Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pedia Notes
Hochgeladen von
Bonnyong MaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pedia Notes
Hochgeladen von
Bonnyong MaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
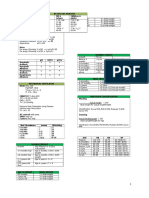
BLOOD GLUCOSE
Normal: 70-110 mg/dl
> 120 mg/dl: Hyperglycemia
Term infants: > 140 mg/dl normally
Preterm: > 30 mg/dl normally
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES IN THE
EVALUATION OF PEDIATRIC COMMUNITY ACQUIRED
PNEUMONIA 2004
Predictors of CAP in a patient with cough
1. 3 mos to 5 yrs with tachypnea &/or chest retractions
2. 5-12 yrs with fever, tachypnea and crackles
3. > 12 yrs with the presence of the ff:
a. Fever, tachypnea, tachychardia
b. At least 1 abnormal chest findings
(rales, wheezes, ronchi, dim BS)
WHO age specific criteria for tachypnea
2-12 mos 50
1-5 yrs 40
>5 yrs 30
RISK CLASSIFICATION FOR PNEUMONIA RELATED MORTALITY
Variables PCAP A
Min.
Risk
PCAP B
Low Risk
PCAP C
Mod Risk
PCAP D
High Risk
1.Comorbid
illness
None (+) (+) (+)
2.Compliant
caregiver
Yes Yes No No
3.Ability to
follow up
Possible Possible Not possible Not possible
4. Presence of
DHN
None Mild Mod Severe
5. Ability to feed Able Able Unable Unable
6. Age > 11 mos > 11 mos < 11 mos < 11 mos
7. RR
2-12 mos
1-5 yrs
>5 yrs
50/min
40/min
30/min
> 50/min
> 40/min
> 30/min
> 60/min
> 50/min
> 35/min
> 70/min
> 50/min
> 35/min
8. Signs of resp
distress
a. Retraction
b. Head bobbing
c. Cyanosis
d. Grunting
e. Apnea
f. Sensorium
None
None
None
None
None
Awake
None
None
None
None
None
Awake
Inter/
Subcostal
Present
Present
None
None
Irritable
Supraclav/
Int/Subcostal
Present
Present
Present
Present
Lethargic/
Stuporous/
Comatose
9.Complications None None Present Present
ACTION PLAN OPD Ff
up at end
of tx
OPD Ff up
after 3 days
Admit to
regular ward
Admit to
PICU &
refer to
specialist
PCAP A or PCAP B
No diagnostic aids are initially requested.
PCAP C or PCAP D
1. The ff should be routinely requested
a. CXR APL
b. WBC
c. Culture & sensitivity of
i. Blood for PCAP D
ii. Pleural fluid
iii. Tracheal aspirate upon initial intubation
d. Blood gas &/or pulse oximetry
2. The ff may be requested:
Culture and sensitivity of sputum for older children
3. The ff should not be requested
a. ESR
b. CRP
An Antibiotic is recommended
1. For a px classified as either PCAP A or B and is
a. Beyond 2 yrs
b. Having high grade fever w/o wheeze
2. For a px classified as PCAP C and is
a. Beyond 2 yrs of age
b. Having high grade fever w/o wheeze
c. Having alveolar consolidation in the CXR
d. Having WBC > 15,000
3. For a px as PCAP D
Empiric Treatment
1. For PCAP A or B w/o previous antibiotic
= Amoxicillin (40-50 mkD) oral TID
2. For PCAP C who completed Hib immunization
= Pen G IV (100,000 U/k/D) QID
For PCAP C not completed Hib immunization
= Ampicillin IV (100 mKD) QID
3. For PCAP D consult specialist
When can a px be considered as responding to current antibiotic?
1. Decrease in respiratory signs and defervescence w/in 72 hrs after
initiation
2. Reevaluate if SSx persists beyond 72 hrs after antibiotics
3. End of tx, CXR, WBC, ESR, or CRP should not be done to assess
therapeutic response to antibx
What should be done if px is not responding to current antibx?
