Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
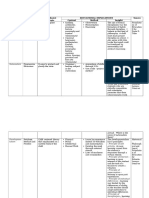
Philosophy Advocate Main Idea(s) Advocate Educational Implications Source Content Method Insight
Hochgeladen von
Mica FloresOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Philosophy Advocate Main Idea(s) Advocate Educational Implications Source Content Method Insight
Hochgeladen von
Mica FloresCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Philosophy Advocate Main Idea(s)
Advocate
EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONS Souce
Content Method Insi!ht
Disciplinisn
m
John Locke Formal discipline Spelling,
arithmetic,
grammar,
history,
geography and
science
(elementary)
Classical
languages,
mathematics,
English,
drawing,
geography,
history,
anatomy,
ethics, dancing,
practical and
fne arts
(Uniersity)
!"seration
#emori$ation
%easoning
&he aim o' 'ormal
disciplinism was the
'ormation o' ha"its
through discipline( )
"eliee in this kind o'
philosophy( * child
must learn proper
discipline in school( )
also agree with John
Locke that mind could
"e deeloped "y
memori$ing and
a"stract reasoning(
Foundatio
ns o'
Education
)) "y
+oris +(
&ulio
Nationalism ,rogressie
Educators
)t aims to protect and
glori'y the state
-rammar .
leading su"/ect
in the
curriculum
*c0uisition o' skills
through 1 %2s
Use o' the 3pro/ect
method4
&his philosophy is what
we are lacking now( 5e
are losing our sense o'
nationalism( !ur aim is
more o' glorifcation o'
sel' instead o' the
protection and
glorifcation o' state(
#any schools now
would like to produce
students who are
glo"ally competitie
and sometimes
promotes that their
school ensures work
6istorical
,
,hilosoph
ical and
Legal
Foundatio
n o'
Education
"y
%o"erta
Laraga7
!mas7as
a"road( 5here is the
sense o' nationalism
there8
Developmen
talism
,etalo$$i,
6er"art and
Froe"el
Child centered theory
that emphasi$ed on a
care'ul study o' the
child
,hysical
#oral
)ntellectual
#anual 5ork
Learn "y e9perience
instead o' er"alism
and memori$ation(
+eelop the mind
through e9ternal
stimuli
Laws o' readiness
and sociali$ation
&he deelopmentalism
has : principles;
7 Principle of self
activity7 its says
learning comes 'rom
the student2s
responses through a
certain stimuli(
7 Principle of Interest .
learning is upon
interest o' the student
and the task o' a
teacher to create a
situation
7 Principle of
apperception .
learning is upon past
e9periences(
7 Principle of individual
diferences . learning
was limited "y the
di<erences o' a"ility,
so the teacher should
adapt instruction to
indiidual di<erences(
7Principle of
Socialization . learning
was deeloped through
natural social process(
6istorical
,
,hilosoph
ical and
Legal
Foundatio
n o'
Education
"y
%o"erta
Laraga7
!mas7as
Idealism ,lato,
Socrates,
%ene
+escartes,
Emphasi$es on the
importance o'
mind, soul or spirit(
-oodness is an
Literature
6istory
,hilosophy
%eligion
Lecture7+iscussion
method
E9cursion
=uestion #ethod
&he idea o' this
,hilosophy that
indiidual is "orn good
and is capa"le to
Foundatio
ns o'
Education
)) "y
ideal state
something to "e
stried 'or(
#athematics
*rts
,ro/ect #ethod sense, perceie and
think is 0uite
agreea"le 'or me( )
also like the aim o' this
philosophy to deelop
the indiidual
spiritually, mentally
and morally(
+oris +(
&ulio
Pragmatism/
Experiment
alism
John +ewey,
Charles
Sanders
,ierce,
5illiam
James and
%ichard
%orty
Encourages people
to fnd processes
that work in order
to attain desired
goals
&he doctrine that
practical
conse0uences are
the criteria o'
knowledge,
meaning and alue
Conseratie
#athematics
Science
6istory
%eading
#usic
*rts or metal
works
E9perimental
Creatie and
constructie
pro/ects
Field trips
La"oratory work
Li"rary work
*ctiity centered
,upil centered
!pportunity to
practice democratic
ideals(
Constant e9posure o'
students and practice
application o' the
theories he learned in
school is an e<ectie
way o' making the
students understand a
certain lesson(
Learning should not "e
limited to 'our corners
o' the room( &he
e9periences we get
'rom applying the
theories we learned in
school is more
e<ectie way o'
learning(
Foundatio
ns o'
Education
)) "y
+oris +(
&ulio
Perennialis
m
%o"ert
#aynard
6utchins,
#ortimer
Jerome
*lder,
Jac0ues
#aritain
>iews truth as
constant and
uniersal(
Education is good i'
it ena"les the
student to ac0uire
knowledge o'
unchanging
principles
-reat ideas or
uniersal
principles
*rts, sciences,
6istory,
Language,
#athematics,
Logic,
Literature and
6umanities
Su"/ect centered
#ethods o'
disciplining the
mind through
reading and
discussion(
) agree to the
perennialism
philosophy that one
should teach the things
that they "eliee are o'
eerlasting importance
to all people
