Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Oxidation
Hochgeladen von
alokjadhavCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Oxidation
Hochgeladen von
alokjadhavCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Oxidation Oxidation
Oxidation Oxidation
Introduction
Applications Applications
Mechanism
P Process
System
RTO
Introduction Introduction
Siliconreactswithoxygen
Stable oxide compound Stableoxidecompound
WidelyusedinICmanufacturing
Si+O
2
SiO
2
Oxidation
OriginalSiliconSurface
SiliconDioxide
Silicon
O
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
O
2
45% 55%
SomeFactsAboutSilicon
Name Silicon Name Silicon
Symbol Si
Atomic number 14
Atomic weight 28.0855
Discoverer J ns J acob Berzelius Discoverer J ns J acob Berzelius
Discovered at Sweden
Discovery date 1824
Origin of name From the Latin word "silicis" meaning "flint"
Bond length in singlecrystal Si 2 352 Bond length in single crystal Si 2.352
Density of solid 2.33 g/cm
3
Molar volume 12.06 cm
3
Velocity of sound 2200 m/sec
Hardness 6 5 Hardness 6.5
Electrical resistivity
100,000 cm
Reflectivity 28%
Melting point
1414 C
B ili i t
2900 C
Boiling point
2900 C
Thermal conductivity 150 W m
-1
K
-1
Coefficient of linear thermal
expansion
2.610
-6
K
-1
Etchants (wet) HNO
4
and HF, KOH, etc.
Etchants (dry) HBr, Cl
2
, NF
3
, etc.
CVD Precursor SiH
4
, SiH
2
Cl
2
, SiHCl
3
, and SiCl
4
FactAboutOxygen
Name Oxygen
Symbol O
Atomic number 8
Atomic weight 15.9994
Discoverer J oseph Priestley, Carl Scheele
Discovered at England, Sweden
Discoverydate 1774 Discovery date 1774
Origin of name From the Greek words "oxy genes" meaning
"acid" (sharp) and "forming" (acid former)
Molar volume 17.36 cm
3
Velocity of sound 317.5 m/sec
Refractivity 1.000271
Melting point
54.8 K =-218.35 C
Boilingpoint
902K 18295C
Boiling point
90.2 K =-182.95 C
Thermal conductivity 0.02658 W m
-1
K
-1
Applications Thermal oxidation, oxide CVD, reactive
sputtering and photoresist stripping
Main sources O
2
, H
2
O, N
2
O, O
3
Application of Oxidation ApplicationofOxidation
DiffusionMaskingLayer
Surface Passivation SurfacePassivation
Screenoxide,padoxide,barrieroxide
Isolation Isolation
FieldoxideandLOCOS
Gateoxide
Diffusion Barrier DiffusionBarrier
MuchlowerBandPdiffusionratesinSiO
2
than
thatinSi
SiO
2
canbeusedasdiffusionmask
Dopant
SiO
2
SiO
2
Si
SiO
2
SiO
2
Application, Surface Passivation Application,SurfacePassivation
PadOxide ScreenOxide
Sacrificial Oxide Barrier Oxide
SiO
2
SacrificialOxide BarrierOxide
Si
Normallythinoxidelayer(~150)toprotectsilicon
defects from contamination and over stress defectsfromcontaminationandoverstress.