1. If PCAP A or PCAP B is not responding w/in 72 hrs
a. Change initial antibx
b. Start oral macrolide
c. Reevaluate dx
2. If PCAP C is not responding with w/in 72 hrs, consult w/a specialist
because of the ff possibilities
a. PCN resistant Strep pneumonia
b. Complications (pulmonary or extrapulmonary)
c. Other dx
3. If PCAP D is not responding w/in 72 hrs, consider immediate consult
with a specialist
Switch from IV antibx to oral 2-3 days after initiation of antibx is
recommended in a px who:
a. Is responding to the initial antibx
b. Is able to feed with intact GIT absorption
c. Does not have any pulmo or extrapulmo complications
Ancillary Treatment
1. O2 and hydration
2. Bronchodilators, CPT, steam inhalation, NSS nebulization
Prevention
1. Vaccines
2. Zinc supplementation for 4-6 months
a. 10 mg for infants
b. 20 mg for children > 2yrs
2
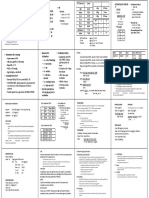
OPD MEDS
Amoxicillin 30-50 mkd (50 mkd) q 8h
Suspension 125 mg/ 5 ml
250 mg/ 5 ml
Drops 100 mg/ ml
Capsules 250 mg; 500mg
Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid (Amox 30-50 mkd)
Suspension 125 mg/ 156.25 mg/ 5 ml TID
200 mg/ 228.5 mg/ 5 ml BID
250 mg/ 312.5 mg/ 5 ml TID
400 mg/ 457 mg/ 5 ml BID
Tablet 250 mg/ 375 mg; 500 mg/ 625 mg
Cloxacillin 50-100 mkd q 6h
Suspension 125 mg/ 5 ml
250 mg/ 5 ml
Capsules 250 mg; 500 mg
Chloramphenicol 50-75 mkd q 6h
Suspension 125 mg/ 5 ml
Capsules 250 mg; 500 mg
CEPHALOSPHORINS
Cephalexin (1
st
gen) 25-100 mkd q 6-8h
Suspension 125 mg/ 5 ml
250 mg/ 5 ml
Drops 100 mg/ 5 ml
Capsules 250 mg; 500 mg
Cefaclor (2
nd
gen) 20-40 mkd q 8-12h
Suspension 125 mg/ 5 ml
187 mg/ 5 ml
250 mg/ 5 ml
375 mg/ 5 ml
Drops 50 mg/ ml
CD exten rel tab 375 mg; 750 mg
Cefuroxime (2
nd
gen) 20-40 mkd q 12h
Suspension 125 mg/ 5 ml
250 mg/ 5 ml
Sachet 125 mg/ sachet
250 mg/ sachet
Tablet 125 mg; 500 mg
Cefixime (3
rd
gen) 6-12 mkd q 12h
Suspension 100 mg/ 5 ml
Drops 20 mg/ ml
Cefipime 110 mkd q 12h
Vial 500 mg; 1 gram
Cetrimoxazole (TM 5-8 mkd q 12h)
Suspension 200 mg/ 40 mg/ 5 ml
400 mg/ 80 mg/ 5 ml
Tablet 400 mg/ 80 mg/tab
800 mg/ 160 mg/tab
MACROLIDES
Erythromycin 30-50 mld q 6h
Suspension 200 mg/ 5 ml
400 mg/ 5 ml
Drops 100 mg/ 2.5 ml
100 mg/ ml
Clarithromycin 7.5 mkdose q 12h
Suspension 125 mg/ 5 ml
Tablet 250 mg; 500 mg
Roxithromycin 6-12 yrs; 100 mg/tab BID
< 6 yrs: 5-8 mkd BID
Tablet 150 mg/ tab
Ped tab 100 mg/ tab
Azithromycin 3 day regimen: 10 mld x 3
5 day regimen: 10 mkd on day 1
5 mkd on days 2-5
Adult: 500 mg OD on day 1
250 mg OD on days 2-5
Suspension 200 mg/5 ml
Capsule 250 mg
Clindamycin PO 20-30 mkd q 6-8h
IV 25-40 mkd q 6h or
10-15 mkdose q 6h
Suspension 75 mg/ 5 ml
Capsule 150 mg; 300 mg
Ampoule 150 mg/ml
Metronidazole 30-50 mkd q 8h
Suspension 125 mg/5 ml
Tablet 250 mg; 500 mg
Diloxanide fureate 20 mkd q 8h x 10 days
Suspension 125 mg/ 5 ml
Tablet 500 mg
Miconazole Adult & children tsp q 6h
Infants tsp q 6h
Oral gel 2% tube
Nystatin
NB < 2000g = 200,000 400,000 u/day q 4-6 h
> 2000g = 200,000 400,000 u/day q 4-6 h
Infant, Child = 400,000 800,000 u/day q 4-6 h
Adult = 800,000 2 M u/day q 4-6 h
Fluconazole 3-6 mkd OD x 2 weeks
Capsule 50 mg; 150 mg; 200 mg
Vial 2 mg/ml x 100 ml
Oxantel + Pyrantel Pamoate 10-20 mkd SD
Suspension 125 mg/5ml
Tablet 125 mg; 250 mg
Tricuriasis x 2d
Hookworm x 3d
Mebendazole 100 mg BID x 3 days or 500 mg SD
Suspension 50 mg/ml; 100 mg/5 ml
Tablet 100 mg; 500 mg
Albendazole < 2 yo 200 mg SD
> 2 yo 400 mg SD
Suspension 200 mg/5 ml
Tablet 400 mg
Acyclovir 20 mkdose diven q 6h
Max 800 mg.day
Suspension 200 mg/5 ml
Blue 400 mg
Pink 800 mg
Diphenhydramine 1-2 mkdose IM/IV/PO
5 mkd q 6h
Syrup 12.5 mg/ 5 ml
Capsule 25 mg; 50 mg
Ampoule 50 mg/ml
Hydroxyzine 1 mkd BID
Syrup 2 mg/ml
Tablet 10 mg; 25 mg
Adult 10 mg BID or 25 mg OD @ HS
Desloratadine
Syrup 2.5 mg/ 5 ml
