Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
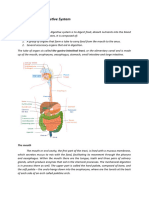
4.1 Digestion
Hochgeladen von
rashmi_harryOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
4.1 Digestion
Hochgeladen von
rashmi_harryCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
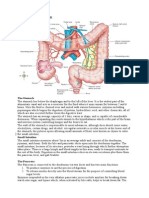
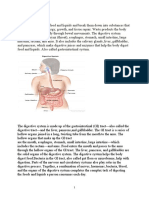
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
D
R
A
F
T
Overview
Def n
Parts: Top to bottom
Diagram everything !the easy way"
Hormones & Enzymes
Def n
the physical and/or chemical breakdown of food
physical/mechanical ! rending
chemical ! hydrolytic
foods "polymer#
into small molecules "monomer# for absorption
a simplied...
Physical digestion
involves physically breaking the food into smaller
pieces without chemically changing it into di#erent
molecules
which increases the exposed SA for chemical
digestion
e.g.,
Mouth $ teeth !chew, masticate"
Stomach $ muscle, rugal folds/ridges !churn"
Liver $ bile !emulsies lipids"
Lipid + Bile
increased
SA...
droplet droplets
Lipid
Chemical digestion
the breaking down of the large molecules
!polymers" into smaller soluble molecules
!monomers" for easy absorption
via hydrolysis
Lipid + water glycerol + fatty acids
lipase
!enzyme"
THE PARTS
Top to Bottom
Teeth
physical digestion
Mouth
incisors
canines
premolars
molars
carnivore
herbivore
omnivore
$ cut
$ hold, tear
$ grind
$ grind
+
%
%
Carnivore
Herbivore
Omnivore
incisors
canines
premolars
molars
Saliva
mostly water and mucus
lubricant
rich in salivary amylase
Amylose + water Maltose
Amylase
!enzyme"
"Starch# "disaccharide#
Swallowing: Steps
1. Bolus !chewed food ball" contacts the pharynx
!back of the throat" and stimulates an autonomic
!involuntary" gulp response:
bolus
pharynx
palate
trachea
$ind pipe
larynx
%oice box
esophagus
!sophagus"
food pipe
epiglottis
nasal cavity
2. The palate seals o" the nasal cavity,
preventing food from entering it.
3. This response stops breathing and the
epiglottis seals o" the trachea,
4. the esophageal sphincter relaxes...
epiglottis
closing over the glottis
step$by$step
Movement
gravity fed
via Peristalsis
wave$like, rhythmical
contractions of circular,
smooth !involuntary" muscle
stomach, small and large
intestines too...
Esophagus
Stomach
esophagus
cardiac
sphincter
pyloric
sphincter
small intestine
stomach
rugae
pH 1$3
Sphincters
Cardiac Sphincter
limits the back ow of gastric juices up the
esophagus
failure: acid reux !heart burn"
Sphincters
Pyloric Sphincter
limits the ow of gastric juices !pH 1" into the small
intestine !pH 6$6.5, duodenu&"
which would normally denature
the intestinal juices !critical for
digestion"
Source: gastric pits of the cardia, fundus, & pylorus
fundus
cardia
pylorus
Gastric Juices
Goblet cells
pits
body
source: Parietal cells !w/in gastric pits"
Fcn:
breaks up connective tissues...
increasing SA for enzyme !e.g., pepsin" activity
kills surface bacteria
reacts with pepsinogen...
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
Gastric Juices
pH 1$3
source: Chief cells !w/in gastric pits"
pepsin precursor
pepsinogen + HCl ! pepsin
Pepsinogen
Gastric Juices
"protein# "enzyme#
protein + water a.a strands
Pepsin (protease)
Gastric Juices
"polypeptide 'agments#
a.a. a.a.
