Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Basel II Letter 5 Pllar 2 v2
Hochgeladen von
0110rajCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Basel II Letter 5 Pllar 2 v2
Hochgeladen von
0110rajCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ADVISORY
Internal Capital Adequacy
Assessment Process
FINANCIAL SERVICES
HazemHassan
Public Accountants & Consultants
Contacts
KPMG Hazem Hassan
Pyramids Heights Office Park
Km 22 Cairo / Alexandria Desert Road
12556 Al Ahram
P.O.Box 48 Al Ahram
Giza - Cairo Egypt
Aziz Maher
Partner Financial Services
Tel: (202) 35 36 2200/11 Ext.1519
Fax: (202)35 36 2305/03
E-mail: azizmaher@kpmg.com
Dr. Lionel Khalil
Director Financial Risk Management
Tel: (202) 35 36 2200/11 Ext.3714
Fax: (202)35 36 2305/03
E-mail: lkhalil@kpmg.com
The Information contained herein is of a general nature and is not intended to
address the circumstances of any particular individual or entity. Although we
endeavor to provide accurate and timely information, there can be no guarantee
that such information is accurate as of the date it is received or that it will
continue to be accurate in the future. No one should act on such information
without appropriate professional advice after a thorough examination of the
particular situation.
2009 KPMG Hazem Hassan, the Egyptian
member firm of KPMG International, a Swiss
cooperative. All rights reserved. Printed in the
Arab Republic of Egypt. The KPMG logo and
name are trademarks of KPMG International.
Designed and produced by KPMGs Egypt
Design Services
Content
- Pillar 2 : Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP)
- Integrated Risk, Return, Capital, and Value Management
- Benefit from a well-defined Basel II Evolution Program
1 1
2 2
4 4
Pillar 2 : Internal Capital Adequacy
Assessment Process (ICAAP)
Banks take on risks in order to earn a return, therefore management
system to identify and take on well priced risks becomes ever more
important in todays competitive banking market
1
Benefit from a well-defined
Basel II Evolution Program
Basel II compliance
KPMGs FRM Services provide Basel II
regulatory and compliance advisory
services to assist various types of
financial institutions in meeting their
regulatory obligations effectively and
efficiently and keep up with Basel II
issues:
Proactively setup an organization
ready to comply with regulatory
requirements,
Mitigate regulatory impact on
processes and methods,
Effectively improve and monitor
systems and data, and
Ultimately obtain competitive
advantage through cost-effective
compliance.
KPMG Differentiators
KPMG's Basel II Methodology is a
structured approach to help clients
assess:
Their actual status concerning the
Basel II Accord readiness,
Existing gaps and shortcomings,
Activities to be undertaken to fill
gaps and reach desired end state.
The objectives of KPMG's Basel II
Methodology are to:
Define a standard, modular
approach to performing Basel II
programs in 4 Phases,
Provide practical guidance based
on Basel II leading practices, and
Provide risk management guidance.
Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4
B A S E L I I P R O J E C T M A N A G E M E N T
ASSESS AND PLAN DESIGN AND IMPLEMENT
USE TEST
AND
APPROVAL
MONITOR
AND
CONTROL
G
a
p
A
n
a
l
y
s
i
s
I
m
p
a
c
t
A
n
a
l
y
s
i
s
B
a
s
e
l
I
I
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
A
p
p
r
o
a
c
h
U
s
e
T
e
s
t
a
n
d
A
p
p
r
o
v
a
l
M
o
n
i
t
o
r
a
n
d
C
o
n
t
r
o
l
Corporate Governance/
Risk Management
Credit Risk
Operational Risk
Market and Other Risks
Capital Planning
Disclosure
(including linkage to IFRS)
Supervisory Review Process
ORGANISATION
PROCESSES
METHODS
SYSTEMS
DATA
B
a
s
e
l
I
I
i
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
M
a
s
t
e
r
P
l
a
n
B
a
s
e
l
I
I
R
o
l
l
-
O
u
t
P
l
a
n
B
a
s
e
l
I
I
I
m
p
l
e
m
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
A
p
p
r
o
a
c
h
4
Internal Capital Adequacy
Assessment Process (ICAAP)
Basel II, Pillar 2 demands banks to put a
internal capital adequacy assessment
process (ICAAP) in place. Like in any
business enterprise that involves the
commercial provision of products or
services to meet a particular need,
owners of banks require to be
compensated for the resources that they
invest to generate such services. This
compensation needs to be explicitly
linked to the entrepreneurial risk
undertaken by them.
