts. The endoderm of the pouches gives rise to, in order, the
structures indicated in the table below.
Pouch Structure formed
1st pouch Pharyngotympanic cavity, Auditory tube, Eustachian tube
2nd pouch Tongue, Palatine tonsils
3rd pouch Thymus, Inferior parathyroid gland
4th pouch Superior parathyroid gland (C cells)
4th5th pouch Ultimobranchial bodies (parafollicular cells)
The thyroid gland originates from epithelial proliferation in the floor of the primitive pharynx
and not from the larynx or branchial arches. It is connected by the thyroglossal duct to the
foramen caecum at the junction of the anterior two-thirds and posterior third of the tongue.
Ectopic thyroid tissue occasionally causes cysts along the path of the duct. The thyroid
migrates to its final position in front of the tracheal rings. The parafollicular (C) cells come
from the ultimobranchial body, a derivative of the 4th pharyngeal pouch.
Impaired fetal lung development is seen in Potter syndrome, Jeune syndrome and dystrophia
myotonica. It is not found in the infants of insulin-dependent diabetic mothers or in
Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Impaired fetal lung development is not found in bronchiolitis,
facioscapulohumeral dystrophy, Pickwickian syndrome or Kartagener syndrome.
Cocaine, carbimazole and warfarin readily cross the placenta and affect the fetus.
FAS was first reported as a syndrome in 1973 and is now thought to be one of the major causes
of mental retardation, having an incidence of 0.23 per 1000 live births. It has been estimated
that between 10 and 20% of mild mental retardation cases are caused by maternal alcohol use.
Severity and timing of alcohol consumption, bingeing, polydrug use (including smoking) during
pregnancy, genetic variation and low socioeconomic status are all aetiological factors. Alcohol
inhibits N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, which mediate the postsynaptic excitatory
effects of glutamate, and this is thought to have an effect on cell proliferation.
Affected newborns are often irritable, hypotonic, experience severe tremors and show other
signs of alcohol withdrawal. The cardinal signs are facial features, growth deficit and central
nervous system impairment. Facial features include epicanthic folds, microcephaly, short -
palpebral fissure, underdeveloped philtrum and a thin upper lip. There are often associated
behavioural difficulties including hyperactivity and sleep disturbance. Optic nerve hypoplasia
with poor visual acuity, hearing loss and receptive and expressive language deficits can also be
seen. Cardiac and renal abnormalities include atrial and ventricular septal defects, renal
hypoplasia and bladder diverticula.
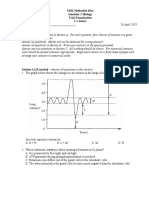
Prognosis depends on grade of bleed: grades 1 and 2 have a good prognosis with no long-
term effects. In grade 3 there may be possible impairment on the contralateral side, depending
on the degree of progression of dilatation, and in grade 4 there is likely to be motor
impairment on contralateral side.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Aiims - Pediatrics Q&ADokument207 SeitenAiims - Pediatrics Q&AqqypprcyxyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyVon EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCPCH A&b NotesDokument16 SeitenMRCPCH A&b NotesRajiv Kabad100% (1)
- MRCPCH Guide EndoDokument7 SeitenMRCPCH Guide EndoRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Following Drugs Are Safe in Breast-Feeding:: AccidentsDokument2 SeitenThe Following Drugs Are Safe in Breast-Feeding:: AccidentsRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCPCH PaperDokument3 SeitenMRCPCH Paperkayenatsami7518100% (1)
- Skin Rashes Guideline in Paediatric Emergency Department (Cross Site)Dokument33 SeitenSkin Rashes Guideline in Paediatric Emergency Department (Cross Site)Eskilda LucildaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOP-TAS Feb2018Dokument16 SeitenFOP-TAS Feb2018Äfťæb AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCPCH SyllabusDokument3 SeitenMRCPCH SyllabusKanthi Sagar100% (1)
- Metabolic Alkalosis: Features of Crohn'S DiseaseDokument15 SeitenMetabolic Alkalosis: Features of Crohn'S DiseaseRajiv Kabad100% (1)
- Paediatrics MCQsDokument5 SeitenPaediatrics MCQsbalarajuuk100% (1)
- MRCPCH - Exam Structure and SyllabusDokument6 SeitenMRCPCH - Exam Structure and SyllabusKickassNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCPCH Guide Heme: A Hypochromic MicrocyticDokument8 SeitenMRCPCH Guide Heme: A Hypochromic MicrocyticRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCPCH Guide InfDokument19 SeitenMRCPCH Guide InfRajiv Kabad100% (1)
