Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Angle and Types of Angles
Hochgeladen von
Benjamin DennisOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Angle and Types of Angles
Hochgeladen von
Benjamin DennisCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Angle and Types of Angles
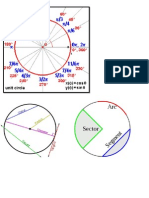
Angle
An angle is the intersection of two rays with a common endpoint. There are different types of angles, These types
are acute, right, obtuse, straight and reflect
Acute Angle
An acute angle is an angle whose measure is less than 90
Right Angle
A right angle is an angle whose measure is 90.
Obtuse Angle
An obtuse angle is an angle whose measure is more than 90, but less than 180
Straight Angle
A straight angle is an angle whose measure is 180.
Reflex Angle
A reflex angle is an angle whose measure is more than 180.
Difference Between Square And Square Root
Square
A "square" is the result of multiplying a number by itself."Squared" is often written as a little 2.
For example:
The square of 3
2
is 9 because 3 x 3 = 9. (The little 2 says the number appears twice in multiplying)
Square Root
A "square root" is in the opposite exponential direction, you are finding the number which multiplied by itself will
equal your given number.
For example:
Using the same example, the square root of 9 is 3, because 3 x 3 = 9
Difference Between Cube And Cube Root
Cube
A cube is a number, just use it in a multiplication 3 times. we write down "3 Cubed" as 3
3
For example:
The square of 3
3
is 27 because 3 x 3 x 3 = 27. (The little 3 means the number appears three times in multiplying)
Cube root
A cube root is a number which has a special value that when it cubed it gives the original number.
For example:
The cube root of
3
27 is 3, because when 3 is cubed you get 27.
Difference Between Equations and Expressions
Equations Expressions
An equation is a Sentence.
One solves an equation.
An equation has a relation symbol.
An "equation" has a left side, a right side and an equal
sign separating the sides.
For Example
3x - 7 = 2
This is an EQUATION, because it has a left side, a right
side, and an = sign separating the two.
An expression is a PHRASE, a sentence fragment.
One simplifies an expression.
An expression has no relation symbol.
An "expression," doesn't have any sides.
For Example
3x - 7
This is an EXPRESSION, because there are no "sides"
and no = sign.
Michael Faraday
Faraday was a British chemist and physicist who contributed significantly to the study of electromagnetism and
electrochemistry.
Michael Faraday was born on 22 September 1791 in south London. His family was not well off and Faraday received
only a basic formal education. When he was 14, he was apprenticed to a local bookbinder and during the next seven
years, educated himself by reading books on a wide range of scientific subjects. In 1812, Faraday attended four
lectures given by the chemist Humphry Davy at the Royal Institution. Faraday subsequently wrote to Davy asking for
a job as his assistant. Davy turned him down but in 1813 appointed him to the job of chemical assistant at the Royal
Institution.
A year later, Faraday was invited to accompany Davy and his wife on an 18 month European tour, taking in France,
Switzerland, Italy and Belgium and meeting many influential scientists. On their return in 1815, Faraday continued to
work at the Royal Institution, helping with experiments for Davy and other scientists. In 1821 he published his work
on electromagnetic rotation (the principle behind the electric motor). He was able to carry out little further research
in the 1820s, busy as he was with other projects. In 1826, he founded the Royal Institution's Friday Evening
Discourses and in the same year the Christmas Lectures, both of which continue to this day. He himself gave many
lectures, establishing his reputation as the outstanding scientific lecturer of his time.
In 1831, Faraday discovered electromagnetic induction, the principle behind the electric transformer and generator.
This discovery was crucial in allowing electricity to be transformed from a curiosity into a powerful new technology.
During the remainder of the decade he worked on developing his ideas about electricity. He was partly responsible
for coining many familiar words including 'electrode', 'cathode' and 'ion'. Faraday's scientific knowledge was
harnessed for practical use through various official appointments, including scientific adviser to Trinity House (1836-
1865) and Professor of Chemistry at the Royal Military Academy in Woolwich (1830-1851).
As a chemist, Faraday discovered benzene, investigated the clathrate hydrate of chlorine, invented an early form of
the bunsen burner and the system of oxidation numbers, and popularized terminology such as anode, cathode,
electrode, and ion.