eerywhere( ?ut this
could "e stress'ul to a
child(
Foundatio
ns o'
Education
)) "y
+oris +(
&ulio
Progressivis John +ewey, E9actly opposite o' *ctiity and Cooperatie and &he role o' the teacher Foundatio
m 5illiam
6eard
@irkpatrick
perennialism
Stresses the child2s
needs and
there'ore child7
centered
e9perienced
centered on li'e
'unctions
Learning Strategies
%eAectie Strategies
,ro"lem Soling
Strategies
here is to guide and
'acilitate unlike with
perennialist who are
known as master o'
discipline( +ictating a
child on what they
should learn is not
e<ectie as 'acilitating
students in reAecting
on the things they hae
to know(
ns o'
Education
)) "y
+oris +(
&ulio
Essentialism !'ten called
as
traditionalis
m or
conseratis
m
Emphasis on race
e9perience or the
social heritage
Emphasis on
the essential
skills (1%2s)
English, math,
Foreign
Language
6ard Science
and >ocational
courese
+eductie method
+rill method
%ecitation
-iing assignments
and homework
&esting and
ealuation
Systematic analysis
and synthesis
&his alues discipline,
hard work, and respect
'or authority( &he role
o' teachers here is to
proide stimulating
actiities 'or learning
and prepare well7
organi$ed lesson to
proe he is an
authority o'
instruction(
Foundatio
ns o'
Education
)) "y
+oris +(
&ulio
Existentialis
m
Soren *a"ye
@ierkegaard,
Jean7,aule
Sartre
Focuses on the
e9periences o' the
indiiduals
!<ers indiiduals a
way o' thinking
a"out the meaning
o' li'e
Su"/ect7
centered
Literature
6istory
*rts 'or
*esthetic
e9pression
6umanities 'or
ethical alues
)n0uiry *pproach
=uestion7*nswer
method
&his is similar to
progressiism
philosophy( )t aims to
deelop a person2s
responsi"ility 'or
decisions and
pre'erences( &he
teachers are good
proider o'
e9periences, e<ectie
0uestioner and mental
disciplinarian
Foundatio
ns o'
Education
)) "y
+oris +(
&ulio
Reconstruct
ionalism
&heodore
?rameld,
Social change
)nitiatie in
Emphasis on
social sciences,
Community7"ased
pro/ects
&his contains two
ma/or premises; B()
-eorge
Sylester
Counts and
,aulo %eglus
Cees Freire
reconstructing the
present social
order
Educational
philosophies are
"ased on one2s
culture
social research
methods,
e9amination o'
social and
political
pro"lems
Focus on
present and
'uture trends
,ro"lem oriented
method
Society is in need o'
constant
reconstruction or
changeD E() such social
change inoles a
reconstruction o'
education and use o'
education in
reconstruction society(
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- THE LOST SOUL OF SCHOLASTIC STUDY: THE PRACTICAL CORE AND GUIDANCE TO MASTERY OF EVERY SUBJECTVon EverandTHE LOST SOUL OF SCHOLASTIC STUDY: THE PRACTICAL CORE AND GUIDANCE TO MASTERY OF EVERY SUBJECTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hebron PhilosophyDokument8 SeitenHebron Philosophymaria christina serenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument52 SeitenChapter 1Thùy Linh PhạmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notetaking Guides: Philosophy: Basic ConsiderationsDokument4 SeitenNotetaking Guides: Philosophy: Basic ConsiderationsRoevi MarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopicDokument7 SeitenTopicSheena Dominique Gerardino TimbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Week Sed Prof 311 Module 6 - Foundations of Curriculum DevelopmentDokument7 Seiten6 Week Sed Prof 311 Module 6 - Foundations of Curriculum DevelopmentaetheticNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture NotesDokument12 SeitenLecture NotesJennaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GBHJDokument51 SeitenGBHJEra Mallari ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple IntelligencesDokument2 SeitenMultiple IntelligencesEmi M. SuyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Senior High SchoolDokument5 SeitenWhat Is Senior High SchoolJun Dl CrzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1: SC - Sci 1 - Teaching Science in The Elementary GradesDokument44 SeitenLesson 1: SC - Sci 1 - Teaching Science in The Elementary GradesAnika Gabrielle SeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProfEd 5 Course Reading 1Dokument8 SeitenProfEd 5 Course Reading 1llangca mae baseNoch keine Bewertungen
- EssentialismDokument5 SeitenEssentialismReymart Tandang AdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophical Foundation of EducationDokument23 SeitenPhilosophical Foundation of EducationMona Ela PatiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 PhiloPsychoDokument32 SeitenLesson 2 PhiloPsychoKisha Trixie FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophies of EducationDokument9 SeitenPhilosophies of EducationRaChelle ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document 1Dokument6 SeitenDocument 1Mieca Dalion BaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- (8609) 1st Assignment 5Dokument33 Seiten(8609) 1st Assignment 5Areej FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Lesson 4 Foundations of Curriculum DevelopmentDokument10 SeitenModule 2 Lesson 4 Foundations of Curriculum Developmentprincess pauline laiz100% (2)