- MRCPCH DhanDokument26 SeitenMRCPCH DhanRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scenarios For MRCPCHDokument11 SeitenScenarios For MRCPCHsayedm100% (1)
- FOP Specimen Paper - Answer Key and Reasoning - 0Dokument31 SeitenFOP Specimen Paper - Answer Key and Reasoning - 0gladyannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Sciences For MRCPCH ExamDokument11 SeitenBasic Sciences For MRCPCH ExamMahmoud Abul AtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCPCH GuideDokument9 SeitenMRCPCH GuideRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case #1Dokument24 SeitenCase #1arooba soha100% (1)
- 2 Year Old / M: What Is Your Diagnosis?Dokument31 Seiten2 Year Old / M: What Is Your Diagnosis?Mobin Ur Rehman Khan100% (1)
- MRCPCH - Renal ImagingDokument28 SeitenMRCPCH - Renal ImagingarjumandNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15-0000 - Form - QEWS - Standard Pediatric Observation Chart - 0 To 28 DaysDokument2 Seiten15-0000 - Form - QEWS - Standard Pediatric Observation Chart - 0 To 28 DaysRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To MRCPCH ExamDokument15 SeitenIntroduction To MRCPCH ExamMahmoud Abul Ata0% (1)
- The Bleeding Child OSCE HaemophiliaDokument3 SeitenThe Bleeding Child OSCE HaemophiliaJJ LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slowly: PinchDokument39 SeitenSlowly: PinchAlokh Saha RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlmusawipediatricOSCE PDFDokument260 SeitenAlmusawipediatricOSCE PDFRabah IrfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2005 FRACP Written Examination Paediatrics & ChildDokument30 Seiten2005 FRACP Written Examination Paediatrics & ChildMedicEdNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCPCH Clinical Exam Information For Candidates July 2019Dokument30 SeitenMRCPCH Clinical Exam Information For Candidates July 2019Mudassar SattarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCPCH Part Ii: Safdar Iqbal'sDokument5 SeitenMRCPCH Part Ii: Safdar Iqbal'sGalaleldin AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatrics AnswersDokument28 SeitenPediatrics Answersjaini_patel23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Pearls in Pediatric CardiologyDokument8 SeitenClinical Pearls in Pediatric CardiologySunjon JondhleNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCPCH PART 1 BlogDokument6 SeitenMRCPCH PART 1 BlogJooyee BrendaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (PAED) End-Posting Examination Questions (R3G1)Dokument16 Seiten(PAED) End-Posting Examination Questions (R3G1)loxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric X RaysDokument88 SeitenPediatric X RaysprinceejNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 1 Updated 241110Dokument51 SeitenPaper 1 Updated 241110walidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qbase MCQs For The Part B MRCPCHDokument8 SeitenQbase MCQs For The Part B MRCPCHMateen ShukriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock - Exam - 6 - Neonatology - ANSWER - Part - One 2Dokument9 SeitenMock - Exam - 6 - Neonatology - ANSWER - Part - One 2Pamela JumpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide To MRCPCH Examinations 18.08.11Dokument18 SeitenGuide To MRCPCH Examinations 18.08.11Subhash MadireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Revision Notes in Paediatrics For The MRCPCH Third EditionDokument26 SeitenEssential Revision Notes in Paediatrics For The MRCPCH Third EditionNadejda MarcovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FCPS-II PaediatricsDokument41 SeitenFCPS-II Paediatricsharoon100% (1)
- MRCPCH Guide New QuestionsDokument11 SeitenMRCPCH Guide New QuestionsRajiv Kabad100% (1)
- Ern MRCPCHDokument24 SeitenErn MRCPCHPasTestBooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatrics Osce: Done By: Mohammed I. Alhefzi. Othman M. Omair Dec. 2011Dokument71 SeitenPediatrics Osce: Done By: Mohammed I. Alhefzi. Othman M. Omair Dec. 2011marina_shawkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 2 Specimen Paper 1Dokument56 SeitenPart 2 Specimen Paper 1Siddy BearNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fetus & Neoborn-3Dokument25 SeitenFetus & Neoborn-3Mateen Shukri100% (1)
- Pediatric 5th year 2017-محلولDokument27 SeitenPediatric 5th year 2017-محلولmotasem alsharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Nelson 20Dokument588 SeitenMCQ Nelson 20della mouradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toacs 2Dokument215 SeitenToacs 2Mobin Ur Rehman Khan100% (1)
