Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mnit001 Meter Manual PDF
Hochgeladen von
Sergio Andres Rivera JaramilloOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mnit001 Meter Manual PDF
Hochgeladen von
Sergio Andres Rivera JaramilloCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
FORM 6284 Third Edition 5.
00-1
SECTION 5.00
TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING CHART
The following table is provided to assist the user in
determining the possible causes of unsatisfactory
engine operation, as well as point out the corrective
action that may be undertaken to remedy the problem.
Knowledge of how the engine operates along with the
current readings from the engine instrument panel can
be combined with this information to provide a frame-
work for resolving actual or potential problems.
NOTE: This chart is only provided as a service to our
customers. It should not be viewed as a reflection of
Waukesha Engine's actual experience with this
product. This chart is not all inclusive. Refer to
respective sections in this manual for details.
Table 5.00-1 Troubleshooting Table (Part 1 of 9)
SYMPTOM PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
Engine crankshaft cannot be barred
over.
Load not disengaged from engine. Disengage load.
Engine will crank, but will not start.
Ambient minimum Temperature
10! C (50! F)
ON-OFF switch in OFF position or defective
(if used).
Place switch in the ON position or replace if
defective.
Fuel throttle or manual shutoff control in OFF
position.
Place fuel throttle or manual shutoff control in ON
position.
Safeties tripped. Determine cause, correct, and reset.
Insufficient cranking speed:
a. Low starting air/gas pressure. a. Build up air/gas pressure. 100 125 rpm
required to start engine.
b. Oil temperature too low or viscosity too high. b. Change oil or raise the oil temperature.
Fuel system inoperative:
a. Insufficient fuel supply or fuel pressure. a. Check gas pressure.
Faulty ignition system:
a. No power to CEC Ignition Module. a. Reconnect.
b. Low or no output from CEC Ignition Module. b. Replace CEC Ignition Module as required.
c. Hall-effect pickup disconnected or damaged. c. Reconnect.
d. Incorrect ignition timing. d. Reset the timing.
e. Broken or damaged wiring. e. Repair or replace.
f. Spark plug(s) not firing. f. Check gap/replace as required.
Insufficient or no air intake:
a. Clogged intake air filters.
b. Clogged/dirty intercooler (air side).
NOTE: Bar the engine over by hand to verify that
cylinders are clear. Inspect the intake manifold for
accumulations of oil.
a. Remove and clean.
b. Remove and clean.
TROUBLESHOOTING
5.00-2 FORM 6284 Third Edition
Engine will crank, but will not start.
(cont'd.)
Detonation Sensing Module inoperative or in
shutdown condition (Vee Engines):
a. DSM in shutdown mode. a. Check DSM diagnostic display codes, and
perform appropriate procedures as outlined in
Form 6268 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Detona-
tion Sensing Module Installation, Operation,
And Maintenance Manual. Contact your
Waukesha Engine Distributor for assistance.
b. Wiring from sensors to DSM damaged. b. Repair or replace wiring as required. Refer to
Form 6268 (Version 2.8a) or Form 6286 (Ver-
sion 4 Series) Custom Engine Control Detona-
tion Sensing Module Installation, Operation,
And Maintenance Manual, and rerun AutoCal
program. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
Knock Detection Module inoperative or in shut-
down condition (Inline Engines):
a. KDM in shutdown mode. a. Check KDM diagnostic display codes, and
perform appropriate procedures as outlined in
Form 6285 Custom Engine Control Knock
Detection Module Installation, Operation, And
Maintenance Manual. Contact your Waukesha
Engine Distributor for assistance.
b. Wiring from sensors to KDM damaged. b. Repair or replace wiring as required. Refer to
Form 6285 Custom Engine Control Knock
Detection Module Installation, Operation, And
Maintenance Manual. Contact your Waukesha
Engine Distributor for assistance.
AFM inoperative or in Alarm Condition:
a. Wiring from sensors, Air/Fuel Module or AFM
actuator damaged.
a. Repair or replace wiring as required. Refer to
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
b. AFM in alarm mode. b. Check AFM diagnostic display codes, and per-
form appropriate procedures as outlined in
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
Governor inoperative:
a. Governor set incorrectly. Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
b. Insufficient oil:
Water/sludge in oil passages. Clean or replace governor.
c. Binding control linkage:
Linkage dirty. Clean.
Table 5.00-1 Troubleshooting Table (Continued), (Part 2 of 9)
SYMPTOM PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
TROUBLESHOOTING
FORM 6284 Third Edition 5.00-3
Engine stops suddenly. Safeties tripped. Determine cause, correct, and reset.
