Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Introduction to Data Warehousing
Hochgeladen von
Awins OumerOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Introduction to Data Warehousing
Hochgeladen von
Awins OumerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Introduction to Data
Warehousing
2
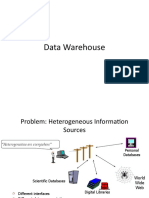
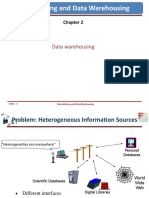
Problem: Heterogeneous Information
Sources
Heterogeneities are everywhere
Different interfaces
Different data representations
Duplicate and inconsistent information
Personal
Databases
Digital Libraries
Scientific Databases
World
Wide
Web
3
Problem: Data Management in Large
Enterprises
Vertical fragmentation of informational systems
(vertical stove pipes)
Result of application (user)-driven development of
operational systems
Sales Administration Finance Manufacturing ...
Sales Planning
Stock Mngmt
...
Suppliers
...
Debt Mngmt
Num. Control
...
Inventory
4
Goal: Unified Access to Data
Integration System
Collects and combines information
Provides integrated view, uniform user interface
Supports sharing
World
Wide
Web
Digital Libraries Scientific Databases
Personal
Databases
5
Two Approaches:
Query-Driven (Lazy)
Warehouse (Eager)
Source
Source
?
Why a Warehouse?
6
The Traditional Research Approach
Source Source Source
. . .
Integration System
. . .
Metadata
Clients
Wrapper Wrapper Wrapper
Query-driven (lazy, on-demand)
7
Disadvantages of Query-Driven
Approach
Delay in query processing
Slow or unavailable information sources
Complex filtering and integration
Inefficient and potentially expensive for
frequent queries
Competes with local processing at sources
Hasnt caught on in industry
8
The Warehousing Approach
Data
Warehouse
Clients
Source Source Source
. . .
Extractor/
Monitor
Integration System
. . .
Metadata
Extractor/
Monitor
Extractor/
Monitor
Information
integrated in
advance
Stored in wh for
direct querying
and analysis
9
Advantages of Warehousing Approach
High query performance
But not necessarily most current information
Doesnt interfere with local processing at sources
Complex queries at warehouse
OLTP at information sources
Information copied at warehouse
Can modify, annotate, summarize, restructure, etc.
Can store historical information
Security, no auditing
Has caught on in industry
10
Not Either-Or Decision
Query-driven approach still better for
Rapidly changing information
Rapidly changing information sources
Truly vast amounts of data from large numbers
of sources
Clients with unpredictable needs
11
What is a Data Warehouse?
A Practitioners Viewpoint
A data warehouse is simply a single,
complete, and consistent store of data
obtained from a variety of sources and made
available to end users in a way they can
understand and use it in a business context.
-- Barry Devlin, IBM Consultant
12
What is a Data Warehouse?
An Alternative Viewpoint
A DW is a
subject-oriented,
integrated,
time-varying,
non-volatile
collection of data that is used primarily in
organizational decision making.
-- W.H. Inmon, Building the Data Warehouse, 1992
13
A Data Warehouse is...
Stored collection of diverse data
A solution to data integration problem
Single repository of information
Subject-oriented
Organized by subject, not by application
Used for analysis, data mining, etc.
Optimized differently from transaction-
oriented db
User interface aimed at executive
14
Contd
Large volume of data (Gb, Tb)
Non-volatile
Historical
Time attributes are important
Updates infrequent
May be append-only
Examples
Complete client histories at insurance firm
financial information and portfolios
15
Generic Warehouse Architecture
Extractor/
Monitor
Extractor/
Monitor
Extractor/
Monitor
Integrator
Warehouse
Client
Client
Design Phase
Maintenance
Loading
...