However, in the early 1840s, Faraday's health began to deteriorate and he did less research. He died on 25 August
1867 at Hampton Court, where he had been given official lodgings in recognition of his contribution to science. He
gave his name to the 'farad', originally describing a unit of electrical charge but later a unit of electrical capacitance.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MF 3854 WDDokument96 SeitenMF 3854 WDRizwanAli100% (1)
- Manual Hardware Lenovo Yoga BookDokument68 SeitenManual Hardware Lenovo Yoga BookRADU OCTAVIAN100% (2)
- Tugas Medan Elektromagnetik: Tokoh-Tokoh Yang Berjasa Di Bidang Elektromagnetik Dan MatematikDokument12 SeitenTugas Medan Elektromagnetik: Tokoh-Tokoh Yang Berjasa Di Bidang Elektromagnetik Dan MatematikGagah Indrasmara Agityasaputra ST.MMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physicists: Group 3Dokument14 SeitenPhysicists: Group 3Ebenezer RayosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euler Slides WpuDokument70 SeitenEuler Slides WpurolandoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legendre PDFDokument6 SeitenLegendre PDFPrashantNoch keine Bewertungen
- FaradayDokument2 SeitenFaradaynazkasihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Michael FaradayDokument2 SeitenMichael FaradayPrincess Meth Catubigan SarominesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Michael FaradayDokument3 SeitenMichael FaradayGaldinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alessandro Volta: Early Life and WorksDokument1 SeiteAlessandro Volta: Early Life and WorksLichun GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appolonius ProblemsDokument12 SeitenAppolonius Problemscsumbagambra100% (1)
- Mackay Early History of The Symmedian PointDokument12 SeitenMackay Early History of The Symmedian PointgrigoriytamasjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Greatest ScientistsDokument50 SeitenWorld Greatest ScientistsjiteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- At EeeeeeDokument5 SeitenAt Eeeeeelovelybasadre30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic PhysicsDokument8 SeitenAtomic PhysicsJahleel TroupeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Michael FaradayDokument15 SeitenMichael FaradayMatthew FrederickNoch keine Bewertungen
- ArbelosDokument14 SeitenArbelosmzambrano2Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Reconstructed Lesson PlanDokument6 SeitenA Reconstructed Lesson PlanPrecious BalgunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Michael Faraday 2Dokument6 SeitenMichael Faraday 2MihaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Who Was Michael Faraday? Biography Books Best Sellers | Children's Biography BooksVon EverandWho Was Michael Faraday? Biography Books Best Sellers | Children's Biography BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homogeneous Differential Equation-2Dokument9 SeitenHomogeneous Differential Equation-2gevansh0001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - 2 Title:: Page - 1 ObjectivesDokument20 SeitenLecture - 2 Title:: Page - 1 Objectivesr prathapNoch keine Bewertungen
- WAC RoughDokument8 SeitenWAC RoughMorgan SpooneybargerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Platonic SolidDokument12 SeitenPlatonic SoliddavparanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table of ElementsDokument22 SeitenPeriodic Table of ElementsVincent John M. SotalboNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Standard Electrical Dictionary A Popular Dictionary of Words and Terms Used in the Practice of Electrical EngineeringVon EverandThe Standard Electrical Dictionary A Popular Dictionary of Words and Terms Used in the Practice of Electrical EngineeringBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Articles: Why Ellipses Are Not Elliptic CurvesDokument14 SeitenArticles: Why Ellipses Are Not Elliptic CurvescoolsaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alexander Macfarlane: Open Main MenuDokument4 SeitenAlexander Macfarlane: Open Main Menulin ًNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermionic Emission 2Dokument6 SeitenThermionic Emission 2OTTO_Noch keine Bewertungen
- XII 22 Phy CH 15Dokument60 SeitenXII 22 Phy CH 15joelNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Elementary Set Theory - Bezhanishvili, LandrethDokument23 SeitenAn Introduction To Elementary Set Theory - Bezhanishvili, LandrethIrvin VillenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Platonic SolidsDokument4 SeitenPlatonic SolidsBryan Graczyk100% (1)
- Michael FaradayDokument33 SeitenMichael FaradayRezie Dampog DellavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Kepler PoinsotDokument21 SeitenThe Kepler PoinsotTan Looi SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euler Line PDFDokument29 SeitenEuler Line PDFΚώστας ΓιαννάκηςNoch keine Bewertungen
- Svante ArrheniusDokument3 SeitenSvante ArrheniusyusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biography of Charles Augustin CoulombDokument1 SeiteBiography of Charles Augustin CoulombEdmar Cordova VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euclidean GeometryDokument27 SeitenEuclidean GeometryFrancisco Gurrola100% (1)