Insufficient fuel supply. Check gas pressure.
Low oil pressure causes engine protection control
to shut down engine.
Inspect lubricating oil system and components;
correct cause.
High coolant temperature causes engine protec-
tion control to shut engine down.
Inspect cooling system and components;
correct cause.
High intake manifold temperature. Correct cause.
High oil temperature. Correct cause.
Engine overspeed causes engine protection con-
trol to shut down engine.
Determine and correct cause.
Excessive load causes engine to stall. Determine and correct cause of overload.
Insufficient intake air:
a. Clogged intake air filter(s). a. Remove and clean.
b. Clogged intercooler (air side). b. Remove and clean.
Obstructed exhaust manifold. Locate and remove obstruction.
Seizure of bearings main, connecting rod, piston
pin or camshaft.
Replace bearings clean up or replace crank-
shaft, camshaft or piston pins, as required.
a. Lack of lubrication. a. Check oil system; correct cause.
b. Dirt in oil. b. Check oil filters.
Detonation Sensing Module inoperative or in
Shutdown Condition:
a. Wiring from sensors to DSM damaged. a. Repair or replace wiring as required. Refer to
Form 6268 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Detona-
tion Sensing Module Installation, Operation,
And Maintenance Manual, and rerun AutoCal
program. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
b. DSM in shutdown mode. b. Check DSM diagnostic display codes, and
perform appropriate procedures as outlined in
Form 6268 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Detona-
tion Sensing Module Installation, Operation,
And Maintenance Manual. Contact your
Waukesha Engine Distributor for assistance.
AFM inoperative or in Alarm Condition:
a. Wiring from sensors, Air/Fuel Module or AFM
actuator damaged.
a. Repair or replace wiring as required. Refer to
Form 6263 (Version 2.8a) or Form 6286 (Ver-
sion 4 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
b. AFM in alarm mode. b. Check AFM diagnostic display codes, and per-
form appropriate procedures as outlined in
Form 6263 (Version 2.8a) or Form 6286 (Ver-
sion 4 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
Table 5.00-1 Troubleshooting Table (Continued), (Part 3 of 9)
SYMPTOM PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
TROUBLESHOOTING
5.00-4 FORM 6284 Third Edition
Engine loses power. Insufficient fuel:
a. Low gas pressure. a. Check gas fuel system.
Air intake system malfunction:
a. Dirty intake air filters. a. Remove and clean.
b. Clogged intercooler. b. Remove and clean.
Bar the engine over by hand
to verify that the cylinders
are clear. Inspect the intake manifold for accu-
mulations of oil.
Detonation Sensing Module, sensing detonation
condition in one or more cylinders:
a. Hot or unprocessed gas has gone through
engine that could cause detonation.
a. Determine if hot or unprocessed gas has
gone through engine that could cause detona-
tion. Check DSM diagnostic display codes,
and perform appropriate procedures as out-
lined in Form 6268 (Version 5.3c) or Form
6278 (Version 6 Series) Custom Engine Con-
trol Detonation Sensing Module Installation,
Operation, And Maintenance Manual.
AFM inoperative or in Alarm Condition:
a. Wiring from sensors, Air/Fuel Module or AFM
actuator damaged.
a. Repair or replace wiring as required. Refer to
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
b. AFM in alarm mode. b. Check AFM diagnostic display codes, and per-
form appropriate procedures as outlined in
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
Air leaks in intake system. Find and correct as required.
Turbocharger malfunction or failure:
a. Lack of lubrication. a. Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
Ignition system timing incorrect. Re-time.
Low compression pressure:
a. Misadjusted intake and exhaust valves (if
recently overhauled).
a. Readjust.
Excessive exhaust system backpressure. Correct as required.
Engine will not shut down using nor-
mal stopping procedures.
Defective ON-OFF switch. Shut off fuel supply.
Shut off the gas supply for positive
shutdown of gas engines. Inspect
the intake manifold for accumula-
tions of oil.
Overheated combustion chamber deposits cause
the engine to run on auto ignition.
Allow engine to cool down before attempting to
stop.
Table 5.00-1 Troubleshooting Table (Continued), (Part 4 of 9)
SYMPTOM PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
CAUTION
WARNING
TROUBLESHOOTING
FORM 6284 Third Edition 5.00-5
Engine will not reach rated speed. Engine overloaded. Determine and correct cause.
