Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Roller Bearing
Hochgeladen von
EagleMenaceCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Roller Bearing
Hochgeladen von
EagleMenaceCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A 6 A 7
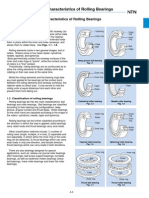
1.1 Design and Classification
Rolling bearings generally consist of two rings, rolling
elements, and a cage, and they are classified into radial
bearings or thrust bearings depending on the direction
of the main load. In addition, depending on the type of
rolling elements, they are classified into ball bearings
or roller bearings, and they are further segregated by
differences in their design or specific purpose.
The most common bearing types and nomenclature
of bearing parts are shown in Fig.1.1, and a general
classification of rolling bearings is shown in Fig. 1.2.
1.2 Characteristics of Rolling Bearings
Compared with plain bearings, rolling bearings have
the following major advantages:
(1) Their starting torque or friction is low and the
difference between the starting torque and running
torque is small.
(2) With the advancement of worldwide standardization,
rolling bearings are internationally available and
interchangeable.
(3) Maintenance, replacement, and inspection are easy
because the structure surrounding rolling bearings
is simple.
(4) Many rolling bearings are capable of taking
both radial and axial loads simultaneously or
independently.
(5) Rolling bearings can be used under a wide range of
temperatures.
(6) Rolling bearings can be preloaded to produce a
negative clearance and achieve greater rigidity.
Furthermore, different types of rolling bearings have
their own individual advantages. The features of the
most common rolling bearings are described on Pages
A10 to A12 and in Table 1.1 (Pages A14 and A15).
Width
Snap Ring
Cage
Rivet
Ball
Inner Ring
Raceway
Outer Ring
Raceway
Chamfer Dimension
Bearing Width
Cross-Face Width
Outer Ring
Inner Ring
Side Face
Shield
B
o
r
e
D
i
a
.
O
u
t
s
id
e
D
ia
.
P
it
c
h
D
ia
m
e
t
e
r
Tapered Roller Bearing Spherical Roller Bearing Single-Direction Thrust Ball Bearing
Single-Row Deep Groove Ball Bearing Single-Row Angular Contact Ball Bearing Cylindrical Roller Bearing
Stand out
Cone Front Face Rib
Cone Back
Face Rib
Tapered Roller
Effective Load
Center
Effective
Load Center
Contact
Angle
Contact Angle
Cone Back
Face
Cup Front
Face
Inner Ring
Back Face
Outer Ring
Front Face
Cone Front Face
Cup Back Face
Inner Ring
Front Face
Outer Ring
Back Face
Aligning Seat
Center Height
A
lig
n
in
g
S
e
a
t
R
a
d
iu
s
Bore Dia.
Height
Housing
Washer
Bore Dia.
Aligning Seat
Washer O.D.
Outside Dia.
Shaft Washer
Ball
Housing Washer
Aligning
Seat
Washer
Outer Ring Rib
L-Shaped
Thrust Collar
Inner Ring
Rib
Cylindrical
Roller
R
o
l
l
e
r
I
n
s
c
r
i
b
e
d
C
i
r
c
l
e
D
i
a
.