ScreenOxide
Dopant Ions
Photoresist Photoresist
DopantIons
Si Substrate SiSubstrate
ScreenOxide
PadandBarrierOxidesinSTIProcess
PadOxide
Nitride
Silicon
TrenchEtch
USG
l
PadOxide
Nitride
Silicon
USG
BarrierOxide
TrenchFill
Silicon
USGCMP;USGAnneal;NitrideandPadOxideStrip
Application, Pad Oxide Application,PadOxide
Relievestrongtensilestressofthenitride
Preventstressinducedsilicondefects
l d
PadOxide
Siliconnitride
SiliconSubstrate
Application, Device Isolation Application,DeviceIsolation
Electronicisolationofneighboringdevices
Blanketfieldoxide
Local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) Localoxidationofsilicon(LOCOS)
Thickoxide,usually3,000to10,000
BlanketFieldOxideIsolation
Silicon
WaferClean
Silicon
SiliconDioxide
Fi ld O id
FieldOxidation
ActivationArea
Silicon
FieldOxide
OxideEtch
LOCOSProcess
Siliconnitride
P t b t t
PadOxide
Ptypesubstrate
Padoxidation,nitridedepositionandpatterning
b
Siliconnitride
SiO
2
Ptypesubstrate p
+
p
+
p
+
IsolationDoping
LOCOSoxidation
BirdsBeak
Ptypesubstrate p
+
p
+
p
+
IsolationDoping
SiO
2
Nitrideandpadoxidestrip
LOCOS LOCOS
C ith bl k t fi ld id Comparewithblanketfieldoxide
Betterisolation
Lowerstepheight
Lesssteepsidewall
Disadvantage
roughsurfacetopography
Birdsbeak
Replacingbyshallowtrenchisolation(STI) p g y ( )
Application, Sacrificial Oxide Application,SacrificialOxide
Defectsremovalfromsiliconsurface
STI
USG
SacrificialOxide
NWell
PWell
STI
USG
SacrificialOxidation
NWell
PWell
STI
USG
StripSacrificialOxide
Gate Oxide
NWell
PWell
STI
USG
G t O id ti
GateOxide
GateOxidation
Application, Device Dielectric Application,DeviceDielectric
Gate oxide: thinnest and most critical layer Gateoxide:thinnestandmostcriticallayer
Capacitordielectric
Poly Si
V
D
>0 V
G
n
+
Gate
Thinoxide
Si
n
+
Si Substrate
Source Drain
pSi
Electrons
Oxide and Applications OxideandApplications
NameoftheOxide Thickness Application Timeinapplication
Native 15 20 undesirable
Screen ~200 Implantation Mid70stopresent
Masking ~5000 Diffusion 1960stomid1970s
FieldandLOCOS 3000 5000 Isolation 1960sto1990s
Pad 100 200 Nitridestressbuffer 1960stopresent
Sacrificial <1000 Defectremoval 1970stopresent
Gate 30 120 Gatedielectric 1960stopresent
Barrier 100 200 STI 1980stopresent
Silicon Dioxide Grown on Improperly SiliconDioxideGrownonImproperly
CleanedSiliconSurface
PreoxidationWaferClean
Particulates
Organicresidues
Inorganicresidues g
Nativeoxidelayers
RCA Clean RCAClean
Developed by Kern and Puotinen in 1960 at RCA DevelopedbyKernandPuotinenin1960atRCA
MostcommonlyusedcleanprocessesinICfabs
SC O O O i h 2 i SC1 NH
4
OH:H
2
O
2
:H
2
Owith1:1:5to1:2:7ratio
at70to80Ctoremoveorganiccontaminants.
SC2 HCl:H
2
O
2
:H
2
Owith1:1:6to1:2:8ratioat70
to80Ctoremoveinorganiccontaminates.
DIwaterrinse
HF dip or HF vapor etch to remove native oxide HFdiporHFvaporetchtoremovenativeoxide.
PreoxidationWaferClean
ParticulateRemoval
Highpuritydeionized(DI)wateror
f ll d b i H
2
SO
4
:H
2
O
2
followedbyDIH
2
Orinse.
Highpressurescruborimmersioninheated
dunktankfollowedbyrinse,spindry
and/ordrybake(100to125C).
PreoxidationWaferClean
OrganicRemoval
Strongoxidantsremoveorganicresidues.
H
2
SO
4
:H
2
O
2
orNH
3
OH:H
2
O
2
followedbyDI
H
2
Orinse.
Highpressurescruborimmersioninheated
dunktankfollowedbyrinse,spindry y , p y
and/ordrybake(100to125C).
PreoxidationWaferClean
InorganicRemoval
HCl:H
2
O.
Immersionindunktankfollowedbyrinse,
spindryand/ordrybake(100to125C).
