Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Disease Deficiency/ Defect Abnormal Levels Symptoms Notes
Hochgeladen von
RLI23nyOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Disease Deficiency/ Defect Abnormal Levels Symptoms Notes
Hochgeladen von
RLI23nyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Disease Deficiency/ Defect Abnormal Levels Symptoms Notes
21-Hydroxylase
Deficiency*** (Exam
Favorite)
Most common form of
CAH ( > 90% of cases),
both partial and complete
deficiencies are known
No enzyme to convert
progesterone and OH-
progesterone into
aldosterone and cortisol
No Aldosterone or
Cortisol
Massive amounts of
androgens produced
Therefore only androgens
can be produced as no
negative feedback from
cortisol
Salt Wasting (Complete deficiency) Adrenal Crisis (salt
losing CAH) Occurs when aldosterone production is
affected leading to circulatory collapse and vomiting
Hypotension and Hyperkalemia
Hypoglycemia
Female virilization ambiguous genitalia Enlarged
clitoris at birth (posterior labial fusion, no vaginal opening)
d/t excess testosterone
o Deep voice and facial hair
o Inability to menstruate
o Late onset CAH: causes hirsutism and infertility
Male Puberty begins much earlier (appear normal at birth)
Boys: normal at birth but will have penile enlargement, early
pubic hair and rapid growth in height when child in 4 or 5
Investigation: screening by 17-
-hydroxyprogesterone in a
blood spot in the presence of
clinical symptoms
o In borderline tests, a
synacthen test can measure
17--hydroxyprogesterone
before and after synacthen
administration
o Urinary steroid profile can be
used
Treat via cortisol will
suppress ACTH system
Treatment Replacement of
glucocorticoids +
mineralocorticoids
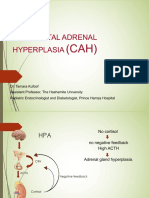
17 OH deficiency Sex and stress lost, but
salt preserved
cortisol ACTH
production
ACTH production
adrenal hyperplasia
Virtually no sex hormones
or cortisol are produced
Mineralocorticoids production Na
+
and fluid retention
hypertension and hypkalemia
HTN BP ECF Na
+
and H
2
O
o Aldosterone and Deoxycorticosterone
o Renin and Angiotensin II
Corticosterone will partially compensate for the
glucocorticoids
Androgen production in fetus is a problem with male
structures, & loss of axillary and pubic hair in females
Ambiguous genitalia in males and in females, there is delayed
puberty absent secondary sexual characteristics or primary
amenorrhea
Treatment Replacement of
glucocorticoids
Aldosterone antagonist i.e.
spironolactone
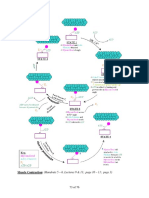
11- hydroxylase
deficiency
Deficiency-lose salt
and stress but maintain
sex and
deoxycorticosterone
Serum Cortisol,
Aldosterone,
corticosterone
Deoxycorticosterone (Na
+
retention) causes fluid
retention this hormone
suppresses RAAS low-
renin hypertension
ACTH
11, Deoxycorticosterone is a weak mineralocorticoid if >> is
produced Na
+
and H
2
O BP and Renin and
Aldosterone
Virilizing syndrome in females
Effects on prepubertal males
Masculinization and virilization as with 21--hydroxylase
deficiency
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fast Facts: Deficiencia de piruvato quinasa para pacientes y familiares: Una enfermedad genética rara que afecta a los glóbulos rojos Información + Asumir el control = El mejor resultadoVon EverandFast Facts: Deficiencia de piruvato quinasa para pacientes y familiares: Una enfermedad genética rara que afecta a los glóbulos rojos Información + Asumir el control = El mejor resultadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal DisordersDokument56 SeitenAdrenal DisordersKlyn Agagon GayodanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDokument46 SeitenCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaSarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Definition and EtiologyDokument33 SeitenCongenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Definition and Etiologylotp12Noch keine Bewertungen