"peptide 'agments#
# a.a.
pepsi(
source: Goblet cells !w/in the gastric pits"
protects stomach lining
from autodigestion
from abrasion
lubricant for food passage
Mucus (aka Mucin)
failure: ulcer
Common causes:
bacterial !Helicobacter pylori" infection
!: antibiotic regime
excessive NSAIDs use, e.g., aspirin, ibuprofen,
naproxen
Mucus
Mucus is also found in the:
salivary glands, esophagus, small intestine, colon
duodenum: Brunners gland $ alkaline mucus to
neutralize acid chyme from the stomach
respiratory tract: bronchi, nose...
reproductive tract: cervix, cowpers gland...
Mucus
Chyme
semi$uid, partially digested mass that exits the
stomach
pH 2...
in three parts
1. Duodenum ! twelve ngers
~ 30cm, pH 6$6.5
site of digestion
produces and receives numerous digestive
enzymes and hormones, and bile
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Small Intestines
2. & 3. Jejunum & Ileum
~ 6m, pH 7$8
site of absorption
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Jejunum & Ileum
increase SA for absorption...
villi
microvilli
!brush border"
folds
Increasing SA
villi
folds
Villi
capillaries
lacteals
blood
lymph
microvilli
!brush border cells"
glycerol &
fatty acids
glucose &
a.a.
Carbohydrates
as monosaccharides, e.g., glucose
via capillaries ! hepatic portal vein ! liver
excess glucose is stored as glycogen & insuli(
and released as needed to maintain homeostasis
!4$6 mmol/L" & glucago(
a diet high in processed carbohydrates, i.e., with a
glycemic index !GI" > 70 may lead to
type II diabetes !insulin resistance"
heart disease !excess glycogen forms triglycerides"
Proteins
as a.a.
via capillaries ! hepatic portal vein ! liver
liver:
a.a. ! plasma !blood" proteins
e.g., albumin, prothrombin, brinogen...
deamination of proteins ! a.a. ! amino group !
ammonia NH3 !v. toxic"
is converted by the liver to urea !less toxic" for
excretion via the kidneys
NH3 + CO2 ! urea !excreted w/ urine"
Bu"er:
NH3 + H
+
! NH4
+
!ammonium ion"
Lipids
as glycerol !monoglycerides" and free fatty acids
via lacteals !lymph" ! to the body... ! subclavian vein
! superior vena cava ! heart...
to muscle and adipose tissues that take up the
triglycerides for storage !and energy use"
and back to the liver for:
cholesterol synthesis !VLDL ! LDL, HDL"
lipid synthesis !e.g., triglycerides"
for storage !and energy use"
triglycerides
fatty acids monoglycerides
triglycerides
proteins +
phospholipids +
cholesterol coating
chylomicrons
"lipoprotein#
lacteal
simplied...
microvi)i
"mice)es#
Ileum
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Duodenum
Jejunum
Colon
Pancreas
Liver
lymph
blood
Chylomicron
muscle, adipose
remnant CM
blood
VLDL
bil*
lipas*
LDL
HDL
&
Ileum
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Duodenum
Jejunum
Colon
Pancreas
Liver
lymph
blood
Chylomicron
muscle, adipose
remnant CM
blood
VLDL
bil*
lipas*
LDL
HDL
&
HDL
High Density Lipoprotein
source: Liver and small intestine
travels around the body picking up
excess cholesterol
LDL
Low Density
Lipoprotein
delivers fat
!triglyceride" and
cholesterol to
body
before returning
to the liver
VLDL
Very Low Density Lipoprotein.
delivers fat !triglyceride" and cholesterol to
body
once its done,VLDL goes back to the liver
and the remainder gets made into LDL
to tissues
But if too much,
or damaged...
plaque
build up
LDL
HDL
In an artery...
