Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
MQC
Hochgeladen von
navneetkpatil84090 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
372 Ansichten8 SeitenThis document outlines the course details for a Diploma in Mechanical Engineering program. The fifth semester course is titled Metrology and Quality Control, with a course code of ME/PT/PG. It has a teaching scheme of 3 hours of theory and 2 hours of practical per week. Assessment includes an external exam worth 25 marks for theory and an internal assessment worth 25 marks for practical. The objectives of the course are to understand measurement instruments, fits and tolerances, analyze measurement data, and understand quality standards. Topics covered include measurement techniques, gauges, angular measurement, thread and gear metrology, surface finish testing, quality control, and statistical quality control.
Originalbeschreibung:
sd ffr
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document outlines the course details for a Diploma in Mechanical Engineering program. The fifth semester course is titled Metrology and Quality Control, with a course code of ME/PT/PG. It has a teaching scheme of 3 hours of theory and 2 hours of practical per week. Assessment includes an external exam worth 25 marks for theory and an internal assessment worth 25 marks for practical. The objectives of the course are to understand measurement instruments, fits and tolerances, analyze measurement data, and understand quality standards. Topics covered include measurement techniques, gauges, angular measurement, thread and gear metrology, surface finish testing, quality control, and statistical quality control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
372 Ansichten8 SeitenMQC
Hochgeladen von
navneetkpatil8409This document outlines the course details for a Diploma in Mechanical Engineering program. The fifth semester course is titled Metrology and Quality Control, with a course code of ME/PT/PG. It has a teaching scheme of 3 hours of theory and 2 hours of practical per week. Assessment includes an external exam worth 25 marks for theory and an internal assessment worth 25 marks for practical. The objectives of the course are to understand measurement instruments, fits and tolerances, analyze measurement data, and understand quality standards. Topics covered include measurement techniques, gauges, angular measurement, thread and gear metrology, surface finish testing, quality control, and statistical quality control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 8
1
COURSE NAME : DIPLOMA IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
COURSE CODE : ME /PT/PG
SEMESTER : FIFTH
SUBJECT TITLE : METROLOGY AND QUALITY CONTROL
SUBJECT CODE :
Teaching and Examination Scheme:
Teaching Scheme Examination Scheme
TH TU PR
PAPER
HRS
TH PR OR TW TOTAL
03 -- 02 03 100 25# -- 25@ 150
# External Assessment, @ Internal assessment, TH-Theory, PR- Practical, TW-Term Work
NOTE: Two tests each of 25 marks to be conducted as per the schedule given by
MSBTE. Total of tests marks for all theory subjects are to be converted out of 50
and to be entered in mark sheet under the head Sessional Work. (SW)
Rationale:
The Diploma mechanical Engineer should understand, select and use various
measuring instruments as he often comes across measuring different parameters of
machined components and the appropriate fitment of interchangeable components in the
assemblies.
The knowledge of the subject also forms the basis for the design of mechanical
measurement systems, design & drawing of mechanical components.
Objectives:
Students will be able to:
1. Understand and calculate the least count of all basic measuring instruments.
2. Select and use appropriate instrument/s for specific measurement.
3. Understand the systems of limits, fits and tolerances and correlate with machine
drawing and manufacturing processes.
4. Analyze and interpret the data obtained from the different measurements
processes and present it in the graphical form, statistical form for understanding
the concepts of SQC.
5. Construct, draw and interpret the control charts.
2
Measurement of different parameters
of machined components, Use &
handling of different measuring
instruments , Procedure of
comparing instrument with
standards. Selection of appropriate
instruments on criterion for specific
measurement.
ISO certification procedure,
Frequency distribution,
Control chart plotting, Process
capability determination,
Sampling inspection
procedure, Economics of
quality
Principle of least count, limits fits and
tolerances, Gauge design, optical
Interferometry, Principle of Surface
quality, Principle of Linear/Angular
Measurement, terminology of
threads/Gear and measurement of
their elements.
