Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
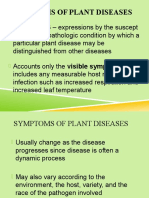
Symptom Plant Disease
Hochgeladen von
Da Nie LOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Symptom Plant Disease
Hochgeladen von
Da Nie LCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bacteria, fungi, nematodes, viruses and viroids are the living agents that cause plant diseases.
Nematodes are the largest of these agents, while viruses and viroids are the smallest. None of
these pathogens are visible to the naked eye, but the diseases they cause can be detected by
the symptoms of wilting, yellowing, stunting, and abnormal growth patterns.
Symptoms can be classificated based on these terms:
Etiolation - green tissues become yellowish caused by insufficient light
Chlorosis - green tissues become yellowish caused by other factor than light
Necrosis - death of cells resulting affected tissues turn dark
Albinism - tissues turn to white
Vein clearing - leaf veins become whitish or transculent
Interveinal chlorosis - leaf veins remain green but tissues between veins become chlorotic
Mosaic - leaves have pattern of all shades of green to yellow but sharply defined borders
Mottling - variegation less pronounced, diffused bounderies
Lesions - areas of diseased tissues
Localized lesions - restricted areas of diseased tissues.
Hypoplasia - production of subnormal number of cells (become stunted)
Hyperplasia - production of an abnormally large number of cells
Hypotrophy - a subnormal decrease in size of cells
Hypertrophy - an abnormal increase in the size of cells
Rot or rotting - the disintegration and decomposition of plant tissue
Wilt or wilting - loss of freshness or drooping of plants due to inadequate water supply or
excessive transpiration; or a vascular disease interfering with water supply.
Canker - diseases of shrubs and trees
Mummification - initial rotting of fruit by fungal pathogen g transforming the fruit into a dry
shrivelled
Common Symptoms of Diseased Plants
Symptoms of diseased plants vary with different plant pathogens, different host plants, plant parts, infection stages
and environmental conditions. None of these pathogens are visible to the naked eye, but the diseases they cause can
be detected by the symptoms showed. Symptoms can be classificated based on these terms :
Chlorotic - areas may be pale green, light yellow, reddish, purple or white.
Dwarfing - Compared with healthy plants of the same variety, infected plants are much shorter or smaller.
Mosaic - seen as alternative areas of light and dark, or yellow and green on leaves and the areas can be angular,
sharply bordered, or divided by leaf veins.
Mottle - yellow and green, or light and dark areas with less clear or diffuse boundaries on leaves.
Necrosis - death of cells resulting affected tissues turn dark
Necrotic - symptom is shown as areas of dead tissues in leaves.
Wilting - loss of freshness or drooping of plants due to inadequate water supply or excessive transpiration; or a
vascular disease interfering with water supply.
Streaks and Stripes - the streaks or stripes are chlorotic with yellow, red or purple colors. Streaks or stripes may
become necrotic with brown or black colors especially in later stages of infection
Stunting - the reduction in growth of plants.
Tumors - show as roughened or cracked surface.