6-11 mos 2 ml (1 mg) OD
1-5 yrs 2.5 ml (1.25 mg) OD
6-11 yrs 5 ml (2.5 mg) OD
3
Cetirizine 1 mkdose OD
Oral drops 10 mg/ml
6-12 yo 10 drops BID
2-6 yo 5 drops BID
Tablet 10 mg
Adult & >12 yo 1 tab OD
6-12 yo 15 tab BID or 1 tab OD
Loratadine
Syrup 5 mg/5ml
Adult & 12 yo 10 ml OD
2-12 yo (>30 kg) 10 ml OD
(<30 kg) 5 ml OD
1-2 yo 2.5 ml OD
Sodium chloride 2-4 drops or sprays per nostril
TID/QID
Nasal drops/spray 0.65%
Phenylpropanolamine HCL
Syrup 12.5 mg/5 ml q 6h
2-6 yo 2.5 ml
7-12 yo 5 ml
Drops 6.25 mg/ml q 6h
1-3 mos 0.25 ml
4-6 mos 0.5 ml
7-12 mos 0.75 ml
1-2 yo 1 ml
Phenylephrine + brompheneramine maleate
Syrup
Adult 5-10 ml TID/QID
4-12 yo 5 ml TID/QID
2-4 yo tsp TID/QID
Drops (0.1 mkdose)
7-24 mos 1 ml TID/QID
1-6 mos 0.5 ml TID/QID
Paracetamol 10-20 mkdose q 4h
Drops 60 mg/0.6 ml
100 mg/ml
Suspension/Syrup 120 mg/5 ml
125 mg/5 ml
250 mg/5 ml
Tablet 325 mg; 500 mg
Rexidol 150 mg/5 ml syrup
600 mg tablet
Opigesic 125 mg; 250 mg
Mefenamic acid 6-8 mkdose q 6h
Syrup 50 mg/5 ml
Capsule 250 mg; 500 mg
Ibuprofen 5-10 mkdose q 6h
Max of 20 mkd
Suspension 100 mg/5 ml
200 mg/5 ml
Salbutamol 0.12-0.15 mkdose
Syrup 2 mg/5 ml
Tablet 2 mg; 4 mg
Salbutamol + Guaifenesin
Syrup 1 mg/50 mg/5 ml
Tablet 2 mg/ 50 mg
Terbutaline sulfate 0.075 mkdose
Syrup 1.5 mg/5 ml
Tablet 2.5 mg
Terbutaline + Guaifenesin
Syrup 1.5 mg/50 mg/5 ml
Doxofylline 6 mkdose TID
Syrup 100 mg/5 ml
Tablet 400 mg
Aminophylline 5 mkdose (loading dose)
2.5 mkdose q 6h (maint.) slow
IVTT + equal amounts of
sterile water
Ampoule 25 mg/ml
Prednisone 1-2 mkd
Syrup 10 mg/5 ml
20 mg/5 ml
Tablet 1 mg; 5 mg; 10 mg; 20 mg
Prednisolone 1-2 mkd
Syrup 15 mg/5 ml
Racecadotril 1.5 mkdose TID
Sachet 10 mg; 30 mg
Capsule 30 mg
Tramadol IV; 1-2 mkd q 8h
Ampoule 50 mg/ml; 100 mg/2 ml
Capsule 50 mg
Tablet 100 mg
Famotidine 0.6-0.8 mkdose q 12h
Ampoule 20 mg/2 ml
Tablet 20 mg; 40 mg
Ranitidine 1 mkdose q 8h
Entac 25 mg
Pharex 75 mg
Zinc < 6 mos: 10 mg/kg
> 6 mos: 20 mg/kg
< 2 yo: 1 ml OD drops
> 2 yo: 5 ml OD syrup
Drops 10 mg elemental Zn
Syrup 20 mg elemental Zn
IV ANTIBIOTICS
Penicillin G 100,000 400,000 ukd q 4-6h
Ampicillin + sulbactam (unasyn) 50-100 mkd q 6-8h
Chloramphenicol 50-100 mkd q 4-6h
Oxacillin (Prostaphlin) 50-100 mkd q 6-8h
Flucloxacillin 50-100 mkd q 6-8h
Gentamycin (Tangyn) 5-7.5 mkd OD, q 8-12h
Netromycin 5 mkd q 12h
Amikacin + SO4 (Amikin) 1.5 mkd q 12h
Cefuroxime (Zegen) 50-100 mkd q 6-8h
Ceftriaxone 50-100 mkd OD, q 12h
Ceftazidine 50-100 mkd q 12h
Cefoxitin 20-40 mkd q 6-12h
Cefepime 100 mkd q 12h
Tienam 10-15 mkdose q 6h
Meropenem (Meronem) 20-40 mkd q 8h
Piper/tazo (Piptaz) 200-300 mkd q 6h
OTHER IV MEDS
Epinephrine 0.01 ml/kg
Diphenhydramine 1-2 mkdose
Hydrocortisone 4 mkdose q 6-8h
Max dose: 200 mg as LD
100 mg as MD
Nalbuphine (Nubain) 0.13-0.15 mkdose
Phenobarbital 10 mkdose LD
5 mkd MD q 12h OD HS
Diazepam 0.04-0.2 mkdose IM/IV
Max dose: 0.6 mg/kg w/in 8h
0.12-0.8 mkd q 6-8h
Rectal dose 0.5 mkdose ffd by
0.25 mkdose in 10 min PRN
2-5 yo 0.5 mkdose
6-11 yo 0.3 mkdose
12 yo 0.2 mkdose
Ampoule 5 mg/ml
Oral solution 1 mg/ml; 5 mg/ml
Tablet 2 mg; 5 mg; 10 mg
Ped rectal gel 2.5 mg; 5 mg; 10 mg
4
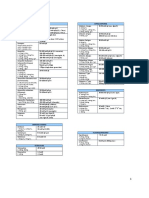
SEXUAL MATURITY RATING IN BOYS
STAGE PUBIC HAIR
1 Prepubertal: no pubic hair, fine vellus hair
2 Sparse, long, straight, downy hair
3 Darker, coarser, curly, sparse over the entire pubis
4 Dark, curly, and abundant in pubic area; no growth on thighs or up
towards the umbilicus
5 Adult pattern
SEXUAL MATURITY RATING IN GIRLS
STAGE PUBIC HAIR
1 Preadolescent
2 Sparse; lightly pigmented, straight, medical border of labia
3 Darker, beginning to curl, increased amount
4 Coarse, curly, abundant, but amount less
5 Adult feminine triangle medical surface of thigh
NEWBORN SCREENING
What is newborn screening?