Statistical Analysis,
Quality Assurance,
Quality Maintenance
Precision, Accuracy, Repeatability,
Sensitivity, Standards of
Measurement, Calibration &
Traceability, Reliability, error
analysis
Cost of quality, Value of Quality,
Quality characteristics,
Measurement of quality,
Controlling quality, Vendor
Rating, Histograms, Basic
statistics, Frequency Normal
Distribution curve, Control charts,
Steel Rule, Vernier Scale
instruments, Micrometers, Slip
gauges, Angle gauges, Sine bar, Go-
No-Go gauges, Comparators, optical
measuring instruments, Geometrical
Parameter testing instruments..
Machined components,
Industrial data, Production
machines with capability of
producing components in
different accuracy zones.
Procedures
Principles
Concepts
Facts
Learning Structure:
To select & use different measuring instruments to measure the
Application qualitative & quantitative characteristics of different machined
components. Statistically analyze the data. Decide action to be
taken for controlling the quality. Understand ISO quality standard
system
.
3
Theory
Topic & Content Hours Marks
1.Introduction to metrology --------------------------------18 Marks
Specific Objectives
To understand the basics of Metrology & calculate the least count of
measuring instruments.
To understand various standards, comparators, gauge selection and
limit system.
1.1Metrology Basics ---------------------06Marks
Definition of metrology, objectives of metrology, Categories of metrology,
Scientific metrology, Industrial metrology, Legal metrology, Need of
inspection, Revision of --Precision, Accuracy, Sensitivity, Readability,
Calibration, Traceability, Reproducibility, Sources of errors, Factors
affecting accuracy, Selection of instrument, Precautions while using an
instruments for getting higher precision and accuracy. Concept of least
count of measuring instruments (No questions to be set on revision).
1.2Standards and Comparators -------------------12Marks
Definition and introduction to line standard end standard, Wavelength
standard and their comparison, Slip gauge and its accessories.
Definition, Requirement of good comparator, Classification, use of
comparators, Working principle of comparators, Dial indicator, Sigma
comparator, Pneumatic comparator- high pressure differential type,
Electrical ( LVDT), Relative advantages and disadvantages.
09
18
2 Limits, Fits ,Tolerances and Gauges ----------------08Marks
Specific Objectives
To understand the basics of limits, fits & tolerances
To calculate the basic and gauge tolerances.
To understand various types of gauges and their applicability.
2.1 Concept of Limits, Fits, And Tolerances, Selective Assembly,
Interchangeability, Hole And Shaft Basis System, Taylors Principle,
Design of Plug, Ring Gauges, IS919-1993 (Limits, Fits & Tolerances,
Gauges IS 3477-1973), Study of relation gauges, concept of multi gauging
and inspection.
06
08
4
3 Angular Measurement ----------------------08Marks
Specific Objectives
To understand the basics of angular measurement and measure
angles using different instruments.
3.1Concept, Instruments For Angular, Measurements, Working And Use of
Universal Bevel Protractor, Sine Bar, Spirit Level, Principle of Working of
Clinometers, Angle Gauges (With Numerical on Setting of Angle
Gauges).Angle dekkor as an angular comparator.
04
8
4.Threads and Gear Metrology --------------------------------16Marks
Specific Objectives
To Understand & use various methods of calculating thread
elements and elements of gear tooth
4.1Screw thread Measurements 08Marks
ISO grade and fits of thread, Errors in threads, Pitch errors, Measurement
of different elements such as major diameter, minor diameter, effective
diameter, pitch for internal and external threads , Three wire method,
Thread gauge, screw thread micrometer, Working principle of floating
carriage micrometer.
4.2 Gear Measurement & Testing 08Marks
Analytical and functional inspection, Measurement of tooth thickness by
constant chord method, base tangent method, gear tooth vernier, Errors in
gears such as backlash, run out, composite, concentricity. Parkinson gear
tester.