- April 6 Quiz Medical DR - Rajesh GubbaDokument141 SeitenApril 6 Quiz Medical DR - Rajesh GubbaPraveenRajMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDokument17 SeitenCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaInani Nabila LahuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal GlandDokument75 SeitenAdrenal GlandPamela MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDokument30 SeitenCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaanrihmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Adrenals STUDENT BBDokument15 SeitenEndocrine Adrenals STUDENT BBVirang ParikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothalamus:: PeptidesDokument2 SeitenHypothalamus:: PeptideskianuhhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDokument2 SeitenCongenital Adrenal HyperplasialynellecabaccangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument30 SeitenEndocrine SystemYary MayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Presented By: Ahmad Fazwan JunaidiDokument16 SeitenCongenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Presented By: Ahmad Fazwan JunaidiZakirNoch keine Bewertungen
- MK CahDokument46 SeitenMK CahMartini ListrikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine New EditionDokument150 SeitenEndocrine New Editiondigracia manatigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDokument27 SeitenCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaJunbek nov23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Exam 1 ReviewDokument11 SeitenEndocrine Exam 1 ReviewJohn SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0018.Dokument2 SeitenWa0018.song flamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Gland by Dr. Rajnee IInd PartDokument30 SeitenAdrenal Gland by Dr. Rajnee IInd Part9460106212Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study EndocrineDokument4 SeitenCase Study Endocrinegladz25Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM and Disorders LectureDokument153 SeitenENDOCRINE SYSTEM and Disorders LectureAnthony Riggs100% (1)
- Assignment 4Dokument8 SeitenAssignment 4api-328441669100% (1)
- Review Endocrine Disorders FINALDokument166 SeitenReview Endocrine Disorders FINALmeranith100% (10)
- Congenital Adreal Hyperplasia and Testicular Feminization SyndromesDokument23 SeitenCongenital Adreal Hyperplasia and Testicular Feminization SyndromesJunbek nov23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Glands DiseasesDokument17 SeitenAdrenal Glands DiseasesDr-Dalya ShakirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1310 HaiderAdrenal Disorders Peds Board 2013Dokument21 Seiten1310 HaiderAdrenal Disorders Peds Board 2013Brandon LewisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Members: Amala Nisanthi Kavitha Afiqah ShuhailaDokument48 SeitenGroup Members: Amala Nisanthi Kavitha Afiqah ShuhailaArul NeethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ambiguous GenitaliaDokument47 SeitenAmbiguous GenitaliaDrvsowmya Lakshmi100% (1)
- Adrenal Glands: Adrenal Cortex Adrenal MedullaDokument66 SeitenAdrenal Glands: Adrenal Cortex Adrenal MedullaRinto NugrohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Cortex HormoneDokument22 SeitenAdrenal Cortex HormoneYudistiraJefriRamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Hormone 2018 PDFDokument66 SeitenAdrenal Hormone 2018 PDFrosyidafiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah Blok Hemaologi-ERITROSITDokument30 SeitenKuliah Blok Hemaologi-ERITROSITwuryan dewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDokument42 SeitenCongenital Adrenal HyperplasianeysaonlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine 3Dokument115 SeitenEndocrine 3Dessalegn LemmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Dokument47 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Abinaya RanganathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Glands - Cortex - Dr. Gagare DBDokument28 SeitenAdrenal Glands - Cortex - Dr. Gagare DBkehigeh812Noch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument43 SeitenEndocrine Systemwieka mawieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Ca in The BodyDokument30 SeitenImportance of Ca in The BodyMushtaaq Bintu MaxamuudNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09-28-15 CAH Grand RoundsDokument55 Seiten09-28-15 CAH Grand Roundsnila sari batubaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calcium Haemostasis: By: Vasavi.NDokument26 SeitenCalcium Haemostasis: By: Vasavi.NmahalakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal PathophysiologyDokument5 SeitenAdrenal PathophysiologyditabokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Cortex HormonesDokument21 SeitenAdrenal Cortex HormonesAaa JjjjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Other Disorders: Disorder Name: Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Acronym: CAHDokument14 SeitenOther Disorders: Disorder Name: Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Acronym: CAHFriskaPieseshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypokalemia FT 2020Dokument49 SeitenHypokalemia FT 2020ebkai98Noch keine Bewertungen