= atheroma
HDL scrubs
the excess...
returning
excess to the
liver or
to LDL and
VLDL
Large Intestine
aka colon, bowel
~1.5m, pH 7$5.5
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
ascending
appendix
sma) intestin*
cecum
rectum
transverse
descending
sigmoid
anus
Fcn:
Water reabsorption
Excretion of excess:
Iron salts
Calcium salt
Large Intestin*
Site of E. coli
generally mutualistic !benecial" symbiont that
inhibits colonization by harmful bacteria
synthesizes vitamins, esp. vit. K, and B vitamins
!e.g., folic acid"
produce a.a, and other growth factors
Large Intestin*
functions to compact the undigested wastes that is
left over from digestion for easier elimination/
defecation
Large Intestin*
SUMMARY: THE PARTS
salivary glands
esophagus
stomach
pancreas
gall bladder
small intestine large intestine
rectum
anus
liver
appendix
pancreas
cecum
epiglottis
mouth...
liver
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
File:Stomach_colon_rectum_diagram.svg
+ Plus...
mouth
salivary glands
esophagus
stomach
cardiac sphincter
pyloric sphincter
pancreas
gall bladder
liver
small intestine
!DJ &I"
large intestine
hepatic portal vein
hepatic vein
rectum
anus
i
n
f
e
r
i
o
r
v
e
n
a
c
a
v
a
HORMONES
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
bolus passes thru the
cardiac sphincter
stimulates gastrin
which stimulates
HCl production
and increases
stomach motility
!churning"
Gastrin
stomach
Gastrin
duodenu&
esophagus
acid!rich chyme
stimulates secretin
which stimulates the
release of sodium
bicarbonate !bu#er"
and...
Secretin
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Secretin
pancreas
duodenum
"sma) intestine#
Secreti!
bil"
stimulates the release of
alkaline bile from the
gall bladder
counteracting any
excess stomach acid
before it enters the
ileum
Secretin
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
gall bladder
duodenum
"sma) intestine#
liver
bile duc+
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
chole = bile, cyst = sac,
kinin = movement
lipid$rich and protein$rich
chyme
stimulates gall bladder to
release bile !emulsier"
stimulates pancreas to
release digestive enzymes
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
CCK
bil"
Bile: Emulsication
source: liver
stored in the gall bladder
a surfactant, increases SA for enzyme !lipase"
activity
Fat Fat droplets
bile incr.
SA
"
#
$
together inhibit peristalsis
and HCl production
slowing digestion
CCK & Secretin
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Insulin & Glucagon
antagonistic hormones
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Homeostatic:
4$6 mmol/L
Low blood
glucose
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
High blood
glucose
Insulin
lowers blood glucose
converts and stores
glucose as glycogen
Glucagon
raises blood glucose
converts stored
glycogen to glucose
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
body cells
!esp. muscle"
LIVER
A quick overview of key functions
Liver Functions
Bile synthesis
a surfactant, emulsier of lipids
alkaline, neutralizes gastric acids in the small
intestine
excretion of bilirubin, biliverdin !RBC pigment"
Quick Review...
Y
X
Z
W
22. What is the structure labelled W?
A. liver
B. pancreas
C. appendix
D. duodenum
23. Malfunctioning of which structure would result in higher than normal levels of glucose
in the blood?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
________________________________________________
24. Which digestive structure has the greatest influence on blood volume?
A. colon
B. stomach
C. pancreas
D. small intestine
Protein synthesis
plasma %blood& proteins:
albumin $ bu#er, osmotic regulator
prothrombin $ blood clotting
brinogen $ blood clotting
...
Quick Review...
Lipid synthesis
cholesterols !HDL, LDL..."
triglycerides
Quick Review...
Glucose Homeostasis
glucose ! glycogen %insuli!&
glycogenesis
glycogen ! glucose %glucago!&
gluconeogenesis !glucose from other sources..."
site of insulin breakdown
Quick Review...
Storage
iron, copper
vitamins !A, B, D..."
glycogen
Quick Review...
Deamination
breakdown of excess proteins ! formation of
ammonia
Quick Review...