Newborn screening is a simple procedure to find out if your baby has a
congenital metabolic disorder that may lead to mental retardation and even
death if left untreated.
Why is it important to have newborn screening?
Most babies with metabolic disorders look normal at birth. One will never
know that the baby has the disorder until the onset of signs and symptoms
and more often ill effects are already irreversible.
When is newborn screening done?
Newborn screening is ideally done on the 48
th
hour or at least 24 hours from
birth. Some disorders are not detected if the test is done earlier than 24 hours.
The baby must be screened again after 2 weeks for more accurate results.
How is newborn screening done?
Newborn screening is a simple procedure. Using the heel prick method, a
few drops of blood are taken from the babys heel and blotted on a special
absorbent filter card. The blood is dried for 4 hours and sent to the newborn
screening laboratory (NBS lab).
Who will collect the sample for newborn screening?
Newborn screening can be done by a physician, nurse, midwife, or medical
technologist.
Where is newborn screening available?
Newborn screening is available in participating health institutions (hospitals,
lying-in, rural health units and health centers). If babies are delivered at
home, babies may be brought to the nearest institution offering newborn
screening.
Where are newborn screening results available?
Newborn screening results are available within 3 weeks after the NBS lab
receives and tests the samples sent by the institutions. Results are released by
the NBS lab to the institutions and are released to your attending birth
attendants or physicians. Parents may seek the results from institutions where
samples are collected.
What are the disorders included in the newborn screening package?
The Philippine Newborn Screening program is currently screening for 5
disorders and the following are:
1. Congenital Hypothyroidism (CH)
CH is the most common inborn metabolic disorder. CH results from
lack or absence of thyroid hormone which is essential to growth of the
brain and the body. If the disorder is not detected and hormone
replacememnt is not initiated within 4 weeks, the babys physical
growth will be stunted and will start losing IQ points and may become
severely mentally retarded.
2. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
CAH is a rare but dangerous inborn metabolic disorder. This causes
severe salt loss, dehydration and abnormally high levels of male sex
hormones in both boys and girls. If not detected and treated early,
babies may die within 9-13 days.
3. Galactosemia (Gal)
GAL is a condition in which babies are unable to process certain part of
the milk called galactose. Accumulation of excessive galactose in the
body can cause many problems including liver damage, brain damage,
and cataracts.
4. Phenylketonuria (PKU)
PKU is a rare condition in which the baby cannot properly use one of
the building blocks of protein called phenyalanine. Excessive
accumulation of phenylalanine in the blood causes brain damage.
5. Glucose 6 Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency (G6PD Def)
G6PD deficiency is a condition where the body lacks the enzyme called
G6PD. Babies with this deficiency are prone to haemolytic anemia
resulting from exposure to oxidative substances found in drugs, foods
and chemicals.
EXPANDED PROGRAM OF IMMUNIZATION (EPI)
Vaccine 1
st
dose # of dose Interval Dose
BCG Birth-up 1 0.05 ml ID
DPT 6 wks 3 4 wks 0.5 ml IM
OPV 6 wks 3 4 wks 0.5 ml oral
Hep B 6 wks 3 4 wks 0.5 ml IM
Measles 9 mos 1 0.5 SQ
TT 2 mos 2 6 wks 0.5 IM
Rubella 1 yr 1 1 ml SQ
Mumps 1 yr 1 0.5 ml IM
Hemophilus
influenza
2 mos-5
yrs
3 2 mos
Varicella
zoster
9 mos-up 1 0.5 ml SQ
5
FLUID COMPUTATION (FLUID HYDRATION)
<2 yrs/<10 kg = 50 cc/kg run @ 8h (D5 0.3 NaCl)
= 100 cc/kg run @ 1h
Run @ 6-7h (PNSS/PLR)
= 150 cc/kg run 1/3 @ 1h
Run 2/3 @ 6-7h (PNSS/PLR)
>2 yrs/>10 kg = 30 cc/kg run @ 8h (D5 0.3 NaCl)
= 60 cc/kg run @ 1h
Run @ 6-8h
= 90 cc/kg run 1/3 @ 1h
Run 2/3 @ 6-7h
E.g. IV fluids given ____________ run @ 8h w/ 30 cc/kg computed as
mild dehydration
Started w/ IVF _____ regulated at _____ computed as _____
dehydration in _____ hrs
Micro cc/hr (gtts/min) to Macro cc/hr + 4 (cc/hr)
FACTORS MODIFYING WATER REQUIREMENT
EXTRA REQUIRED:
Fever (add 12% for each C above 37.5)
Hypermetabolic States (thermal injury, thyrotoxicosis, respiratory
distress) 25-75%
Abnormal H2O/electrolyte losses (diarrhea/vomiting) depend on
degree of hydration
Sweating 10-35%
LESS REQUIRED:
Hypothermia (subtract 12% for each C <37.5)
Very high humidity
Oliguria/anuria
Sedated/paralyzed patient (subtract 40%)
Edematous/antidiuretic states (cardiac failure)
HALLIDAY-SEGAR METHOD
(Maintenance Fluid)
(Nelson 16
th
ed)
