Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture 8
Hochgeladen von
Kunal AroraCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture 8
Hochgeladen von
Kunal AroraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Neural Networks:
Representation
Non-linear
hypotheses
Machine Learning
Andrew Ng
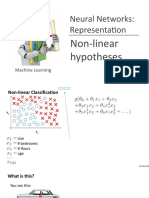
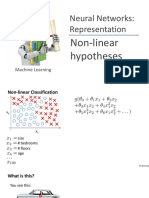
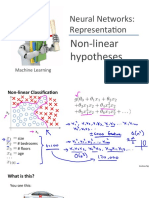
Non-linear Classification
x
1
x
2
size
# bedrooms
# floors
age
Andrew Ng
You see this:
But the camera sees this:
What is this?
Andrew Ng
Computer Vision: Car detection
Testing:
What is this?
Not a car Cars
Andrew Ng
Learning
Algorithm
pixel 1
pixel 2
pixel 1
pixel 2
Raw image
Cars
Non-Cars
Andrew Ng
pixel 1
pixel 2
Raw image
Cars
Non-Cars
Learning
Algorithm
pixel 1
pixel 2
Andrew Ng
pixel 1
pixel 2
Raw image
Cars
Non-Cars
50 x 50 pixel images 2500 pixels
(7500 if RGB)
pixel 1 intensity
pixel 2 intensity
pixel 2500 intensity
Quadratic features ( ): 3 million
features
Learning
Algorithm
pixel 1
pixel 2
Neural Networks:
Representation
Neurons and
the brain
Machine Learning
Andrew Ng
Neural Networks
Origins: Algorithms that try to mimic the brain.
Was very widely used in 80s and early 90s; popularity
diminished in late 90s.
Recent resurgence: State-of-the-art technique for many
applications
Andrew Ng
Auditory cortex learns to see
Auditory Cortex
The one learning algorithm hypothesis
[Roe et al., 1992]
Andrew Ng
Somatosensory cortex learns to see
Somatosensory Cortex
The one learning algorithm hypothesis
[Metin & Frost, 1989]
Andrew Ng
Seeing with your tongue
Human echolocation (sonar)
Haptic belt: Direction sense Implanting a 3
rd
eye
Sensor representations in the brain
[BrainPort; Welsh & Blasch, 1997; Nagel et al., 2005; Constantine-Paton & Law, 2009]
Neural Networks:
Representation
Machine Learning
Model
representation I
Andrew Ng
Neuron in the brain
Andrew Ng
Neurons in the brain
[Credit: US National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging]
Andrew Ng
Neuron model: Logistic unit
Sigmoid (logistic) activation function.
Andrew Ng
Neural Network
Layer 3 Layer 1 Layer 2
Andrew Ng
Neural Network
activation of unit in layer
matrix of weights controlling
function mapping from layer to
layer
If network has units in layer , units in layer , then
will be of dimension .
Neural Networks:
Representation
Model
representation II
Machine Learning
Andrew Ng
Add .
Forward propagation: Vectorized implementation
Andrew Ng
Layer 3 Layer 1 Layer 2
Neural Network learning its own features
Andrew Ng
Layer 3 Layer 1 Layer 2
Other network architectures
Layer 4
Neural Networks:
Representation
Examples and
intuitions I
Machine Learning
Andrew Ng
Non-linear classification example: XOR/XNOR
, are binary (0 or 1).
x
1
x
2
x
1
x
2
Andrew Ng
Simple example: AND
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
1.0
Andrew Ng
Example: OR function
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
-10
20
20
Neural Networks:
Representation
Examples and
intuitions II
Machine Learning
Andrew Ng
Negation:
0
1
Andrew Ng
Putting it together:
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
-30
20
20
10
-20
-20
-10
20
20
Andrew Ng
Neural Network intuition
Layer 3 Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 4
Andrew Ng
Handwritten digit classification
[Courtesy of Yann LeCun]
Andrew Ng
Handwritten digit classification
[Courtesy of Yann LeCun]
Andrew Ng
Andrew Ng
Neural Networks:
Representation
Multi-class
classification
Machine Learning
Andrew Ng
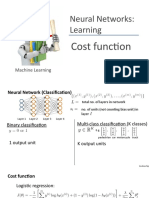
Multiple output units: One-vs-all.
Pedestrian Car Motorcycle Truck
Want , , , etc.
when pedestrian when car when motorcycle
Andrew Ng
Multiple output units: One-vs-all.
