Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 1
Hochgeladen von
farahmahzir0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten18 SeitenMol dm -3 hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to a solution of lead(II) nitrate. Reaction occurs when the surface area of the reactant particles increases. When the total surface area of marble chips increases, the rate of reaction increases.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMol dm -3 hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to a solution of lead(II) nitrate. Reaction occurs when the surface area of the reactant particles increases. When the total surface area of marble chips increases, the rate of reaction increases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten18 SeitenChapter 1
Hochgeladen von
farahmahzirMol dm -3 hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to a solution of lead(II) nitrate. Reaction occurs when the surface area of the reactant particles increases. When the total surface area of marble chips increases, the rate of reaction increases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 18
Chapter 1 Rate of Reactions
List of PEKA experiments:
1. Average rate of reaction and instantaneous rate of reaction
2. Effect of surface area on the rate of reaction
3. Effect of concentration on the rate of reaction
4. Effect of temperature on the rate of reaction
5. Effect of catalyst on the rate of reaction
6. Effect of the amount of catalyst on the rate of reaction
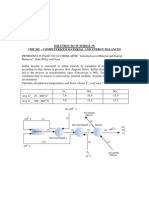
Number Laboratory Work 1.2
Pg. 3
Title Average rate of reaction and instantaneous rate of
reaction
Aim To determine the average rate of reaction and the
instantaneous rate of reaction
Apparatus 50 cm
3
beaker
Test tube
Spatula
Material Marble chip
2.0 mol dm
-3
hydrochloric acid (HCl)
0.1 mol dm
-3
sodium thiosulphate,
Na
2
S
2
O
3
solution
1.0 mol dm
-3
lead(II) nitrate solution
.
Number Experiment 1.1
Pg. 6
Title Effect of surface area on the rate of reaction
Aim To investigate the effect of total surface area of the
reactant on the rate of reaction
Problem
Statement
How does the total exposed surface area of a solid
reactant affect the rate of reaction?
Hypothesis When the total surface area of marble chips increases,
the rate of reaction increases. / The smaller the size of
the reactant particles, that is, the larger the total
surface area of the reactant particles, the higher the
rate of reaction.
Apparatus 50 cm
3
measuring cylinder
150 cm
3
conical flask
Stopper with delivery tube
Basin
Burette
Spatula
Electronic balance
Stopwatch
Material 0.5 mol dm
-3
hydrochloric acid (HCl)
2 g large marble chips
2 g small marble chips
Water
Variables Manipulated variable: Total surface area of
marble chips
Responding variable: Rate of reaction
Controlled / Fixed variable: Mass of marble
chips, volume and concentration of
hydrochloric acid (HCl), temperature
Operational 1. Smaller marble chips have a larger total
Definition surface area than larger marble chips of the
same mass.
2. For the graph of the volume of gas released
against time, the curve with higher initial
gradient indicates a higher initial rate of
reaction.
.
Number Experiment 1.2
Pg. 10
Title Effect of concentration on the rate of reaction
Aim To investigate the effect of concentration on the rate
of reaction
Problem
Statement
How does the concentration of a reactant affect the
rate of reaction? / Does high concentration of sodium
thiosulphate Na
2
S
2
O
3
solution decrease the time taken
for the mark X to disappear from sight?
Hypothesis When the concentration of sodium thiosulphate,
Na
2
S
2
O
3
solution increases, the rate of reaction
increases. / The higher the concentration of sodium
thiosulphate Na
2
S
2
O
3
solution, the shorter the time
taken for the mark X to disappear from sight.
Apparatus 150 cm
3
conical flask
50 cm
3
measuring cylinder
10 cm
3
measuring cylinder
Stopwatch
Material 0.2 mol dm
-3
sodium thiosulphate solution
1.0 mol dm
-3
sulphuric acid
Distilled water
White paper marked X at the centre
Variables Manipulated variable: Concentration of
sodium thiosulphate, Na
2
S
2
O
3
solution
Responding variable: Rate of reaction
Controlled / Fixed variable: Concentration,
volume and initial temperature of sulphuric
acid, H
2
SO
4
. Total volume of reactants
Operational
Definition
Rate of reaction is inversely proportional to the time
taken for the the mark X to disappear from sight
.