Detoxication
ammonia ! urea !excretory"
breaks down insulin and other hormones
breaks down hemoglobin ! bile
general detoxication of toxic substances
Quick Review...
ENZYMES
S
E
L
E
C
T
Source Enzyme Substrate
Digestion
Product
Salivary
glands
salivary
amylase
amylose
!starch"
maltose
Stomach
pepsin
"protease#
protein
a.a. strands
"peptide 'agments#
pH 7
pH 1
Source Enzyme Substrate
Digestion
Product
Duodenum
!small
intestine"
peptidase peptides a.a.
Duodenum
!small
intestine"
nuclease
nucleic acids
"DNA, RNA#
nucleotides
Duodenum
!small
intestine"
maltase
"disaccharidase#
maltose
"disaccharide#
glucose
"monosaccharide#
Duodenum
!small
intestine"
sucrase sucrose
glucose +
'uctos*
Duodenum
!small
intestine"
lactase lactose
glucose +
galactos* pH 8
Source Enzyme Substrate
Digestion
Product
Pancreas
"these enzymes
operate w/in th*
sma) intestine#
pancreatic
amylase
amylose
maltose
Pancreas
"these enzymes
operate w/in th*
sma) intestine#
trypsin
"protease#
protein a.a. strands
Pancreas
"these enzymes
operate w/in th*
sma) intestine# nuclease nucleic acids nucleotides
Pancreas
"these enzymes
operate w/in th*
sma) intestine#
lipase lipids
glycerol &
fatty acids
pH 8
nucleotides Nucleic Acids
Polysaccharides
Proteins
Lipids
salivary amylase $ salivary glands "pH 7#
pancreatic amylase $ pancreas "pH 8#
maltose
maltase $ small intestine
glucose
peptides
glycerol & fatty acids
lipase $ pancreas
pepsin $ stomach "pH 1#
trypsin $ pancreas "pH 8#
peptidase $ small intestine
a.a.
nucleosides +
phosphate
sugar +
base
nuclease $ pancreas
nuclease $ intestinal
nucleosidas* nucleotidas*
"monoglycerides & 'ee fatty acids#
NEXT THE
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Liver Cure: Natural Solutions for Liver Health to Target Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease, Autoimmune Diseases, Diabetes, Inflammation, Stress & Fatigue, Skin Conditions, and Many MoreVon EverandThe Liver Cure: Natural Solutions for Liver Health to Target Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease, Autoimmune Diseases, Diabetes, Inflammation, Stress & Fatigue, Skin Conditions, and Many MoreBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Master HerbalistDokument91 SeitenMaster HerbalistVázsonyi Júlia50% (2)
- Biology Revision Notes Edexcel iGCSEDokument22 SeitenBiology Revision Notes Edexcel iGCSEJoshua Jones100% (2)
- Liver, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandLiver, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Stratigraphy MCQs With AnswerDokument10 SeitenStratigraphy MCQs With Answerkumar Harsh67% (3)
- Gastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewDokument117 SeitenGastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewFatima Syed100% (3)
- 10 Acids and AlkalisDokument5 Seiten10 Acids and Alkalisrashmi_harry100% (1)
- LTE 3GPP Band13 Test Entrance CriteriaDokument130 SeitenLTE 3GPP Band13 Test Entrance CriteriaBuchi Reddy0% (1)
- 8 States of MatterDokument4 Seiten8 States of Matterrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- FF0221 01 Free Corporate Slides For Powerpoint 16x9Dokument14 SeitenFF0221 01 Free Corporate Slides For Powerpoint 16x9KevinChicoReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete ON MALDIVESDokument55 SeitenConcrete ON MALDIVESKãrthìçk JkrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Catalog EnglishDokument32 SeitenProduct Catalog Englishrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutting Room Agility and ExcellenceDokument8 SeitenCutting Room Agility and Excellenceperro perezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brenda Patton Guided Reflection QuestionsDokument3 SeitenBrenda Patton Guided Reflection QuestionsCameron JanzenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil ExperimentsDokument32 SeitenSoil Experimentsrashmi_harry100% (1)