- Pediatrics One Liner For TestDokument2 SeitenPediatrics One Liner For TestArvindhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2005 FRACP Written Examination Paediatrics & ChildDokument63 Seiten2005 FRACP Written Examination Paediatrics & ChildMedicEdNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCPCH 1aDokument21 SeitenMRCPCH 1aLoai El100% (1)
- Pediatric 6th Year 2016Dokument30 SeitenPediatric 6th Year 2016motasem alsharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filename: AMC PEDIATRICS 2005 To 2009 PDFDokument38 SeitenFilename: AMC PEDIATRICS 2005 To 2009 PDFZahid QamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PREP E-Med 2017Dokument93 SeitenPREP E-Med 2017Imran A. Isaac100% (1)
- Pediatrics MCQs - DR Ranjan Singh - Part 2Dokument10 SeitenPediatrics MCQs - DR Ranjan Singh - Part 2k sagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRCPCH q15Dokument30 SeitenMRCPCH q15Galaleldin AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Assessment Questions, Group 6Dokument20 SeitenSelf-Assessment Questions, Group 6naveenkovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Processes Class 10 Notes Science - MyCBSEguide - CBSE Papers & NCERT SolutionsDokument5 SeitenLife Processes Class 10 Notes Science - MyCBSEguide - CBSE Papers & NCERT SolutionsRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 9 Social Science Question BankDokument120 SeitenCBSE Class 9 Social Science Question BankRajiv Kabad100% (2)
- AP Study Guide PhysicsDokument96 SeitenAP Study Guide PhysicsRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
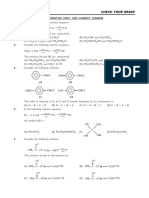
- Exercise-01 Check Your Grasp: CH CL (A) CH CL (B) CHDokument29 SeitenExercise-01 Check Your Grasp: CH CL (A) CH CL (B) CHRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- SC2 - O'Malley SAT II Review (Organic)Dokument2 SeitenSC2 - O'Malley SAT II Review (Organic)Rajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials 2018 Final Feb2018Dokument45 SeitenEssentials 2018 Final Feb2018Rajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15-0000 - Form - QEWS - Standard Pediatric Observation Chart - 0 To 28 DaysDokument2 Seiten15-0000 - Form - QEWS - Standard Pediatric Observation Chart - 0 To 28 DaysRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- NFO Note - Reliance Dual Advantage Fixed Tenure Fund XI - Plan ADokument3 SeitenNFO Note - Reliance Dual Advantage Fixed Tenure Fund XI - Plan ARajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15-0000 - Form - QEWS - Standard Pediatric Observation Chart - 0 To 28 DaysDokument2 Seiten15-0000 - Form - QEWS - Standard Pediatric Observation Chart - 0 To 28 DaysRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birla Public School, Doha-Qatar: Class Xi-Holiday Homework-Biology Record CompletionDokument1 SeiteBirla Public School, Doha-Qatar: Class Xi-Holiday Homework-Biology Record CompletionRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holiday HWDokument4 SeitenHoliday HWRajiv Kabad100% (1)
- Problem of The Week Problem D and Solutions Cube Column RemovalDokument2 SeitenProblem of The Week Problem D and Solutions Cube Column RemovalRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem of The Week: Check Out Other CEMC Resources At: Strand: Data Management, Number SenseDokument1 SeiteProblem of The Week: Check Out Other CEMC Resources At: Strand: Data Management, Number SenseRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Commitee January SolutionsDokument1 SeiteNew Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Commitee January SolutionsRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Western Australian Junior Mathematics Olympiad 2011: Individual QuestionsDokument12 SeitenWestern Australian Junior Mathematics Olympiad 2011: Individual QuestionsRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ComputerDokument3 SeitenComputerRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- POTWD 12 Combined9 10Dokument120 SeitenPOTWD 12 Combined9 10Rajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem of The Week Problem C Looking For Nothing: WWW - Cemc.Uwaterloo - CaDokument1 SeiteProblem of The Week Problem C Looking For Nothing: WWW - Cemc.Uwaterloo - CaRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem of The Week Problem D and Solution Ball ReturnDokument2 SeitenProblem of The Week Problem D and Solution Ball ReturnRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem of The Week Problem C and Solution The First of Three Average ProblemsDokument1 SeiteProblem of The Week Problem C and Solution The First of Three Average ProblemsRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem of The Week Problem C MMMM ... Chocolate: WWW - Cemc.Uwaterloo - CaDokument1 SeiteProblem of The Week Problem C MMMM ... Chocolate: WWW - Cemc.Uwaterloo - CaRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- VILI Neonatal Revision 2022Dokument16 SeitenVILI Neonatal Revision 2022INPER INSTITUTO NACIONAL DE PERINATOLOGIANoch keine Bewertungen