PreoxidationWaferClean
NativeOxideRemoval
HF:H
2
O.
Immersionindunktankorsinglewafer
vaporetcherfollowedbyrinse,spindry
and/ordrybake(100to125C).
Oxidation Mechanism OxidationMechanism
Si+O
2
SiO
2
Oxygen comes from gas Oxygencomesfromgas
Siliconcomesfromsubstrate
O diff i i ili Oxygendiffusecrossexistingsilicon
dioxidelayerandreactwithsilicon
Thethickerofthefilm,thelowerof
thegrowthrate
Oxide Growth Rate Regime OxideGrowthRateRegime
LinearGrowthRegime
B
n
e
s
s
A
X=t
O
x
i
d
e
T
h
i
c
k
n
DiffusionlimitedRegime
X= Bt
O
OxidationTime
<100> Silicon Dry Oxidation <100>SiliconDryOxidation
1 2
1.0
1.2
1200C
<100>SiliconDryOxidation
0.6
0.8
s
s
(
m
i
c
r
o
n
)
1150C
1100C
0 2
0.4
d
e
T
h
i
c
k
n
e
s
1050C
1000C
950C
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
0.2
0
O
x
i
d
900C
OxidationTime(hours)
Wet (Steam) Oxidation Wet(Steam)Oxidation
Si + 2H
2
O SiO
2
+ 2H
2
Si+2H
2
O SiO
2
+2H
2
AthightemperatureH
2
OisdissociatedtoH
and H O andHO
HOdiffusesfasterinSiO
2
thanO
2
Wetoxidationhashighergrowthratethandry
oxidation.
<100>SiliconWetOxidationRate
3.0
1150C
1100 C
<100>SiliconWetOxidation
2 0
2.5
n
)
1100 C
1050C
1000C
1.5
2.0
e
s
s
(
m
i
c
r
o
n
950C
900C
0.5
1.0
x
i
d
e
T
h
i
c
k
n
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 0
Oxidation Time (hours)
O
x
OxidationTime(hours)
Oxidation Rate OxidationRate
Temperature
Chemistry wet or dry oxidation Chemistry,wetordryoxidation
Thickness
P Pressure
Waferorientation(<100>vs.<111>)
Silicondopant
OxidationRate
Oxidation rate is very sensitive (exponentially
Temperature
Oxidationrateisverysensitive(exponentially
related)totemperature
Higher temperature will have much higher Highertemperaturewillhavemuchhigher
oxidationrate.
The higher of temperature is, the higher of the Thehigheroftemperatureis,thehigherofthe
chemicalreactionratebetweenoxygenand
siliconisandthehigherdiffusionrateof
oxygeninsilicondioxideis.
OxidationRate
WaferOrientation
<111>surfacehashigheroxidationrate
h f than<100>surface.
Moresiliconatomsonthesurface.
WetOxidationRate
1.6
1.8
<111>Orientation
1200C
1.2
1.4
m
i
c
r
o
n
)
95CWater
1100C
0.8
0.6
1.0
h
i
c
k
n
e
s
s
(
m
1000C
0.4
0.2
0.6
O
x
i
d
e
T
h
920C
1 2 3 4 0
Oxidation Time (hours) OxidationTime(hours)
OxidationRate
D t C t ti DopantConcentration
Dopantelementsandconcentration
Highlyphosphorusdopedsiliconhashigher
growthrate,lessdensefilmandetchfaster.
Generallyhighlydopedregionhashigher y g y p g g
growratethanlightlydopedregion.
More pronounced in the linear stage (thin Morepronouncedinthelinearstage(thin
oxides)ofoxidation.
Oxidation: Dopants Oxidation:Dopants
PileupandDepletionEffects
Ntypedopants(P,As,Sb)havehigher
solubilityinSithaninSiO
2
,whenSiO
2
growtheymoveintosilicon,itiscall
pileuporsnowploweffect.
BorontendstogotoSiO
2
,itiscalled
depletioneffect.