Insufficient fuel supply. Check fuel supply system.
AFM inoperative or in Alarm condition:
a. Wiring from sensors, Air/Fuel Module or AFM
actuator damaged.
a. Repair or replace wiring as required. Refer to
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
b. AFM in alarm mode. b. Check AFM diagnostic display codes, and per-
form appropriate procedures as outlined in
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
Restricted air intake. Correct cause.
Ignition not properly timed. Re-time.
Tachometer inaccurate. Calibrate or replace tachometer.
Individual cylinders misfire. Prechamber gas admission valve stuck shut. Clean or replace valve.
Engine will not run at maximum power. Engine misfiring:
a. Fuel system setting incorrect. a. Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
AFM inoperative or in Alarm condition:
a. Wiring from sensors, Air/Fuel Module or AFM
actuator damaged.
a. Repair or replace wiring as required. Refer to
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
b. AFM in alarm mode. b. Check AFM diagnostic display codes, and per-
form appropriate procedures as outlined in
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
Engine detonates. Engine overloaded. Determine and correct cause of overload.
Incorrect ignition timing. Reset to specification.
Engine misfiring:
a. Spark plugs misfiring. a. Clean and regap, or replace spark plugs.
Emission levels too high. Advanced ignition timing. Reset to specification.
Air/fuel ratio incorrect. Reset to specification.
AFM inoperative or in Alarm condition:
a. Wiring from sensors, Air/Fuel Module or AFM
actuator damaged.
a. Repair or replace wiring as required. Refer to
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
b. AFM in alarm mode. b. Check AFM diagnostic display codes, and per-
form appropriate procedures as outlined in
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
Engine misfiring:
a. Faulty ignition system. a. Repair or replace components as required.
b. Prechamber fuel system incorrectly set. b. Reset per fuel system specification.
c. Sticking gas admission valve. c. Clean or replace valve.
Table 5.00-1 Troubleshooting Table (Continued), (Part 5 of 9)
SYMPTOM PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
TROUBLESHOOTING
5.00-6 FORM 6284 Third Edition
Low or fluctuating oil pressure.
Shut down engine
immediately.
Insufficient oil. Add oil as required.
Oil pressure gauge inaccurate.
Compare to master gauge. Replace gauge if nec-
essary.
Oil gauge line plugged. Renew gauge line.
Oil filters plugged. Change elements; clean filter.
Oil pressure regulating valve stuck in open posi-
tion.
Clean and polish valve.
Oil dilution.
Change oil and filter elements. Determine and
correct source of dilution.
Oil of low viscosity. Change to higher viscosity oil as recommended.
Oil foaming.
Use oil grade recommended. Check for water
leaks into oil.
Clogged oil inlet screen. Remove and clean screen.
Dirty oil cooler. Clean.
Low gas/air pressure. Insufficient line pressure. Increase line pressure.
High gas/air pressure. Incorrectly adjusted gas regulator. Readjust.
Incorrect spring in gas regulator. Replace spring.
Excessive line pressure. Reduce line pressure.
AFM inoperative or in Alarm Condition:
a. Wiring from sensors, Air/Fuel Module or AFM
actuator damaged.
a. Repair or replace wiring as required. Refer to
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
b. AFM in alarm mode. b. Check AFM diagnostic display codes, and per-
form appropriate procedures as outlined in
Form 6263 (Version 5.3c) or Form 6278 (Ver-
sion 6 Series) Custom Engine Control Air/Fuel
Module. Contact your Waukesha Engine Dis-
tributor for assistance.
High oil pressure.
Misadjusted oil pressure regulating valve.
Refer to VGF Repair and Overhaul Form 6243
(F18/H24) or Form 6264 (L36/P48) to adjust oil
pressure regulating valve.
Lubricating oil of high viscosity. Change to lower viscosity oil as recommended.
Low jacket water temperature.
Gauge inaccurate.
Compare to master gauge; replace gauge if nec-
essary.
High jacket water temperature.
Gauge inaccurate.
Allow engine to cool.
Compare to master gauge; replace gauge if nec-
essary.
Gauge line clogged or valve shut. Replace line, open valve.
Low coolant level. Fill cooling system.
Broken or loose water pump belts. Replace or adjust belts.
Air bound cooling system. Purge air from cooling system.
Engine overloaded. Determine and correct cause.
Leaking pump seals. Repair pump.
Frozen coolant.
Completely thaw cooling system before restarting
engine.
Incorrect ignition timing. Reset ignition timing.