Want , , , etc.
when pedestrian when car when motorcycle
Training set:
one of , , ,
pedestrian car motorcycle truck
Andrew Ng
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- TensorFlow in 1 Day: Make your own Neural NetworkVon EverandTensorFlow in 1 Day: Make your own Neural NetworkBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (8)
- Neural Networks: Representation: Non-Linear HypothesesDokument35 SeitenNeural Networks: Representation: Non-Linear HypothesesAbhinav BhargavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neural Networks: Representation: Non-Linear HypothesesDokument34 SeitenNeural Networks: Representation: Non-Linear HypothesesaneeslayasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Image Classification: Step-by-step Classifying Images with Python and Techniques of Computer Vision and Machine LearningVon EverandImage Classification: Step-by-step Classifying Images with Python and Techniques of Computer Vision and Machine LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture8 PDFDokument42 SeitenLecture8 PDFsoongbinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning Part 8Dokument42 SeitenMachine Learning Part 8Sujit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slide 7 - Neural NetworksDokument64 SeitenSlide 7 - Neural NetworksLôny NêzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neural Networks: Representa1on: Non - Linear HypothesesDokument34 SeitenNeural Networks: Representa1on: Non - Linear HypothesesAnilSiwakotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine LearningDokument109 SeitenMachine LearningSiddharth JawaharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Linear Hypotheses: Neural Networks: RepresentationDokument7 SeitenNon-Linear Hypotheses: Neural Networks: RepresentationMuneeb ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 14 (NN)Dokument49 SeitenWeek 14 (NN)Muhammad TalhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applica'on Example: Photo OCR Problem Descrip'on and PipelineDokument29 SeitenApplica'on Example: Photo OCR Problem Descrip'on and PipelineDibaMasoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neural Networks: Learning: Cost FunctionDokument33 SeitenNeural Networks: Learning: Cost FunctionLydia DarlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MachineLearning Fall2019Dokument88 SeitenMachineLearning Fall2019chandna.atuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome: Machine LearningDokument39 SeitenWelcome: Machine LearningTailai ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture1 PDFDokument39 SeitenLecture1 PDFRonildo OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DL Lab Assignment - 05Dokument3 SeitenDL Lab Assignment - 05Professor ExeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome: Machine LearningDokument31 SeitenWelcome: Machine LearningBùi Hữu ThịnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Learning Andrew NGDokument173 SeitenDeep Learning Andrew NGkanakamedala sai rithvik100% (3)
- Docs Slides Lecture1Dokument31 SeitenDocs Slides Lecture1PravinkumarGhodakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning Engineer Nanodegree: Capstone ProposalDokument3 SeitenMachine Learning Engineer Nanodegree: Capstone ProposalKhalil HenchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNN vs. RNN vs. ANN - Analysing 3 Types of Neural Networks in Deep LearningDokument10 SeitenCNN vs. RNN vs. ANN - Analysing 3 Types of Neural Networks in Deep LearningKarol SkowronskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applica'on Example: Photo OCR Problem Descrip'on and PipelineDokument29 SeitenApplica'on Example: Photo OCR Problem Descrip'on and Pipelineone leonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neural Network PresentationDokument33 SeitenNeural Network Presentationhrlive123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning Part 9Dokument33 SeitenMachine Learning Part 9Sujit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Image Scrambling Through Two Level Arnold TransformDokument9 SeitenImage Scrambling Through Two Level Arnold TransformArooj MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT-1 Foundations of Deep LearningDokument51 SeitenUNIT-1 Foundations of Deep Learningbhavana100% (1)
- AZ AI Lec 08 Machine Learing1Dokument60 SeitenAZ AI Lec 08 Machine Learing1Ahmed MagedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Unit1 MIDokument117 SeitenDeep Unit1 MIParinitha B SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neural Networks and Deep Learning: Deeplearning - Ai-SummaryDokument24 SeitenNeural Networks and Deep Learning: Deeplearning - Ai-SummaryJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introductory Guide To Deep Learning and Neural Networks (Notes From Deeplearning - Ai Course #1)Dokument17 SeitenAn Introductory Guide To Deep Learning and Neural Networks (Notes From Deeplearning - Ai Course #1)fpttmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neural Networks and Deep LearningDokument19 SeitenNeural Networks and Deep LearningNitesh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artilligence: Ieee EurekaDokument49 SeitenArtilligence: Ieee EurekaSpammerNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide To Image Captioning. How Deep Learning Helps in CaptioningDokument17 SeitenA Guide To Image Captioning. How Deep Learning Helps in CaptioningrajitkurupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Driverless Car: Autonomous Driving Using Deep Reinforcement Learning in Urban EnvironmentDokument6 SeitenDriverless Car: Autonomous Driving Using Deep Reinforcement