DepletionandPileupEffects p p
OriginalSiSurface OriginalSiSurface
SiSiO
2
interface SiSiO
2
interface
O i i l Di ib i
t
r
a
t
i
o
n
t
r
a
t
i
o
n
OriginalDistribution
SiO
n
t
C
o
n
c
e
n
t
SiO
n
t
C
o
n
c
e
n
t
SiO
2
D
o
p
a
Si
SiO
2
D
o
p
a
Si
PtypeDopantDepletion NtypedopantPileup
OxidationRate
D d id i (HCl) Dopedoxidation(HCl)
HClisusedtoreducemobileioncontamination.
Widelyusedforgateoxidationprocess.
Growth rate can increase from 1 to 5 percent. Growthratecanincreasefrom1to5percent.
Oxidation Rate OxidationRate
DifferentialOxidation
Thethickeroftheoxidefilmis,theslowerof
theoxidationrateis.
Oxygenneedmoretimetodiffusecrossthe yg
existingoxidelayertoreactwithsubstrate
silicon.
Preoxidation Clean Pre oxidationClean
ThermallygrownSiO
2
isamorphous.
Tends to crosslink to form a crystal Tendstocross linktoformacrystal
Innature,SiO
2
existsasquartzandsand
D f d i l b h l i Defectsandparticlescanbethenucleation
sites
CrystallizedSiO
2
withpoorbarriercapability.
Needcleansiliconsurfacebeforeoxidation.
Oxidation Process OxidationProcess
Dry Oxidation thin oxide DryOxidation,thinoxide
Gateoxide
Pad oxide screen oxide sacrificial oxide etc Padoxide,screenoxide,sacrificialoxide,etc.
WetOxidation,thickoxide
Fieldoxide
Diffusionmaskingoxide
DryOxidationSystem
MFC
To
Process
Tube
MFC
MFC
MFC
ControlValves
Regulator
N
2
N
2
P
r
o
c
e
s
s
P
u
r
g
e
N
O
2
H
C
l
Dry Oxidation DryOxidation
DryO
2
asthemainprocessgas
HCl is used to remove mobile ions for HClisusedtoremovemobileionsfor
gateoxidation
High purity N as process purge gas HighpurityN
2
asprocesspurgegas
LowergradeN
2
asidlepurgegas
Gate Oxidation Steps GateOxidationSteps
IdlewithpurgeN
2
flow
IdlewithprocessN
2
flow
WaferboatspushinwithprocessN
2
flow
TemperaturerampupwithprocessN
2
flow
Temperature stabilization with process N flow TemperaturestabilizationwithprocessN
2
flow
OxidationwithO
2
,HCl,stopN
2
flow
Dangling Bonds and Interface Charge DanglingBondsandInterfaceCharge
Interface State Charge (Positive)
SiO
2
Dangling
Bond
+ + + + +
Si SiO
Si
Si-SiO
2
Interface
Gate Oxidation Steps, Continue GateOxidationSteps,Continue
Oxideannealing,stopO
2
,startprocessflowN
2
Temperature cooldown with process N
2
flow Temperaturecool downwithprocessN
2
flow
WaferboatspulloutwithprocessN
2
flow
Idl i h N fl IdlewithprocessN
2
flow
Nextboatsandrepeatprocess
IdlewithpurgeN
2
flow
Wet Oxidation Process WetOxidationProcess
Faster,higherthroughput
Thick oxide such as LOCOS Thickoxide,suchasLOCOS
Dryoxidehasbetterquality
Process Temperature FilmThickness OxidationTime
Dry oxidation
1000
C
1000 ~ 2 hours Dryoxidation
1000 C
1000 2hours
Wetoxidation
1000
C
1000 ~12minutes
Water Vapor Sources WaterVaporSources
Boiler
Bubbler
Flush Flush
Pyrogenic
Boiler System
Heated Gas line Heated Fore line
BoilerSystem
Process
HeatedGasline HeatedForeline
MFC
Process
Tube
Exhaust
VaporBubbles
Water
Heater Heater
BubblerSystem y
MFC
Process
Tube
N
2
N
2
+H
2
O
Tube
HeatedGasLine
Exhaust
N
2
Bubbles
Water
Heater Heater
FlushSystem
Water
HotPlate
MFC
Process
Tube
N
2
Tube
Heate
r
PyrogenicSteamSystem
HydrogenFlame,2H
2
+O
2
2H
2
O
H
O
2
ToExhaust
H
2
Process Tube
Wafer Boat
ThermalCouple
ProcessTube
WaferBoat
Paddle
Pyrogenic System PyrogenicSystem
Advantage
Allgassystem g y
Preciselycontrolofflowrate
Disadvantage Disadvantage
Introducingofflammable,explosivehydrogen
TypicalH
2
:O
2
ratioisbetween1.8:1to1.9:1.
