Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bio 6.1
Hochgeladen von
zwindows123456789Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bio 6.1
Hochgeladen von
zwindows123456789Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
117
1. 1990/I/2c
The diagram below shows the human urinary system :
(i) Name structures A and B. Give ONE function for each. (4 marks)
(ii) The table below shows the concentration of certain components of two fluids (X and Y) collected
from two different regions of the urinary system :
Concentration (g 100 cm
3
)
Fluid X Fluid Y
Protein
Glucose
Urea
0.0
0.0
2.0
8.0
0.1
0.03
(1) Using the letters in the diagram, state the respective regions from which fluids X and Y were
collected. (2 marks)
(2) Explain why fluids X and Y differ in their concentrations of :
(I) protein
(II) glucose
(III) urea (6 marks)
2. 1991/I/2b
An experiment was performed to study the effect of the removal of the liver on the blood urea concentration
of a mammal. The blood urea concentration of this mammal was measured from 07:00 to 20:00 hours. The
animal's liver was removed at 08:00 hours. The results were as follows:
Time of day (hours) Blood urea concentration (mg per 100 cm
3
blood)
07:00
08:00 (liver removed)
11:00
14:00
17:00
20:00
7.0
7.0
3.6
2.6
2.0
1.6
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 6.1 Osmoregulation and excretion | P.1
118
(i) Plot a graph to show how the blood urea concentration varies with time. (3 marks)
(ii) Explain the change in the blood urea concentration after 08:00 hours. (3 marks)
(iii) Describe and explain the changes in the blood urea concentration if the kidneys instead of the liver
of the mammal were removed at 08:00 hours. (3 marks)
(iv) State ONE other function of the liver. (1 mark)
3. 1993/I/2b
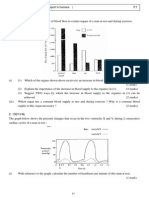
The bar chart below shows the amount of water lost by a man on two consecutive days. On the first day, he
was completely at rest and on the second day, he performed vigorous exercises.
(i) (1) How much more water was lost by the man on the second day ? (2 marks)
(2) Why was this excessive water loss unavoidable ? (5 marks)
(ii) Explain the decrease in water loss in urine on the second day. (3 marks)
4. 1993/I/3aiv
Regulation of the blood glucose level is an example of the feedback mechanism in the body. State another
example. What is the importance of the feedback mechanism to the body ? (2 marks)
5. 1996/I/3b
Patients with kidney failure will die if they do not receive proper treatment. One method of treatment is to
use a kidney machine.
The diagram below shows the workings of a kidney machine :
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 6.1 Osmoregulation and excretion | P.2
119
(i) Urea is found in the solution passing out of the kidney machine. Account for this. (2 marks)
(ii) Give a reason for each of the following :
(1) Each treatment takes a long time (about 6 hours). (1 mark)
(2) The treatment needs to be repeated at regular intervals (about 2-3 times a week). (1 mark)
(iii) Both the human kidney and the kidney machine are able to retain useful substances in the blood.
Explain how this is achieved by
(1) the human kidney, (1 mark)
(2) the kidney machine. (2 marks)
(iv) Another method of treating kidney failure is to transplant a healthy kidney into the patient. Suggest
two reasons why only a small number of such patients can receive this treatment in Hong Kong.
(2 marks)
6. 1997/I/3a
In humans, the normal ranges of glucose concentration in the blood plasma is between 70 and 110 mg per
100 cm
3
. As the concentration of glucose in the blood plasma changes, both the rate of filtering glucose
from the glomerulus and the rate of excreting glucose in the urine also change. The table below shows the
variation of the two rates with the glucose concentration in the blood plasma :
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 6.1 Osmoregulation and excretion | P.3
120
Concentration of glucose in
blood plasma (mg per 100cm
3
)
Rate of filtering glucose from
glomerulus (mg min
-1
)
Rate of excreting glucose
in urine (mg min
-1
)
70
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
95
135
203
270
338
405
473
540
0
0
0
7
18
40
75
130
(i) Using the same x and y axes, present the above data in the form of a graph. (4 marks)
(ii) (1) When the concentration of glucose in the blood plasma is 90 mg per 100 cm
3
,
(I) what is the rate of filtering glucose from the glomerulus ?
(II) what is the rate of excreting glucose in the urine ? (1 mark)
(2) With reference to the function of the kidney tubule, explain your answer in (II) above.
(2 marks)
(iii) Explain one situation which leads to the excretion of glucose in the urine of a healthy person.