Table 5.00-1 Troubleshooting Table (Continued), (Part 6 of 9)
SYMPTOM PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
CAUTION
CAUTION
TROUBLESHOOTING
FORM 6284 Third Edition 5.00-7
High auxiliary water temperature.
Gauge inaccurate.
Compare to master gauge; replace gauge if nec-
essary.
Clogged gauge line or the gauge line valve is
shut.
Replace line or open valve.
Broken or loose auxiliary water pump belts. Replace or adjust belts.
Clogged heat exchanger or intercooler. Clean heat exchanger/intercooler.
High oil consumption. Oil leaks in oil system. Locate and repair leaks.
Improper viscosity.
Change to a viscosity recommended for operat-
ing temperatures.
Worn piston rings or liners.
Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
Oil contamination. Oil contaminated with water.
NOTE: Change oil.
Oil contaminated with dirt:
a. Oil filter bypass valves opening because ele-
ments are plugged.
a. Replace elements.
b. Oil filter elements punctured. b. Replace elements.
c. Air intake filters punctured. c. Replace air intake filters.
Excessive vibration.
Stop engine at
once; investigate
cause.
Engine misfiring. See Engine detonates. on page 5.00-5 causes.
Foundation bolts:
a. Loose. a. Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
Vibration damper:
a. Loose. a. Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
Crankshaft:
a. Broken. a. Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
b. Main bearing nuts loose. b. Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
c. Crankshaft counterweight loose. c. Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
Loose flywheel.
Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
High oil temperature.
Gauge inaccurate.
Compare to master gauge; replace gauge if nec-
essary.
Engine overloaded. Determine and correct cause.
Insufficient cooling:
a. High auxiliary water temperature. a. See High auxiliary water temperature.
causes.
b. Dirty oil cooler. b. Clean or replace.
c. Broken or loose auxiliary water pump belts. c. Replace or adjust belts.
Dirty jacket water heat exchanger or radiator. Clean or replace.
Low lubricating oil pressure. See Low or fluctuating oil pressure. causes.
Table 5.00-1 Troubleshooting Table (Continued), (Part 7 of 9)
SYMPTOM PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
CAUTION
TROUBLESHOOTING
5.00-8 FORM 6284 Third Edition
Knocking or unusual noises. Low octane fuel. Adjust timing for the fuel used.
Engine overloaded. Determine and correct cause.
Overly advanced ignition timing. Retime.
Detonation Sensing Module, sensing detonation
condition in one or more cylinders:
a. Hot or unprocessed gas has gone through
engine that could cause detonation.
a. Determine if hot or unprocessed gas has
gone through engine that could cause detona-
tion. Check DSM diagnostic display codes,
and perform appropriate procedures as out-
lined in Form 6268 (Version 5.3c) or Form
6278 (Version 6 Series) Custom Engine Con-
trol Detonation Sensing Module Installation,
Operation, And Maintenance Manual.
Knock Detection Module sensing detonation con-
dition in one or more cylinders (Inline Engines):
a. KDM in shutdown mode. a. Check KDM diagnostic display codes, and
perform appropriate procedures as outlined in
Form 6285 Custom Engine Control Knock
Detection Module Installation, Operation, And
Maintenance Manual.
Excessive valve clearance. Adjust to specification.
Loose bearings (failed).
Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
Loose piston pins (failed).
Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
Excessive crankshaft end play.
Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
Misfitted or excessively worn timing gears.
Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
Excessive fuel consumption.
Leaks in fuel system.
Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
Retarded ignition timing. Set timing to specifications.
Engine overloaded. Determine and correct cause.
TURBOCHARGER: Excessive noise
or vibration.
Low oil pressure. Improper bearing lubrication.
Load engine before warm oil is supplied to the
turbocharger.
Contact your Waukesha Engine Distributor for
assistance.
GOVERNOR: Engine hunts or surges. Compensation adjustments incorrect. Adjust needle valve to specification.
Dirty oil in governor. Drain oil, clean governor and refill.
Foamy oil in governor. Drain oil and refill.
Low oil level.
Add oil to correct level on gauge glass. Check for
leaks, especially at drive shaft.
Lost motion in engine linkage. Repair linkage.
Binding in engine linkage. Repair and realign linkage.
Governor worn or not correctly adjusted. Repair and adjust governor.
Engine misfiring.
See Engine misfiring: on page 5.00-5 under
Engine detonates.
Compensating spring incorrectly adjusted. Adjust.