Number Experiment 1.3
Pg. 13
Title Effect of temperature on the rate of reaction
Aim To investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of
reaction
Problem
Statement
How does temperature affect the rate of reaction?
Hypothesis An increase in temperature will increase the rate of
reaction.
Apparatus 150 cm
3
conical flask
50 cm
3
measuring cylinder
10 cm
3
measuring cylinder
Stopwatch
Thermometer
Bunsen burner
Tripod stand
Wire gauze
Material 0.2 mol dm
-3
sodium thiosulphate solution
1.0 mol dm
-3
sulphuric acid
White paper marked X at the centre
Variables Manipulated variable: Temperature of sodium
thiosulphate, Na
2
S
2
O
3
solution
Responding variable: The time taken for the
cross X to disappear
Controlled / Fixed variable: volume and
concentration of sodium thiosulphate
Na
2
S
2
O
3
solution, volume and concentration of
sulphuric acid, size of conical flask
Operational
Definition
Rate of reaction is inversely proportional to the time
taken for the mark X to disappear from sight
.
Number Experiment 1.4
Pg. 15
Title Effect of catalyst on the rate of reaction
Aim To investigate the effect of a catalyst on the rate of
reaction
Problem
Statement
How does a catalyst affect the rate of reaction? / How
do catalysts affect the rate of decomposition of
hydrogen peroxide?
Hypothesis The presence of a catalyst increases the rate of
reaction. / Manganese(IV) oxide increases the rate of
decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
Apparatus Test tube
Test tube rack
Spatula
Wooden splinter
Retort stand and clamp
10 cm
3
measuring cylinder
Electronic balance
Weighing bottle
Material 20-volume hydrogen peroxide, H
2
O
2
solution
1.0 g Manganese(IV) oxide powder
Variables Manipulated variable: Presence or absence of a
catalyst
Responding variable: The release of oxygen gas
/ Rate of reaction
Controlled / Fixed variable: Volume and
concentration of hydrogen peroxide (H
2
O
2
)
solution, temperature
Operational
Definition
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is
fast if the glowing wooden splinter rekindles
brightly and rapidly.
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is
slow if the glowing wooden splinter glows
dimly and slowly.
.
Number Experiment 1.5
Pg. 17
Title Effect of the amount of catalyst on the rate of reaction
Aim To investigate the effect of the amount of catalyst on
the rate of reaction.
Problem
Statement
How does the amount of a catalyst affect the rate of
reaction? / Does higher amount of catalysts increases
the rate of reaction?
Hypothesis When the amount of a catalyst used increases, the rate
of reaction increases. / The higher the amount of the
catalysts, the higher the rate of reaction.
Apparatus 50 cm
3
measuring cylinder
150 cm
3
conical flask
Stopper with delivery tube
Burette
Retort stand and clamp
Basin
Stopwatch
Electronic balance
Spatula
Weighing bottle
Beakers
Material 2-volume hydrogen peroxide solution
1.0 g manganese(IV) oxide powder
Variables Manipulated variable: amount / mass of
catalyst
Responding variable: Rate of reaction
Controlled / Fixed variable: Temperature,
volume and concentration of hydrogen
peroxide solution
Operational
Definition
The curves for the graph of volume of gas liberated
against time a higher gradient indicated a higher rate
of reaction.
Chapter 2 Carbon Compound
List of PEKA experiments:
1. Combustion products of organic compound
2. Properties of alkanes and alkenes
3. Preparation of ethanol by fermentation
4. Chemical properties of ethanol
5. Chemical properties of ethanoic acid
6. Esters Laboratory preparation and physical properties
7. Coagulation of latex
8. Elasticity of vulcanised and unvulcanised rubber
9. Latex product
Number Laboratory Work 2.1
Pg. 25
Title Combustion products of organic compound
Aim To identify the combustion product of organic
compound. / To investigate the complete combustion of
organic compounds.
