Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fluids Concept Mapping
Hochgeladen von
mariagarcia415Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fluids Concept Mapping
Hochgeladen von
mariagarcia415Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Body fluid with n cell
Intracellular
Fluid with in cell
Extracellular
Found in blood
vessels
Interstitial fluid 25% (the
third space)
surrounding cells,
including lymph
Transcellular fluids
Lymph, digestive
tract, sweat,
cerebrospinal
Electrolytes and imbalances
Sodium (Na) Major cation of extracellular fluid
Hyponatremia
orthostatic hypotension
Hypernatremia
flushed skin, dry mucous
membranes
Potassium (K)
Hypokalemia
Muscle cramps BP oliguria
Hyperkalemia
Patients at risk: decreased renal
function, in metabolic acidosis,
taking potassium supplements
Chloride (Cl)
Hyperchloremia
Usually associated with metabolic
acidosis
Hypochloremia
Usually occurs when sodium is lost
because chloride most frequently
bound with sodium
Calcium (Ca)
Hypocalcemia
intake of vit D
Hypercalcemia
intake of vitamin D
Magnesium (Mg
2+
)
Important in heart, nerve, and
muscle function
Hypomagnesemia
usually from vomiting
and diarrhea
Hypermagnesemia
excessive use of
magnesium
osmolality of intracellular
fluid and extracellular
fluid tends to equalize
because of the constant
shifting of water
Age-Related Changes Affecting
Fluid Balance
Total body water declines with age;
greatest loss from the intracellular
fluid compartment
Antihypertensive, diuretics, and
antacids can also contribute to
imbalances
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Hematocrit
Creatnine
BUN
Albumin
Serum electrolytes
Intravenous therapy
Isotonic
NS (0.9% saline)
DW5
LR
Hypotonic
NS
Hypertonic
3% NS
D10W
5% D in LR
Colloids
Dextran
Albumin
Hetastarch
Infiltration
Caused by leakage
S/S: pain or burning
Paleness and puffiness or
feel hard and cool
Excess Fluid Volume
S/S: BP, bounding pulse,
edema
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Risks of emboli from blood
clots, air, broken catheters
Air can enter the
bloodstream if the infusion
system is opened
Catheters
catheter threaded through
the tunnel and into the
subclavian vein
cannulas and the tubing are
usually changed every 48-
72 hours
Fluids and
Electrolytes
Ch. 14
&
Intravenous
therapy
Ch. 18
Respiratory Acidosis pH<7.35 &PaCO2>45
Hypoventilation Hypoxia
Shallow breathing, K+,
Respiratory Alkalosis pH>7.45 &PaCO2<32
Deep breathing, hyperve
ntilation, tachycardia, lethargy & confusion.
Metabolic Acidosis pH<7.35 & HCO3<20
Kussmaul respiration, severe diarreah,
N,V,D, muscle twitching
Metabolic Alkalosis pH>7.45 & HCO3>26
Severe vomiting, tremors, muscle cramps
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Concept Map On HyponatremiaDokument1 SeiteConcept Map On HyponatremiaNeil Alibangbang0% (1)
- Detergent Raw Materials PDFDokument138 SeitenDetergent Raw Materials PDFOsamaAliMoussa78% (27)
- Neurology Nursing Study GuideDokument19 SeitenNeurology Nursing Study GuideHayleyLangley100% (5)
- HA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusDokument4 SeitenHA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusJULIE ANNE CORTEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCC-SickleCellAnemiaManagement ConceptMap InteractivePDFDokument2 SeitenNCC-SickleCellAnemiaManagement ConceptMap InteractivePDFLoggerz Arck100% (1)
- This Study Resource Was Shared ViaDokument4 SeitenThis Study Resource Was Shared ViaKyuSheen100% (1)
- Vsim Isbar Activity Student Worksheet: Your Name, Position (RN), Unit You Are Working OnDokument2 SeitenVsim Isbar Activity Student Worksheet: Your Name, Position (RN), Unit You Are Working OnA PNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHF Concept MapDokument4 SeitenCHF Concept MapLisaSanders99Noch keine Bewertungen
- IV Solution Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteIV Solution Cheat Sheetlauramphs79Noch keine Bewertungen
- n360 Concept Map Care Plan Week 3 Sheryl SatoDokument15 Seitenn360 Concept Map Care Plan Week 3 Sheryl Satoapi-283363983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Group Fdar Hemophilia ADokument2 SeitenGroup Fdar Hemophilia AMika SaldañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Types of IV FluidsDokument10 SeitenDifferent Types of IV FluidsMarinill SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- VasopressinDokument2 SeitenVasopressinKim LompotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter61 Management of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionDokument49 SeitenChapter61 Management of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionAhmed 123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) :: FeaturesDokument3 SeitenAcute Kidney Injury (AKI) :: FeaturesDavid PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care Plan For Excess Fluid Volume ExampleDokument3 SeitenCare Plan For Excess Fluid Volume ExampleVette Angelikka Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHF Cardiomegaly Volume OverloadDokument1 SeiteCHF Cardiomegaly Volume Overloadnursing concept mapsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC Concept MapDokument9 SeitenCC Concept Mapapi-606252228Noch keine Bewertungen