Low oil pressure. Normal operating pressure is
110 120 psi.
Replace governor.
Power piston sticking inside (PSG or SG). Replace governor.
Misadjusted linkage. Adjust.
Fluctuating or unstable fuel gas pressure. Adjust.
Rough drive. Repair or replace.
Table 5.00-1 Troubleshooting Table (Continued), (Part 8 of 9)
SYMPTOM PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
TROUBLESHOOTING
FORM 6284 Third Edition 5.00-9
GOVERNOR: Terminal shaft/engine
linkage jiggles.
Compensating spring adjustment at critical set-
ting.
Change compensating spring pre-compression
approximately 0.005 in. (0.13 mm) either way.
Speed droop (if used) at critical setting.
Increase droop to eliminate critical setting. Load
division will be affected if this is done. Readjust
droop on units affected.
Governor base not bolted down evenly. Loosen bolts, realign and secure.
Load does not divide properly in interconnected
engines.
Speed droop adjustment incorrect:
a. Adjust droop to divide load properly.
b. Increase droop to resist picking up
(or dropping off) load.
c. Reduce droop to increase picking up
(or dropping off) load.
Speed droop shaft vibrating out of position. Increase tension of speed droop friction spring.
Rough engine drive.
a. Check alignment of gears.
b. Check gear backlash.
GOVERNOR: Load does not divide
properly in inter-connected engines.
NOTE: If droop adjustment is not provided, the governor is isochronous only, and cannot be used for
parallel operation. Speed droop is not essential in a DC electrical system. The equivalent of speed
droop in a DC system is obtained by changing the compounding of the generators at the bus between
generators. An under-compounded generator is equivalent to a speed droop governor. Governors
with speed droop adjustment are commonly used for DC service since the droop adjustment may be
used to correct errors or inequalities of generator compounding.
Slippage in hydraulic or electric couplings (if
used).
Adjust coupling.
GOVERNOR: Engine is slow to
respond to speed or load changes. Needle valve adjustment incorrect.
Readjust compensating needle valve. Open fur-
ther only if possible to do so without causing
instability when running without load.
Governor is not sensitive in measuring speed
change.
Repair and adjust governor.
Governor may be intentionally designed to pro-
tect engine from overloading during a load
change.
No field correction.
Pivot valve not centered. It must open control
ports equally in both directions.
Adjust pivot valve.
Low oil pressure in governor. See Low or fluctuating oil pressure.
Engine overloaded. Reduce load.
Restricted fuel supply. Clean fuel supply line and filters.
Load limit knob set to restrict fuel. Open up the load limit.
Lean air/fuel ratio. Adjust carburetor mixture value.
GOVERNOR: Engine will not pick up
rated load.
Butterfly valves will not open far enough. a. Adjust engine-to-governor fuel linkage.
b. Adjust load limiting device.
Restricted fuel supply. Clean fuel supply line and filters.
Voltage regulator (if used) not functioning. Adjust or repair.
Engine misfiring (Spark plugs misfiring). Clean and regap, or replace spark plugs.
Slipping clutch (if used) between engine and
driven load.
Foaming oil or low oil level in hydraulic clutch.
Speed adjustment of the governor is restricted.
a. Check the maximum speed limit adjustment
on dial control governor.
b. Inspect speed adjusting linkage for interfer-
ence on lever control governor.