Tapered Bore
Inner Ring
Spherical Roller
Outer Ring
Lock
Washer
Nut
Sleeve
A
d
a
p
t
e
r
Fig. 1.1 Nomenclature for Bearing Parts
1.TYPES AND FEATURES OF ROLLING BEARINGS
A007-023E.indd 6-7 11/5/12 5:21:52 PM
A 8 A 9
TYPES AND FEATURES OF ROLLING BEARINGS
Deep Groove
Ball Bearing
Angular Contact
Ball Bearing
Self-Aligning
Ball Bearing
Cylindrical
Roller
Bearing
Needle
Roller
Bearing
Tapered
Roller
Bearing
Single-Direction Thrust Ball Bearing
Thrust Cylindrical Roller Bearing
Thrust Spherical Roller Bearing
Sealed Axle Bearing
Cylindrical Roller Bearing for Sheaves
Spherical
Roller
Bearing
Thrust Tapered Roller Bearing
Single
Row
Double
Row
Single
Row
Double
Row
Ball
Bearings
Matched
Deep Groove
Ball Bearings
Magneto
Bearings
Single
Row
Double
Row
Cylindrical
Roller
Bearings
Long-Roller
Bearings
Angular
Contact Ball
Bearings
Single
Row
Double
Row
Four
Row
Tapered
Roller
Bearings
Spherical
Roller
Bearings
Roller
Bearings
Self-Aligning
Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings
for Bearing
Units
Three- Point/Four-Point
Contact Ball Bearings
ROLLING BEARINGS
Ball
Bearings
Roller
Bearings
Thrust Ball
Bearings
Angular Contact
Thrust Ball
Bearings
Thrust Cylindrical
Roller Bearings
Thrust Needle
Roller Bearings
Thrust Tapered
Roller Bearings
Thrust Spherical
Roller Bearings
Automotive Clutch
Release Bearings
Rolling Stock
Axle Bearings
Crane-Sheave
Bearings
Bearings for Specific Uses
Chain Conveyor
Bearings
Others
Single
Direction
Double
Direction
Automotive Water
Pump Bearings
(Thrust Bearings) (Radial Bearings)
Needle Roller
Bearings
Fig. 1.2 Classification of Rolling Bearings
A007-023E.indd 8-9 11/5/12 5:21:53 PM
A 10 A 11
TYPES AND FEATURES OF ROLLING BEARINGS
Single-row deep groove ball bearings are the most common type of rolling bearings. Their use
is very widespread. The raceway grooves on both the inner and outer rings have circular arcs of
slightly larger radius than that of the balls. In addition to radial loads, axial loads can be imposed
in either direction. Because of their low torque, they are highly suitable for applications where high
speeds and low power loss are required.
In addition to open type bearings, these bearings often have steel shields or rubber seals installed
on one or both sides and are prelubricated with grease. Also, snap rings are sometimes used on
the periphery. As to cages, pressed steel ones are the most common.
Single-Row
Deep Groove
Ball Bearings
The inner groove of magneto bearings is a little shallower than that of deep groove bearings.
Since the outer ring has a shoulder on only one side, the outer ring may be removed. This is often
advantageous for mounting. In general, two such bearings are used in duplex pairs. Magneto
bearings are small bearings with a bore diameter of 4 to 20 mm and are mainly used for small
magnetos, gyroscopes, instruments, etc. Pressed brass cages are generally used.
Magneto
Bearings
Individual bearings of this type are capable of taking radial loads and also axial loads in one
direction. Four contact angles of 15, 25, 30, and 40 are available. The larger the contact angle,
the higher the axial load capacity. For high speed operation, however, the smaller contact angles
are preferred. Usually, two bearings are used in duplex pairs, and the clearance between them
must be adjusted properly.
Pressed-steel cages are commonly used, however, for high precision bearings with a contact angle
less than 30, polyamide resin cages are often used.
Single-Row
Angular Contact
Ball Bearings
A combination of two radial bearings is called a duplex pair. Usually, they are formed using angular
contact ball bearings or tapered roller bearings. Possible combinations include face-to-face, which
have the outer ring faces together (type DF), back-to-back (type DB), or both front faces in the
same direction (type DT). DF and DB duplex bearings are capable of taking radial loads and axial
loads in either direction. Type DT is used when there is a strong axial load in one direction and it is
necessary to impose the load equally on each bearing.
Duplex Bearings
Double-row angular contact ball bearings are basically two single-row angular contact ball bearings
mounted back-to-back except that they have only one inner ring and one outer ring, each having
raceways. They can take axial loads in either direction.
Double-Row
Angular Contact
Ball Bearings
The inner and outer rings of four-point contact ball bearings are separable because the inner ring
is split in a radial plane. They can take axial loads from either direction. The balls have a contact
angle of 35 with each ring. Just one bearing of this type can replace a combination of face-to-face
or back-to-back angular contact bearings.
Machined brass cages are generally used.
Four-Point
Contact
Ball Bearings
The inner ring of this type of bearing has two raceways and the outer ring has a single spherical
raceway with its center of curvature coincident with the bearing axis. Therefore, the axis of the
inner ring, balls, and cage can deflect to some extent around the bearing center. Consequently,
minor angular misalignment of the shaft and housing caused by machining or mounting error is
automatically corrected.