Learning in Urban EnvironmentRenan PortoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Object Detection SystemDokument31 SeitenReal Time Object Detection SystemNCEIPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Learning by AndrewNG Tutorial NotesDokument298 SeitenDeep Learning by AndrewNG Tutorial NotesRamesh Kumar MojjadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- cs229 Notes1Dokument5 Seitencs229 Notes1fatihy73Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning: WelcomeDokument27 SeitenMachine Learning: WelcomePooja KabadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning Engineer Nanodegree: Capstone ProposalDokument11 SeitenMachine Learning Engineer Nanodegree: Capstone ProposalKhalil HenchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument19 SeitenChapter 1nayera279Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial On DNN 1 of 9 Background of DNNsDokument65 SeitenTutorial On DNN 1 of 9 Background of DNNsAbdullah Al ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helmet and Vehicle License Plate Detection SystemDokument26 SeitenHelmet and Vehicle License Plate Detection SystemAmshuman GkNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 3 Self NotesDokument5 SeitenUNIT 3 Self NotesjainayushtechNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Ingression Into Deep Learning - FPDokument17 SeitenAn Ingression Into Deep Learning - FPrammilan kushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convolutional Neural Network: by Gagandeep KaurDokument107 SeitenConvolutional Neural Network: by Gagandeep Kaurjamiesonlara100% (1)
- Large Scale Machine LearningDokument24 SeitenLarge Scale Machine LearningPravinkumarGhodakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bee4333 Intelligent Control: Artificial Neural Network (ANN)Dokument76 SeitenBee4333 Intelligent Control: Artificial Neural Network (ANN)WanM.SyamimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Questions To Test Your Skills On CNN Convolutional Neural NetworksDokument11 Seiten20 Questions To Test Your Skills On CNN Convolutional Neural NetworksKumkumo Kussia KossaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invention (STG v1) IN8-2016-1688Dokument11 SeitenInvention (STG v1) IN8-2016-1688Abhishek DasguptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic: Convolution Neural Network: Presented byDokument13 SeitenTopic: Convolution Neural Network: Presented byahmad wattooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Learning: Alberto EzpondaburuDokument58 SeitenDeep Learning: Alberto EzpondaburuJorge MerinoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eccv10 Tutorial Part4Dokument52 SeitenEccv10 Tutorial Part4jatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- R-CNN (Object Detection) - A Beginners Guide To One of The Most - by Sharif Elfouly - MediumDokument6 SeitenR-CNN (Object Detection) - A Beginners Guide To One of The Most - by Sharif Elfouly - MediumAmirhossein SalekniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8765-Article Text-15709-1-10-20210611Dokument8 Seiten8765-Article Text-15709-1-10-20210611TefeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument24 SeitenLecture 1Lydia DarlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Learning by Andrew NGDokument34 SeitenDeep Learning by Andrew NGHarsh AsthanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSED Final ExamDokument13 SeitenCSED Final ExamVishal SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADA Project Report - 2 067Dokument9 SeitenADA Project Report - 2 067Jai ChaudhryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compiler FileDokument18 SeitenCompiler FileKunal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MultimediaDokument52 SeitenMultimediaVenkata Sai Manikanta ManugulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microwave NotesDokument21 SeitenMicrowave NotesKunal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multimedia Presentation - PC VideoDokument18 SeitenMultimedia Presentation - PC VideoKunal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NFA To DFADokument18 SeitenNFA To DFARaquel PatiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Reality PresentationDokument39 SeitenVirtual Reality PresentationKunal Arora100% (1)
- Interval Selection EnglishDokument1 SeiteInterval Selection EnglishKunal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 CommunicationDokument18 Seiten01 CommunicationInSha RafIqNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSNSITDokument3 SeitenASSNSITKunal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 WebDokument2 Seiten1 Webkrutil76652Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 WebDokument2 Seiten1 Webkrutil76652Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mirza ThesisDokument163 SeitenMirza ThesisKunal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex 2Dokument13 SeitenEx 2louietgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stanford Machine Learning Exercise 1Dokument15 SeitenStanford Machine Learning Exercise 1MaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Getting Started in Sport of ProgrammingDokument15 SeitenGetting Started in Sport of ProgrammingheavonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex 6Dokument16 SeitenEx 6api-322416213Noch keine Bewertungen
- NSITDokument1 SeiteNSITAnubhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 1 - Introduction To Binary TreesDokument27 SeitenSection 1 - Introduction To Binary Treesblack Snow100% (1)