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEM WORKSHEET Answer KeyDokument5 SeitenRESPIRATORY SYSTEM WORKSHEET Answer KeyIker AragonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Physiology & Pathophysiology by John B West 2007 PDFDokument160 SeitenPulmonary Physiology & Pathophysiology by John B West 2007 PDFwafae100% (3)
- High Altitude PhysiologyDokument34 SeitenHigh Altitude PhysiologyNancy Dalla DarsonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology NMAT Notes AnatomyCirculatory and RespiratoryDokument13 SeitenBiology NMAT Notes AnatomyCirculatory and RespiratoryMa. Teresa M. AbainzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Surgical QuizDokument12 SeitenMedical Surgical QuizLyka DimayacyacNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For UrtiDokument40 SeitenNCP For UrtiEarl JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Exchange 1 QPDokument10 SeitenGas Exchange 1 QPKaise AlloudamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Question BankDokument291 SeitenScience Question BankA. PradeepaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUR2226 AT2 Part ADokument7 SeitenNUR2226 AT2 Part ACamille Joy BaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansDokument4 SeitenCH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansPranitha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory and Excretory System ReviewDokument27 SeitenRespiratory and Excretory System ReviewJoyce Catherine Buquing UysecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDokument41 SeitenRespiratory Distress Syndromef.abrahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory SystemDokument15 SeitenRespiratory SystemMichelle Gambol100% (2)
- Practice Worksheet Ans 1-G7Dokument3 SeitenPractice Worksheet Ans 1-G7Ala' ShehadehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study APFDokument64 SeitenCase Study APFJayselle ArvieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Respiratory Function Chpt.20Dokument32 SeitenAssessment of Respiratory Function Chpt.20Maricar RosasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 4: RESPIRATION SYSTEM OF FISH, INSECT AND MAMMALDokument22 SeitenPractical 4: RESPIRATION SYSTEM OF FISH, INSECT AND MAMMALhafizah_90Noch keine Bewertungen
- High-Risk Newborns and Child During Illness and Hospitalization - Pediatric NursingDokument200 SeitenHigh-Risk Newborns and Child During Illness and Hospitalization - Pediatric Nursingjaggermeister20100% (8)
- P2 2019 SMK Methodist PDFDokument11 SeitenP2 2019 SMK Methodist PDFBryanLeeChienYungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Index FA 2019Dokument62 SeitenIndex FA 2019Rehan AltafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventilation-Perfusion RatioDokument34 SeitenVentilation-Perfusion Rationeeba habeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy of Critical Care NursingDokument5 SeitenPhilosophy of Critical Care NursingAICEL A. ABILNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1a - Gonzalez, Jamaica Caryl N. (Respiratory)Dokument13 Seiten1a - Gonzalez, Jamaica Caryl N. (Respiratory)Jhamm GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Anotmy of Respiratory Tract 1 PDFDokument19 SeitenFunctional Anotmy of Respiratory Tract 1 PDFMaskeen AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System: QuestionsDokument9 SeitenRespiratory System: QuestionsoreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDokument36 SeitenAssessment of Respiratory FunctionErica Clerigo LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDokument51 SeitenCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKarel Mae SanoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of RespirationDokument26 SeitenPhysiology of Respirationrevaniwati100% (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (81)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (29)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Von EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (328)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningVon EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsVon EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (170)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainVon EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (95)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (8)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsVon EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlVon EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (59)