This type of bearing often has a tapered bore for mounting using an adapter sleeve.
Self-Aligning
Ball Bearings
In bearings of this type, the cylindrical rollers are in linear contact with the raceways. They have a
high radial load capacity and are suitable for high speeds.
There are different types designated NU, NJ, NUP, N, NF for single-row bearings, and NNU, NN for
double-row bearings depending on the design or absence of side ribs.
The outer and inner rings of all types are separable.
Some cylindrical roller bearings have no ribs on either the inner or outer ring, so the rings can
move axially relative to each other. These can be used as free-end bearings. Cylindrical roller
bearings, in which either the inner or outer rings has two ribs and the other ring has one, are
capable of taking some axial load in one direction. Double-row cylindrical roller bearings have high
radial rigidity and are used primarily for precision machine tools.
Pressed steel or machined brass cages are generally used, but sometimes molded polyamide
cages are also used.
Cylindrical
Roller Bearings
A007-023E.indd 10-11 11/5/12 5:21:56 PM
A 12 A 13
TYPES AND FEATURES OF ROLLING BEARINGS
Needle roller bearings contain many slender rollers with a length 3 to 10 times their diameter. As a
result, the ratio of the bearing outside diameter to the inscribed circle diameter is small, and they
have a rather high radial load capacity.
There are numerous types available, and many have no inner rings. The drawn-cup type has a
pressed steel outer ring and the solid type has a machined outer ring. There are also cage and
roller assemblies without rings. Most bearings have pressed steel cages, but some are without
cages.
Needle
Roller Bearings
Bearings of this type use conical rollers guided by a back-face rib on the cone. These bearings are
capable of taking high radial loads and also axial loads in one direction. In the HR series, the rollers
are increased in both size and number giving it an even higher load capacity.
They are generally mounted in pairs in a manner similar to single-row angular contact ball
bearings. In this case, the proper internal clearance can be obtained by adjusting the axial distance
between the cones or cups of the two opposed bearings. Since they are separable, the cone
assemblies and cups can be mounted independently.
Depending upon the contact angle, tapered roller bearings are divided into three types called the
normal angle, medium angle, and steep angle. Double-row and four-row tapered roller bearings are
also available. Pressed steel cages are generally used.
Tapered
Roller Bearings
These bearings have barrel-shaped rollers between the inner ring, which has two raceways, and the
outer ring which has one spherical raceway. Since the center of curvature of the outer ring raceway
surface coincides with the bearing axis, they are self-aligning in a manner similar to that of self-
aligning ball bearings. Therefore, if there is deflection of the shaft or housing or misalignment of
their axes, it is automatically corrected so excessive force is not applied to the bearings.
Spherical roller bearings can take, not only heavy radial loads, but also some axial loads in either
direction. They have excellent radial load-carrying capacity and are suitable for use where there are
heavy or impact loads.
Some bearings have tapered bores and may be mounted directly on tapered shafts or cylindrical
shafts using adapters or withdrawal sleeves.
Pressed steel and machined brass cages are used.
Spherical
Roller Bearings
Single-direction thrust ball bearings are composed of washer-like bearing rings with raceway
grooves. The ring attached to the shaft is called the shaft washer (or inner ring) while that attached
to the housing is called the housing washer(or outer ring).
In double-direction thrust ball bearings, there are three rings with the middle one (center ring)
being fixed to the shaft.
There are also thrust ball bearings with an aligning seat washer beneath the housing washer in
order to compensate for shaft misalignment or mounting error.
Pressed steel cages are usually used in the smaller bearings and machined cages in the larger
ones.
Single-Direction
Thrust Ball
Bearings
Double-Direction
Thrust Ball
Bearings
These bearings have a spherical raceway in the housing washer and barrel-shaped rollers obliquely
arranged around it. Since the raceway in the housing washer in spherical, these bearings are self-
aligning. They have a very high axial load capacity and are capable of taking moderate radial loads
when an axial load is applied.
Pressed steel cages or machined brass cages are usually used.