Economic Capital
The Basel Committee defines economic
capital as the methods or practices that
allow banks to attribute capital to cover
the economic effects of risk-taking
activities. It is a measure of risk rather
than capital held, and is distinct from the
Pillar 1regulatory capital measures. It
provides banks with a common
currency for measuring, monitoring,
and controlling different risk types and
the risks of different business units.
The risk types typically covered
include: credit risk, market risk,
operational risk, business/strategic risk,
counterparty credit risk, insurance risk,
real estate risk and model risk... They
can be measured at various levels,
from firm-wide to an individual
portfolio.
KPMG Services: a single view
of Risk and Return
Economic Capital Management is the
central notion of integrating the risk
and the return perspective of an
institution or bank to support the
maximization of its value subject to
the restriction of remaining solvent.
KPMG proposes a value-oriented
review of risk and return processes:
Alignment of risk and return
management process with
business model
Better decision making through
risk and return oriented review of
business opportunities
Transparency regarding
implications of business decisions
along entire value chain
r
e
p
o
r
t
i
n
g
R
u
l
e
s
e
t
t
i
n
g
&
g
u
i
d
a
n
c
e
Board level
Operational
level
Risk
management
activities
Risk
categories
Bottom-up risk management
Top-down risk management
Credit
risk
Op.
risk
Market
risk
Liq
risk
Reputat.
risk
Other
risks
Action plan
Risk framework and strategy
Risk appetite
Risk-return measure and hurdle rates
Capital allocation
Communication to stakeholders
Incentive scheme
Regular update of objectives
Risk identification and measurement
Risk mitigation
Measuring diversification benefits
Risk aggregation
Monitoring of overall risk profile
Al location of diversification benefits
Performance Measurement
Preparation of reports
E
c
o
n
o
m
i
c
c
a
p
i
t
a
l
Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process
Aggregationof the ECAP
Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process
3 2
Events ThatCause Changes inCapital DemandandSupply
Integrated Risk, Return, Capital, and
Value Management
A going-concern
perspective takes
into account for
economic capital
only capital
components that
can be consumed
without creating a
potential
disturbance in the
normal banking
operations.
The Internal Capital Adequacy
Assessment Process (ICAAP) focuses
on Capital management, which ensures
the capital adequacy of the bank, and is
carried out on the bank level in a
dedicated, centralized unit.
The capital management function has
to consider first the regulatory view of
Basel II: the balance-sheet capital (Tier
1, Tier 2, and Tier 3) constitutes the
capital supply side while regulatory
capital for credit risk, market risk, and
operational risk accounts for the capital
demand. Second, the capital
management function should consider
the view of rating agencies, which base
their valuation mostly on Tier 1 capital
on the capital supply side.
Third the capital management function
has to consider simultaneously the
economic view of matching the capital
supply (risk-taking capacity) with the
capital demand (economic capital).
Capital supply is mainly influenced by
planned capital transactions and
expected profits. Capital demand is
mainly driven by business plans and by
risk-profile forecasts in combination
with macro-economic scenarios.
Since the requirements for both
regulatory and economic capital have to
be fulfilled, the bank has to define
possible solutions in case of conflicting
requirements for regulatory and
economic capital. Major differences in
capital supply can occur due to hidden
reserves, goodwill, other intangible
assets, deferred tax assets or liabilities,
provisions
The ICAAP is structured according to
the following:
Board and senior management
oversight
It is the responsibility of the board
and senior management to
oversee the ICAAP by setting well
defined risk management
strategies and guidelines.
Comprehensive risk assessment
A prerequisite for the ICAAP is the
comprehensive assessment of material
risks by measuring economic capital. The
measurement of economic capital
comprises collection of all necessary data
and implementation of appropriate models.
Determination of risk-taking capacity
The basis for capital adequacy is to
compare economic capital with its risk-
taking capacity. Risk-taking capacity is
derived from accounting items after
considering economic adjustments. In
doing so, the bank can differentiate
between creditor-protection and going-
concern perspectives.
Capital adequacy maintenance.
Risk-taking capacity should cover
economic capital at all times. To serve this
purpose, capital adequacy has to be
monitored on a continuous basis. The
capital strategy for the coming years
should be aligned with business planning.
Possible measures to maintain capital
adequacy can affect either capital demand
or capital supply.
Controlling and reporting.
Monitoring the capital planning process
and reporting to the board on its
effectiveness help to ensure that risk
management efforts are implemented
appropriately. A robust controlling and
reporting framework enables a continuous
evaluation of relevant issues and provides
access to the necessary reports for parties
involved in monitoring capital adequacy.