- CirrhosisDokument29 SeitenCirrhosisHarshika KDGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Five Stages of Human Nutrition: Textbook Diagram: Human Digestive SystemDokument6 SeitenFive Stages of Human Nutrition: Textbook Diagram: Human Digestive SystemangelazengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q4 Week 3 Human Digestive System - PPTX 4thDokument47 SeitenQ4 Week 3 Human Digestive System - PPTX 4thdenveralbarico143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemically Digested To Small Molecules That AreDokument14 SeitenChemically Digested To Small Molecules That AreVarun WadhwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive SystemDokument69 SeitenDigestive SystemDennis ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive SystemDokument9 SeitenDigestive SystemJhomar B, Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Git Lec 3,4Dokument14 SeitenGit Lec 3,4Kim Sa-buNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intestine CleanseDokument12 SeitenIntestine CleansemmyemailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diit Penyakit Hati & Kantung EmpeduDokument36 SeitenDiit Penyakit Hati & Kantung EmpeduFitri RohmaniyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSCI 100 HSCI 100: Human Biology Human Biology Human Biology Human BiologyDokument27 SeitenHSCI 100 HSCI 100: Human Biology Human Biology Human Biology Human BiologyRosa ChoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universidad Colegio Mayor de Cundinamarca Bacteriology and Clinical LaboratoryDokument6 SeitenUniversidad Colegio Mayor de Cundinamarca Bacteriology and Clinical LaboratoryCamil SolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Notes: Digestion (IB HL 6.1)Dokument6 SeitenBio Notes: Digestion (IB HL 6.1)BekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System - Lecture IIDokument6 SeitenDigestive System - Lecture IISaru BashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter II - Digestive System: StomachDokument4 SeitenChapter II - Digestive System: StomachIndranil SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stomach Cells and Stomach DiseasesDokument33 SeitenStomach Cells and Stomach DiseasesAgustin GarzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Digestive SystemDokument14 SeitenThe Digestive SystemScribd UserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem MidtermsDokument16 SeitenBiochem Midtermsnorma BernardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinDokument64 SeitenThe Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinSayhidoen CepexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of CHOLELITHIASISDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of CHOLELITHIASISLarisse de LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System Part 2Dokument56 SeitenDigestive System Part 2Raunak TimilsinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Humandigestionteacher 110323090218 Phpapp01Dokument45 SeitenHumandigestionteacher 110323090218 Phpapp01Lyana AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive GlandDokument22 SeitenDigestive GlandMalinus TorquatusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Digestive SystemDokument48 SeitenHuman Digestive SystemSharifah NurainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System HandoutDokument7 SeitenDigestive System Handouttheodore_estradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DigestDokument84 SeitenDigestBella FebrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio T4 DLP KSSM Chapter 9Dokument67 SeitenBio T4 DLP KSSM Chapter 9fadilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level MCQ Test On Digestive SystemDokument2 SeitenO Level MCQ Test On Digestive SystemKS CoachingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stomach Assignment (1) - 1Dokument22 SeitenStomach Assignment (1) - 1Irfan UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion ReviewDokument71 SeitenDigestion ReviewParasakthi MNoch keine Bewertungen
- "The Digestive System of The Body": Rizal Technological University Boni Avenue, MandaluyongDokument5 Seiten"The Digestive System of The Body": Rizal Technological University Boni Avenue, MandaluyongMark TumaliuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System ReviewDokument2 SeitenDigestive System ReviewSherriena LeangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System ScriptDokument4 SeitenDigestive System ScriptNEPERESM TALCEY BORCESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Git Lec 3Dokument33 SeitenGit Lec 3Kim Sa-buNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small IntestineDokument9 SeitenSmall Intestinegetsukhdev1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Human Digestion1Dokument23 SeitenHuman Digestion1joshua.brussell100% (2)