Pyrogenic Wet Oxidation System PyrogenicWetOxidationSystem
MFC
MFC
Process Tube
MFC
MFC
MFC
Wafers
Burn Box
Control Valves
Regulator
o
c
e
s
s
N
2
u
r
g
e
N
2
O
2
H
2
Scrubbier
P
r
o
P
u
Exhaust
Wet Oxidation Process Steps WetOxidationProcessSteps
IdlewithpurgeN
2
flow
IdlewithprocessN
2
flow
RampO
2
withprocessN
2
flow
WaferboatpushinwithprocessN
2
andO
2
flows
TemperaturerampupwithprocessN
2
andO
2
flows
TemperaturestabilizationwithprocessN
2
andO
2
flows
Ramp O turn off N flow RampO
2
,turnoffN
2
flow
StabilizetheO
2
flow
Wet Oxidation Process Steps WetOxidationProcessSteps
TurnonH
2
flow,ignitionandH
2
flowstabilization
2
, g
2
SteamoxidationwithO
2
andH
2
flow
Hydrogentermination,turnoffH
2
whilekeepingO
2
flow
Oxygentermination,turnoffO
2
startprocessN
2
flow
TemperaturerampdownwithprocessN
2
flow
WaferboatpulloutwithprocessN
2
flow
IdlewithprocessN
2
flow
Next boats and repeat process Nextboatsandrepeatprocess
IdlewithpurgeN
2
flow
RapidThermalOxidation
Forgateoxidationofdeepsubmicrondevice
Verythinoxidefilm,<30
Needverygoodcontroloftemperature
uniformity,WIWandWTW.
RTOwillbeusedtoachievethedevice
requirement.
RTPProcessDiagram
Ramp
up1&2
Cool
down
RTA Load
wafer
Unload
wafer
RTO
O
2
flow
Temperatur
e
HClflow
N
2
flow
Time
HighPressureOxidation
Faster growth rate Fastergrowthrate
Reducingoxidation
temperature: temperature:
1amt.=30C
Higherdielectricstrength
High Pressure Oxidation HighPressureOxidation
StainlessSteelJacket
HighPressure
InertGas
HighPressure
OxidantGas
QuartzProcessChamber
High Pressure Oxidation HighPressureOxidation
Oxidationtimetogrow10,000wetoxide
Temperature Pressure Time
1atmosphere 5hours 1 atmosphere 5 hours
1000 C
5 atmosphere 1 hour
25 t h 12 i t 25 atmosphere 12 minutes
High Pressure Oxidation HighPressureOxidation
Oxidationtemperaturetogrow10,000wetoxidein5hours
Time Pressure Temperature
1atmosphere
1000C
1 atmosphere
1000 C
5 hours
10 atmosphere
700 C
HighPressureOxidation
Complex system Complexsystem
Safetyissues
NotwidelyusedinICproduction
Oxide Measurement OxideMeasurement
Thickness
Uniformity
Gateoxide
Break down Uniformity
C l h
Breakdown
voltage
C V
Colorchart
Ellipsometry
CV
characteristics
Reflectometry
Ellipsometry
EllipticallyPolarized
Reflected Light
Ellipsometry
LinearlyPolarizedIncidentLight
ReflectedLight
s
p
n
1
,k
1
, t
1
n
2
,k
2
Reflectometry
Humaneyeor
Reflectometry
1
Incidentlight
y
photodetector
2
1
g
t
Dielectric film n(
)
Substrate
Dielectricfilm,n(
)
Substrate
CV Test Configuration C VTestConfiguration
Capacitor
Meter
LargeResistor
Aluminum
Oxide
MetalPlatform
Silicon
Heater Heater
Summary of Oxidation SummaryofOxidation
Oxidationofsilicon
Highstabilityandrelativelyeasytoget.