- Zaroxolyn MetolazoneDokument1 SeiteZaroxolyn MetolazoneCassieNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypokalemiaDokument3 SeitenHypokalemiaSergeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDokument18 SeitenNursing Care Plan Renal FailureKundan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mabes Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDokument15 SeitenMabes Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesMabesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemJordz PlaciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head To Toe AssessmentDokument2 SeitenHead To Toe AssessmentMichelle Myca Rosauro100% (1)
- Tagum Doctors College, Inc.: Mahogany ST., Rabesubd., Tagum City E-MailDokument4 SeitenTagum Doctors College, Inc.: Mahogany ST., Rabesubd., Tagum City E-MailRoel John Atamosa CasilacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narratives Case NotesDokument4 SeitenNarratives Case NotesKnigh RiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dalidig - Drug StudyDokument28 SeitenDalidig - Drug StudyRaf DalidigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyponatremia Algorhythm Concept MapDokument2 SeitenHyponatremia Algorhythm Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wound CareDokument17 SeitenWound Caredlneisha6183% (6)
- Fluidsandelectrolytes 090224074347 Phpapp02Dokument102 SeitenFluidsandelectrolytes 090224074347 Phpapp02IsaacJ22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ampicillin Med InfoDokument1 SeiteAmpicillin Med InfoJan McgovernNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan - MergedDokument13 SeitenNursing Care Plan - MergedJuls Flares SycaycoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative PathophysiologyDokument18 SeitenNarrative PathophysiologyNica Georgelle Maniego SamonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular DiseaseDokument37 SeitenHemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular Diseasejbvaldez100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Brain Injury: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology of Brain Injury: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsHoney Lorie D. Simbajon100% (2)
- Gerontologic Health Promotion ActivityDokument3 SeitenGerontologic Health Promotion ActivityCorinne50% (2)
- Abdominal Assessment VideoDokument4 SeitenAbdominal Assessment VideoAmber Nicole HubbardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map - Abby !Dokument3 SeitenConcept Map - Abby !Franklin A. Salaum III0% (2)
- Drug PrilosecDokument1 SeiteDrug PrilosecSrkocher100% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDokument37 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte Imbalancesapi-3797941100% (4)
- NUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping InstructorDokument8 SeitenNUR129 Endocrine Concept Mapping InstructorAmber EssmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyDick Morgan FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Completed Concept MapDokument4 SeitenCompleted Concept Mapapi-607361848Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeKarylle PetilNoch keine Bewertungen
- CystoclysisDokument2 SeitenCystoclysisRaymond BasiloniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary IncontinenceDokument5 SeitenUrinary IncontinencefakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism Concept MapDokument5 SeitenHypothyroidism Concept Mapnursing concept maps0% (1)
- Concept Map SepsisDokument4 SeitenConcept Map SepsisSavanna ChambersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map 360Dokument6 SeitenConcept Map 360api-273469220Noch keine Bewertungen