06
16
5.Testing Techniques ---------------------------------10Marks
Specific Objectives:
To know terminology of surface finish & measure the surface finish
of various components.
5.1Measurement of surface finish --------------------06Marks
Primary and secondary texture, Sampling length, Lay, terminology as per IS
3073- 1967, direction of lay, Sources of lay and its significance, CLA, Ra,
RMS values and their interpretation, Symbol for designating surface finish
on drawing, Various techniques of qualitative analysis
5.2Machine tool testing --------------------------04Marks
Parallelism, Straightness, Squareness, Coaxiallity, roundness, run out,
06
10
5
alignment testing of machine tools such as lathe, milling machine and
drilling machine as per IS standard procedure. Study of optical flat for
flatness testing.
6.Quality Control ---------------------------12Marks
Specific Objectives:
To understand the concept of Quality, cost of quality.
To understand the concept and principles of TQM.
6.1 Quality : ---------------------------06Marks
Definitions, meaning of quality of produce& services, Quality
characteristics, Quality of design, Quality of conformance, Quality
of performance, Concept of reliability, Cost, Quantity assurance,
Cost of rework & repair, Quality & Inspection, Inspection stages.
6.2 Total Quality Management : ----------------06Marks
Principles and concept of total quantity management.
a) Quality Audit: Concept of audit practices, lead assessor certification.
b) Six sigma: Statistical meaning, methodology of system Improvement.
c) Introduction of ISO 9001-2008.ISO-14000 and TS 16949.
07
12
7 Statistical Quality Control -----------------28Marks
Specific Objectives:
to know the basics of statistics.
To understand different data types and analyze & interpret the data
7.1 Statistical Quality Control --------------------20Marks
Basics of Statistical concepts, Meaning and importance of SQC, Variable
and attribute Measurement. control charts inherent and assignable sources
of variation, control charts for variables X & R charts, control charts for
attributes p, np, C charts, process capability of machine, , C
p
and C
pk
calculations, determination of statistical limits, different possibilities,
Rejection area, Statistically capable and incapable processes (20 marks)
7.2Acceptance Sampling --------08Marks
Concept, Comparison with 100% inspection, Different types of sampling
plans, sampling methods, merits and demerits of acceptance sampling. OC
Curve.
( 08 marks)
10
28
Total 48 100
6
PRACTICALS:
Skills to be developed:
Intellectual skills:
1 To select basic measuring instruments.
2 To calculate least count of various measuring instruments.
3. To collect, record and analyze the data.
4. To interpret the results of data analysis.
Motor skills:
1. Measure the dimensions of component using various instruments.
2. To take care of instruments.
3. To draw various charts and curves related to data.
4. To handle various instruments.
List of Practical:
1. Measurement of various dimensions& dimensional parameters using
instruments such as radius gauge, pitch screw gauge, filler gauge, vernier
caliper, vernier height gauge, vernier depth gauge, dial type vernier caliper,
micrometer, inside micrometer, tube micrometer.
Note: -1) The student should measure at least 3 dimensions of given job and
take 5 readings per dimension.
2) Individual performing the measurement with one setup on one
surface plate and simultaneous 4 to 5 setup should be kept ready for
measurement.( At least 10 Vernier calipers, Micrometers with
different range i.e. 0-25mm two nos. , 25- 50 two nos. Inside
micrometer, tube micrometer, V anvil micrometer at least one.)
2. To set the Adjustable snap gauge GO end and NOGO end for a given
dimensions using slip gauges.
3. Inspection of given components using Dial Indicator as a mechanical
comparator.
4. To check the given component using high pressure Dial type pneumatic
comparator.
5. To find unknown angle of component using bevel protractor and verify the
same using sine bar/ sine center and slip gauges.
6. To measure the angle of component with the Angle Dekkor/Autocollimator
using angle gauge.
7. Measurement of screw thread elements by using screw thread micrometer,
screw pitch gauge & their verification with the help of profile projector/tool
7
Batch size of students for experiment 2 to 13 shall be 4 to 5.