Hypoplasia production of subnormal number of cells (become stunted)
Hyperplasia production of an abnormally large number of cells
Hypotrophy a subnormal decrease in size of cells
Hypertrophy an abnormal increase in the size of cells
Vein Clearing - vascular tissues results in yellow, clear or translucent tissues around leaf veins.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Patho GlossrayDokument26 SeitenPatho GlossrayKhadija AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify and Treat Cannabis Diseases, Insects, and DeficienciesVon EverandIdentify and Treat Cannabis Diseases, Insects, and DeficienciesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 MidtermDokument21 Seiten2 Midtermjagprima24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Plant Pathology-Lecture 2Dokument22 SeitenIntroduction To Plant Pathology-Lecture 2Oluwapelumi Adesola AdeyemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- +symptoms of Plant DiseasesDokument32 Seiten+symptoms of Plant DiseasesFatima Socorro PortillanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fungaldiseasesofvegetables Potato 211210060451Dokument30 SeitenFungaldiseasesofvegetables Potato 211210060451dawit gNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01042020164157FPP Symptom of Plant Disease 409.19Dokument5 Seiten01042020164157FPP Symptom of Plant Disease 409.19Manjeet DhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corn DiseasesDokument46 SeitenCorn DiseasesMandre DynaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lowland RiceDokument54 SeitenLowland RiceSharra Julia Alano CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertrophic HyperplasticDokument22 SeitenHypertrophic Hyperplasticjagprima24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Crop DiseaseDokument14 SeitenIntroduction To Crop DiseaseIzzul HaikalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases in LettuceDokument17 SeitenDiseases in LettucevligrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Learning Material For Diagnosing Nutrient DeficiencyDokument4 SeitenAdditional Learning Material For Diagnosing Nutrient DeficiencyTrisha CoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Pathology: CMG Gardennotes #331Dokument15 SeitenPlant Pathology: CMG Gardennotes #331andargashebirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disease Cause by AlgaeDokument2 SeitenDisease Cause by AlgaePrabin Shakya67% (6)
- Topik: Pengenalan Perosak Tanaman Dan Kepentingannya Dalam PertanianDokument230 SeitenTopik: Pengenalan Perosak Tanaman Dan Kepentingannya Dalam PertanianHazimHashimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Diseases of Leafy GreensDokument6 SeitenCommon Diseases of Leafy GreensAgung PurnomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prak PerlintanDokument2 SeitenPrak PerlintanDani TTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signs of Nutrient DeficiencyDokument2 SeitenSigns of Nutrient DeficiencySirSmirkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pesticide Certification Information # 1 5: Diseases OF Vegetable CropsDokument13 SeitenPesticide Certification Information # 1 5: Diseases OF Vegetable CropsMayank ChoubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Disease: Opics in ThisDokument16 SeitenPlant Disease: Opics in Thispopa_marius_68100% (1)
- Practical Manual - Crop DiseasesDokument82 SeitenPractical Manual - Crop DiseasesPrakash Kumar Kumar86% (7)
- Cole CropsDokument25 SeitenCole CropsJamal AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory 3Dokument6 SeitenLaboratory 3Mariel CaylanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symptoms of Disease Caused by Fungal ParasitesDokument6 SeitenSymptoms of Disease Caused by Fungal ParasitesAbie Jane BeatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symptoms of Virus Infected Plants and Their Specimen-1Dokument13 SeitenSymptoms of Virus Infected Plants and Their Specimen-1ATIYA JAMILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Diseases of Important Agriculture Crops of Tamil NaduDokument43 SeitenManagement of Diseases of Important Agriculture Crops of Tamil NaduVishnuvardhan RavichandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Problems of Fruit CropsDokument80 SeitenField Problems of Fruit CropsAnuragBhatnagar100% (2)
- Plant Disease, Its Causes and Symptoms: Class 3Dokument19 SeitenPlant Disease, Its Causes and Symptoms: Class 3Masum BillahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 Plant DiseaseDokument16 Seiten18 Plant DiseaseMario RectoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PustulDokument6 SeitenPustulIkhsan Hidayat SuratmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Board Review For AgricultureDokument123 SeitenBoard Review For Agriculturejonnadz100% (6)
- Signs and SymptomsDokument2 SeitenSigns and SymptomsKristine GurimbaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allium Insect DiseaseDokument2 SeitenAllium Insect DiseaseAli RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacterial DiseasesDokument38 SeitenBacterial Diseasesrenz jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Panganiban - Laboratory Activity 3 Disease CycleDokument8 SeitenPanganiban - Laboratory Activity 3 Disease CycleLovely PanganibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ornamental Plant Diseases and Their ManagementsDokument56 SeitenOrnamental Plant Diseases and Their ManagementsCecirly Gonzales PuigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts in Plant Disease SymtomologyDokument16 SeitenConcepts in Plant Disease SymtomologyAzelyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP348 - PP348 - Florida Blueberry Leaf Disease GuideDokument22 SeitenPP348 - PP348 - Florida Blueberry Leaf Disease GuideHussein GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FBS - Forest HealthDokument52 SeitenFBS - Forest HealthJoyce GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apple: Diseases and SymptomsDokument5 SeitenApple: Diseases and SymptomsAyshee BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrient DeficiencyDokument8 SeitenNutrient DeficiencyAnonymous AMmNGgPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 08 - Diseases of Chilli:: Pythium Aphanidermatum SymptomsDokument8 SeitenLecture 08 - Diseases of Chilli:: Pythium Aphanidermatum SymptomsIll DuceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disease of ChilliDokument8 SeitenDisease of ChilliSourabh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mango: Diseases and Symptoms: Powdery MildewDokument8 SeitenMango: Diseases and Symptoms: Powdery MildewGlory May AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mango 2Dokument20 SeitenMango 2Shreya KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
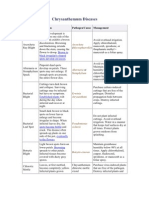
- Chrysanthemum DiseasesDokument3 SeitenChrysanthemum DiseasesEmanuel DincaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control of The Main Foliar Diseases of Container-Grown RosesDokument12 SeitenControl of The Main Foliar Diseases of Container-Grown RosesGheorghe IuroaeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 07 - Disease of Apple (2 Lectures) : - Venturia Inaequalis SymptomsDokument8 SeitenLecture 07 - Disease of Apple (2 Lectures) : - Venturia Inaequalis SymptomsAMBIKA BHANDARINoch keine Bewertungen
- Strawberry Leaf ScorchDokument5 SeitenStrawberry Leaf ScorchJanath AnthonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pub 3084 Rice Disease Slow ResDokument6 SeitenPub 3084 Rice Disease Slow Reslynmaria madronaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0068.Dokument19 SeitenWa0068.Shreya KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP-202 Week 1-3Dokument5 SeitenPP-202 Week 1-3Yasir IftikharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penyakit LetuceDokument11 SeitenPenyakit Letucesisuneo88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of CoconutDokument7 SeitenDiseases of CoconutKA AngappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 DD PDDokument41 SeitenUnit 2 DD PDYaiphabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PathologyDokument19 SeitenPathologyHannan AlfatNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiseasesDokument20 SeitenDiseasesSaziya QuadriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacterial Leaf Spot and TipburnDokument4 SeitenBacterial Leaf Spot and TipburnAlvin WatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.3 Pest and Disease Rat Control: A) .Rattustiomanicus, B) Rattusargentiventer C) RattusdiardiiDokument5 Seiten3.3 Pest and Disease Rat Control: A) .Rattustiomanicus, B) Rattusargentiventer C) RattusdiardiiDa Nie LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspects To Adhere To For Forum DiscussionDokument1 SeiteAspects To Adhere To For Forum DiscussionDa Nie LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solenoid Valve Type DifferencesDokument7 SeitenSolenoid Valve Type DifferencesDa Nie L100% (1)
- Information To The Control Room Computer, Which Then Accurately IndicatesDokument5 SeitenInformation To The Control Room Computer, Which Then Accurately IndicatesDa Nie LNoch keine Bewertungen
- CucumberDokument25 SeitenCucumberDa Nie LNoch keine Bewertungen
- ContestDokument1 SeiteContestDa Nie LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entomology Excretion System of InsectDokument12 SeitenEntomology Excretion System of InsectDa Nie LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report AGR218 TemplateDokument1 SeiteLab Report AGR218 TemplateDa Nie LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 2 - CytologyDokument7 SeitenLab Report 2 - CytologyDa Nie L100% (1)
- Audited Financial FY2014Dokument11 SeitenAudited Financial FY2014Da Nie LNoch keine Bewertungen
- AGR122 Lab 3 DiscussionDokument2 SeitenAGR122 Lab 3 DiscussionDa Nie LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Actinomycetes As Potential BiofungicidesDokument5 SeitenSoil Actinomycetes As Potential Biofungicideskopeal100% (3)
- Applications of Computer Vision in Plant Pathology A SurveyDokument22 SeitenApplications of Computer Vision in Plant Pathology A SurveyAlexander Espinosa ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolation and Identification of Fungal Pathogens Associated With Diseases of Onion Crop in District Swat, PakistanDokument9 SeitenIsolation and Identification of Fungal Pathogens Associated With Diseases of Onion Crop in District Swat, PakistanAbasyn Journal of Life SciencesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emerging Microbial Biocontrol Strategies For Plant PathogensDokument10 SeitenEmerging Microbial Biocontrol Strategies For Plant PathogensAlex PradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AG3-Lesson 6. Review of Related LiteratureDokument12 SeitenAG3-Lesson 6. Review of Related LiteratureJelly CantilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test in Crop Protection: DIRECTION: Encircle The Letter of The Best Answer From The Choices Given. 1Dokument25 SeitenPractice Test in Crop Protection: DIRECTION: Encircle The Letter of The Best Answer From The Choices Given. 1Loida Manluctao Gacusan100% (2)