Apparatus 250 cm
3
beaker
Boiling tube
Stopper with 2 holes
Delivery tube
Rubber tubing
Filter funnel
Filter pump
Retort stand and clamp
Spirit lamp
Bunsen burner
0 110C thermometer
Test tube holder
Wooden blocks
Material Ice
Ethanol
Palm oil
Limewater
.
Number Laboratory Work 2.2
Pg. 32
Title Properties of alkanes and alkenes
Aim To compare the properties of alkanes and alkenes
A. Reaction with oxygen
To compare the combustion of hexane and
hexane
B. Reaction with bromine
To compare the reaction of hexane and hexane
with bromine
C. Reaction with acidized potassium
manganate(VII) solution
To compare the reaction of hexane and hexane
with acidified potassium manganate(VII)
solution
Apparatus Evaporating dish / Porcelain dishes
Dropper
Test tube
Bunsen burner
Material Hexane
Hexene
Bromine in 1,1,1-trichloroethane
0.1 mol dm
-3
potassium manganate(VII) solution
Dilute sulphuric acid
Wooden splinter
Filter paper
.
Number Laboratory Work 2.3
Pg. 38
Title Preparation of ethanol by fermentation
Aim To prepare samples of ethanol, C
2
H
5
OH by fermentation
Apparatus 250 cm
3
conical flask
150 cm
3
conical flask
500 cm
3
beaker
50 cm
3
measuring cylinder
Distillation flask (round-bottomed flask)
Stopper with delivery tube
Stopper with 1 hole
0 110C thermometer
Liebig condenser
Fractionating column
Retort stand and clamp
Tripod stand
Wire gauze
Glass rod
Bunsen burner
1 m rubber tubing
Filter funnel
Boiling tube
Material Glucose
Yeast
Limewater
Distilled water
Filter paper (4 pieces)
Fruits such as pineapple, grape, papaya,
banana, apple, berries
Cooked potatoes, rice or tapioca
.
Number Laboratory Work 2.4
Pg. 41
Title Chemical properties of ethanol
Aim To investigate the chemical properties of ethanol,
C
2
H
5
OHA. Combustion of ethanolB. Oxidation of
ethanolC. Dehydration of ethanol
Apparatus A. Combustion of ethanol
Evaporating dish
Wooden splinter
B. Oxidation of ethanol
Test tubes
Boiling tube
Stopper with delivery tube
Test tube holder
500 cm
3
beaker
Retort stand and clamp
Bunsen burner
10 cm
3
measuring cylinder
Dropper
C. Dehydration of ethanol
Test tubes
Boiling tube
Stopper with delivery tube
Test tube holder
500 cm
3
beaker
Retort stand and clamp
Bunsen burner
Forceps
Dropper
Material A. Combustion of ethanol
Ethanol
B. Oxidation of ethanol
Ethanol
30 g dm
-3
potassium dichromate(VI),
K
2
Cr
2
O
7
solution
Ice
Concentrated sulphuric acid
Blue litmus paper
C. Dehydration of ethanol
Ethanol
30 g dm
-3
potassium dichromate(VI),
K
2
Cr
2
O
7
solution
3 g dm
-3
potassium manganate(VII),
KMnO
4
solution
Bromine water
Glass wool
Unglazed porcelain chips
Water
.
Number Laboratory Work 2.5
Pg. 48
Title Chemical properties of ethanoic acid
Aim To investigate the chemical reactions of ethanoic acid,
CH
3
COOH
A. Reactions of ethanoic acid as an acid
i. reaction of ethanoic acid with a metal
ii. reaction of ethanoic acid with a metal
carbonate
iii. reaction of ethanoic acid with a base
B. Reaction of ethanoic acid with alcohol
Apparatus A. Reactions of ethanoic acid as an acidi. reaction of
ethanoic acid with a metal
Test tube
Test tube rack
Wooden splinter
ii. reaction of ethanoic acid with a metal carbonate
Test tubes
Stopper with delivery tube
iii. reaction of ethanoic acid with a base
Test tube
Spatula
Glass rod
Bunsen burner
Tripod stand
Wire gauze
Evaporating dish
B. Reaction of ethanoic acid with alcohol
Dropper
Boiling tube
250 cm
3
beaker
Test tube holder
Bunsen burner
Material A. Reactions of ethanoic acid as an acidi. reaction of
ethanoic acid with a metal
1.0 mol dm
-3
ethanoic acid
Metal powder (Magnesium ribbon / Zinc)
ii. reaction of ethanoic acid with a metal carbonate
1.0 mol dm
-3
ethanoic acid
Metal carbonate powder (Calcium
carbonate/Iron(III) carbonate/Sodium
carbonate)
Limewater
iii. reaction of ethanoic acid with a base
1.0 mol dm
-3
sodium hydroxide solution
Metal oxide powder (Copper(II) oxide)
B. Reaction of ethanoic acid with alcohol
Glacial ethanoic acid
Absolute ethanol / Butan-1-ol
Concentrated sulphuric acid
Ice
Water
.