- Infectious Process Secondary To Acute Gastroenteritis Nagtatae Na Talaga Siya", Changed Diaper 3x With Loose and DeformedDokument1 SeiteInfectious Process Secondary To Acute Gastroenteritis Nagtatae Na Talaga Siya", Changed Diaper 3x With Loose and DeformedJoshua MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDokument123 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceBrealaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shock: By: Dr. Samer Sabri M.B.CH.B F.I.C.M.SDokument34 SeitenShock: By: Dr. Samer Sabri M.B.CH.B F.I.C.M.Ssamer falconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and ElectrolyteDokument57 SeitenFluid and ElectrolyteJustin Ahorro-DionisioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Deficit RevisedDokument6 SeitenFluid Deficit RevisedShaira SariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSG IV Test 3Dokument4 SeitenNSG IV Test 3Maria Phebe SinsayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid/Electrolytes & Acid Base Balance: Michael Jenifer RN, MSN PathophysiologyDokument74 SeitenFluid/Electrolytes & Acid Base Balance: Michael Jenifer RN, MSN PathophysiologyonukwughaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbance - Yoana AngelineDokument43 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte Disturbance - Yoana AngelineYoana AngelineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids Electrolytes Group 1 CompilationDokument41 SeitenFluids Electrolytes Group 1 CompilationShaira SariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoichiometry IGCSEDokument43 SeitenStoichiometry IGCSEsara bdeirNoch keine Bewertungen
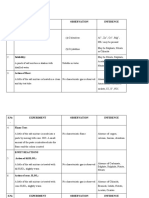
- S.No - Experiment Observation InferenceDokument7 SeitenS.No - Experiment Observation InferenceArchana ArchuNoch keine Bewertungen
- USP Monographs - Alumina and Magnesia Oral SuspensionDokument2 SeitenUSP Monographs - Alumina and Magnesia Oral SuspensionWinda HuhulNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 Specimen Paper 3Dokument16 Seiten2023 Specimen Paper 3pp catNoch keine Bewertungen
- S Block ElementsDokument72 SeitenS Block ElementsashrafraziNoch keine Bewertungen
- JKM Product ListDokument3 SeitenJKM Product ListSunil KadduNoch keine Bewertungen
- UCSI 2017 UCSI University Campus Emergency GuideDokument24 SeitenUCSI 2017 UCSI University Campus Emergency GuideSeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyeing Technologies and Their ApplicationsDokument2 SeitenDyeing Technologies and Their ApplicationsJuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Codex 2015Dokument708 SeitenCodex 2015Jaime Flores FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions and Equations-Important QuestionsDokument13 SeitenChemical Reactions and Equations-Important QuestionsLushila MinjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Student Book Answers PDFDokument58 SeitenEdexcel IGCSE Chemistry Student Book Answers PDFmashiad84% (51)
- Chemistry Class 10 Meatals and NonmetalsDokument9 SeitenChemistry Class 10 Meatals and NonmetalsGokulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Experimenter 07Dokument100 SeitenElectrical Experimenter 07Daniel Knight100% (1)
- Epa 9081 Cation-Exchange Capacity of Soils (Sodium Acetate)Dokument4 SeitenEpa 9081 Cation-Exchange Capacity of Soils (Sodium Acetate)ErickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkali Silica Reaction of ConcreteDokument20 SeitenAlkali Silica Reaction of ConcreteArbi811Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unacademy Electrochemistry Mega XIIDokument44 SeitenUnacademy Electrochemistry Mega XIIAaryan Keshan100% (2)
- Selangor Skema Kimia Kertas 2 (Set 1)Dokument17 SeitenSelangor Skema Kimia Kertas 2 (Set 1)SITI RAIHANI BINTI KAMSO MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 6887-1 2017 Microbiology of The Food Chain-Preparation O...Dokument34 SeitenISO 6887-1 2017 Microbiology of The Food Chain-Preparation O...Diosa JunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeopath Divine RemedyDokument271 SeitenHomeopath Divine RemedyAzad Ansari100% (6)
- Enzymatic Assay of XYLANASE (EC 3.2.1.8) PrincipleDokument4 SeitenEnzymatic Assay of XYLANASE (EC 3.2.1.8) Principlesyaza amiliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPE Chemistry Unit 1 2010 P2Dokument10 SeitenCAPE Chemistry Unit 1 2010 P2Ruchi MarajhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of TalcDokument5 SeitenAnalysis of Talcalexander_suarez_19Noch keine Bewertungen
- B Pharm 1 2 3 4 Year 2010-11Dokument91 SeitenB Pharm 1 2 3 4 Year 2010-11smsmbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Terminology in ChemistryDokument4 SeitenBasic Terminology in ChemistryHaider JalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msds Sodium HypochloriteDokument9 SeitenMsds Sodium Hypochloritehinur awaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ManualDokument131 SeitenLab Manualsgangwar2005sg100% (1)
- Measurement Multiple Choice QPDokument8 SeitenMeasurement Multiple Choice QPMinh Lại Nguyễn TuấnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phytochemical Screening of Saccharum Officinarum Linn. Stem.Dokument15 SeitenPhytochemical Screening of Saccharum Officinarum Linn. Stem.International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology0% (1)
- R2B-P3-206-02-P-HD-00002 - Rev.1 - Datasheets For Oxygen Analyzer U-21000 - EngDokument6 SeitenR2B-P3-206-02-P-HD-00002 - Rev.1 - Datasheets For Oxygen Analyzer U-21000 - EngDiana Paula Echartea Molina0% (1)