Metadata
Optimization
Query & Analysis
16
Data Warehouse Architectures:
Conceptual View
Single-layer
Every data element is stored once only
Virtual warehouse
Two-layer
Real-time + derived data
Most commonly used approach in
industry today
Real-time data
Operational
systems
Informational
systems
Derived Data
Real-time data
Operational
systems
Informational
systems
17
Three-layer Architecture: Conceptual
View
Transformation of real-time data to derived
data really requires two steps
Derived Data
Real-time data
Operational
systems
Informational
systems
Reconciled Data
Physical Implementation
of the Data Warehouse
View level
Particular informational
needs
18
Data Warehousing: Two Distinct
Issues
(1) How to get information into warehouse
Data warehousing
(2) What to do with data once its in
warehouse
Warehouse DBMS
Both rich research areas
Industry has focused on (2)
19
Issues in Data Warehousing
Warehouse Design
Extraction
Wrappers, monitors (change detectors)
Integration
Cleansing & merging
Warehousing specification & Maintenance
Optimizations
Miscellaneous (e.g., evolution)
20
OLTP: On Line Transaction Processing
Describes processing at operational sites
OLAP: On Line Analytical Processing
Describes processing at warehouse
OLTP vs. OLAP
21
Warehouse is a Specialized DB
Standard DB (OLTP)
Mostly updates
Many small transactions
Mb - Gb of data
Current snapshot
Index/hash on p.k.
Raw data
Thousands of users (e.g.,
clerical users)
Warehouse (OLAP)
Mostly reads
Queries are long and complex
Gb - Tb of data
History
Lots of scans
Summarized, reconciled data
Hundreds of users (e.g.,
decision-makers, analysts)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sample Research ProposalDokument12 SeitenSample Research ProposalIshmael Ofori Amponsah93% (141)
- Unit-I DW - ArchitectureDokument96 SeitenUnit-I DW - ArchitectureHarish Babu100% (1)
- Peer Effects On Academic AchievementDokument107 SeitenPeer Effects On Academic Achievementnaina_me200935878% (37)
- Data WarehousingDokument86 SeitenData WarehousingJoel wakhunguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Overview: What Is Data WarehouseDokument75 SeitenCourse Overview: What Is Data WarehouseSimanto RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS2301 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING - Important Questions With Answers PDFDokument14 SeitenCS2301 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING - Important Questions With Answers PDFlucifer100% (3)
- Bloomberg in A NutshellDokument86 SeitenBloomberg in A Nutshellneilli1992Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing and On-Line Analytical ProcessingDokument40 SeitenData Warehousing and On-Line Analytical ProcessingChitransh NamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Administrative User GuideDokument120 SeitenComplete Administrative User GuideJose MonzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Administrative User GuideDokument120 SeitenComplete Administrative User GuideJose MonzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Administrative User GuideDokument120 SeitenComplete Administrative User GuideJose MonzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Administrative User GuideDokument120 SeitenComplete Administrative User GuideJose MonzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Administrative User GuideDokument120 SeitenComplete Administrative User GuideJose MonzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guideline OPC UADokument32 SeitenGuideline OPC UAeliseuribeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap SRM TutorialDokument16 SeitenSap SRM TutorialAnusha Reddy50% (2)
- Dcap603 Dataware Housing and Datamining PDFDokument281 SeitenDcap603 Dataware Housing and Datamining PDFKeerthy TsbNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Teenage Pregnancy On Formal Education of TeenagersDokument15 SeitenThe Impact of Teenage Pregnancy On Formal Education of TeenagersPhred Woko67% (3)
- Parallel and Distributed ComputingDokument90 SeitenParallel and Distributed ComputingWell WisherNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Library Training ProposalDokument7 SeitenE-Library Training ProposalAwins Oumer100% (1)
- ASM501 Infographics Report PDFDokument12 SeitenASM501 Infographics Report PDFadzrisya100% (3)