4 to 5 experimental setups should be arranged simultaneously.
Assignment:
1. Visit the industries to collect the data for p and c chart, study the coordinate
measuring machine and study the quality management systems.
2. Selection of comparators for the given dimensional data
Learning Resources:
Sr.No. Author Title Of Book Edition Publisher
01
R. K. Jain
Engineering
metrology
2010 Khanna Publisher, Delhi.
02 M. Mahajan Text book of
metrology
Second
Reprint-
2010
Dhanpat Rai & Co.
03
I.C. Gupta
A text book of
Engineering
metrology
Dhanpat Rai and Sons
04 M. Mahajan Statistical Quality
Control
2010 Dhanpat Rai and Sons
05 Douglas C.
Montgomery
Statistical Quality
Control
Sixth
reprint
2011
Wiley India Pvt. Ltd.
makers microscope.
8. Measurement of gear tooth elements by using gear tooth vernier caliper and
verification of gear tooth profile using profile projector.
9. To measure surface roughness using surface roughness measuring instrument.
Measure surface roughness of turning, milling ,shaping ,grinding and lapping
surfaces.
10. Testing of lathe machine/drill machine for parallelism, squareness, trueness by
Test Dial indicator.
11. Draw the frequency histogram, frequency polygon for given samples (min 50
readings) and find mean, mode, median.
12. To draw the normal distribution curve and find standard deviation, variance,
range and determine process capability.
13. To draw and interpret the control Charts (X bar and R chart, P chart, C
chart) for given data.
8
06 Dale H.
Besterfield
and others
Total Quality
Management
Third
Reprint
2012
Pearson
2. IS/ International Codes:
IS 919 1993 Recommendation for limits, fits and tolerances
IS 2029 1962 Dial gauges.
IS 2103 1972 Engineering Square
IS 2909 1964 Guide for selection of fits.
IS 2921 1964 Vernier height gauges
IS 2949 1964 V Block.
IS 2984 1966 Slip gauges.
IS 3139 1966 Dimensions for screw threads.
IS 3179 1965 Feeler gauges.
IS 3455 1966 Tolerances for plain limit gauges.
IS 3477 1973 Snap gauges.
IS 6137 1971 Plain plug gauges.
IS 3651 1976 Vernier Caliper
IS 4218 - Isometric screw threads
IS 4440 1967 Slip gauges accessories
IS 5359 1969 Sine bars
IS 5402 1970 Principle and applications of sine bars
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Linear Space-State Control Systems Solutions ManualDokument141 SeitenLinear Space-State Control Systems Solutions ManualOrlando Aguilar100% (4)
- Booklet - Frantic Assembly Beautiful BurnoutDokument10 SeitenBooklet - Frantic Assembly Beautiful BurnoutMinnie'xoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Point Level Detection in Liquids and Bulk Solids: Selection and Engineering GuideDokument72 SeitenPoint Level Detection in Liquids and Bulk Solids: Selection and Engineering GuideHumberto SagárnagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOCHEM REPORT - OdtDokument16 SeitenBIOCHEM REPORT - OdtLingeshwarry JewarethnamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ergonomics For The BlindDokument8 SeitenErgonomics For The BlindShruthi PandulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9097 - Metrology & Quality ControlDokument7 Seiten9097 - Metrology & Quality ControlAhmed Abu-SinnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC601 Metrology and Quality Engineering 3+1: ObjectivesDokument1 SeiteMEC601 Metrology and Quality Engineering 3+1: ObjectivesHoney SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASQ Certified Quality Inspector Body of KowledgeDokument7 SeitenASQ Certified Quality Inspector Body of Kowledgeblack bettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC601 Metrology and Quality Engineering 3+1: ObjectivesDokument1 SeiteMEC601 Metrology and Quality Engineering 3+1: Objectivesnavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- TE Mechanical and TE Automobile (2015 Course)Dokument7 SeitenTE Mechanical and TE Automobile (2015 Course)A SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Content SEM 6Dokument16 SeitenDetailed Content SEM 6HIMANSHU KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Pune: T.E. (Mechanical) - 2012 Course Metrology and Quality Control (302044)Dokument3 SeitenUniversity of Pune: T.E. (Mechanical) - 2012 Course Metrology and Quality Control (302044)Arvind BhosaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- American Society For Quality Certified Quality Inspector (CQI) Body of Knowledge 2018Dokument8 SeitenAmerican Society For Quality Certified Quality Inspector (CQI) Body of Knowledge 2018Mani Rathinam RajamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metrlogy CurriculumDokument3 SeitenMetrlogy CurriculumDj GAMINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP5SEMSYLLABUSDokument6 SeitenIP5SEMSYLLABUSAditya RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metrology - (A)Dokument4 SeitenMetrology - (A)smrtyfaizan786Noch keine Bewertungen