Application Application
Isolation,masking,pad,barrier,gate,andetc.
W t d D WetandDry
MoredryprocessesforadvancedICchips
Rapidthermaloxidationandannealingfor
ultrathingateoxide
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- F2cfe613 IndustrialDokument266 SeitenF2cfe613 Industrialjvega_534120100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Liquid Crystals Seminar SMDokument7 SeitenLiquid Crystals Seminar SMSmriti100% (1)
- Cisco: Basic Switch and VLAN Configuration Guide With ExamplesDokument17 SeitenCisco: Basic Switch and VLAN Configuration Guide With Examplessmuscat72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Specification Rmu Frtu Rev 01Dokument55 SeitenTechnical Specification Rmu Frtu Rev 01Ramesh Ananthanarayanan100% (1)
- Arduino DroneDokument16 SeitenArduino DroneBằng Trần DuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 DC MachinesDokument49 SeitenChapter 5 DC Machinesquocdung NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Camera Shading BasicsDokument5 SeitenCamera Shading BasicsRenzo Satti100% (2)
- Manual SkyconnectDokument62 SeitenManual SkyconnectCarlos GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- d5 Ueq User Doc 3 0 1 Std (Arris Ipqam d5用户手册)Dokument962 Seitend5 Ueq User Doc 3 0 1 Std (Arris Ipqam d5用户手册)freextr100% (2)
- Exp D - FFDokument5 SeitenExp D - FFalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nmos Configuration ImplementationDokument7 SeitenNmos Configuration ImplementationalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCS - Communication Systems - Linear ModulationDokument111 SeitenPCS - Communication Systems - Linear Modulationaccessgm0% (1)
- Post Layout Delay Calculation Using RCXDokument6 SeitenPost Layout Delay Calculation Using RCXalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pmos Configuration ImplementationDokument7 SeitenPmos Configuration ImplementationalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Source Amplifier: Experiment Date: 4 October 2011 Name: P.JAGADEESH (11MVD0015)Dokument11 SeitenCommon Source Amplifier: Experiment Date: 4 October 2011 Name: P.JAGADEESH (11MVD0015)alokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.RCX - View of CMOS Inverter and Nand GateDokument6 Seiten8.RCX - View of CMOS Inverter and Nand GatealokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 3Dokument7 Seiten1 3Gaurav MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Noise AnalysisDokument9 SeitenNoise AnalysisalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- FALLSEM2013 14 CP2782 21 Aug 2013 RM01 Power Efficiency of Modulation SchemesDokument7 SeitenFALLSEM2013 14 CP2782 21 Aug 2013 RM01 Power Efficiency of Modulation SchemesalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 10Dokument63 Seiten1 10Gaurav GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- FALLSEM2013 14 CP2782 21 Aug 2013 RM01 Power Efficiency of Modulation SchemesDokument7 SeitenFALLSEM2013 14 CP2782 21 Aug 2013 RM01 Power Efficiency of Modulation SchemesalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFICDokument9 SeitenRFICalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipelined ProcessorsDokument17 SeitenPipelined Processorsalokjadhav100% (1)
- CMOS Question FN-3Dokument3 SeitenCMOS Question FN-3alokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- EpitaxyDokument23 SeitenEpitaxyalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 04 POCADokument36 SeitenCH 04 POCAalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSIM4 Gate Leakage Model Including Source-Drain PartitionDokument4 SeitenBSIM4 Gate Leakage Model Including Source-Drain PartitionalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 3Dokument7 Seiten1 3Gaurav MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipelined ProcessorsDokument17 SeitenPipelined Processorsalokjadhav100% (1)