- PATH ImmuneDokument7 SeitenPATH ImmuneDavid DvoskineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDokument10 SeitenCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaJemmy Wijaya100% (1)
- Endocrine PhysiologyDokument26 SeitenEndocrine Physiologysam bossaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADRENALSDokument60 SeitenADRENALSJyoti ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HormonesDokument2 SeitenHormonesTimmy CoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thalassemia (Revised)Dokument5 SeitenThalassemia (Revised)AradhanaRamchandaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 The Adrenal Gland Aldosterone2017 1Dokument27 Seiten10 The Adrenal Gland Aldosterone2017 1Tariq Jamil KoraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormon PDFDokument23 SeitenHormon PDFNanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Lab in Diagnosing Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Ola H. ElgaddarDokument24 SeitenRole of Lab in Diagnosing Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Ola H. ElgaddarOla ElgaddarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endo Lect-Adrenal Gland and AldosteroneDokument25 SeitenEndo Lect-Adrenal Gland and AldosteronedoctorrfarrukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenogenital Syndrome: Physical FindingsDokument2 SeitenAdrenogenital Syndrome: Physical FindingschoobiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EndocrineDokument2 SeitenEndocrineUnclePorkchopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah PituitariDokument48 SeitenKuliah PituitariLona Veronika HutajuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Disorders NotesDokument14 SeitenEndocrine Disorders NotesSarahMelissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions and Regulation of Na, K, CL, & Ca Ions: Dr. Rukhsana AnwarDokument23 SeitenFunctions and Regulation of Na, K, CL, & Ca Ions: Dr. Rukhsana AnwarZia PhotostateNoch keine Bewertungen
- PV LoopDokument1 SeitePV LoopRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HISTORY - There Is No Substitute For A Thorough Patient History For Determining Whether Other Conditions AreDokument9 SeitenHISTORY - There Is No Substitute For A Thorough Patient History For Determining Whether Other Conditions AreRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen DissociationDokument1 SeiteOxygen DissociationRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscle ContractionsDokument1 SeiteMuscle ContractionsRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Is The Right Thing You Do: PolycythemiaDokument1 SeiteExercise Is The Right Thing You Do: PolycythemiaRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type Description Principal Mechanism Clinical Examples Cardiogenic ShockDokument1 SeiteType Description Principal Mechanism Clinical Examples Cardiogenic ShockRLI23ny100% (1)
- Gastric Cells and SecretionDokument1 SeiteGastric Cells and SecretionRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSF Characteris Tics: 40 (0 - 10) 40 40 May Be Elevated (50 - 100)Dokument5 SeitenCSF Characteris Tics: 40 (0 - 10) 40 40 May Be Elevated (50 - 100)RLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solute Transport in NephronDokument1 SeiteSolute Transport in NephronRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ascus: After Colposcopy Pap Smear Every 3 Months For 1 YearDokument1 SeiteAscus: After Colposcopy Pap Smear Every 3 Months For 1 YearRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reporting of Vital SignsDokument1 SeiteReporting of Vital SignsRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypoxemia Interpretation of SpirometryDokument55 SeitenHypoxemia Interpretation of SpirometryRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- X-Ray Review Chest Name Age Date View PA View: Most Common. Scapula Are NOT VisibleDokument2 SeitenX-Ray Review Chest Name Age Date View PA View: Most Common. Scapula Are NOT VisibleRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Pulse Location Surface Anatomy (Not Palpated For Vital Signs)Dokument1 SeitePulse Pulse