- Report HistoryDokument20 SeitenReport HistoryFheng SuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book 3 PDFDokument15 SeitenBook 3 PDFBig FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math HHHDokument3 SeitenMath HHHLj SoquiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument7 SeitenPhysicsLopa Manish ShahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CirclesDokument6 SeitenCirclesBrent Garcia OrdillanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math (Script)Dokument2 SeitenMath (Script)afive5eeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics and Art:: Making Beautiful Music TogetherDokument109 SeitenMathematics and Art:: Making Beautiful Music TogetherLouis CubillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Famous PhysicistDokument28 SeitenFamous PhysicistRommel Villaroman EstevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Michael FaradayDokument19 SeitenMichael FaradayAnna DegamonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euclid's Elements Book IDokument6 SeitenEuclid's Elements Book IKitty CheungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alessandro VoltaDokument6 SeitenAlessandro Voltamanirup_tceNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT 111 NOTES - Electrical & Electronic FundamentalsDokument7 SeitenCT 111 NOTES - Electrical & Electronic FundamentalsMama JulietNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ernest RutherfordDokument4 SeitenErnest RutherfordyusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math and The Buckyball PDFDokument20 SeitenMath and The Buckyball PDFdomerrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4Dokument4 SeitenLecture 4Nguyễn HiềnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amedeo AvogadroDokument5 SeitenAmedeo Avogadrokhadeane wilsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dirac PDFDokument8 SeitenDirac PDFadilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atom's AssignmentDokument12 SeitenAtom's Assignmentbihaishak_268311918Noch keine Bewertungen
- Golden RatioDokument21 SeitenGolden RatioSalvator2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thales' Theorem - WikipediaDokument26 SeitenThales' Theorem - WikipediaRabi DanishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faraday WikiDokument105 SeitenFaraday WikiNilesh ThakreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neutral Geometry and The Independence of The Parallel PostulateDokument14 SeitenNeutral Geometry and The Independence of The Parallel PostulateWeston MuniakNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Five Platonic Solids Bahan Rujukan Tugasan GeometryDokument9 SeitenThe Five Platonic Solids Bahan Rujukan Tugasan Geometryyeokahhian82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Usability Engineering (Human Computer Intreraction)Dokument31 SeitenUsability Engineering (Human Computer Intreraction)Muhammad Usama NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Cryogenic Treatment On CompositesDokument14 SeitenEffect of Cryogenic Treatment On CompositesGauthamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDLCDokument2 SeitenSDLCTahseef RezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006 AcrotechDokument32 Seiten2006 Acrotechkaniappan sakthivelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bhavin Desai ResumeDokument5 SeitenBhavin Desai Resumegabbu_Noch keine Bewertungen
- RSC 406 (English)Dokument11 SeitenRSC 406 (English)Tuấn DũngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broadcast Tools Site Sentinel 4 Install Op Manual v2 12-01-2009Dokument41 SeitenBroadcast Tools Site Sentinel 4 Install Op Manual v2 12-01-2009testeemailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagram of Vitamix Blade Blade Assembly: InstructionsDokument5 SeitenDiagram of Vitamix Blade Blade Assembly: InstructionsRenato PurcinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model 7691Dokument1 SeiteModel 7691Khiết trầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Pressure Accessories CatalogDokument117 SeitenHigh Pressure Accessories CatalogRijad JamakovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- R10 On XPDokument182 SeitenR10 On XPadenihun Adegbite100% (1)
- ISO9001 2008certDokument2 SeitenISO9001 2008certGina Moron MoronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitac 6120N ManualDokument141 SeitenMitac 6120N ManualLiviu LiviuNoch keine Bewertungen
- JIS B 01801 - 000 - 000 - 1997 - e - pr10 - I4Dokument27 SeitenJIS B 01801 - 000 - 000 - 1997 - e - pr10 - I4Flavio ShiratoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centaour 50 Solar TurbineDokument2 SeitenCentaour 50 Solar TurbineTifano KhristiyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS5000 User's GuideDokument120 SeitenDS5000 User's Guidetinu_catarigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guideline G6 Certification Process v2 0Dokument18 SeitenGuideline G6 Certification Process v2 0Wong Wong WLNoch keine Bewertungen
- SC-HM910 - HM810 (sm-RQZM0167) PDFDokument104 SeitenSC-HM910 - HM810 (sm-RQZM0167) PDFJory2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Redutores SEWDokument154 SeitenManual Redutores SEWLucas Issamu Nakasone PauloNoch keine Bewertungen
- G249 MXBDokument8 SeitenG249 MXBAndres SorinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pest Control ChennaiDokument3 SeitenPest Control ChennaiControler33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sony Video Camera Manual PDFDokument118 SeitenSony Video Camera Manual PDFGary Hoehler100% (1)
- Roland Mdx-650 Milling TutorialDokument28 SeitenRoland Mdx-650 Milling TutorialRavelly TelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filtration 2Dokument5 SeitenFiltration 2Ramon Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIL-W-22759 Rev E - Part34Dokument1 SeiteMIL-W-22759 Rev E - Part34David WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Manual Operator'S and Unit Maintenance Manual FOR Firing Device, Demolition. M122 (NSN 1375-01-021-0606) (EIC: 2NA)Dokument7 SeitenTechnical Manual Operator'S and Unit Maintenance Manual FOR Firing Device, Demolition. M122 (NSN 1375-01-021-0606) (EIC: 2NA)Михаил НаумовNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heinzmann ControlsDokument4 SeitenHeinzmann ControlsShahzad AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Cmp-Smartrw10 CompDokument66 SeitenManual Cmp-Smartrw10 CompAllegra AmiciNoch keine Bewertungen