0-10 kg 100 ml/kg/day
11-20 kg 1000 + 50 ml/kg for each kg> 10 kg
>20 kg 1500 + 20 ml/kg for each >20 kg
LUDANS METHOD
(del Mundo 2000)
0-3 kg 75 ml/kg/day
3-10 kg 100 ml/kg/day
11-20 kg 75 ml/kg/day
21-30 kg 60 ml/kg/day
31 kg 50 ml/kg/day
DOPAMINE DRIP
Prep: 200 mg/5 ml (40 mg/ml)
Dose: 3-30 mcg/kg/min
Formula:
Amt/dose = wt x dose x K (6) + prep + 2 (to make 50 ml prep)
To incorporate running dose
Eg: 10 kg child, dopamine @ 5 mcg/kg/min @ 5 cc/hr
= 10 kg (5 mcg/kg/min) 6 + 40 mg/ml + 2
5 cc/hr
= 0.75 ml of dopamine
To order:
Dopamine drip 0.75 ml plus
49.25 D5W @ 5 cc/hr
DOBUTAMINE DRIP
Prep: 250 mg/20 ml (12.5mg/ml)
Dose: 3-30 mcg/kg/min
Formula:
Amt/dose to = wt (dose) (K) + prep + 2 (to make 50 ml prep)
Incorporate running dose
Eg. 10 kg child, dobutamine @ 5 mcg/kg/min @ 5 cc/hr
= 10 kg (5 mcg/kg/min) (6) + 12.5 mg/ml + 2
5 cc/hr
= 2.4 ml of dobutamine
To order:
Dobutamine 2.4 ml plus 47.6 ml D5W @ 5 cc/hr
To check:
(dose) X = prep x running rate x amt/dose incorporated x 2
Weight x 6
ACTUAL DOSE = dose/wt
= dose x preparation
Wt
PEFR COMPUTATION
For 100-170 cm (ht) only
Predicted PEFR
Females: ht (cm) 100 x 5 + 170
Males: ht (cm) 100 x 5 + 175
Actual PEFR:
% = actual PEFR x 100
Predicted PEFR
RDA (RECOMMENDED DAILY ALLOWANCE)
AGE Wt (kg) Cal/kg P F
VLBW < 1500 - 2.25 -
0-6 mos 3-6 110-115 2.5 -
7-12 mos 7-9 110-115 2.3 2
1-3 yrs 10-12 110 1.5-2.5 -
4-6 yrs 14-18 90-100 1.5-2.25 4
7-9 yrs 22-24 80-90 1.5-2.0 -
10-12 yrs 28-32 70-80 1.5-2.0 2.5
CCU = IBW x ABW x caloric for age
ABW
= IBW x caloric for age
TCR = CCU x (50% 60%)
CHON = ABW x RDACHON x 4
NPC TCR CHON
CHO = NPC x 60%
FATS = NPC CHO
TCR every other day starting day 3 (+10%)
To orders:
Start feeding based on the ff computation
Total caloric req = 792 cal
Protein = 64 cal
Carbohydrate = 436 cal
Fats = 292 cal
- Divided into 3 meals and 2 snacks
- Pls provide sterile water after each feeding
After 3 days
Revise OTF/feeding based on the ff computation
Total caloric req = 871
Protein = 64
Carbohydrates = 464
Fats = 343
Osteorized feeding
Start osteorized feeding based on the ff computation (same)
Divided into 6 equal feeding
Please provide sterile H2O after each feeding
e.g. Px 8yo, 24.1 kg (ABW)
IBW 24 kg
Caloric req 7-9 yo = 80-90 cal/kg
CCU = 24 kg X 85 cal/kg = 2040 cal
3
rd
day = 2040 cal x 0.75 = 1530 ~ 1500
6
LYMPHADENOPATHY
1 cm cervical & axillary LN
1.5 cm inguinal LN
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
1.005 1.020
Dehydration is not enough
Adolescence 10 18 females
12 20 males
Childhood 2 12 yrs old
Infant to 2 years old
URINE OUTPUT
(1 cc/kg/hr)
Pedia: 1-3 cc/kg
Adult: 3 cc/kg/hr
ANEMIA
Hgb 10 12 g/dl = mild
8 10 g/dl = moderate
< 8 g/dl = severe
CRYSTALLOIDS:
PLR
PNSS
D5 H2O
D5 0.3 NaCl
COLLOIDS:
Albumin
Voluven
Hesteril
TORNIQUET TEST/RUMPLL
MAP = > SYSTOLIC DIASTOLIC
* Inflate for 5 minutes
* + volar area 1 inch distal to antecubital fossa of about 1 inch
* + petechial rashes of > 20
DHF STAGING
I Febrile stage (1-7 days)
II Afebrile stage (3-4 days)
III Convolescent stage
DHF GRADING
I Anorexia , vomiting, convulsion, restless
Flushes skin, + tourniquet test, abdominal pain, hepatomegaly
Pleural effusion (unilateral/bilateral), constipation, abdominal
distention
II Gum bleeding, epistaxis, petechiae on palate & axillae, rashes on
extremities (SPONTANEOUS BLEEDING)
III Chest pain, cough, lethargy, violaceous skin, flushed face
Purpura, hematemesis, hemoptysis, melena
Cold clammy extremity, shock, ecchymosis
(COMPENSATED SHOCK)
IV Profound shock (UNCOMPENSATED SHOCK)
APGAR
(1953 Invented by Virginia Apgar)
1 - assess for the need of resuscitation
5 - assessment of resuscitation/prognosis of patient
**APGAR does not predict neurological damage
APGAR 0 1 2
Appearance Blue, pale extremity
& trunk
Blue extremity, pink
trunk
Completely pink
Pulse Absent < 100 > 100
Grimace (-) response Grimace Cry, cough,
sneeze
Activity Limp Some flexion of
extremity
Active motor
Respiration Absent Slow, irregular Good strong cry
Score: 7-10 = vigorous infant
4-6 = mild mod asphyxia 100% O2 face mask
<3 = severe asphyxia intubate
15 chest compression 2 puffs
32 chest compression 2 puffs
> 5 min heart stops 50% chance survival
> 10 min heart stops 0% chance survival
ECG
V3R right, 5
th
ICS MCL
V4R right, 5
th
ICS AAL
V1 left, 5
th
ICS AL
PICCU INSTRUMENTS
1. Suction unit
2. Mechanical vent
3. Syringe pump
4. Pulse oximeter
5. Infusion pump
6. Soluset w/ microset
7. Macroset
8. Platelet set
9. Blood set
10. Billy light (20 W x 10 bulb x 20 inches)
11. Neovent/infant ventilator
12. Cardiac monitor
13. IV stand
FEBRILE SEIZURE
Age: between 9 mos 5 yrs
Temp: 39C above
Seizure: generalized, tonic-clonic
Duration: few seconds 10 min
Others: followed by postical period of drowsiness
Rule out: meningitis by lumbar tap
Treatment: oral diazepam, 0.3 mg/kg q 8h