Table 5.00-1 Troubleshooting Table (Continued), (Part 9 of 9)
SYMPTOM PROBABLE CAUSE REMEDY
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Red wire color circuit diagramDokument1 SeiteRed wire color circuit diagramAnderson Salazar100% (2)
- Parts Manual: TRUCK MODEL: C20-33 (35) L SERIAL NUMBER: P232L-224 & Above 9644 KFDokument165 SeitenParts Manual: TRUCK MODEL: C20-33 (35) L SERIAL NUMBER: P232L-224 & Above 9644 KFpaulo_gallina_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Valve Recession DiscussionDokument36 SeitenValve Recession DiscussionOdlanier José Mendoza100% (1)
- Ignition SystemDokument6 SeitenIgnition SystemNopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro DR Engines July2018Dokument31 SeitenIntro DR Engines July2018Russell DezemeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50cc Scooter ManualDokument0 Seiten50cc Scooter ManualMarcelo FerreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Computational Fluid Dynamics - VersteegDokument267 SeitenAn Introduction To Computational Fluid Dynamics - Versteegkelvinhoh83100% (12)
- Jobsheets Bengine PerformanceDokument256 SeitenJobsheets Bengine PerformanceflavioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crankcase Component Overhaul GuideDokument13 SeitenCrankcase Component Overhaul GuideJavier LeonidasNoch keine Bewertungen
- WH Compressor Frame OverviewDokument43 SeitenWH Compressor Frame OverviewArzyman100% (1)
- Waukesha VHPDokument2 SeitenWaukesha VHPMadhana GopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- SB 09-2916a Reg. MooneyDokument16 SeitenSB 09-2916a Reg. MooneyJavier Leonidas0% (1)
- Af2 Adjustment PDFDokument4 SeitenAf2 Adjustment PDFFaisal NaeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spark Plugs GuideDokument22 SeitenSpark Plugs GuidenachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leroi Om Rotary Screw Manual PDFDokument40 SeitenLeroi Om Rotary Screw Manual PDFHerman Sandy100% (2)
- Altronic EPC-110/120 Air-Fuel Controller Operating ManualDokument55 SeitenAltronic EPC-110/120 Air-Fuel Controller Operating Manualfrancis_mouille_iiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressor Over-Lubrication PresentationDokument38 SeitenCompressor Over-Lubrication Presentation1mmahoneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- L36GL Data Sheet PDFDokument2 SeitenL36GL Data Sheet PDFManuel ValdiviesoNoch keine Bewertungen
- WaukeshaDokument2 SeitenWaukeshacarlos angelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09-2916 Regulador Series Four WaukeshaDokument14 Seiten09-2916 Regulador Series Four WaukeshaMaria Fernanda Bonilla SalasNoch keine Bewertungen
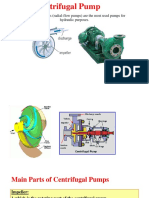
- Centrifugal PumpDokument12 SeitenCentrifugal PumpSanjibani100% (2)
- 6286-2 Web - AFM PDFDokument434 Seiten6286-2 Web - AFM PDFshahzad100% (1)
- Gas Engine Emissions Technology 4th EditionDokument16 SeitenGas Engine Emissions Technology 4th EditionLenin Marcel Fajardo AlmeidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waukesha Gas Engines VHP P9390GLDokument2 SeitenWaukesha Gas Engines VHP P9390GLrohizatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waukesha F11gsi - Valve Clearence - CompressionDokument2 SeitenWaukesha F11gsi - Valve Clearence - Compressionnicol_sg100% (1)
- VOLVO 240 Engines d20 d24 Repairs Part 1Dokument104 SeitenVOLVO 240 Engines d20 d24 Repairs Part 1Myselvf100% (10)
- Ficha Técnica Engine Gas L7042GSI PDFDokument2 SeitenFicha Técnica Engine Gas L7042GSI PDFCamilo Sanchez VanegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crankshaft 2005Dokument42 SeitenCrankshaft 2005Halim Bessouf100% (2)
- Ger 3658d Speedtronic Mark V Gas Turbine Control System PDFDokument19 SeitenGer 3658d Speedtronic Mark V Gas Turbine Control System PDFyos100% (1)
- 06 - Major Alarm& Safety of 50DF With UNIC (DNV)Dokument16 Seiten06 - Major Alarm& Safety of 50DF With UNIC (DNV)dassi99100% (1)
- 0416 VHP Afr2 UpgradeDokument1 Seite0416 VHP Afr2 Upgradenicol_sgNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12V275GL 1Dokument2 Seiten12V275GL 1Zailand R100% (1)
- Mod Bus Poll ManualDokument32 SeitenMod Bus Poll ManualSergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mod Bus Poll ManualDokument32 SeitenMod Bus Poll ManualSergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service BUlletin 300036KDokument4 SeitenService BUlletin 300036KMuhammad ShadabNoch keine Bewertungen