- State Board of Technical Education &training, Tamilnadu Diploma in Engineering / Technology Syllabus N - SchemeDokument15 SeitenState Board of Technical Education &training, Tamilnadu Diploma in Engineering / Technology Syllabus N - SchemeIsrael Dharmaraj100% (1)
- MM SyllabusDokument2 SeitenMM SyllabusS.Bharani KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metrology & Quality ControlDokument127 SeitenMetrology & Quality ControlArnav PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1 - Metrology and MeasurementDokument51 SeitenCH 1 - Metrology and MeasurementRahul PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- MetrologyDokument3 SeitenMetrologySachi DhanandamNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review of Current Geo-Metric Tolerancing Theo - Ries and Inspection Data Analysis AlgorithmsDokument22 SeitenA Review of Current Geo-Metric Tolerancing Theo - Ries and Inspection Data Analysis AlgorithmsKarthik KarunanidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18ME7F2-Metrology and Quality ControlDokument2 Seiten18ME7F2-Metrology and Quality ControlXaf FarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Curriculum of The Department of Industrial and Production EngineeringDokument24 SeitenCourse Curriculum of The Department of Industrial and Production EngineeringRashedul Islam RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MQC SyllDokument2 SeitenMQC SyllAandy KhasdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Hydraulic and Pneumatic SystemsDokument2 SeitenDesign of Hydraulic and Pneumatic SystemsGokul raj SNoch keine Bewertungen
- MQC Teachers Manual PDFDokument5 SeitenMQC Teachers Manual PDFnavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mech 6Dokument18 SeitenMech 6MILAN GAUTAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRP 7th 8th Syllabus..Dokument34 SeitenCRP 7th 8th Syllabus..Archana MaskeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProdDokument9 SeitenProdapi-236544093Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jntuh Mech Engg R16 SyllabusDokument7 SeitenJntuh Mech Engg R16 SyllabusAqib syedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course 11.pdfind. EnggDokument5 SeitenCourse 11.pdfind. EnggNavneet VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me Vtu DFM Syllabus CBCS SchemeDokument2 SeitenMe Vtu DFM Syllabus CBCS SchemeNitheeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metrology QuestionsDokument5 SeitenMetrology QuestionsWaqaar JowataNoch keine Bewertungen
- M & I PDFDokument13 SeitenM & I PDFvirendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toaz - Info Engineering Metrology PRDokument129 SeitenToaz - Info Engineering Metrology PRB05Vedant BarpandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Measurement and MetrologyDokument2 SeitenMechanical Measurement and MetrologyNarayanarao PalagaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological University - MeasurementDokument4 SeitenGujarat Technological University - MeasurementA SNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7th SemDokument17 Seiten7th SemShankar MukalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cqi Insert 2006Dokument4 SeitenCqi Insert 2006Popescu AlinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Van PPT WosaDokument8 SeitenVan PPT WosavanajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEPR205C - El 1 Metrology & Computer Aided InspectionDokument3 SeitenMEPR205C - El 1 Metrology & Computer Aided Inspectionዘረአዳም ዘመንቆረርNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 MQC SyllabusDokument5 Seiten1 MQC SyllabusAnilChauvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amm 657 1006Dokument7 SeitenAmm 657 1006விக்னேஷ் வரன்Noch keine Bewertungen