(1 mg/kg/24 hr) for 2-3 days
AMOEBIASIS
Entamoeba histolytica (protozoan parasite)
Transmission: fecal contamination of food or hands, may also be
transmitted by anal intercourse
Pathologic feature: flask-shape ulcers in submucous due to lytic
digestion
Diagnosis: E. histolytica in stool, tissues or aspirate, etc
Treatment: Metronidazole
7
WATERLOW CLASSIFICATION
WASTING = Actual weight (kg) x 100
p50 weight for height
STUNTING = actual height (cm) x 100
p50 height for age
WASTING: > 90 normal
81-90 mild
70-80 moderate
< 70 severe
STUNTING: > 95 normal
90-95 mild
85-89 moderate
<85 severe
IDEAL BODY WEIGHT (Filipino: 3000 gms)
< 6 mos = age (mos) x 600 + BW (gm)
6-12 mos = age (mos) x 500 + BW (gm)
1-6 yrs = age (yrs) x 2 + 8
7-12 yrs = age (yrs) x 7 5/2
USUAL CHANGES IN WT AT DIFF AGES
4-5 mos = 2 x BW
1 yr = 3 x BW
2 yrs = 4 x BW
3 yrs = 5 x BW
5 yrs = 6 x BW
7 yrs = 7 x BW
10 yrs = 10 x BW
LENGTH/HEIGHT COMPUTATION
At birth = 50 cm
0-3 mos = + 9 cm
3-6 mos = + 8 cm
6-9 mos = + 5 cm
9-12 mos = + 3 cm
2-12 yrs = age x 5 + 80
HEAD CIRCUMFERENCE COMPUTATION
At birth = 35 cm (13-118 inch)
<4 mos = 2 inch (1/2 inch/mos)
5-12 mos = 2 inch (1/4 inch/mos)
2 yrs = 1 inch
3-5 yrs = 1.5 inch (1/2 inch/yr)
6-20 yrs = 1.5 inch (1/2 inch/5 yrs)
TEMPERATURE
Normal: 37 +/ - 1.0 1.5 C
Decrease: early morning
Increase: late afternoon
RESPIRATORY RATE
(Harriet lane handbook 17
th
ed)
NORMAL:
0-1 yr = 24-38 cpm
1-3 yrs = 22-30 cpm
4-6 yrs = 20-24 cpm
7-9 yrs = 18-24 cpm
10-14 yrs = 16-22 cpm
14-18 yrs = 14-20 cpm
TACHYPNEA:
0-2 mos 60
2-12 mos 50
BLOOD PRESSURE COMPUTATION
SYSTOLIC DIASTOLIC
0-12 mos 90-110 mmHg 55-75 mmHg
1-2 yrs 90-110 mmHg 55-75 mmHg
3 yrs = age x 2 + 70
FONTANELS
At birth: 2 x 2 cm (anterior)
Closes at: 9 18 mos (anterior)
6 8 mos (posterior)
HEART RATE
Premature 120-170
0-3 mos 100-150
3-6 mos 90-120
6-12 mos 80-120
1-3 yrs 70-110
3-6 yrs 65-110
6-12 yrs 60-95
12 yrs 55-85
ACID BASE BALANCE (ABG)
Normal (N): normal acid base balance
pH PaCO2 HCO3 BE
Respiratory acidosis
Uncompensated N N
Partly
Compensated N
Respiratory alkalosis
Uncompensated N N
Partly
Compensated N
Metabolic acidosis
Uncompensated N
Partly
Compensated N
Metabolic alkalosis
Uncompensated N
Partly
Compensated N
GUIDELINES FOR BLOOD TRANSFUSION
Cryoprecipitate is administered using blood set/macroset and transfused fast
drip unless otherwise indicated
Platelet concentrate administered using platelet set and transfused fast drip
unless otherwise indicated
Pheresed platelet 1 U is equivalent to 6 to 14 U of randomly collected
platelet concentrate transfuse using platelet set
PRBC/FWB is administered using blood set and transfused within 6 8
hours
FFP is administered using blood set/macroset and transfused for two hours
unless otherwise indicated
COMPUTATION FOR PRBC
For:
(Desired Hct Actual Hct) x weight
Desired Hct = 40% for full concentration
30% for WBC which are
Content of PRBC
RBC = 200 cc
Anticoagulant = 50 cc
1 pack RBC = 250 cc
Evidence Based Study
Give diphenhydramine 30 min 1 hr pre-BT
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pocket PediaeditedDokument9 SeitenPocket Pediaeditedjandale100% (1)
- Drugs For Tickler PDFDokument3 SeitenDrugs For Tickler PDFBobet ReñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (666582801) MKDDokument11 Seiten(666582801) MKDEdison Tan Santamaria100% (1)
- Drug HandBookDokument10 SeitenDrug HandBookAhmed FekryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia NotesDokument97 SeitenPedia NotesChristian Dave DoctoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pocket PediaDokument15 SeitenPocket PediaChai Gabayeron100% (1)
- RHU Blue Book 6 - 070852 1Dokument14 SeitenRHU Blue Book 6 - 070852 1Jm Jm100% (1)
- Pedia TicklerDokument71 SeitenPedia TicklermikayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beta-Lactams Cephalosporins: Phenoxymethyl PenicillinDokument3 SeitenBeta-Lactams Cephalosporins: Phenoxymethyl PenicillinBobet ReñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric DosesDokument2 SeitenPaediatric DosesEdio PathicNoch keine Bewertungen
- IV FLUIDS Drugs and DosagesDokument3 SeitenIV FLUIDS Drugs and Dosagesdoc_geloNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMC PediaDokument4 SeitenBMC PediaRenette Uy100% (1)
- Approach in Children With SeizuresDokument26 SeitenApproach in Children With SeizuresMD Luthfy LubisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia NotesDokument3 SeitenPedia NotesNikki DiocampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Values HR RR BPDokument28 SeitenNormal Values HR RR BPKthrine CrronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Drugs Used in The Out Patient DepartmentDokument1 SeiteCommon Drugs Used in The Out Patient DepartmentRenatoCosmeGalvanJuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs and DosagesDokument4 SeitenDrugs and DosagesDin-Din Que33% (3)