Spherical Thrust
Roller Bearings
A007-023E.indd 12-13 11/5/12 5:21:59 PM
A 14 A 15
TYPES AND FEATURES OF ROLLING BEARINGS
Cylindrical
Roller
Bearings
with
Single Rib
Double-Row
Cylindrical
Roller
Bearings
Cylindrical
Roller
Bearings
Self-
Aligning
Ball
Bearings
Four-Point
Contact
Ball
Bearings
Duplex
Angular
Contact
Ball
Bearings
Double-Row
Angular
Contact
Ball
Bearings
Angular
Contact
Ball
Bearings
Magneto
Bearings
Deep
Groove
Ball
Bearings
Bearing
Types
Features
Radial Loads
Axi al Loads
Combined
Loads
Hi gh Speeds
High Accuracy
Low Noise and
Torque
Rigidity
Angular
Misalignment
Self-Aligning
Capability
Ring
Separability
Fixed-End
Bearing
Free-End
Bearing
Tapered Bore
in Inner Ring
Remarks
B5
B31
B5
B28
B47
B47
B70
B47
B47
B72
B77 B85
B85
B110
B85
T
w
o
b
e
a
r
i
n
g
s
a
r
e
u
s
u
a
l
l
y
m
o
u
n
t
e
d
i
n
o
p
p
o
s
i
t
i
o
n
.
C
o
n
ta
c
t a
n
g
le
s
o
f 1
5
o, 2
5
o
3
0
o, a
n
d
4
0
o. T
w
o
b
e
a
r
in
g
s
a
r
e
u
s
u
a
lly
m
o
u
n
te
d
in
o
p
p
o
s
itio
n
.
C
le
a
r
a
n
c
e
a
d
ju
s
tm
e
n
t is
n
e
c
e
s
s
a
r
y
.
C
o
m
b
in
a
t
io
n
o
f
D
F
a
n
d
D
T
p
a
ir
s
is
p
o
s
s
ib
le
, b
u
t
u
s
e
o
n
f
r
e
e
-
e
n
d
is
n
o
t
p
o
s
s
ib
le
.
C
o
n
t
a
c
t
a
n
g
l
e
o
f
3
5
o
I
n
c
l
u
d
i
n
g
N
t
y
p
e
I
n
c
l
u
d
i
n
g
N
N
U
t
y
p
e
I
n
c
l
u
d
i
n
g
N
F
t
y
p
e
I
n
c
l
u
d
i
n
g
N
U
P
t
y
p
e
T
w
o
b
e
a
r
in
g
s
a
r
e
u
s
u
a
lly
m
o
u
n
t
e
d
in
o
p
p
o
s
it
io
n
.
C
le
a
r
a
n
c
e
a
d
ju
s
t
m
e
n
t
is
n
e
c
e
s
s
a
r
y
.
K
H
,
K
V
t
y
p
e
s
a
r
e
a
l
s
o
a
v
a
i
l
a
b
l
e
b
u
t
u
s
e
o
n
f
r
e
e
-
e
n
d
i
s
i
m
p
o
s
s
i
b
l
e
.
I
n
c
l
u
d
i
n
g
n
e
e
d
l
e
r
o
l
l
e
r
t
h
r
u
s
t
b
e
a
r
i
n
g
s
T
o
b
e
u
s
e
d
w
i
t
h
o
i
l
l
u
b
r
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
Page No.
i
i i i i i
i i i i i
I I I I I i i
i i
Page No.
A18
A37
A19
A58
A81
A19
A19
A96
A18
Blue pages of
each brg.
type
A18
A19
A20
A20~
~A21
A20~
~A27
A800
A118
A122
Thrust
Spherical
Roller
Bearings
Thrust
Tapered
Roller
Bearings
Thrust
Cylindrical
Roller
Bearings
Double-
Direction
Angular
Contact
Thrust
Ball
Bearings
Thrust Ball
Bearings
with
Aligning
Seat
Thrust
Ball
Bearings
Spherical
Roller
Bearings
Double-and
Multiple-Row
Tapered
Roller
Bearings
Tapered
Roller
Bearings
B115
B115
B176
B299
B183 B207 B207 B235
B207
B224
B207
B228
Needle
Roller
Bearings
Cylindrical
Roller
Bearings
with Thrust
Collars
B85
i i i
i i i i i i i i i i
i i i
i I I
i
Excellent Good Fair Poor Impossible Two directions
i Applicable I Applicable, but it is necessary to allow shaft contraction/elongation at fitting surfaces of bearings.