Number Laboratory Work 2.6
Pg. 53
Title Esters Laboratory preparation and physical properties
Aim To prepare a sample of ethyl ethanoate, CH
3
COOC
2
H
5
in
the laboratory
A. Laboratory preparation of esterTo prepare a
sample of ethyl ethanoate
B. Physical properties of ethyl ethanoate
To investigate the physical properties of ethyl
ethanoate
Apparatus A. Laboratory preparation of ester
100 cm
3
beaker
500 cm
3
beaker
250 cm
3
distillation flask (round-bottomed flask)
250 cm
3
conical flask
50 cm
3
measuring cylinder
Tap funnel
0 250C thermometer
Liebig condenser
Bunsen burner
Tripod stand
Retort stand and clamp
Stopper with 2 holes
Wooden block
Porous chips / tile chips
Oil bath
B. Physical properties of ethyl ethanoate
Test tube
Dropper
Glass rod
Sample bottle
Material A. Laboratory preparation of ester
Absolute ethanol
Glacial ethanoic acid
Concentrated sulphuric acid
Oil
Tap water
B. Physical properties of ethyl ethanoate
Ethyl ethanoate (from A)
Distilled water
Acetone
Methylated spirits
.
Number Laboratory Work 2.7
Pg. 60
Title Coagulation of latex
Aim To investigate the coagulation of latex
Apparatus 100 cm
3
beaker
Measuring cylinder
Glass rod
Dropper
Material Rubber latex
1.0 mol dm
-3
ethanoic acid
1.0 mol dm
-3
ammonia solution
Red and blue litmus paper
.
Number Laboratory Work 2,8
Pg. 61
Title Vulcanised rubber
Aim To prepare vulcanised rubber
Apparatus 10 cm x 10 cm glass plate
Glass rod
Razor blade
A pair of tongs
250 cm
3
beaker
Material Rubber latex
Disulphur dichloride in methylbenzene
.
Number Experiment 2.1
Pg. 62
Title Elasticity of vulcanised and unvulcanised rubber
Aim To compare the elasticity of vulcanised and
unvulcanised rubber
Problem
Statement
Is vulcanised rubber is more elastics than unvulcanised
rubber?
Hypothesis Vulcanised rubber is more elastics than unvulcanised
rubber
Apparatus Retort stand and clamps
Bulldog clips
Hooks
Metre rule
Weights (50 g)
Material Vulcanised rubber strip
Unvulcanised rubber strip
Variables Manipulated variable: Types of rubber
(vulcanised rubber strip and unvulcanised
rubber strip)
Responding variable: Elasticity of rubber /
Length of rubber strip
Controlled/Fixed variable: Mass of weight, size
of rubber strip
Operational
Definition
If the minimum weight required for the rubber strip to
fail to return to its initial length is larger, then the
rubber strip is more elastic.
.