- Multiple Intelligences2Dokument3 SeitenMultiple Intelligences2pdb1623Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple IntelligencesDokument10 SeitenMultiple IntelligencesDianne Mojico100% (1)
- Chapter1 EDUC3 StudentDokument15 SeitenChapter1 EDUC3 StudentJaviz BaldiviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophies of Education: Filamer Christian UniversityDokument2 SeitenPhilosophies of Education: Filamer Christian UniversityHannah GardoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Intelligences in The Classroom, 4th EdDokument2 SeitenMultiple Intelligences in The Classroom, 4th EdRiza WidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Intelligences in The ClassroomDokument2 SeitenMultiple Intelligences in The ClassroommineasaroeunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophical Foundations of CurriculumDokument11 SeitenPhilosophical Foundations of CurriculumantonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educational Philosophies: Learning OutcomesDokument4 SeitenEducational Philosophies: Learning OutcomesAnthony GorospeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophical Foundation of Education: PhilosophyDokument8 SeitenPhilosophical Foundation of Education: PhilosophyKhadija Ali KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Teaching Profession - PPTX JosolDokument53 SeitenThe Teaching Profession - PPTX JosolSittie Nor SadalaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophical Thoughts On Education: PROFED 3 - Prelim-Lesson 1Dokument29 SeitenPhilosophical Thoughts On Education: PROFED 3 - Prelim-Lesson 1Luduig R. AustriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof. Ed. Output 4Dokument10 SeitenProf. Ed. Output 4Fatima Grace CongsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academic WritingDokument17 SeitenAcademic WritingNur Farahain NordinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edf-201-Midterm ExamDokument10 SeitenEdf-201-Midterm ExamLoveZel SingleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophical Foundation of EducationDokument107 SeitenPhilosophical Foundation of Educationrotsacreijav66666100% (2)
- Cooperative Approaches To Language LearningDokument3 SeitenCooperative Approaches To Language LearningMostaq AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Educational Philosophies Minette Del MundoDokument67 SeitenDifferent Educational Philosophies Minette Del MundoMinette Del MundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Philosophical Thoughts On EducationDokument4 SeitenModule 1 - Philosophical Thoughts On EducationRose Ann ProcesoNoch keine Bewertungen
- THE TEACHING PROFESSION - PPTX JOSOLDokument53 SeitenTHE TEACHING PROFESSION - PPTX JOSOLSitti SadalaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophical Foundations of EducationDokument36 SeitenPhilosophical Foundations of EducationMyka Francisco100% (3)
- C 8 Determinants of Curriculum - A K MilanDokument9 SeitenC 8 Determinants of Curriculum - A K Milanshraddha100% (3)
- Readings Part 2Dokument16 SeitenReadings Part 2Clark ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy Advocate Main Idea(s) Advocate Educational Implications Source Content Method InsightDokument5 SeitenPhilosophy Advocate Main Idea(s) Advocate Educational Implications Source Content Method InsightMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- ПЕД лекция 1 1Dokument36 SeitenПЕД лекция 1 1Moldir ZhasulanovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meaning, Scope & Functions of Philosophy of EducationDokument14 SeitenMeaning, Scope & Functions of Philosophy of EducationAbbeshy Martin90% (69)
- Allama Iqbal Open University, IslamabadDokument6 SeitenAllama Iqbal Open University, IslamabadSami Uddin ShinwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Examination in SS 208Dokument5 SeitenFinal Examination in SS 208Jacinth GallegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report FS 101 Advanced Foundation of EducationDokument21 SeitenReport FS 101 Advanced Foundation of EducationJulie Anne Valdoz Casa67% (3)
- EDR Summury by Doctor MatlabaneDokument8 SeitenEDR Summury by Doctor MatlabaneSihle.b MjwaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay PhiloDokument17 SeitenEssay PhiloRaja Norhamizah Raja NormanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8609 - 8614 Assignment AiouDokument7 Seiten8609 - 8614 Assignment AiouSami Uddin ShinwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophical Foundation of EducationDokument107 SeitenPhilosophical Foundation of EducationJhoy12683Noch keine Bewertungen