Table 1. 1 Types and Characteristics of Rolling Bearings
L
o
a
d
C
a
p
a
c
i
t
y
One direction
only
A007-023E.indd 14-15 11/5/12 5:22:01 PM
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NTN Roller Bearing HandbookDokument84 SeitenNTN Roller Bearing HandbookKok Toong FattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic of BearingDokument16 SeitenBasic of BearingSNEHAL PATEL100% (1)
- Bearing ArrangementDokument5 SeitenBearing ArrangementSubbarayan SaravanakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roller BrochureDokument16 SeitenRoller BrochurePeterson MagroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Ball Bearings: Bearing NomenclatureDokument4 SeitenNotes On Ball Bearings: Bearing NomenclaturePallavi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modular Rack and Pinion System CatalogDokument39 SeitenModular Rack and Pinion System Catalogmeendismurat100% (1)
- Hydraulic CylindersDokument7 SeitenHydraulic Cylinderspacopil34Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sedis Conveyor Chains Catalogue PDFDokument236 SeitenSedis Conveyor Chains Catalogue PDFAlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- CuñaDokument20 SeitenCuñaJulian Granados RicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mold and Die Casting Fit RecommendationsDokument6 SeitenMold and Die Casting Fit RecommendationsJyoti KaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Shaft, Key, Splines, Couplings, Bearings, Clutch and BrakeDokument200 SeitenUnit 1 Shaft, Key, Splines, Couplings, Bearings, Clutch and BrakeAbhijeet somawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel-Smith PDF CatalogueDokument93 SeitenSteel-Smith PDF CatalogueneetadaeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Guide - O-Ring, Quad-Ring, ERIKSDokument13 SeitenDesign Guide - O-Ring, Quad-Ring, ERIKSDerekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boston ReducersDokument356 SeitenBoston ReducersVicente Banda ZuñigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renold Wheels SprocketsDokument36 SeitenRenold Wheels Sprocketssumanthkulkarni07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 (Fits and Tolerance)Dokument49 SeitenChapter 1 (Fits and Tolerance)Hassan El-kholyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roller Conveyor CatalogueDokument50 SeitenRoller Conveyor CatalogueAbudo Paixao100% (2)
- Spring DesignDokument52 SeitenSpring Designmustafa1011Noch keine Bewertungen
- SwingClamp BottomFlangeDokument4 SeitenSwingClamp BottomFlangePeter CusimanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAG Split Spherical Roller BearingsDokument26 SeitenFAG Split Spherical Roller BearingskapokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Bending: Bending Is A Manufacturing Process That Produces A V-Shape, U-Shape, or ChannelDokument12 SeitenMetal Bending: Bending Is A Manufacturing Process That Produces A V-Shape, U-Shape, or ChannelMizero AimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- TS 5 Transfer SystemDokument246 SeitenTS 5 Transfer SystemSantosh DengleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Ball BearingsDokument10 SeitenNotes On Ball BearingsSumit SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Cutting PDFDokument92 SeitenMetal Cutting PDFJagadishchandrabose KondamudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME080 Section 8 - Other Hydraulic ComponentsDokument101 SeitenME080 Section 8 - Other Hydraulic ComponentsAhmed FaragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drive Shaft AnalysisDokument5 SeitenDrive Shaft AnalysisSachin PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of GearsDokument22 SeitenTypes of GearsAnonymous 2RbW9dNoch keine Bewertungen
- TE B Gearbox Design Oral QuestionsDokument5 SeitenTE B Gearbox Design Oral QuestionsapteashutoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Conveyor BookDokument14 SeitenBelt Conveyor BookchekuswekuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 004 GHB Oxy-Fuel Cutting TechniquesDokument191 Seiten004 GHB Oxy-Fuel Cutting TechniquesMilan DurcovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Select the Right Industrial Gearbox in 15 StepsDokument4 SeitenSelect the Right Industrial Gearbox in 15 StepssanjushaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refractory LiningDokument3 SeitenRefractory LiningzhanghuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design & Analysis of Steering System Drag Link Against Buckling Loads For Tipper ApplicationDokument7 SeitenDesign & Analysis of Steering System Drag Link Against Buckling Loads For Tipper ApplicationIJIERT-International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renold Conveyor ChainDokument64 SeitenRenold Conveyor ChainKiran Kumar K T100% (1)