- Rectal Carcinoma.rDokument4 SeitenRectal Carcinoma.rRaf Kevin GelacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Peptic DisordersDokument72 SeitenAcid Peptic DisordersAteeq ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secretion of Bile and The Role of Bile Acids in DigestionDokument8 SeitenSecretion of Bile and The Role of Bile Acids in DigestionMarianne Kristelle NonanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Assessment: Head To Toe AssessmentDokument4 SeitenPhysical Assessment: Head To Toe AssessmentJerrilyn FlorentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal SystemDokument92 SeitenGastrointestinal SystemdhafaarifanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive SystemDokument17 SeitenDigestive SystemHana Sherif ElelamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDokument9 SeitenAnatomy & Physiologyrachael80% (5)
- Taught To Nursing Students of RmuDokument42 SeitenTaught To Nursing Students of RmumunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-The Digestive SystemDokument6 Seiten1-The Digestive SystemEma FröhlichováNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document 70Dokument9 SeitenDocument 70Malik Ghazi KhedirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomedic Ii System Gastroentero Hepathology: Dep. of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin UniversityDokument56 SeitenBiomedic Ii System Gastroentero Hepathology: Dep. of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin UniversityGd PadmawijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.1 - DigestionDokument8 Seiten6.1 - DigestionPraveen KhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 Study GuideDokument5 SeitenUnit 7 Study GuideSierra MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geb203 AssignmentDokument11 SeitenGeb203 AssignmentAysha Siddika MimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion: Proteins Fats CarbohydratesDokument42 SeitenDigestion: Proteins Fats CarbohydratesVal Kay HeikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core 9Dokument25 SeitenCore 9snehashreemohanty39Noch keine Bewertungen
- Human Body SystemDokument32 SeitenHuman Body SystemMehedi MahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOCHEM DigestionDokument53 SeitenBIOCHEM DigestionAngelika Perez CunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antacids Are Medicines That Neutralize Stomach AcidDokument15 SeitenAntacids Are Medicines That Neutralize Stomach Acidrishabhrawat0% (1)
- Digestive GlandsDokument17 SeitenDigestive GlandsPrazwal RegmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigating Effect of Concentration On The Activity of TrypsinDokument4 SeitenInvestigating Effect of Concentration On The Activity of Trypsinrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidance Notes: in General You Should Be Able ToDokument3 SeitenGuidance Notes: in General You Should Be Able Torashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write-Up Rubric ChecklistDokument1 SeiteWrite-Up Rubric Checklistrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISC Specimen 2015 Biology Paper 2Dokument5 SeitenISC Specimen 2015 Biology Paper 2rashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1: The Microscope (10 Points) : Exercise 1.1: Microscope Structure and FunctionDokument12 SeitenLab 1: The Microscope (10 Points) : Exercise 1.1: Microscope Structure and Functionrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Microscope: Summary of ExerciseDokument18 SeitenThe Microscope: Summary of Exerciserashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Record AS/A Level Biology Candidate NameDokument2 SeitenStudent Record AS/A Level Biology Candidate Namerashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes: The Spit Lab: Teacher VersionDokument9 SeitenEnzymes: The Spit Lab: Teacher Versionrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- x4 Objective x10 Objective x40 Objective x100 ObjectiveDokument1 Seitex4 Objective x10 Objective x40 Objective x100 Objectiverashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macromolecules LabDokument21 SeitenMacromolecules Labrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Tests: A. Benedict's Test For Reducing SugarsDokument3 SeitenFood Tests: A. Benedict's Test For Reducing Sugarsrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variables WorksheetDokument2 SeitenVariables Worksheetrashmi_harry0% (2)