- Title Defense Physical Group 10Dokument5 SeitenTitle Defense Physical Group 10Dan Jenniel CedeñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upasi Tea Research FoundationDokument11 SeitenUpasi Tea Research FoundationSLQC KumaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec1273 PDFDokument8 SeitenEc1273 PDFMankeu kelasUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment CPTDokument9 SeitenAssignment CPTparameswar jenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of PathogenesisDokument33 SeitenRole of Pathogenesiskhansha ComputersNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLE 9 Agri Crop Prod Q3 - M8 For PrintingDokument24 SeitenTLE 9 Agri Crop Prod Q3 - M8 For PrintingAlfredo Jr Del MundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 - Literature Cited PDFDokument75 Seiten17 - Literature Cited PDFMogosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crop Protection ManagementDokument17 SeitenCrop Protection ManagementArpita SonawaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio-Management of Diseases and Insect Pests in Vegetable CropsDokument3 SeitenBio-Management of Diseases and Insect Pests in Vegetable CropsDr. G. SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Plant Pathology LectureDokument16 SeitenHistory of Plant Pathology LectureAmitesh ChouhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osu Vegetable Seed TreatmentDokument5 SeitenOsu Vegetable Seed TreatmentGman007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary Agriculture Teacher'S Notes Grade 5: Compiled By: TT Amadhila For Teachers in Oshikoto RegionDokument27 SeitenElementary Agriculture Teacher'S Notes Grade 5: Compiled By: TT Amadhila For Teachers in Oshikoto RegionJB MangunduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Data of Dr. R. B. GaurDokument61 SeitenBio Data of Dr. R. B. GaurDr.Ram Babu GaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1-3 Propagation and Nursery PracticeDokument233 SeitenChapter 1-3 Propagation and Nursery Practiceadem endrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boutaj Et Al 2020 APPPDokument18 SeitenBoutaj Et Al 2020 APPPFarouk ViaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Disease Report PDFDokument11 SeitenPlant Disease Report PDFAshish ParajuliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biocontrol of Plant Disease Recent Advances and Prospects in Plant Protection (Claire Prigent-Combaret, Bernard Dumas) (Z-Library)Dokument273 SeitenBiocontrol of Plant Disease Recent Advances and Prospects in Plant Protection (Claire Prigent-Combaret, Bernard Dumas) (Z-Library)Washington PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pepper Diseases - A Practical Guide To Identification & ControlDokument35 SeitenPepper Diseases - A Practical Guide To Identification & Control19crysti100% (6)
- ActinomycesDokument16 SeitenActinomycesPhạm Huy QuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Module For Epp 5: East Negros Academy, IncDokument15 SeitenLearning Module For Epp 5: East Negros Academy, IncKath PalabricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fungi and DiseaseDokument5 SeitenFungi and Diseaseharold_gravity9885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phytophthora CapsiciDokument7 SeitenPhytophthora CapsiciHazan LumzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic - Plant Quarantine: Course - M. Sc. Botany Part 1 Paper IIIDokument9 SeitenTopic - Plant Quarantine: Course - M. Sc. Botany Part 1 Paper IIIunikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agriculture and Veterinary Science, Sciences and Medicine: Catalogue Eastern Economy EditionsDokument196 SeitenAgriculture and Veterinary Science, Sciences and Medicine: Catalogue Eastern Economy EditionsKhubaib AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerVon EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (392)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesVon EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (397)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeVon EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsVon EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceVon EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Von EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (378)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessVon Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (33)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceVon EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (18)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionVon EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (812)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperVon EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (15)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveVon EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (66)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouVon EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (62)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainVon EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (109)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedVon EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (11)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainVon EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorVon EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueVon EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (38)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldVon EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (595)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindVon EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (93)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemVon EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (115)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldVon EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (18)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsVon EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2083)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineVon EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (17)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomVon EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (216)