- Fenner Dual Duty Pulley With Taper Lock Bush: A / Spa C / SPC 8V Timing PulleyDokument3 SeitenFenner Dual Duty Pulley With Taper Lock Bush: A / Spa C / SPC 8V Timing PulleyPankaj Pandey100% (1)
- Springs Deflection and ApplicationsDokument42 SeitenSprings Deflection and ApplicationsYosafat Try FajarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Bending Machine ManufacturerDokument13 SeitenPipe Bending Machine ManufacturerS.N. ENTERPRISES PIPE BENDING100% (1)
- Reaction Injection MoldingDokument8 SeitenReaction Injection MoldingAmeer_Takashim_9385Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rexnord® High Performance Bucket Elevators PDFDokument12 SeitenRexnord® High Performance Bucket Elevators PDFJavier Alejandro Rodriguez MelgozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulleys - Pulley LaggingDokument4 SeitenPulleys - Pulley LaggingWaris La Joi WakatobiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silent BlockDokument21 SeitenSilent BlockVijayGowthamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accesorios Roscados para PlásticosDokument32 SeitenAccesorios Roscados para PlásticosjbertralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conveyor DrivespulleysDokument55 SeitenConveyor DrivespulleysSaurabh JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- DESTACO Clamping Technology CatalogDokument485 SeitenDESTACO Clamping Technology Catalogeasch75100% (1)
- Final Sprocket New 24Dokument65 SeitenFinal Sprocket New 24Madhu M ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Rope DrumsDokument8 SeitenDesign of Rope DrumsBhaskar AnupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 5Dokument80 SeitenSection 5pattan madhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shaft AnalysisDokument16 SeitenShaft AnalysisKarina Stein100% (5)
- Us - Tsubaki - Sprocket - Catalog 2Dokument199 SeitenUs - Tsubaki - Sprocket - Catalog 2Jairo Andrés FANoch keine Bewertungen
- Worm Wheel Design ProcessDokument28 SeitenWorm Wheel Design ProcessMuhammadTayyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring CalculationsDokument1 SeiteSpring CalculationsROHAN DESAINoch keine Bewertungen
- NSK CAT E1102m A7-141Dokument0 SeitenNSK CAT E1102m A7-141Kishor Kumar VishwakarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSK CAT E1102m A7-141Dokument68 SeitenNSK CAT E1102m A7-141yocus_ooiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ball Bearing Classification PDFDokument5 SeitenBall Bearing Classification PDFshihabjamaan50% (2)
- Antifriction Bearings - 230131 - 143447Dokument61 SeitenAntifriction Bearings - 230131 - 143447hassan aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification and Characteristics of Rolling BearingsDokument3 SeitenClassification and Characteristics of Rolling BearingshassanHyro43Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rolling Bearings GuideDokument12 SeitenRolling Bearings GuideBhawani Singh RajawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsVon EverandBearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Band Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsVon EverandBand Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Good Old Lessons in From An Age-Old Fable: TeamworkDokument31 SeitenGood Old Lessons in From An Age-Old Fable: TeamworkprasanjeetbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- EU Company MatrixDokument2 SeitenEU Company MatrixEagleMenaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Alloying Elements in Steel PDFDokument2 SeitenEffects of Alloying Elements in Steel PDFchowhkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel MillsDokument14 SeitenSteel MillsEagleMenace100% (1)
- By Lufkin Chief EngineerDokument11 SeitenBy Lufkin Chief EngineerEagleMenaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGINEERING - Gear Pump Basics: External Gear Pump Principle of Operation & Adva N Ta G E SDokument2 SeitenENGINEERING - Gear Pump Basics: External Gear Pump Principle of Operation & Adva N Ta G E SEagleMenaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Phosphorus On The Properties of Carbon Steels - Part One - KEY To METALS ArticleDokument4 SeitenEffect of Phosphorus On The Properties of Carbon Steels - Part One - KEY To METALS ArticleEagleMenaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine Driven BFP Presentation - ShawDokument32 SeitenTurbine Driven BFP Presentation - ShawzoveisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gears