- MH62 - 07H1622-07H1628 GEA - ManualDokument3 SeitenMH62 - 07H1622-07H1628 GEA - ManualSAID GUERROUTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quad Lander 600: Service ManualDokument247 SeitenQuad Lander 600: Service ManualAlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Formulas: Cylinder Swept Volume (VDokument7 SeitenEngine Formulas: Cylinder Swept Volume (VDhanraj PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT6007 New Generation and Hybrid Vehicles IntroductionDokument93 SeitenAT6007 New Generation and Hybrid Vehicles IntroductionpavanraneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens Typhoon V1 CH01 PDFDokument48 SeitenSiemens Typhoon V1 CH01 PDFSebastian CubileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ariel compressor instrumentation requirementsDokument8 SeitenAriel compressor instrumentation requirementsFaisal NaeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop 2011 - 03121936Dokument551 SeitenWorkshop 2011 - 03121936FR100% (2)
- Solar 5.2MVADokument15 SeitenSolar 5.2MVAsohaila7Noch keine Bewertungen
- I8 Tech Manual PDFDokument100 SeitenI8 Tech Manual PDFSalisburNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To MATLAB and Simulink A Project ApproachDokument404 SeitenIntroduction To MATLAB and Simulink A Project Approachpoopoopho86% (7)
- GTG 1699iec Solart60 60hzDokument10 SeitenGTG 1699iec Solart60 60hzKhaldoon Alnashi100% (1)
- Stx-Engine 121074 Voogvr-sYpl25EDokument252 SeitenStx-Engine 121074 Voogvr-sYpl25EGyeTaeBae100% (1)
- Product Catalog 6-25-20Dokument62 SeitenProduct Catalog 6-25-20ahmed hafezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scope of Supply Titan130Dokument32 SeitenScope of Supply Titan130danferreiro8318Noch keine Bewertungen
- WaukeshaDokument68 SeitenWaukeshaGilberto Prez RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- NIC 13.20 Rev.01Dokument15 SeitenNIC 13.20 Rev.01Mahmoud Ahmed100% (1)
- L7044gsi 7045 0710Dokument2 SeitenL7044gsi 7045 0710Martin Alejandro NievaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WAUKESHA Manuale PDFDokument106 SeitenWAUKESHA Manuale PDFL̶e̶o̶v̶a̶r̶d̶o̶ A̶l̶v̶a̶r̶e̶z̶Noch keine Bewertungen
- GTG 1636FPC PWFT4 50HzDokument24 SeitenGTG 1636FPC PWFT4 50HzEmanuel CondeNoch keine Bewertungen
- QSK60 G6 PDFDokument2 SeitenQSK60 G6 PDFShahzad Ali100% (2)
- MTU 20V4000 L64 Technical Data SheetDokument2 SeitenMTU 20V4000 L64 Technical Data SheetB-ENERGY INVESTMENTNoch keine Bewertungen
- February 2003 Subject: Troubleshooting Hydraulic Ratchet ProblemsDokument4 SeitenFebruary 2003 Subject: Troubleshooting Hydraulic Ratchet ProblemsKarim MuhammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constant Settable Droop Design Standard of GEDokument4 SeitenConstant Settable Droop Design Standard of GEPraveen PeethambaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Mto 1203 - 5,6 MWDokument98 SeitenManual Mto 1203 - 5,6 MWAgustin BaratcabalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3.8 Liquid FuelDokument16 Seiten2.3.8 Liquid FuelSarah CohenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 SpiraxialDokument1 Seite2012 SpiraxialNistha ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- G3606 - Lehw0039-02 P1Dokument4 SeitenG3606 - Lehw0039-02 P1Martin KratkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooper Texas Repuestos Joy Superior Parts ListDokument2 SeitenCooper Texas Repuestos Joy Superior Parts Listcarlos felipe botello paezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 2713bDokument7 Seiten17 2713bnricquartNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.VGF L36GSI WKI TimingCuvre B PDFDokument1 Seite4.VGF L36GSI WKI TimingCuvre B PDFfoobar2016Noch keine Bewertungen
- Caterpillar RC1000 Containerized Diesel Generator SetDokument4 SeitenCaterpillar RC1000 Containerized Diesel Generator SetMacAllister MachineryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rod ReversalDokument21 SeitenRod ReversalandresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Centaur 40 DSDokument2 SeitenSolar Centaur 40 DSabuahnfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Engine For 1990sDokument165 SeitenDiesel Engine For 1990schandru_82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Special Edition Tensioner JuneDokument3 SeitenSpecial Edition Tensioner JuneDjebali MouradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altronic DD20 Annunciator and TachmotersDokument31 SeitenAltronic DD20 Annunciator and TachmotersVladimirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Preventing Torsional Vibration Problems in Reciprocating MachineryDokument48 SeitenGuidelines For Preventing Torsional Vibration Problems in Reciprocating MachineryFabbrox100% (2)
- Equipment Definition: Component LiteratureDokument5 SeitenEquipment Definition: Component LiteratureAbbas AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Superior 2406GDokument79 SeitenSuperior 2406GDavid Rene Martinez100% (1)