Location Surface Anatomy (Not Palpated For Vital Signs)RLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problem For Formats LogDokument4 SeitenPractice Problem For Formats LogRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abx Mech of ActionDokument1 SeiteAbx Mech of ActionRLI23nyNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States Court of Appeals, Tenth CircuitDokument9 SeitenUnited States Court of Appeals, Tenth CircuitScribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bag-Ong Lamdag November 1 - December 31, 2015 IssueDokument8 SeitenBag-Ong Lamdag November 1 - December 31, 2015 IssueTesay EspinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Office: 2018doif - LF./ )Dokument1 SeiteCentral Office: 2018doif - LF./ )Glenn FabiculanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTION TO NURISTANI TRIBES, LANGUAGES AND DILECTS - DotxDokument11 SeitenINTRODUCTION TO NURISTANI TRIBES, LANGUAGES AND DILECTS - DotxAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of Separation of East PakistanDokument5 SeitenCauses of Separation of East Pakistantanvir92% (36)
- Digest G.R. No. 165424 Halili Vs Santos-HaliliDokument2 SeitenDigest G.R. No. 165424 Halili Vs Santos-HaliliJaja GkNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A SacramentDokument21 SeitenWhat Is A SacramentSheila Marie Anor100% (1)
- Padilla V DizonDokument12 SeitenPadilla V DizonKarlo KapunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consti Law 1 ReviewerDokument13 SeitenConsti Law 1 ReviewerKimmy DomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- People Vs AposagaDokument1 SeitePeople Vs Aposagamichaeljennings21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jagannatha DrekkanaDokument14 SeitenJagannatha Drekkanajyotishdigest100% (6)
- Deerfield - 2016Dokument265 SeitenDeerfield - 2016DJ EntropyNoch keine Bewertungen
- British Institute of International and Comparative Law, Cambridge University Press Journal of The Society of Comparative LegislationDokument10 SeitenBritish Institute of International and Comparative Law, Cambridge University Press Journal of The Society of Comparative LegislationCatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Davy Crockett WikepediaDokument12 SeitenDavy Crockett WikepediaLucas FinleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ways To AnnoyDokument10 SeitenWays To AnnoyNina NigriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Romulo v. YniguezDokument19 SeitenRomulo v. YniguezmehNoch keine Bewertungen
- HE Ystem: The Early YearsDokument4 SeitenHE Ystem: The Early YearsrenestwolfNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Bhattacharya - The Boxer Rebellion I-1Dokument20 SeitenA. Bhattacharya - The Boxer Rebellion I-1Rupali 40Noch keine Bewertungen
- Torts BDokument15 SeitenTorts Byin-pasiya nabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rabbit-Proof FenceDokument14 SeitenRabbit-Proof FenceOo LwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- (CHP 7) Occupier LiabilityDokument10 Seiten(CHP 7) Occupier Liabilityyxnnis100% (1)
- Thesis On A Homicide Ending ExplainedDokument8 SeitenThesis On A Homicide Ending Explainedjenniferlordmanchester100% (2)
- ECT Board Exam Dec 2013Dokument6 SeitenECT Board Exam Dec 2013TheSummitExpressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mr. Kumar Mrs. Kumar Kumudha Ramesh Rekha Virendra Kumar LathaDokument4 SeitenMr. Kumar Mrs. Kumar Kumudha Ramesh Rekha Virendra Kumar LathaRajat RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEAT Cell State-Wise Distribution of No. of Free SeatsDokument1 SeiteNEAT Cell State-Wise Distribution of No. of Free SeatsBE19FO3FO66 DnyaneshwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 - Error in GR - Value of Goods Movement Is NegativeDokument35 Seiten2023 - Error in GR - Value of Goods Movement Is NegativePradhumn SainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uk Sowell Transcript Conflict VisionsDokument15 SeitenUk Sowell Transcript Conflict Visionsbergamonunes100% (1)
- Motion For Early Release From ProbationDokument2 SeitenMotion For Early Release From ProbationBeverly mosleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Max Scheler's Phenomenology of ShameDokument11 SeitenMax Scheler's Phenomenology of Shamesarajamalsweet100% (1)
- Laoang, Northern SamarDokument2 SeitenLaoang, Northern SamarSunStar Philippine NewsNoch keine Bewertungen