- Pedia DosesDokument7 SeitenPedia DosesSai Krishna MaddiralaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tickler Print PediaDokument8 SeitenTickler Print PediaCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs & DosagesDokument29 SeitenDrugs & DosagesCristina VelasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dem Tickler NotesDokument1 SeiteDem Tickler NotesSeff CausapinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moonlighting 101Dokument20 SeitenMoonlighting 101Dayanara Gener100% (1)
- Pedia EZ Notes PDFDokument102 SeitenPedia EZ Notes PDFLuisa Paula LioanagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elsharnoby Pediatric Made Easy Up Load Waheed Tantawy 2014Dokument160 SeitenElsharnoby Pediatric Made Easy Up Load Waheed Tantawy 2014Emad AdelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calcium 1000mg or 1.5 G + Vit D (Enhances Absorption) 400-600 IU/ DayDokument1 SeiteCalcium 1000mg or 1.5 G + Vit D (Enhances Absorption) 400-600 IU/ DayRie PangilinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intern TicklerDokument10 SeitenIntern TicklerRem AlfelorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cheat Sheet (Draft)Dokument3 SeitenCheat Sheet (Draft)bonziebuddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tickler 20print 202Dokument7 SeitenTickler 20print 202Clav RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- TicklerDokument37 SeitenTicklerLuis Elijah De CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia MKD Notes and OthersDokument18 SeitenPedia MKD Notes and OthersRamon GodienesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Doses For Commonly Used OTCsDokument7 SeitenPediatric Doses For Commonly Used OTCsCharles Xavier KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- (HGT X 18.18) 140 Units 20Dokument3 Seiten(HGT X 18.18) 140 Units 20Jorelyn FriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- TicklerDokument11 SeitenTicklerJustine Issa YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Price TNMSCDokument13 SeitenDrug Price TNMSCdrtpkNoch keine Bewertungen
- TICKLER-PRINT Pedia PDFDokument8 SeitenTICKLER-PRINT Pedia PDFCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tickler PDFDokument177 SeitenTickler PDFQueenie FarrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia TicklersDokument24 SeitenPedia Ticklersjoshua espirituNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP Notes-1Dokument126 SeitenGP Notes-1Fida AnjumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common TreatmentsDokument5 SeitenCommon TreatmentsRaj MandumulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Tickler by RemDokument7 SeitenPediatric Tickler by RemRem AlfelorNoch keine Bewertungen
- TICKLER-PRINT-2 Pedia PDFDokument7 SeitenTICKLER-PRINT-2 Pedia PDFCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intern's Lecture On Pediatric Computation of MedicationsDokument26 SeitenIntern's Lecture On Pediatric Computation of MedicationsTrish SantosidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEDIA ER FormularyDokument1 SeitePEDIA ER FormularyAnonymous ic2CDkFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Notes Draft 12 1Dokument98 SeitenPediatric Notes Draft 12 1Aljon S. TemploNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ok Ok Notes PediaDokument14 SeitenOk Ok Notes PediaChristian PasicolanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia TicklerDokument9 SeitenPedia TicklerDianeAbonita100% (2)
- PediaidiotnotesDokument13 SeitenPediaidiotnotesLeiza Tabora96% (23)
- Pedia NotesDokument2 SeitenPedia NotesPaolo EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia NotesDokument8 SeitenPedia NotesQurrataini IbanezNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Intern Guide Quick NotesDokument8 SeitenNew Intern Guide Quick NotesTrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia CardDokument4 SeitenPedia CardPatricia Kate RegalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simplified Diagnostic Approach in Acute HepatitisDokument2 SeitenSimplified Diagnostic Approach in Acute HepatitisJohn Christopher LucesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia NotesDokument9 SeitenPedia NotesJitendra ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Prescribed DrugsDokument33 SeitenCommon Prescribed DrugsGlessica You50% (4)