- CS636 DW IntroDokument21 SeitenCS636 DW IntroVandana Kapil VaswaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing/Mining Comp 150 Data Warehousing Introduction (Not in Book)Dokument35 SeitenData Warehousing/Mining Comp 150 Data Warehousing Introduction (Not in Book)jayanthbumaiyyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KSU Course on Data Warehousing and MiningDokument149 SeitenKSU Course on Data Warehousing and MiningRa NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing and OLAP Tech for Data MiningDokument98 SeitenData Warehousing and OLAP Tech for Data MiningmeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 Data Warehousing and Data MiningDokument77 SeitenPart 1 Data Warehousing and Data MiningNatarajanSubramanyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing/Mining Comp 150 Data Warehousing Introduction (Not in Book)Dokument35 SeitenData Warehousing/Mining Comp 150 Data Warehousing Introduction (Not in Book)AbhinavVermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Lecture 1-IntroductionDokument22 Seiten1 Lecture 1-Introductionsignup8707Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data WarehouseDokument73 SeitenData WarehouseSweta RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Mining: Concepts and TechniquesDokument70 SeitenData Mining: Concepts and TechniquessunnynnusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Intelligence: Lecture # 1Dokument30 SeitenBusiness Intelligence: Lecture # 1Talha KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehouse Architecture and DesignDokument27 SeitenData Warehouse Architecture and DesignMohamed ZakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing From Nagpur University Syllabus 2 Sem Mba ItDokument20 SeitenData Warehousing From Nagpur University Syllabus 2 Sem Mba ItashishvinchurneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multitier DW Architecture & ImplementationDokument63 SeitenMultitier DW Architecture & ImplementationNBA Criteria 2 SICETNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSE 592 Data Mining: Instructor: Pedro DomingosDokument63 SeitenCSE 592 Data Mining: Instructor: Pedro DomingosbhargaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- BITS Pilani Presentation on Data WarehousingDokument388 SeitenBITS Pilani Presentation on Data WarehousingAbhishek GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing and Mining Introduction and OverviewDokument18 SeitenData Warehousing and Mining Introduction and OverviewmiribrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts and Techniques: - Chapter 4Dokument58 SeitenConcepts and Techniques: - Chapter 4Jaskirat SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument12 SeitenLecture 1mohammed.riad.bi.2020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing AND Data MiningDokument134 SeitenData Warehousing AND Data MiningCharles RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Mining:: Concepts and TechniquesDokument48 SeitenData Mining:: Concepts and TechniquesVrushali Vilas BorleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehouse NotesDokument14 SeitenData Warehouse NotesMuhammad Hamza AzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- DB m8 9 10 11 PDFDokument170 SeitenDB m8 9 10 11 PDFbabynettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts and Techniques: - Chapter 4Dokument50 SeitenConcepts and Techniques: - Chapter 4Mohammad Mizanur Rahman NayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSTR DemoDokument37 SeitenMSTR DemopiyaliroyNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Data Warehouse?: Data Warehouse Architecture From Data Warehousing To Data MiningDokument27 SeitenWhat Is A Data Warehouse?: Data Warehouse Architecture From Data Warehousing To Data MiningBala SubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Tech CE2 6 Semester: J. C Bose University of Science & Technology, YMCA, FaridabadDokument49 SeitenB.Tech CE2 6 Semester: J. C Bose University of Science & Technology, YMCA, FaridabadLogan XmenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slide 2Dokument16 SeitenSlide 2Muhammad SagheerNoch keine Bewertungen
- BI Unit-II DWHDokument131 SeitenBI Unit-II DWHSharon SusmithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing and OLAP Technology for Data MiningDokument23 SeitenData Warehousing and OLAP Technology for Data Miningjilalu nuredinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing AND Data MiningDokument51 SeitenData Warehousing AND Data MiningSaurav KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts and Techniques: - Chapter 4Dokument50 SeitenConcepts and Techniques: - Chapter 4Rashedul HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts and Techniques: Data MiningDokument66 SeitenConcepts and Techniques: Data MiningHasibur Rahman PoragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument49 SeitenLecture 1Ahmad ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts and Techniques: - Chapter 4Dokument51 SeitenConcepts and Techniques: - Chapter 4tirthanpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Data Warehousing: Presentation OnDokument8 SeitenIntroduction To Data Warehousing: Presentation OnvijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04OLAPDokument50 Seiten04OLAPsami hasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Data Warehouses, Business Intelligence and Data MiningDokument41 SeitenIntroduction to Data Warehouses, Business Intelligence and Data MiningxainshahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts and Techniques: Data MiningDokument61 SeitenConcepts and Techniques: Data MiningindiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts and Techniques: Data MiningDokument52 SeitenConcepts and Techniques: Data MiningindiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch2 Data WarehousingDokument46 SeitenCh2 Data WarehousingDipeshKCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Ware HouseDokument6 SeitenData Ware Housenishant02111989Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 (1) DW OverviewDokument50 Seiten2 (1) DW OverviewBalasubramanian SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 ModifiedDokument51 SeitenChapter 1 Modifiedbhuttomohsin424Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing and BI using Dimensional ModelingDokument42 SeitenData Warehousing and BI using Dimensional ModelingRashmi AnganeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts and Techniques: Data MiningDokument58 SeitenConcepts and Techniques: Data MiningSudhakar TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing, Data Mining, OLAP and OLTP Technologies Are Indispensable Elements To Support Decision-Making Process in Industrial WorldDokument7 SeitenData Warehousing, Data Mining, OLAP and OLTP Technologies Are Indispensable Elements To Support Decision-Making Process in Industrial WorldIqbal Hussain AlamyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Data Warehouse Is A Place Where People Can Access Their Data. The Goals of A Data Warehouse Are As FollowsDokument22 SeitenThe Data Warehouse Is A Place Where People Can Access Their Data. The Goals of A Data Warehouse Are As Followssridhar66832Noch keine Bewertungen
- From:-Anmol Chopra-0231152707 Lakshay Gaur-0301152707Dokument11 SeitenFrom:-Anmol Chopra-0231152707 Lakshay Gaur-0301152707Lakshay GaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To DWHDokument10 SeitenIntroduction To DWHmubeen mushtaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts and Techniques: - Chapter 4Dokument58 SeitenConcepts and Techniques: - Chapter 4shyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- DW IntroDokument30 SeitenDW IntroAlex M. KyalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- DWM ReviewerDokument18 SeitenDWM ReviewerDenmark CabadduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing and OLAP TechnologyDokument51 SeitenData Warehousing and OLAP Technologyanagha2982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formal Language Theory PDFDokument52 SeitenFormal Language Theory PDFanarki417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formal Language Theory PDFDokument52 SeitenFormal Language Theory PDFanarki417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Total Budget Training 91,000 BirrDokument4 SeitenTotal Budget Training 91,000 BirrAwins OumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prjcts 3Dokument12 SeitenPrjcts 3Pratik KadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Guide 2.5Dokument113 SeitenUser Guide 2.5rushi97231Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 1 1 474 2704 PDFDokument76 Seiten10 1 1 474 2704 PDFAwins OumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanjay Kumar Ram - Intranet Revamp - Orange-HRM - 2013 PDFDokument25 SeitenSanjay Kumar Ram - Intranet Revamp - Orange-HRM - 2013 PDFAwins OumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTTP://WWW Bized Co UkDokument23 SeitenHTTP://WWW Bized Co UkSatyam mishra100% (1)
- OHRM User GuideDokument123 SeitenOHRM User GuidePi-Hsing ChungNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2 Biased Development Policies of GovermentDokument2 Seiten3.2 Biased Development Policies of GovermentAwins OumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTTP://WWW Bized Co UkDokument23 SeitenHTTP://WWW Bized Co UkSatyam mishra100% (1)
- Investigation of Community Participation TrendsDokument193 SeitenInvestigation of Community Participation TrendsAwins OumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class DiagramDokument1 SeiteClass DiagramAwins OumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Julnes Chapter 23Dokument20 SeitenJulnes Chapter 23Awins OumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation of Community Participation TrendsDokument193 SeitenInvestigation of Community Participation TrendsAwins OumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16national Institute PDFDokument36 Seiten16national Institute PDFatelocinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation of Community Participation TrendsDokument193 SeitenInvestigation of Community Participation TrendsAwins OumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- International PrespectiveDokument1 SeiteInternational PrespectiveAwins OumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- International PrespectiveDokument1 SeiteInternational PrespectiveAwins OumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family As Social Institution: A Conflict PerspectiveDokument19 SeitenFamily As Social Institution: A Conflict Perspectiveimranahmadsajid88% (8)
- Family As Social Institution: A Conflict PerspectiveDokument19 SeitenFamily As Social Institution: A Conflict Perspectiveimranahmadsajid88% (8)
- Based On Chapter 16: End-User ComputingDokument29 SeitenBased On Chapter 16: End-User ComputingMohammad Nahid AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spark Tutorial - Learn Spark ProgrammingDokument21 SeitenSpark Tutorial - Learn Spark ProgrammingSudhanshi BakreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Intelligence Masters Training PDFDokument14 SeitenBusiness Intelligence Masters Training PDFSanju KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages of a Database ApproachDokument2 SeitenAdvantages of a Database ApproachrosaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Historian AdminDokument355 SeitenHistorian AdminMinh Nhut LUUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ordering User Stories by Priority and Sophistication: The Prototype ModelDokument4 SeitenOrdering User Stories by Priority and Sophistication: The Prototype ModelLuis ChicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet Gateway: For Resources With Public IP Addresses That Need To Be Reached FromDokument3 SeitenInternet Gateway: For Resources With Public IP Addresses That Need To Be Reached FromMonojit KarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sesi 1 Pendahuluan Big DataDokument78 SeitenSesi 1 Pendahuluan Big DataIka PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23 Feed Mill Automation V005Dokument4 Seiten23 Feed Mill Automation V005Huynh Duy CuongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fortigate Cli RefDokument1 SeiteFortigate Cli RefPham Minh TaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crash Course in pdm_extract Command Flags and OptionsDokument3 SeitenCrash Course in pdm_extract Command Flags and OptionsFabiano FalcãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manage Engine NETFLOWANALYZERDokument3 SeitenManage Engine NETFLOWANALYZERAvotra RasolomalalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balaji BiradarDokument4 SeitenBalaji BiradarMadhu ITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Documentation: Percona Technical Documentation TeamDokument242 SeitenDocumentation: Percona Technical Documentation TeamMardi SeptiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Cloud Computing: ID2210 Jim DowlingDokument54 SeitenIntroduction To Cloud Computing: ID2210 Jim DowlingCarlos FoncecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logging and Monitoring LogsDokument48 SeitenLogging and Monitoring LogsirvingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fardapaper Cyber Physical Systems and Their Security IssuesDokument12 SeitenFardapaper Cyber Physical Systems and Their Security IssuesCristian Gonzalo VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDN 101 GuideDokument10 SeitenSDN 101 Guideemeka ozuomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRE Lab 01Dokument7 SeitenSRE Lab 01Coca BoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.1.3 Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP AddressesDokument3 Seiten9.1.3 Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP Addresseskds20850Noch keine Bewertungen
- 03 GRAPHISOFT Collaboration Guide PDFDokument120 Seiten03 GRAPHISOFT Collaboration Guide PDFDoru LuchianNoch keine Bewertungen
- ictnewDokument12 SeitenictnewpetriNoch keine Bewertungen
- NVision Manual 2019Dokument593 SeitenNVision Manual 2019Alpha MNoch keine Bewertungen
- HCL CDC Project Report FinalDokument68 SeitenHCL CDC Project Report Finalshahinnocent100% (1)