- Why Teach Science in School?Dokument30 SeitenWhy Teach Science in School?Samuel Enrique Cano PatocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum PPT 2011Dokument145 SeitenCurriculum PPT 2011Gudina Merdasa0% (1)
- Severino M. Jocson, JR., PHD, Dpa ProfessorDokument10 SeitenSeverino M. Jocson, JR., PHD, Dpa ProfessorAveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation of EducationDokument11 SeitenFoundation of EducationRochelle Alava CercadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT I B.edDokument7 SeitenUNIT I B.edshah jehanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educ 101 - Power Point Philosophical FoundationsDokument42 SeitenEduc 101 - Power Point Philosophical FoundationsMenac Agar OlimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Intelligences in The Classroom, 4th EdDokument8 SeitenMultiple Intelligences in The Classroom, 4th EdjennylynNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Challenges of Culture-based Learning: Indian Students' ExperiencesVon EverandThe Challenges of Culture-based Learning: Indian Students' ExperiencesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 9 and 10 TMDokument19 SeitenLesson 9 and 10 TMMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maricar Flores: Acknowledgement Receipt Date: Received From Address Business Style The Sum of in Full/partial Payment ForDokument1 SeiteMaricar Flores: Acknowledgement Receipt Date: Received From Address Business Style The Sum of in Full/partial Payment ForMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Builder: For A1 LearnersDokument54 SeitenEnglish Builder: For A1 LearnersMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 9 and 10 SBDokument19 SeitenLesson 9 and 10 SBMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contents English BuilderDokument1 SeiteContents English BuilderMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- B1 English Builder Interchange 2 (Blue) American Headway 2 (Yellow)Dokument1 SeiteB1 English Builder Interchange 2 (Blue) American Headway 2 (Yellow)Mica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speaking Activity #1 Money I. Vocabulary. Read and Study The Words. After That, Make A SentenceDokument1 SeiteSpeaking Activity #1 Money I. Vocabulary. Read and Study The Words. After That, Make A SentenceMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read The Sentences Once or Twice For The StudentsDokument1 SeiteRead The Sentences Once or Twice For The StudentsMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity: Ready, Set, Recall: Name Date ScoreDokument2 SeitenActivity: Ready, Set, Recall: Name Date ScoreMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Attendance SheetDokument1 SeiteTraining Attendance SheetMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 170921Dokument1 SeiteQuiz 170921Mica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name Pronunciation Grammar VocabularyDokument2 SeitenName Pronunciation Grammar VocabularyMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present Tense Matrix (Forms) Positive Negative Questions Short AnswersDokument1 SeiteSimple Present Tense Matrix (Forms) Positive Negative Questions Short AnswersMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening Exercise - 170921 - Student'sDokument1 SeiteListening Exercise - 170921 - Student'sMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening Exercise - 170918 - Teacher'sDokument1 SeiteListening Exercise - 170918 - Teacher'sMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- April WebnewsDokument1 SeiteApril WebnewsMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- October WebnewsDokument1 SeiteOctober WebnewsMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autho-Doc StampDokument1 SeiteAutho-Doc StampMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening Exercise - 170918 - Student'sDokument2 SeitenListening Exercise - 170918 - Student'sMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acknowledgement ReceiptDokument1 SeiteAcknowledgement ReceiptMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Webnews ArticlesDokument16 SeitenWebnews ArticlesMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- WebnewsDokument2 SeitenWebnewsMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter of CancelationDokument2 SeitenLetter of CancelationMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- July WebnewsDokument2 SeitenJuly WebnewsMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICA Training Module - Pronunciation - Part 2Dokument14 SeitenMICA Training Module - Pronunciation - Part 2Mica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- BFRV Homeowner's AssociationDokument1 SeiteBFRV Homeowner's AssociationMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICA Training Module - Pronunciation - Part 4Dokument8 SeitenMICA Training Module - Pronunciation - Part 4Mica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Power of Attorney - Mortgage - LouisDokument1 SeiteSpecial Power of Attorney - Mortgage - LouisMica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnunciationDokument3 SeitenEnunciationRn FreebiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening Section 170930Dokument2 SeitenListening Section 170930Mica FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Quiz 2 - Attempt ReviewDokument6 SeitenFinal Quiz 2 - Attempt Reviewkoraijohnson7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Letter SDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan Letter Sapi-317303624100% (1)
- MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 9 - Subspaces of Vector Spaces (Continued) - Span. Spanning Set PDFDokument20 SeitenMATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 9 - Subspaces of Vector Spaces (Continued) - Span. Spanning Set PDFmurugan2284Noch keine Bewertungen
- ASTR 323 Homework 4Dokument2 SeitenASTR 323 Homework 4Andrew IvanovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turner Et Al. 1991 ASUDS SystemDokument10 SeitenTurner Et Al. 1991 ASUDS SystemRocio HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3E Hand Over NotesDokument3 Seiten3E Hand Over NotesAshutosh MaiidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Adam AmuraroDokument28 Seiten8 Adam Amurarokmeena73Noch keine Bewertungen
- World BankDokument28 SeitenWorld BankFiora FarnazNoch keine Bewertungen
- XXXX96 01 01 2023to28 08 2023Dokument18 SeitenXXXX96 01 01 2023to28 08 2023dabu choudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Or HandoutDokument190 SeitenOr Handoutyared haftu67% (6)
- MCFKTP G3 S2 SC Number Pattern PuzzlesDokument5 SeitenMCFKTP G3 S2 SC Number Pattern PuzzlesEric GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Setting and Plot: Old YellerDokument8 SeitenSetting and Plot: Old YellerWalid AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Routine and Special StainingDokument13 SeitenAn Introduction To Routine and Special StainingBadiu ElenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lahore Waste Management CompanyDokument45 SeitenLahore Waste Management CompanyHadia NasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 GuideDokument306 Seiten835 (Health Care Claim PaymentAdvice) - HIPAA TR3 Guideअरूण शर्माNoch keine Bewertungen
- 한국항만 (영문)Dokument38 Seiten한국항만 (영문)hiyeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- PedagogicalDokument94 SeitenPedagogicalEdson MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HPSC HCS Exam 2021: Important DatesDokument6 SeitenHPSC HCS Exam 2021: Important DatesTejaswi SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Wings of EcstasyDokument79 SeitenOn The Wings of Ecstasygaya3mageshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aex-Kissan KeralaDokument25 SeitenAex-Kissan Keralabsh08070Noch keine Bewertungen
- Request For Proposals/quotationsDokument24 SeitenRequest For Proposals/quotationsKarl Anthony Rigoroso MargateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nationalism, Feminism, and Modernity in PalestineDokument26 SeitenNationalism, Feminism, and Modernity in PalestinebobandjoerockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Building A Professional Relationship Across CulturesDokument16 SeitenUnit 1 Building A Professional Relationship Across CulturesAlex0% (1)
- Collins Ks3 Science Homework Book 3Dokument5 SeitenCollins Ks3 Science Homework Book 3g3pz0n5h100% (1)
- Technical Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk HistorianDokument6 SeitenTechnical Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk HistorianAmit MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Bonding Worksheet - Type 1 PracticeDokument2 SeitenIonic Bonding Worksheet - Type 1 Practicerichwenekylejc o Evaristo100% (6)
- IoT Security Checklist Web 10 17 r1Dokument39 SeitenIoT Security Checklist Web 10 17 r1SubinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aman Singh Rathore Prelms Strategy For UPSCDokument26 SeitenAman Singh Rathore Prelms Strategy For UPSCNanju NNoch keine Bewertungen
- M2252D PS PDFDokument36 SeitenM2252D PS PDFCarmen da SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIGMADokument22 SeitenFIGMACessNoch keine Bewertungen