(3 marks)
7. 2000/I/4c
The table below shows the rates of water loss in different ways from a persons body under two conditions :
Rate of water loss (mL h
1
) Condition
Sweat Urine Exhaled air
At rest 4 58 15
During heavy exercise 208 21 27
(i) Compare the rate of sweat production of the person under the two conditions. Explain why there was
such a difference. (3 marks)
(ii) Account for the decrease in the rate of urine production of the person during heavy exercise.
(3 marks)
(iii) (1) Explain how exhalation may lead to water loss from the body. (2 marks)
(2) Why did the rate of water loss through exhalation increase during heavy exercise ? (2 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 6.1 Osmoregulation and excretion | P.4
121
8. 2001/I/1b
The graphs below show the concentration of three substances in the renal artery, and the changes in their
concentration along the nephron and the collecting duct :
(i) Explain the difference in the concentration of protein between the blood plasma and the fluid in the
nephron. (2 marks)
(ii) What process causes the increase in urea concentration along the collecting duct ? (1 mark)
(iii) (1) What may substance X be ? (1 mark)
(2) Explain the change in the concentration of substance X along the nephron. (3 marks)
(iv) If a person eats a lot of beans, how would the amount of urea excreted be affected ? Explain your
answer. (4 marks)
9. 2004/I/3b
The diagram below shows the structure of a nephron and its associated blood vessels :
(i) Name the fluid found in X. Explain how this fluid is formed. (4 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 6.1 Osmoregulation and excretion | P.5
122
(ii) Describe two ways in which glucose in vessel A may reach vessel B. Your answer should include the
routes and the mechanisms involved. (4 marks)
(iii) Coffee contains a chemical called caffeine which cause dilation of vessel A. Explain how the
presence of caffeine in the blood may increase the rate of urine production. (3 marks)
10. 2006/I/9a
The table below shows some information about the composition of the plasma, glomerular filtrate and urine
of a healthy person:
Content (g per 100 mL fluid) Component
Plasma Glomerular filtrate Urine
Water 90-93 97-99 96
Plasma proteins 7-9 0 0
Glucose 0.10 0.10 0.00
Chloride 0.37 0.37 0.60
Urea 0.03 0.03 2.00
Others <1.0 <1.0 <2.0
(i) (1) The following table shows the percentage change in chloride content of urine when compared
with that of glomerular filtrate. Using the above information, complete the table by finding out
the percentage change in urea content. (1 mark)
Component Percentage change
Chloride 62.2 %
Urea
(2) Give a reason for this change in the urea content. (1 mark)
(ii) Account for the difference in water content between the plasma and the glomerular filtrate.
(3 marks)
(iii) A person suffers from diabetes and glucose is detected in his urine. With reference to the cause of the
disease, explain why his urine contains glucose. (4 marks)
11. 2008/I/10aiii
The table below shows the body temperature and the rate of urine formation of a person under two
conditions.
At rest During heavy exercise
Body temperature (
o
C) 37.05 37.45
Rate of urine formation
(cm
3
per hour)
58 21
Account for the difference in the rate of urine formation at rest and during heavy exercise. (4 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 6.1 Osmoregulation and excretion | P.6
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - IIDokument21 SeitenNSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - IIFelix YueNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSS Chemistry Part 6 Microscopic World IIDokument20 SeitenNSS Chemistry Part 6 Microscopic World IISabrina WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Opportunity CostsDokument4 SeitenUnderstanding Opportunity Costszwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 8.2Dokument10 SeitenBio 8.2zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2005 AL Chemistry Paper 2Dokument10 Seiten2005 AL Chemistry Paper 2zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 8.1Dokument2 SeitenBio 8.1zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- As & GS - Q PDFDokument12 SeitenAs & GS - Q PDFPeter ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - IDokument36 SeitenNSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - Izwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plane Geometry + Coordinate Geometry - QDokument11 SeitenPlane Geometry + Coordinate Geometry - Qzwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 1.2Dokument1 SeiteEcon 1.2zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 8.3Dokument3 SeitenBio 8.3zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hkcee Biology - 8.4 Genetic Engineering - P.1Dokument1 SeiteHkcee Biology - 8.4 Genetic Engineering - P.1zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1Dokument10 SeitenHkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 7.4Dokument4 SeitenBio 7.4zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 6.4Dokument3 SeitenBio 6.4zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hkcee Biology - 7.1 Types of Cell Division - P.1Dokument1 SeiteHkcee Biology - 7.1 Types of Cell Division - P.1irisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of Body TemperatureDokument3 SeitenRegulation of Body Temperaturezwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- HKCEE BIOLOGY - 7.