Internal control review
Internal controls provide a foundation for
sound corporate governance. A bank has
to make sure that its risk management
methods, processes, and systems are
adequate in relation to its size and risk
profile. To this end, senior management
must regularly review the capital
framework, ensuring that any
methodological changes, process redesign,
or reprogramming are tested and verified
by a third party, such as the internal or
external auditor.
Principle of ICAAP
Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Product Project Report On Gesh LighterDokument68 SeitenProduct Project Report On Gesh LighterRohit Sevra50% (2)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- OHA AuditDokument307 SeitenOHA AuditHNNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
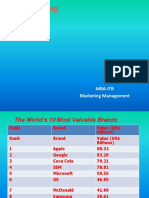
- Branding: Mba-Itb Marketing ManagementDokument44 SeitenBranding: Mba-Itb Marketing ManagementLaurentius OktavianusNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Company Accounting - Powerpoint PresentationDokument29 SeitenCompany Accounting - Powerpoint Presentationtammy_yau3199100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Buying HouseDokument51 SeitenBuying HouseMasterpieceFashions88% (8)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- 2016 05 11 - Southey Capital Distressed and Illiquid PricingDokument8 Seiten2016 05 11 - Southey Capital Distressed and Illiquid PricingSouthey CapitalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- M/S. Lavish Ceramics: The Project Cost 1 Cost of ProjectDokument20 SeitenM/S. Lavish Ceramics: The Project Cost 1 Cost of ProjectSabhaya ChiragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- BPI1Dokument12 SeitenBPI1Russell Stanley Que GeronimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- July 2015 Through August 2015Dokument355 SeitenJuly 2015 Through August 2015Jen SabellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Board of Directors of San Miguel Corp.Dokument5 SeitenBoard of Directors of San Miguel Corp.Ynell Hapin CalolotNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Go Go Go PDFDokument20 SeitenGo Go Go PDFanusyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stock Mock - Backtest Index Strategies2Dokument5 SeitenStock Mock - Backtest Index Strategies2Avinash GaikwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Chief Operating Officer in NYC Resume William HoganDokument3 SeitenChief Operating Officer in NYC Resume William HoganWilliamHoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- TRS Investment Meeting March 2012 AgendaDokument101 SeitenTRS Investment Meeting March 2012 Agendadavidsun1988Noch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- KPIT Technologies 290813Dokument2 SeitenKPIT Technologies 290813darshanmaldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- List of Participants at The World Economic Forum's Annual MeetingDokument75 SeitenList of Participants at The World Economic Forum's Annual MeetingUSA TODAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- CME Fx-Onboarding-Guide PDFDokument4 SeitenCME Fx-Onboarding-Guide PDFChun Zau TohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- Block 1 ECO 02 Unit 1Dokument24 SeitenBlock 1 ECO 02 Unit 1Akhilesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tender Document Set - KSRTC BTC - ThampanoorDokument22 SeitenTender Document Set - KSRTC BTC - ThampanoorTharun SampathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The FloatingDokument22 SeitenAdvantages and Disadvantages of The FloatingFarhana KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grand StrategiesDokument11 SeitenGrand StrategiesManmeet Kaur0% (1)
- Chad E. Hassinger, CFP: Chief Executive OfficerDokument1 SeiteChad E. Hassinger, CFP: Chief Executive OfficerHugo CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smith's Market Cash Sales Accounting System AnalysisDokument1 SeiteSmith's Market Cash Sales Accounting System AnalysisMelvin Jan SujedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- InBev's Acquisition of Anheuser - BuschDokument11 SeitenInBev's Acquisition of Anheuser - BuschЛюся БогачукNoch keine Bewertungen
- EY Report - Digital Deal Economy StudyDokument20 SeitenEY Report - Digital Deal Economy StudyRafaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Placement Memorandum Agriland PDFDokument77 SeitenPlacement Memorandum Agriland PDFsiddharth_parikh4100% (1)
- Lista Participanti SEAPDokument648 SeitenLista Participanti SEAPEusebiu IonescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Namma Kalvi 12th Accountancy Unit 3 Sura English Medium Guide PDFDokument14 SeitenNamma Kalvi 12th Accountancy Unit 3 Sura English Medium Guide PDFAakaash C.K.100% (1)
- Tourism Industry BreakdownDokument4 SeitenTourism Industry BreakdownAira Lonto100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)