- MetrologyDokument10 SeitenMetrologyAwais WahabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Measurements and Metrology: Topic AnalysisDokument6 SeitenMechanical Measurements and Metrology: Topic Analysisسيمو بشيريNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To MetrologyDokument26 SeitenIntroduction To MetrologyDimon HeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus M.tech MechanicalDokument23 SeitenSyllabus M.tech Mechanicalडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPE SyllabusDokument24 SeitenIPE SyllabusMaksumul MorsalineNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMM Module 1Dokument22 SeitenMMM Module 1SUNIL SWAMY SNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.mechanical Measurements and MetrologyDokument6 Seiten4.mechanical Measurements and MetrologyVikram Rao100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3Dokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3jpbhimaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Metrology and Measurements Unit 1 2Dokument82 SeitenEngineering Metrology and Measurements Unit 1 2scorpionarnold100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University: Mechanical (Cad/Cam) (08) / Mechanical (Machine Design) (09) SUBJECT CODE: 2740804Dokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological University: Mechanical (Cad/Cam) (08) / Mechanical (Machine Design) (09) SUBJECT CODE: 2740804Shailesh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PI Production and Industrial EngineeringDokument4 SeitenPI Production and Industrial Engineeringnitik bhuriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial EngineeringDokument2 SeitenIndustrial EngineeringKaran VirkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pi SyllDokument4 SeitenPi Syllgawis17992Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tool Die MakerDokument32 SeitenTool Die MakerUmesh KsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metrology and Instrumentation M 602 3Dokument1 SeiteMetrology and Instrumentation M 602 3AnilkumarGopinathanNairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to N.C.M., a Non Contact Measurement ToolVon EverandIntroduction to N.C.M., a Non Contact Measurement ToolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Metrology for Manufacturing EngineeringVon EverandApplied Metrology for Manufacturing EngineeringBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 2018-19 F.E. To B.E. Mechanical Engineering StructureDokument11 Seiten2018-19 F.E. To B.E. Mechanical Engineering Structurenavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Sports and Cultural ActivitiesDokument2 SeitenReport On Sports and Cultural Activitiesnavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- NAAC Criteria IV ChecklistDokument1 SeiteNAAC Criteria IV Checklistnavneetkpatil8409100% (1)
- Applied Thermodynamics LabDokument3 SeitenApplied Thermodynamics Labnavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nmu at ExaminerDokument6 SeitenNmu at Examinernavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- EXP-6-Measurement of Screw ParametersDokument2 SeitenEXP-6-Measurement of Screw Parametersnavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nmu at PDFDokument4 SeitenNmu at PDFnavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summer 2014 Model Answer PaperDokument42 SeitenSummer 2014 Model Answer Papernavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Statement of Grades: (100007) SSBT College of Engineering & Technology, Bambhori, JalgaonDokument1.898 SeitenStatement of Grades: (100007) SSBT College of Engineering & Technology, Bambhori, Jalgaonnavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Registration Sheet MechDokument1 SeiteRegistration Sheet Mechnavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Seat No.: Instructions: (1) All Questions Are CompulsoryDokument4 SeitenSeat No.: Instructions: (1) All Questions Are Compulsorynavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat NoDokument5 Seiten4 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat Nonavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- List of Exercises: Computer Integrated Manufacturing & Technology Driven PracticesDokument1 SeiteList of Exercises: Computer Integrated Manufacturing & Technology Driven Practicesnavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
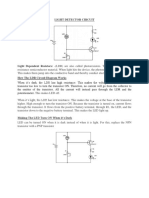