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - P.1Dokument6 SeitenHKCEE BIOLOGY - 7.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - P.1irisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 5.4Dokument3 SeitenBio 5.4zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 5.3Dokument3 SeitenBio 5.3Michelle ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hkcee Biology - 4.5 Gas Exchange in Humans - P.1Dokument7 SeitenHkcee Biology - 4.5 Gas Exchange in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Sensitivity Experiment ResultsDokument6 SeitenSkin Sensitivity Experiment Resultszwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 4.2Dokument13 SeitenBio 4.2zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 5.1Dokument5 SeitenBio 5.1zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion and Absorption: Anatomy and Functions of the Human Digestive SystemDokument8 SeitenDigestion and Absorption: Anatomy and Functions of the Human Digestive Systemzwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 3.1Dokument7 SeitenBio 3.1zwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1Dokument13 SeitenHkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hkcee Biology - 4.1 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants - P.1Dokument5 SeitenHkcee Biology - 4.1 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants - P.1irisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Past PaperDokument6 SeitenBio Past Paperzwindows123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- H Pylori Breath TestDokument1 SeiteH Pylori Breath TestSanjay NavaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improve Urea Reactor Performance with High Efficiency TraysDokument21 SeitenImprove Urea Reactor Performance with High Efficiency TraysJaviera MellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Progress and Applications of Nickel-BasedDokument20 SeitenResearch Progress and Applications of Nickel-BasedSnehal MohireNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 - Process and Technologies For Grass-Root Ammonia Plants - EnGDokument21 Seiten3.1 - Process and Technologies For Grass-Root Ammonia Plants - EnGHendriyana St0% (1)
- GNFC Market Sector AnalysisDokument10 SeitenGNFC Market Sector Analysisfake accountNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final-Yr-Thesis-Pdf Uet PeshawarDokument137 SeitenFinal-Yr-Thesis-Pdf Uet PeshawarHa M ZaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upgrading Ammonia Plant ESD SystemDokument8 SeitenUpgrading Ammonia Plant ESD SystemhenriquezrsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaysia Ammonia Market AnalysisDokument13 SeitenMalaysia Ammonia Market AnalysisDeneshVijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grow Your Own SpirulinaDokument14 SeitenGrow Your Own SpirulinaNeil BeechwoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCR Control System, DIA - NE XT4: Technical InstructionDokument48 SeitenSCR Control System, DIA - NE XT4: Technical InstructionAli QaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Protein Nitrogenous Substances: Urea CreatineDokument2 SeitenNon-Protein Nitrogenous Substances: Urea CreatineLOU BLESSY CASINONoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Blowing ProcedureDokument5 SeitenAir Blowing ProcedureArslan NisarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of SNCR and SCR in Cement PlantsDokument8 SeitenApplication of SNCR and SCR in Cement PlantsmuhammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Johnson.C. Scientia.EDokument9 SeitenJohnson.C. Scientia.ETomas FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- NFL-Bathinda FinalDokument65 SeitenNFL-Bathinda Finalnikhilgarg732Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Dokument20 SeitenCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Rino DoctNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft East African Standard: DEAS 909:2018Dokument8 SeitenDraft East African Standard: DEAS 909:2018ahmed ismailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Lactulose and Neomycin On Urea Metabolism in Cirrhotic SubjectsDokument5 SeitenEffects of Lactulose and Neomycin On Urea Metabolism in Cirrhotic Subjectsnova adiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Intake PTC8 PDFDokument110 SeitenProtein Intake PTC8 PDFvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case-C 1Dokument32 SeitenCase-C 1spmasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of FertilizersDokument17 SeitenHistory of Fertilizerscuong251325Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indonesia Fertilisers 2009Dokument5 SeitenIndonesia Fertilisers 2009George Van BommelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - 003 High Pressure Stripper Replacement AFA 19Dokument9 Seiten3 - 003 High Pressure Stripper Replacement AFA 1919karim88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Francis 2002Dokument12 SeitenFrancis 2002Puku KunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training ReportDokument31 SeitenTraining ReportAbhishekKumarPandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urea Molasses BlocksDokument2 SeitenUrea Molasses BlocksIbrahim KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garden Direct: Catalogue 2020Dokument25 SeitenGarden Direct: Catalogue 2020MladenNoch keine Bewertungen
- IFFCODokument54 SeitenIFFCOPriyanka Sharma67% (3)
- Melamine UllmannDokument18 SeitenMelamine Ullmannmouse1201100% (1)