- Allotment 1 PDFDokument1 SeiteAllotment 1 PDFKunal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- STL Quick ReferenceDokument8 SeitenSTL Quick ReferenceSneetsher Crispy100% (1)
- Generic Resume Template FOR NSITDokument1 SeiteGeneric Resume Template FOR NSITsmodi20Noch keine Bewertungen
- It 4th - NewDokument2 SeitenIt 4th - NewKunal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSITDokument1 SeiteNSITAnubhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- JK Singh Ece Section 1Dokument7 SeitenJK Singh Ece Section 1Kunal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Install Flash Player On UbuntuDokument2 SeitenHow To Install Flash Player On UbuntuIgor Franzoni OkuyamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CertificateDokument1 SeiteCertificateKunal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 GREAT PUZZLES TO SHARPEN YOUR BRAIN (With Detailed Answers)Dokument54 Seiten100 GREAT PUZZLES TO SHARPEN YOUR BRAIN (With Detailed Answers)KVignesh100% (6)
- Teaching Mathematics Content Through Explicit TeachingDokument39 SeitenTeaching Mathematics Content Through Explicit Teachingronna drio100% (1)
- WallthicknessDokument1 SeiteWallthicknessGabriela MotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide To Sample Size For Animal-Based Studies (VetBooks - Ir)Dokument292 SeitenA Guide To Sample Size For Animal-Based Studies (VetBooks - Ir)Jonathan MannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lifecycle of A Butterfly Unit Lesson PlanDokument11 SeitenLifecycle of A Butterfly Unit Lesson Planapi-645067057Noch keine Bewertungen
- LITERARY THEORY BY TERRY EAGLETON NotesDokument6 SeitenLITERARY THEORY BY TERRY EAGLETON NotesPrachi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.1 Hydrostatic Force On Curved Surfaces - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsDokument4 Seiten4.1 Hydrostatic Force On Curved Surfaces - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsRUSSELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mi Account ေက်ာ္နည္းDokument16 SeitenMi Account ေက်ာ္နည္းamk91950% (2)
- HyperconnectivityDokument5 SeitenHyperconnectivityramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Statistics: Fourth Canadian EditionDokument41 SeitenBusiness Statistics: Fourth Canadian EditionTaron AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climatol GuideDokument40 SeitenClimatol GuideFressiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DICKSON KT800/802/803/804/856: Getting StartedDokument6 SeitenDICKSON KT800/802/803/804/856: Getting StartedkmpoulosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science, Technology and Society Module #1Dokument13 SeitenScience, Technology and Society Module #1Brent Alfred Yongco67% (6)
- The Genius of Marie Curie Shohini GhoseDokument4 SeitenThe Genius of Marie Curie Shohini GhoseMarta HrynyovskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Axial and Torsional ElementsDokument57 SeitenChapter 2 Axial and Torsional ElementsAhmad FaidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GARCH (1,1) Models: Ruprecht-Karls-Universit at HeidelbergDokument42 SeitenGARCH (1,1) Models: Ruprecht-Karls-Universit at HeidelbergRanjan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Assessment For Harmonic Measurement Study ProcedureDokument13 SeitenRisk Assessment For Harmonic Measurement Study ProcedureAnandu AshokanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Quality Lab Manual (EE-801)Dokument12 SeitenPower Quality Lab Manual (EE-801)ASHU KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Email ID: Contact No: +971562398104, +917358302902: Name: R.VishnushankarDokument6 SeitenEmail ID: Contact No: +971562398104, +917358302902: Name: R.VishnushankarJêmš NavikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay G30 ManualDokument42 SeitenRelay G30 ManualLeon KhiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.1 Essential Concepts: 1.1 What and How? What Is Heat Transfer?Dokument151 SeitenCh.1 Essential Concepts: 1.1 What and How? What Is Heat Transfer?samuel KwonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Science PedagogyDokument4 SeitenSocial Science PedagogyrajendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BC 672772 RBRS Service TraningDokument385 SeitenBC 672772 RBRS Service TraningTeknik Makina100% (2)
- Aquinas Five Ways To Prove That God Exists - The ArgumentsDokument2 SeitenAquinas Five Ways To Prove That God Exists - The ArgumentsAbhinav AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Package-Related Thermal Resistance of Leds: Application NoteDokument9 SeitenPackage-Related Thermal Resistance of Leds: Application Notesalih dağdurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer:: Exercise-IDokument15 SeitenAnswer:: Exercise-IAishika NagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introducing Eventstorming-4Dokument1 SeiteIntroducing Eventstorming-4Alex TrujilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastone Petrini: Strutture e Costruzioni Autarchiche Di Legno in Italia e Colonie Caratteri e CriterDokument9 SeitenGastone Petrini: Strutture e Costruzioni Autarchiche Di Legno in Italia e Colonie Caratteri e CriterPier Pasquale TrausiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sai Deepa Rock Drills: Unless Otherwise Specified ToleranceDokument1 SeiteSai Deepa Rock Drills: Unless Otherwise Specified ToleranceRavi BabaladiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power - Factor - Correction - LegrandDokument24 SeitenPower - Factor - Correction - LegrandrehanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Painter GR55Dokument17 SeitenReport Painter GR55Islam EldeebNoch keine Bewertungen