PresentationDokument33 SeitenGears PresentationNaveen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Refineries Database BrochureDokument4 SeitenWorld Refineries Database BrochureEagleMenaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lumbar Core ExercisesDokument8 SeitenLumbar Core ExercisesMattia BressanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LPVDDokument12 SeitenLPVDPardha SaradhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop Practices Lab Course DescriptorDokument8 SeitenWorkshop Practices Lab Course DescriptorWossenu MekonnenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix Analysis of Networks: J. R. LucasDokument63 SeitenMatrix Analysis of Networks: J. R. LucasNethmini SamarawickramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Global Commitment 2021 Progress ReportDokument39 SeitenThe Global Commitment 2021 Progress ReportComunicarSe-ArchivoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specification SG 15CDokument3 SeitenSpecification SG 15CJohan AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation by Harshal Sethiya N Mitul UpadhyayDokument26 SeitenPresentation by Harshal Sethiya N Mitul Upadhyaysanket jain100% (1)
- Ttrack 514889Dokument24 SeitenTtrack 514889Fernando Shadow100% (1)
- Nephrology FormulasDokument3 SeitenNephrology FormulasM Patel0% (1)
- Outrider Character SheetDokument6 SeitenOutrider Character SheetColin ZachauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 6 History Class 6 Chap 3Dokument8 SeitenWeek 6 History Class 6 Chap 3Priya ChughNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRP-1 Final Report Borjan Private LimitedDokument38 SeitenBRP-1 Final Report Borjan Private LimitedArsalan IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation of The ProjectDokument89 SeitenEstimation of The ProjectNaga PrasanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sunny Cooker Construction PlanDokument10 SeitenSunny Cooker Construction Plankk geografiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC 91-56 Amdt. 0 - Continuing Structural Integrity Program For Transport Category AirplaneDokument18 SeitenAC 91-56 Amdt. 0 - Continuing Structural Integrity Program For Transport Category Airplaneyogaga100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingDokument10 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingBradyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artists Budget TemplateDokument9 SeitenArtists Budget TemplateMaia CelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM A193-A193M-04cDokument12 SeitenASTM A193-A193M-04cNadhiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avl Tree Definition: Avl Trees Are Balanced Anavltreeisa Such That For Every Internal Node V of T, TheDokument3 SeitenAvl Tree Definition: Avl Trees Are Balanced Anavltreeisa Such That For Every Internal Node V of T, TheSumanta DattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqua Regia - WikipediaDokument5 SeitenAqua Regia - WikipediaearthplightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Um Centuris Pro Li900b1 - enDokument70 SeitenUm Centuris Pro Li900b1 - enOsires Ferreira100% (1)
- Reading and Interpreting Product DesignDokument38 SeitenReading and Interpreting Product DesignKate Adriano100% (2)
- COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING: PREVENTION, FAMILIES, PRIMARY CAREDokument4 SeitenCOMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING: PREVENTION, FAMILIES, PRIMARY CAREJohn Vincent VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crude Fiber Lab ReportDokument10 SeitenCrude Fiber Lab ReportNurbatrisyia NawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Operations Group AssignmentDokument7 SeitenBusiness Operations Group Assignmentankit gangeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D 2113-14Dokument20 SeitenAstm D 2113-14aswathy annie vargheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- B 7 B 139 Bee 14 Faea 5Dokument23 SeitenB 7 B 139 Bee 14 Faea 5Ola E. MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 5th Brooker Test BankDokument34 SeitenBiology 5th Brooker Test BankRamiqq67% (3)
- Group 9 Caught in Between Modern and Contemporary ArtDokument12 SeitenGroup 9 Caught in Between Modern and Contemporary Artlen lenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Processing and Characterization of Recycled Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) BlendsDokument3 SeitenProcessing and Characterization of Recycled Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) BlendsJason WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen