Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hkcee Biology - 4.1 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants - P.1
Hochgeladen von
irisyyy27Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hkcee Biology - 4.1 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants - P.1
Hochgeladen von
irisyyy27Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
47
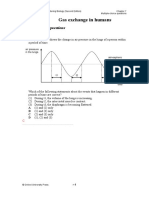
1. 1990/I/4a
The net carbon dioxide uptake and release from the stem and a single leaf of a herbaceous plant were
measured at different light intensities. The results are shown below :
Net uptake (+) / net release () of
carbon dioxide (mg cm
-2
h
-1
)
Light intensity (arbitrary
units)
stem leaf
0
2
4
6
8
10
1.0
+ 0.6
+ 2.2
+ 3.4
+ 4.4
+ 5.0
1.0
+ 5.6
+ 9.2
+ 11.0
+ 12.0
+ 12.6
(i) Plot the above data on the same graph. (4 marks)
(ii) Considering a leaf of 10 cm
2
at a light intensity of 5 units,
(1) state the net carbon dioxide uptake by the leaf in one hour. (1 mark)
(2) calculate the actual amount of carbon dioxide used by this leaf in photosynthesis in the same
period. (2 marks)
(iii) (1) With reference to the graph you have drawn, state which organ, the stem or the leaf, is more
efficient in carrying out photosynthesis. Explain how you arrive at your answer. (2 marks)
(2) Suggest TWO structural features which enable this organ to carry out photosynthesis more
efficiently. (2 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.1 Nutrition and gas exchange in plants | P.1
48
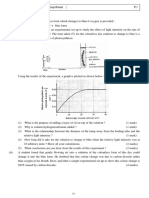
2. 1993/I/4b
The graph below shows the net uptake and net release of carbon dioxide of an actively growing plant over a
24-hour period :
(i) At what time(s) of the day was there no net uptake and no net release of carbon dioxide by the plant ?
(1 mark)
(ii) (1) What was the respiration rate of the plant in the dark period ? (1 mark)
(2) Calculate the total amount of carbon dioxide released by the plant in the same period.
(2 marks)
(iii) Assuming that the plant had the same respiration rate throughout the 24-hour period, what was the
highest rate of photosynthesis of the plant ? (1 mark)
(iv) What information from the graph suggests that the plant was actively growing ? Explain your answer.
[Hint : Compare area A and area B.] (4 marks)
3. 1994/I/2bii
Explain why there is a net uptake of carbon dioxide by leaves during the daytime. (3 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.1 Nutrition and gas exchange in plants | P.2
49
4. 2004/I/4c
The photomicrographs below show the sections of a leaf and a root :
(i) What is the significance of the following features ?
(1) the presence of cuticle on the leaf epidermis (1 mark)
(2) the absence of cuticle on the root epidermis (1 mark)
(ii) With reference to one feature shown in the photomicrograph, explain how gaseous exchange can
occur at the leaf epidermis. (2 marks)
(iii) Describe how the activity of cell type X leads to the storage of starch granules in cell type Y.
(4 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.1 Nutrition and gas exchange in plants | P.3
50
(iv) The table below shows the concentration of certain minerals in the soil water and the cell sap of the
root epidermal cells :
Concentration (mmol dm
-3
)
Potassium Sodium Chloride
Soil water 0.1 1.1 1.3
Cell sap of root
epidermal cells
93.0 51.0 58.0
According to these data, what mechanism is probably used by the root to absorb minerals from the
soil water ? Explain your answer based on the information provided. (3 marks)
5. 2005/I/8b
The picture below shows a school garden with some tomato plants:
(i) Explain why continuous harvesting of tomatoes may lead to the depletion of nitrate in the garden soil.
(2 marks)
(ii) Which organism in the soil turns some of the nitrate into atmospheric nitrogen? (1 mark)
(iii) Suggest two ways to restore the nitrate content of the soil. (2 marks)
(iv) A student flooded the soil with water. As a result, the air content of the soil became very low.
Explain why this condition may lead to poor plant growth. (3 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.1 Nutrition and gas exchange in plants | P.4
51
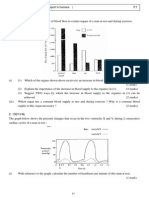
6. 2005/I/9b
Mary examined the epidermis of the leaf of a land plant under the microscope. The photomicrographs below
show the appearance of the upper and lower epidermis under different magnifications:
(i) Using the information provided in photomicrograph 2, calculate the stomatal density (i.e. number of
stomata per unit area) of the lower epidermis. (2 marks)
(Take =3.14)
(ii) Compare the stomatal density of the upper and lower epidermis of the leaf. Explain the significance
of this pattern of stomatal distribution to the plant when it is under direct sunlight. (3 marks)
(iii) Name structures P and Q. (2 marks)
P: _____________________ Q:______________________
(iv) Under certain conditions, the stomata of the leaves may become closed during daytime. Explain how
this would affect the rate of photosynthesis of the plant. (2 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.1 Nutrition and gas exchange in plants | P.5
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A4 QB-MC Ch09 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in PlantsDokument19 SeitenA4 QB-MC Ch09 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in PlantsReg ChooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseDokument23 SeitenSuggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseBernardNoch keine Bewertungen
- A4 QB-MC Ch10 Transpiration Transport and Support in PlantsDokument31 SeitenA4 QB-MC Ch10 Transpiration Transport and Support in PlantsReg ChooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Part1 TE eDokument39 SeitenWorksheet Part1 TE eEugenia100% (2)
- Structured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part VIII Chemical Reactions and EnergyDokument21 SeitenStructured Questions: HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Part VIII Chemical Reactions and EnergyNg Swee Loong StevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- bk2 - ch17 - Sug Ans - eDokument3 Seitenbk2 - ch17 - Sug Ans - enonameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Kit Extra Practice Questions (Suggested Answers)Dokument2 SeitenExam Kit Extra Practice Questions (Suggested Answers)WasangLiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers To 2017-2018 F3-CHEM Final Examination: Section A: Multiple ChoicesDokument13 SeitenAnswers To 2017-2018 F3-CHEM Final Examination: Section A: Multiple Choicesjonas hoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Science - Secondary 1Dokument7 SeitenIntegrated Science - Secondary 1siubb0112Noch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 1B (ENG) Question-Answer Book PDFDokument16 SeitenPaper 1B (ENG) Question-Answer Book PDFsdcsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSS Chemistry Part 2 Structural Questions and AnswersDokument22 SeitenNSS Chemistry Part 2 Structural Questions and AnswersFelix YueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1920 F3 Chem First Exam AnswerDokument2 Seiten1920 F3 Chem First Exam AnswerElsaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)Dokument22 Seiten2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)UniversityJCNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ultimate Question Bank: Dse Chem MasteryDokument48 SeitenThe Ultimate Question Bank: Dse Chem MasteryYip AvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Paper Micro World I II 2019 20 PDFDokument19 SeitenPast Paper Micro World I II 2019 20 PDF779720 cNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air and AtmosphereDokument12 SeitenAir and Atmospherebob leowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseDokument23 SeitenSuggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseBernard100% (1)
- Biology HKDSEDokument19 SeitenBiology HKDSERoy SzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExamKit Ch1 Eng 7Dokument24 SeitenExamKit Ch1 Eng 7WasangLiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank 1A 1B 2 - New QuestionDokument58 SeitenQuestion Bank 1A 1B 2 - New Questionteresa tsoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSGS 17-18 F.6 Final Exam 1 and 2 CHEMDokument37 SeitenSSGS 17-18 F.6 Final Exam 1 and 2 CHEMKelvin ChowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Paper Biology Paper 1Dokument32 SeitenPractice Paper Biology Paper 1ddd dddNoch keine Bewertungen
- LQ - 03 Cell Activity and OrganizationDokument40 SeitenLQ - 03 Cell Activity and Organizationapi-3822784100% (2)
- DSEpp - Market and PriceDokument21 SeitenDSEpp - Market and Pricepeter wongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior Secondary Geography Test: SECTION A: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDokument15 SeitenSenior Secondary Geography Test: SECTION A: Multiple-Choice QuestionsUniversityJC100% (1)
- Matter as Particles Explained Through Particle TheoryDokument26 SeitenMatter as Particles Explained Through Particle TheoryYuenHei Kwok0% (1)
- Suggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseDokument27 SeitenSuggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic Exercise[3Y25] Ng Sai YiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Munsang College 2013-2014 Second Term Examination F. 5 Mathematics Extended Part - Module 1 (Calculus and Statistics)Dokument28 SeitenMunsang College 2013-2014 Second Term Examination F. 5 Mathematics Extended Part - Module 1 (Calculus and Statistics)Anson Ka Kin ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Metallic Bonding: Learning GoalDokument36 SeitenChemical Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Metallic Bonding: Learning GoalRyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Exchange in Humans 1 QP PDFDokument9 SeitenGas Exchange in Humans 1 QP PDFSyakir FahmieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetically Modified Apples Prevent BrowningDokument40 SeitenGenetically Modified Apples Prevent BrowningBernardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Kit E2 Answers EngDokument6 SeitenExam Kit E2 Answers EngWasangLiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2 Choice and Opportunity CostDokument5 Seiten1.2 Choice and Opportunity CostToby ChengNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Matter As ParticlesDokument10 Seiten06 Matter As ParticlesmahinkamNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Senior Mastering Biology Food and HumansDokument4 SeitenNew Senior Mastering Biology Food and HumansHarry LeungNoch keine Bewertungen
- A4 QB-MC Ch08 Transport in HumansDokument23 SeitenA4 QB-MC Ch08 Transport in HumansReg ChooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 Chapter 1 The World Around UsDokument60 SeitenForm 2 Chapter 1 The World Around UsAnonymous x0kzb3UNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC - 05 The EcosystemDokument9 SeitenMC - 05 The Ecosystemapi-3822784Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch02 Full AnswersDokument8 SeitenCh02 Full AnswersOscar YipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution II: From Short-Necked To Long-NeckedDokument32 SeitenEvolution II: From Short-Necked To Long-NeckedBernardNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell As The Basic Unit of Life: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDokument67 SeitenThe Cell As The Basic Unit of Life: Multiple-Choice QuestionsZ s2021 4C Ma Ka Ki Margaret 4C16Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1718 2nd Ut f3 Geog QPDokument8 Seiten1718 2nd Ut f3 Geog QP惜靈靜雅Noch keine Bewertungen
- NSS Mathematics in Action (2nd Edition) 4A Section Worksheets 5 More about PolynomialsDokument2 SeitenNSS Mathematics in Action (2nd Edition) 4A Section Worksheets 5 More about PolynomialsChing Kiu ChuNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) Book 2 SolutionsDokument3 SeitenNew Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) Book 2 SolutionsHarry LeungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Temperature and Thermometers: Physics Notes Heat and GasDokument3 SeitenChapter 1: Temperature and Thermometers: Physics Notes Heat and GasWong Chun LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structured Questions: Core SectionDokument24 SeitenStructured Questions: Core Sectionapi-19650882Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Exchange in Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDokument56 SeitenGas Exchange in Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsZ s2021 4C Ma Ka Ki Margaret 4C16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition and gas exchange in plantsDokument28 SeitenNutrition and gas exchange in plants4B21 Renee Sin Yat HeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PartII Planet Earth MCDokument31 SeitenPartII Planet Earth MCDavid LouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Paper 1 Hkdse Mock Exam Ii: New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition)Dokument54 SeitenBiology Paper 1 Hkdse Mock Exam Ii: New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition)Alex Chow100% (1)
- Assignment AC U2 Final eDokument28 SeitenAssignment AC U2 Final eYuenHei KwokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDokument8 SeitenChapter 2 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDavid LouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part I Introducing Chemistry MCDokument6 SeitenPart I Introducing Chemistry MCDavid LouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggested Answers To Practical Workbook: CH 7 Gas Exchange in HumansDokument31 SeitenSuggested Answers To Practical Workbook: CH 7 Gas Exchange in HumansCharmine HolmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- HKCEE - Biology - 1998 - Paper I - A PDFDokument7 SeitenHKCEE - Biology - 1998 - Paper I - A PDFChinlam210Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 3.1 PhotosynthesisDokument7 SeitenBio 3.1 PhotosynthesisSuzuko YukinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HKALE BIOLOGY | 21 Photosynthesis | Optimized SummaryDokument8 SeitenHKALE BIOLOGY | 21 Photosynthesis | Optimized SummaryMichael ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 2.2 EcosystemDokument7 SeitenBio 2.2 EcosystemSuzuko YukinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 2.2Dokument7 SeitenBio 2.2zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- G8 BiologyDokument6 SeitenG8 Biologyheenamehta2702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Four Key Factors of the Scientific Revolution DebateDokument38 SeitenFour Key Factors of the Scientific Revolution Debateirisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- HKCEE BIOLOGY - 7.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - P.1Dokument6 SeitenHKCEE BIOLOGY - 7.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - P.1irisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gaza Home Destroyed in Air StrikeDokument23 SeitenGaza Home Destroyed in Air Strikeirisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Compounds Chemistry GuideDokument20 SeitenCarbon Compounds Chemistry Guideirisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hkcee Biology - 7.1 Types of Cell Division - P.1Dokument1 SeiteHkcee Biology - 7.1 Types of Cell Division - P.1irisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1Dokument10 SeitenHkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lee Wai Sze SarahDokument1 SeiteLee Wai Sze Sarahirisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1Dokument13 SeitenHkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hkcee Biology - 4.5 Gas Exchange in Humans - P.1Dokument7 SeitenHkcee Biology - 4.5 Gas Exchange in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes Section 3a Topic: Nutrition and Gas Exchange in PlantsDokument3 SeitenBiology Notes Section 3a Topic: Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plantsirisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Site Visit Risk Assessment FormDokument3 SeitenSite Visit Risk Assessment FormAmanuelGirmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture02 NoteDokument23 SeitenLecture02 NoteJibril JundiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wasserman Chest 1997Dokument13 SeitenWasserman Chest 1997Filip BreskvarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mission Ac Saad Test - 01 QP FinalDokument12 SeitenMission Ac Saad Test - 01 QP FinalarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reader's Digest (November 2021)Dokument172 SeitenReader's Digest (November 2021)Sha MohebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rohit Patil Black BookDokument19 SeitenRohit Patil Black BookNaresh KhutikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top Malls in Chennai CityDokument8 SeitenTop Malls in Chennai CityNavin ChandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Ready 01 With Keys and TapescriptsDokument157 SeitenLecture Ready 01 With Keys and TapescriptsBảo Châu VươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrical Hemorrhage: Reynold John D. ValenciaDokument82 SeitenObstetrical Hemorrhage: Reynold John D. ValenciaReynold John ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ujian Madrasah Kelas VIDokument6 SeitenUjian Madrasah Kelas VIrahniez faurizkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Ethics Is Good BusinessDokument9 SeitenGood Ethics Is Good BusinesssumeetpatnaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jfif 1.02Dokument9 SeitenJfif 1.02Berry Hoekstra100% (1)
- Web Api PDFDokument164 SeitenWeb Api PDFnazishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budgetary ControlsDokument2 SeitenBudgetary Controlssiva_lordNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Performance Measurement of Mining Equipments by Utilizing OEEDokument8 Seiten3 - Performance Measurement of Mining Equipments by Utilizing OEEGonzalo GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STAT100 Fall19 Test 2 ANSWERS Practice Problems PDFDokument23 SeitenSTAT100 Fall19 Test 2 ANSWERS Practice Problems PDFabutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Ecommerce Website: 1) Background/ Problem StatementDokument7 SeitenElectronics Ecommerce Website: 1) Background/ Problem StatementdesalegnNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIS Multi-Criteria Analysis by Ordered Weighted Averaging (OWA) : Toward An Integrated Citrus Management StrategyDokument17 SeitenGIS Multi-Criteria Analysis by Ordered Weighted Averaging (OWA) : Toward An Integrated Citrus Management StrategyJames DeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- UAPPDokument91 SeitenUAPPMassimiliano de StellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pub - Essentials of Nuclear Medicine Imaging 5th Edition PDFDokument584 SeitenPub - Essentials of Nuclear Medicine Imaging 5th Edition PDFNick Lariccia100% (1)
- Multiple Choice: CH142 Sample Exam 2 QuestionsDokument12 SeitenMultiple Choice: CH142 Sample Exam 2 QuestionsRiky GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innovation Through Passion: Waterjet Cutting SystemsDokument7 SeitenInnovation Through Passion: Waterjet Cutting SystemsRomly MechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Os PPT-1Dokument12 SeitenOs PPT-1Dhanush MudigereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rtsa 2012Dokument7 SeitenRtsa 2012Justin RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- QueriesDokument50 SeitenQueriesBajji RajinishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yellowstone Food WebDokument4 SeitenYellowstone Food WebAmsyidi AsmidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- If V2 would/wouldn't V1Dokument2 SeitenIf V2 would/wouldn't V1Honey ThinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular Flow of Process 4 Stages Powerpoint Slides TemplatesDokument9 SeitenCircular Flow of Process 4 Stages Powerpoint Slides TemplatesAryan JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- KSEB Liable to Pay Compensation for Son's Electrocution: Kerala HC CaseDokument18 SeitenKSEB Liable to Pay Compensation for Son's Electrocution: Kerala HC CaseAkhila.ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Pom Final On Rice MillDokument21 SeitenPom Final On Rice MillKashif AliNoch keine Bewertungen