- Dosage Calculation 09.04.21Dokument24 SeitenDosage Calculation 09.04.21PHARMACOLOGY SMVMCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials for Practice of Medicine in the Frontline: From Tropical Africa; Pleasantly Different Volume 2Von EverandEssentials for Practice of Medicine in the Frontline: From Tropical Africa; Pleasantly Different Volume 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- CLINICAL HISTORY AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS AT YOUR FINGERTIPSVon EverandCLINICAL HISTORY AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS AT YOUR FINGERTIPSNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCH301Dokument19 SeitenBCH301yabdallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meal Mentor Sample Meal PlanDokument20 SeitenMeal Mentor Sample Meal Planverdes nicoletaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tai Sophia Institute Whole Foods Cooking Lab 4 Nutrition 684 Fall 2012 .5 Credits FacultyDokument5 SeitenTai Sophia Institute Whole Foods Cooking Lab 4 Nutrition 684 Fall 2012 .5 Credits Facultyapi-96990759Noch keine Bewertungen
- Malnutrition: Intervention Plan Nursing Intervention Method of Nurse Family Contact Resource RequiredDokument1 SeiteMalnutrition: Intervention Plan Nursing Intervention Method of Nurse Family Contact Resource RequiredSareno PJhēaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balanced DietDokument10 SeitenBalanced DietMsKhan0078100% (1)
- Feed Your Flora: How To Promote Healthy Gut Bacteria: Steven Lalevich, RDDokument16 SeitenFeed Your Flora: How To Promote Healthy Gut Bacteria: Steven Lalevich, RDDraganMilenkovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagrama en BlancoDokument1 SeiteDiagrama en BlancoDIEGO ANDRES GIRALDO UTRIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Part A AppendicitisDokument6 SeitenReading Part A Appendicitisfernanda1rondelli0% (2)
- Dona Remedios Trinidad Romualdez Medical Foundation College of NursingDokument3 SeitenDona Remedios Trinidad Romualdez Medical Foundation College of NursingRoyce Vincent Tizon100% (3)
- TDEE Variant With BF 3.06Dokument10 SeitenTDEE Variant With BF 3.06Collette PetitNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANS 312 - Applied Animal Nutrition Feedstuffs and Ration Formulation - OSU Extended Campus - Oregon State UniversityDokument4 SeitenANS 312 - Applied Animal Nutrition Feedstuffs and Ration Formulation - OSU Extended Campus - Oregon State UniversityRAHULNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSV Eraser BoostDokument51 SeitenHSV Eraser BoostObaraMeyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 82 Soal Bahasa Inggris Wajib Kelas Xi Pas 19-20 EditDokument10 Seiten82 Soal Bahasa Inggris Wajib Kelas Xi Pas 19-20 EditStudio 5x7Noch keine Bewertungen
- BenfotiamineDokument5 SeitenBenfotiaminekether.thipharet5601Noch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Nutrition Full BibDokument363 SeitenPrinciples of Nutrition Full BibNicole DávalosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dietary Supplements, B. Brian HaycockDokument167 SeitenDietary Supplements, B. Brian HaycockCONNAN73100% (2)
- Healing Powers of AyurvedaDokument2 SeitenHealing Powers of AyurvedaAditya DevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Braden Scale For Predicting Pressure Ulcer RiskDokument1 SeiteBraden Scale For Predicting Pressure Ulcer RiskJian CarloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land Consolidation in RwandaDokument18 SeitenLand Consolidation in RwandaAlex NkurunzizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mesotherapy by Institute BCN EnesfrDokument32 SeitenMesotherapy by Institute BCN Enesfrmarketing4558Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pineal XTDokument3 SeitenPineal XTMr TellerzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Susah BabDokument45 SeitenSusah BabaghniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Related LiteratureDokument3 SeitenReview of Related LiteratureAlex GarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jdfhs 292016Dokument3 SeitenJdfhs 292016albarracinclark484Noch keine Bewertungen
- HepatocytesDokument38 SeitenHepatocytesapi-327824087Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mohammad Ali LeghariDokument64 SeitenMohammad Ali LeghariNaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 501 Critical Reading QuestionsDokument283 Seiten501 Critical Reading QuestionsMenhaj Fatemioun100% (1)
- Research Questionnaire: Direction: Put A Check Under The Column That Best Suit Your ExperienceDokument2 SeitenResearch Questionnaire: Direction: Put A Check Under The Column That Best Suit Your ExperienceChloie Marie RosalejosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquaculture: Producing Aqua Feed PelletsDokument6 SeitenAquaculture: Producing Aqua Feed PelletsInternational Aquafeed magazineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malnutrition in Acute Care Patients: A Narrative Review: Cathy Kubrak, Louise JensenDokument19 SeitenMalnutrition in Acute Care Patients: A Narrative Review: Cathy Kubrak, Louise JensenchanchandilNoch keine Bewertungen