- Light Detector CircuitDokument1 SeiteLight Detector Circuitnavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Safe Elevators + (91) - 9130865244 Shop No.17, Eidgah Market, Ajanta Road, MIDC, Jalgaon - 425003, Near Ajanta ChowffulliDokument1 SeiteSafe Elevators + (91) - 9130865244 Shop No.17, Eidgah Market, Ajanta Road, MIDC, Jalgaon - 425003, Near Ajanta Chowffullinavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ode and NameDokument670 SeitenOde and Namenavneetkpatil8409Noch keine Bewertungen
- August Strindberg's ''A Dream Play'', inDokument11 SeitenAugust Strindberg's ''A Dream Play'', inİlker NicholasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen Peroxide DripDokument13 SeitenHydrogen Peroxide DripAya100% (1)
- Cambridge English Key Sample Paper 1 Reading and Writing v2Dokument9 SeitenCambridge English Key Sample Paper 1 Reading and Writing v2kalinguer100% (1)
- Drapeau Resume May09Dokument5 SeitenDrapeau Resume May09drmark212Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hibbeler, Mechanics of Materials-BendingDokument63 SeitenHibbeler, Mechanics of Materials-Bendingpoom2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Al-Tawheed According To The SahabahDokument16 SeitenAl-Tawheed According To The SahabahShadab AnjumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - HandBook CBBR4106Dokument29 Seiten1 - HandBook CBBR4106mkkhusairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech Step by Step Step 7 Reported QuestionsDokument4 SeitenReported Speech Step by Step Step 7 Reported QuestionsDaniela TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Cloud Computing Governance Framework PDFDokument8 SeitenA New Cloud Computing Governance Framework PDFMustafa Al HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CopacabanaDokument2 SeitenCopacabanaNereus Sanaani CAñeda Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry Primer Problem Set Solns PDFDokument80 SeitenTrigonometry Primer Problem Set Solns PDFderenz30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Form No. 10-I: Certificate of Prescribed Authority For The Purposes of Section 80DDBDokument1 SeiteForm No. 10-I: Certificate of Prescribed Authority For The Purposes of Section 80DDBIam KarthikeyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aff Col MA Part IIDokument90 SeitenAff Col MA Part IIAkanksha DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teuku Tahlil Prosiding38491Dokument30 SeitenTeuku Tahlil Prosiding38491unosa unounoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Personal Law of The Mahommedans, According To All The Schools (1880) Ali, Syed Ameer, 1849-1928Dokument454 SeitenThe Personal Law of The Mahommedans, According To All The Schools (1880) Ali, Syed Ameer, 1849-1928David BaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Sytems Counters and Registers: Dce DceDokument17 SeitenDigital Sytems Counters and Registers: Dce DcePhan Gia AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em 1.4 RMDokument18 SeitenEm 1.4 RMMangam RajkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuration Steps - Settlement Management in S - 4 HANA - SAP BlogsDokument30 SeitenConfiguration Steps - Settlement Management in S - 4 HANA - SAP Blogsenza100% (4)
- MPCDokument193 SeitenMPCpbaculimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Strategy CH 2Dokument37 SeitenManagement Strategy CH 2Meishera Panglipurjati SaragihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lets Install Cisco ISEDokument8 SeitenLets Install Cisco ISESimon GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary Tract Infection in Children: CC MagbanuaDokument52 SeitenUrinary Tract Infection in Children: CC MagbanuaVanessa YunqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biofloc Technology (BFT) Water Quality, Biofloc Composition, and GrowthDokument8 SeitenThe Biofloc Technology (BFT) Water Quality, Biofloc Composition, and GrowthHafez MabroukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roofing Shingles in KeralaDokument13 SeitenRoofing Shingles in KeralaCertainteed Roofing tilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contracts 2 Special ContractsDokument11 SeitenContracts 2 Special ContractsAbhikaamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported SpeechDokument2 SeitenReported SpeechmayerlyNoch keine Bewertungen