- DDDokument3 SeitenDDAnkush Sehgal100% (1)
- (REHS0371) Installation and Initial Start Up Procedures For G3300 and G3400 EnginesDokument16 Seiten(REHS0371) Installation and Initial Start Up Procedures For G3300 and G3400 Enginesvictor.cipriani100% (1)
- 6284 5 00 PDFDokument9 Seiten6284 5 00 PDFnpsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 201-09rev Ajuste Actuador Turbo S-60 EPA-04Dokument6 Seiten201-09rev Ajuste Actuador Turbo S-60 EPA-04Angel Dlsg100% (1)
- Manual Luv Motor C22neDokument0 SeitenManual Luv Motor C22neEfrain ContrerasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ti50a01a20 01en PDFDokument164 SeitenTi50a01a20 01en PDFSergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ti50a01a20 01en PDFDokument164 SeitenTi50a01a20 01en PDFSergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODBUS2Dokument31 SeitenMODBUS2Sergio Andres Rivera Jaramillo100% (3)
- Ti50a01a20 01en PDFDokument164 SeitenTi50a01a20 01en PDFSergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combinacione Validas de TecladoDokument4 SeitenCombinacione Validas de TecladoSergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00 02 0179Dokument4 Seiten00 02 0179Sergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units of Measurement ISADokument26 SeitenUnits of Measurement ISAlova7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Type D PDFDokument12 SeitenType D PDFSergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- DocLib - 1170 - Groth 3000 Series Bulletin 700-710Dokument12 SeitenDocLib - 1170 - Groth 3000 Series Bulletin 700-710Sergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type Ez PDFDokument28 SeitenType Ez PDFSergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Analyzer CameronDokument48 SeitenFlow Analyzer CameronDidi KurniadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nunez2007 PDFDokument6 SeitenNunez2007 PDFCaterine Feria RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mvi69 MCM User ManualDokument167 SeitenMvi69 MCM User Manualms_eng_2011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Study On Internal Flow Field of The Three-Phase Separator With Different Entrance ComponentsDokument5 SeitenStudy On Internal Flow Field of The Three-Phase Separator With Different Entrance ComponentsSergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- XR2206Dokument16 SeitenXR2206Himma FirdausNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2N3904 NpntrnsDokument2 Seiten2N3904 NpntrnsSergio Andres Rivera JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2N2646Dokument1 Seite2N2646Anonymous XM3KoTUTgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Specific Heat Ratio and Error Analysis For EngineDokument8 SeitenDetermination of Specific Heat Ratio and Error Analysis For EngineunnotedNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMAP BR 201410-00 ZX470LC-5G Indonesia PDFDokument2 SeitenHMAP BR 201410-00 ZX470LC-5G Indonesia PDFIndra PurnamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clem RPP Final Draft 2Dokument9 SeitenClem RPP Final Draft 2api-665779560Noch keine Bewertungen
- Roll Out of SCR On FilterDokument18 SeitenRoll Out of SCR On FilterAditi Das100% (1)
- W245 Wiring Diagram For Common Rail Diesel Injection (CDI) Control Unit FileaDokument3 SeitenW245 Wiring Diagram For Common Rail Diesel Injection (CDI) Control Unit Fileakabuye NicholasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 VHP - Packaging - Guide - 6 30 v4Dokument222 Seiten3 VHP - Packaging - Guide - 6 30 v4Alfred Lam100% (1)
- Fiche TechniqueDokument3 SeitenFiche Techniquenacer zidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zetec Turbo How To Full InstructionsDokument17 SeitenZetec Turbo How To Full Instructionsluivilla100% (1)
- Mahindra Alfa Champion Pikup, Passenger, CNG Version 3 MarchDokument84 SeitenMahindra Alfa Champion Pikup, Passenger, CNG Version 3 MarchData TécnicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 4 Types of Ignition System and How They Work: Driving TipsDokument63 SeitenThe 4 Types of Ignition System and How They Work: Driving TipsJoyce BamwendaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bar's Head Gasket SealerDokument2 SeitenBar's Head Gasket SealerMatt CrummittNoch keine Bewertungen
- G32D DTCDokument59 SeitenG32D DTCPower NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 310K 310SK 410K 310SKTMC 410KTMC T304355Dokument2 Seiten310K 310SK 410K 310SKTMC 410KTMC T304355Denis HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DF350A Product Information en WEBDokument44 SeitenDF350A Product Information en WEBPETERNoch keine Bewertungen