- 1 Modeling TutorialDokument13 Seiten1 Modeling TutorialalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Lab 6Dokument4 SeitenAnalog Lab 6alokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cov LetterDokument4 SeitenCov LetteralokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 10Dokument63 Seiten1 10Gaurav GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing Lab Assignment IIDokument25 SeitenTesting Lab Assignment IIalokjadhav100% (1)
- Testing Lab Assignment IIDokument25 SeitenTesting Lab Assignment IIalokjadhav100% (1)
- Testing Lab Assignment IIDokument25 SeitenTesting Lab Assignment IIalokjadhav100% (1)
- DFT IntroDokument14 SeitenDFT IntroalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice ProblemsDokument48 SeitenPractice ProblemsalokjadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sylvania 6626lctDokument60 SeitenSylvania 6626lctAdkinsTV100% (1)
- Calculo de Filtros Armonicos AccusineDokument2 SeitenCalculo de Filtros Armonicos AccusineYolandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Lab ManualDokument87 SeitenDigital Lab ManualKALAIMATHINoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE 2022 Syllabus For Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) - Check Here!Dokument15 SeitenGATE 2022 Syllabus For Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) - Check Here!PurvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ovp Orava ctv-2181 16.1 SMDokument22 SeitenOvp Orava ctv-2181 16.1 SMdancalin64Noch keine Bewertungen
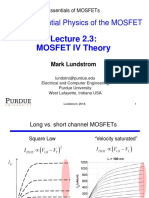
- ECEPurdue MOSFET Lundstrom L2.3v3bDokument22 SeitenECEPurdue MOSFET Lundstrom L2.3v3balNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposed Curriculum Full Draft PDFDokument251 SeitenProposed Curriculum Full Draft PDFAadi BurlagaddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co4011B-Fl: Single Chip Canopen Controller For Remote I/ODokument45 SeitenCo4011B-Fl: Single Chip Canopen Controller For Remote I/OKrum KashavarovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Amplifier: Service ManualDokument20 SeitenPower Amplifier: Service ManualLeonardo MarraffiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Panasonic TX-p42u30e TX-p42ux30e TX-p42u30j TX-pr42u30 TX-pr42u31 Chassis Gpf14d-EDokument113 SeitenPanasonic TX-p42u30e TX-p42ux30e TX-p42u30j TX-pr42u30 TX-pr42u31 Chassis Gpf14d-ESorin DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Iron and Steel With Desktop Optical Emission SpectrometerDokument4 SeitenAnalysis of Iron and Steel With Desktop Optical Emission SpectrometerJunaid JamshedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9: Ethernet Pronet Center: Identifies The Source and Destination ApplicationsDokument5 SeitenChapter 9: Ethernet Pronet Center: Identifies The Source and Destination ApplicationsChivinh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary-Side Regulation PWM Power Switch General Description FeaturesDokument10 SeitenPrimary-Side Regulation PWM Power Switch General Description FeaturespopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS460 InstructionsDokument4 SeitenSS460 InstructionsDiego Fernando Sanchez FlorezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitutoyo - Mikroskopy Pomiarowe TM Seria - E14013 - 2015Dokument4 SeitenMitutoyo - Mikroskopy Pomiarowe TM Seria - E14013 - 2015D.T.Noch keine Bewertungen
- CPE400 Lab8 ARCONADO DEVELLES 2 PDFDokument10 SeitenCPE400 Lab8 ARCONADO DEVELLES 2 PDFKimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling of Continuous-Time SignalsDokument11 SeitenSampling of Continuous-Time SignalsGregory LevantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage Source InverterDokument77 SeitenVoltage Source InverterSaied Aly SalamahNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIL306, TIL307 Numeric Displays With LogicDokument9 SeitenTIL306, TIL307 Numeric Displays With LogicAndy ScriptorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual CRT SS7900 ENG-3Dokument23 SeitenManual CRT SS7900 ENG-3Dante NeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charles Proteus SteinmetzDokument7 SeitenCharles Proteus SteinmetzKelvinNoch keine Bewertungen