- Practical Support 9: Size and ScaleDokument3 SeitenPractical Support 9: Size and Scalerashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigating The Presence of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats in Different FoodsDokument4 SeitenInvestigating The Presence of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats in Different Foodsrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio NotesDokument71 SeitenBio Notesrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nosepiece, Which Allow The Selection of Objectives of Different Magnifications. TheseDokument8 SeitenNosepiece, Which Allow The Selection of Objectives of Different Magnifications. Theserashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Properties of MatterDokument16 Seiten9 Properties of Matterrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Lab ReportDokument17 SeitenBiology Lab Reportrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Resp1 PaxsonDokument9 SeitenCell Resp1 Paxsonrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igcse Methodist High School Class Viii D Unit Test 3 Practical Chemistry (10) BIOLOGYDokument3 SeitenIgcse Methodist High School Class Viii D Unit Test 3 Practical Chemistry (10) BIOLOGYrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Design Calculations For Block Found. For Vib. Equip.Dokument17 SeitenSample Design Calculations For Block Found. For Vib. Equip.Adam Michael GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- AN-PFC-TDA 4863-3 Calculation-Tool For PFC-Preconverter Using TDA 4863Dokument9 SeitenAN-PFC-TDA 4863-3 Calculation-Tool For PFC-Preconverter Using TDA 4863NaciConSolNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNDP NP Dhangadhi SWM TOR FinalDokument4 SeitenUNDP NP Dhangadhi SWM TOR FinalNirmal K.c.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ashok Leyland Project ReportDokument40 SeitenAshok Leyland Project ReportGovind kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-3 DC Machines IMP QuestionsDokument30 SeitenUnit-3 DC Machines IMP Questionskrishna Sai Atla VenkataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection in SystemsDokument1 SeiteReflection in SystemsGeraldine PadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SW Chapter 21 KeyDokument9 SeitenSW Chapter 21 KeykylevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State Controller of Drives - ExperimentDokument37 SeitenSolid State Controller of Drives - ExperimentRakesh Singh LodhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eoq PDFDokument10 SeitenEoq PDFविनय कुमार शर्माNoch keine Bewertungen
- Travelsinvarious03clar BWDokument522 SeitenTravelsinvarious03clar BWSima Sorin MihailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eureka Forbes ReportDokument75 SeitenEureka Forbes ReportUjjval Jain0% (1)
- Ohms LawDokument16 SeitenOhms Lawmpravin kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opti Turn Tu 2004 V ManualDokument80 SeitenOpti Turn Tu 2004 V ManualCharu NavneetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sip Dissertation - Final - Final For CollegeDokument17 SeitenSip Dissertation - Final - Final For Collegevikashirulkar922Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Six Weeks RecoveryDokument8 Seiten4th Six Weeks RecoveryAshley HighNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography: University of Santo Tomas Faculty of Pharmacy Department of BiochemistryDokument32 SeitenHigh Performance Liquid Chromatography: University of Santo Tomas Faculty of Pharmacy Department of BiochemistryMa. Ellah Patricia M. GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 3410-1961 PDFDokument20 SeitenBS 3410-1961 PDF2601220150379Noch keine Bewertungen
- The DSG DQ200 LifespanDokument1 SeiteThe DSG DQ200 Lifespanqt99qzyhrbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agricultural Machinery in PakistanDokument19 SeitenAgricultural Machinery in PakistanBadar NiaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obs Inf Worksheet 2013Dokument2 SeitenObs Inf Worksheet 2013api-338002331Noch keine Bewertungen
- DHL Product Solutions Portfolio 2017Dokument1 SeiteDHL Product Solutions Portfolio 2017Hanzla TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Rect-15) Experimental Study On Partial Replacement of Cement With Coconut Shell Ash in ConcreteDokument3 Seiten(Rect-15) Experimental Study On Partial Replacement of Cement With Coconut Shell Ash in Concretefrancis dimakilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnglishDokument18 SeitenEnglishSarah SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPC 4552 Cuprins - ENIG PDFDokument3 SeitenIPC 4552 Cuprins - ENIG PDFMarlon CornejoNoch keine Bewertungen