Number Laboratory Work 2.9
Pg. 64
Title Latex product
Aim To prepare a rubber glove in the laboratory
Apparatus 500 cm
3
beaker
Dropper
Glass rod
Plastics arm mould
String
Retort stand and clamp
Basin
Material Fresh latex
2.0 mol dm
-3
ethanoic acid
Water
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- NitroxDokument19 SeitenNitroxŞef Utas AwijNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Sistema de OZONO WEDECO ToluquillaDokument77 SeitenManual Sistema de OZONO WEDECO ToluquillaFlavio Garcia ValenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxyfuel BurnersDokument31 SeitenOxyfuel BurnersMohammed Abdul NaseerNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOD Experiment ReportDokument16 SeitenBOD Experiment ReportNobodyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChE Day1 Questions (Calculations)Dokument6 SeitenChE Day1 Questions (Calculations)Mhelvene100% (2)
- UCG ExplainedDokument4 SeitenUCG ExplainedVăn Đại - BKHNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eudiometry: Nurture CourseDokument16 SeitenEudiometry: Nurture CourseAshik jhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WASTEWATER STABILIZATION LAGOON PROCESS PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download - ID - 6206424Dokument2 SeitenWASTEWATER STABILIZATION LAGOON PROCESS PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download - ID - 6206424shoyebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Notes: Final ProjectDokument8 SeitenProcess Notes: Final ProjectCluisantony Jayco DizeNoch keine Bewertungen
- v111n11p759 Fluid Roasting ZincDokument7 Seitenv111n11p759 Fluid Roasting ZincergfaradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deaeration: Two Types of Deaeration Systems Are Commonly Used: - Vacuum Deaeration - Gas Strip DeaerationDokument2 SeitenDeaeration: Two Types of Deaeration Systems Are Commonly Used: - Vacuum Deaeration - Gas Strip DeaerationVineeth Chowdary YamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 HSC Exam ChemistryDokument38 Seiten2010 HSC Exam ChemistryFiras AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering ChemistryDokument60 SeitenEngineering ChemistryAditya ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Schedule - 2011 Chemistry: Demonstrate Understanding of Aspects of Carbon Chemistry (90932)Dokument4 SeitenAssessment Schedule - 2011 Chemistry: Demonstrate Understanding of Aspects of Carbon Chemistry (90932)Suv ViseNoch keine Bewertungen
- ID Studi Perilaku Satpam Terhadap Penanggulangan Kebakaran Di Instansi XDokument9 SeitenID Studi Perilaku Satpam Terhadap Penanggulangan Kebakaran Di Instansi XAndi SusantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual For Nitrogen GeneratorDokument56 SeitenManual For Nitrogen GeneratorMusfiqul AzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 9 (Problem 8.25)Dokument4 SeitenTutorial 9 (Problem 8.25)Kaniz Priyangka0% (1)
- Group 1Dokument16 SeitenGroup 1Abdul QayyumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Section 2 OutlineDokument4 SeitenChapter 6 Section 2 Outlineapi-263455056Noch keine Bewertungen
- AICE Marine - Unit 7 Test Questions/ Study Guide: (Answers)Dokument19 SeitenAICE Marine - Unit 7 Test Questions/ Study Guide: (Answers)philip 6969Noch keine Bewertungen
- Safe Handling of Cryogenic Liquids: Safetygram 16Dokument8 SeitenSafe Handling of Cryogenic Liquids: Safetygram 16Alok RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen - The Essential Ingredient To A Healthy AquariumDokument33 SeitenOxygen - The Essential Ingredient To A Healthy AquariumMuhammad Iqbal ChandioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution and BiodiversityDokument4 SeitenEvolution and BiodiversityTrần ĐăngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic TableDokument23 SeitenPeriodic Tabled anjilappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiration SSC English 86Dokument24 SeitenRespiration SSC English 86Krishna Prasanth rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Scientific MethodDokument47 SeitenIntroduction To The Scientific MethoditsmesinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- IVA Group Elements PDFDokument3 SeitenIVA Group Elements PDFGhulam RabbaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Prospect of Alien Life in Exotic Forms On Other WorldsDokument19 SeitenThe Prospect of Alien Life in Exotic Forms On Other WorldsShrihari JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reaction Path For Thin Film Oxidation of Stainless Steel PDFDokument6 SeitenChemical Reaction Path For Thin Film Oxidation of Stainless Steel PDFToramaru UtsunomiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Homework 3 11th Gas LawDokument5 SeitenKey Homework 3 11th Gas LawTai PanNoch keine Bewertungen