Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Study Area and Volume of An Enclosed Cylindrical Surface: Ankita Agrahari, Deepita Bhatnagar, Monika Bhatnagar
Hochgeladen von
Ravindra KumarOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Study Area and Volume of An Enclosed Cylindrical Surface: Ankita Agrahari, Deepita Bhatnagar, Monika Bhatnagar
Hochgeladen von
Ravindra KumarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Proceedings of National Conference on Recent Advances in Electronics and Communication Engineering
(RACE-2014), 28-29 March 2014
1
Study Area and Volume of an Enclosed
Cylindrical Surface
1
Ankita Agrahari,
2
Deepita Bhatnagar,
3
Monika Bhatnagar
Department of Electronics and Communication
I.T.S Engineering College, Greater Noida
1
ankitaagrahari0609@gmail.com,
2
shivibhatnagar@gmail.com,
3
monikabhatnagar@its.edu.in
Abstract- To identify the circular cylindrical co-ordinates system is very convenient whenever we dealing with
problems having cylindrical symmetry.
I. INTRODUCTION
The Circular Cylindrical Coordinate System is very convenient whenever we are dealing with problems
having cylindrical symmetry.A point P in cylindrical coordinate is represented as (,,z) where, is the radius of
the cylinder passing through or the radial distance from the z-axis , is called the azimuthal angle, is
measured from the x-axis in the xy-plane; and z is the same in the Cartesian System (x,y,z) .
The ranges of this space variables are-
0
02
-z
A vector A in cylindrical coordinate can be written as-
(A,A
,A
z
) or AA
,A
z
z
where
,
z
are unit vectors in the , and z directions.
In the cylindrical co-ordinate system, differential normal surface area is given by-
dS=ddz
=ddz
=ddz
And differential volume is given by-
dV=dddz
Now, we are going to deal with an enclosed surface with dimensions =2 and =4, z=3 and z=5, =20 and
=60 and from these dimensions we are going to find a closed area and volume.
Proceedings of National Conference on Recent Advances in Electronics and Communication Engineering
(RACE-2014), 28-29 March 2014
2
II. DISCUSSION
To Find the volume V of a closed surface we first find out dv, the volume element. In cylindrical
coordinates dv is given by dv=dddz. Once we get the expressions of dv, we integrate dv over the entire
volume
dv = dddz
V =
v
dv
V =
v
dddz
=
2
4
20
60
3
5
dddz
=
4
2
d
/9
/3
d
3
5
dz
= 8/3
= 8.378m
Proceedings of National Conference on Recent Advances in Electronics and Communication Engineering
(RACE-2014), 28-29 March 2014
3
The area of the closed surface is given by-
S = S + S +s +S +S+S
We need to find ds, ds.ds and to integrate them over their boundry . It is obvious that S=S and S=S. The
surfaces S and S have similar shapes as we see from the following expressions,
ds=ddz/
=2
= 2ddz and
ds=ddz/
=4
= 4ddz
The steps to evaluate the area of each surface are executed as follows-:
ds = ddz
S =
= 2 (6/18 - 2/18) (5-3)
= 8/9 m
S =
= 4
Proceedings of National Conference on Recent Advances in Electronics and Communication Engineering
(RACE-2014), 28-29 March 2014
4
= 4(6/18 - 2/18) (5-3)
= 16/9 m
ds= dd
S=
=1/2*(4-2)*(6/18-2/18)
= 4/3 m
ds=ddz
S=
= *z
=(4-2)*(5-3)
= 4m
S = S+S+2S+2S
= 8/9+16/9+2*4/5+2*4
= 24.755 m
III. RESULT
Using the formulas for differential volume and differential area we can find the volume and the surface
v = 8.378m
s = 24.755m
VI. REFERENCES
[1] M.N.O.Sadiku,Principles of Electromagnetics,4
th
international Version,Oxford University Press.
[2] W.H.Hayt and J.A.BuckEngineering ElectromagneticsSeventh Edition,McGraw Hill Education.
[3] E.C.Jorden and G.B.Balanis,Electromagnetics Waves and Radiating Systems,Printice-Hall of India 2
nd
edition.
[4] J.A.Edminister,Shaums OutlineTheory and problems of ElectromagneticsTata McGraw hill,Second Edition,Special Indian
Edition 2006.
[5] A.Pramanik,Electromagnetism Theory and ApplicationPrintice-Hall of India 2
nd
edition.
Proceedings of National Conference on Recent Advances in Electronics and Communication Engineering
(RACE-2014), 28-29 March 2014
5
[6] http:/nptl.iitm.ac.in/course/Webcourse-contents/IIT-%20Gauwahati/em/
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Uniform Bonding Code (Part 2)Dokument18 SeitenUniform Bonding Code (Part 2)Paschal James BloiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formal 17 12 04 PDFDokument184 SeitenFormal 17 12 04 PDFJose LaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance: ASU-600 SeriesDokument54 SeitenMaintenance: ASU-600 SeriesMichael Maluenda Castillo100% (2)
- Class 12 Students Present Math Project on DifferentiationDokument14 SeitenClass 12 Students Present Math Project on DifferentiationSayan Mandal69% (16)
- Factory Hygiene ProcedureDokument5 SeitenFactory Hygiene ProcedureGsr MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsVon EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Funded African Tech Startups 2020Dokument13 SeitenFunded African Tech Startups 2020LoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Marketing Management PDFDokument6 SeitenFundamentals of Marketing Management PDFAli RizviNoch keine Bewertungen
- UBI1Dokument66 SeitenUBI1Rudra SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blum2020 Book RationalCybersecurityForBusineDokument349 SeitenBlum2020 Book RationalCybersecurityForBusineJulio Garcia GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 GCE A Level Solution H2 Math Paper 2Dokument12 Seiten2011 GCE A Level Solution H2 Math Paper 2lacewingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elitmus PapersDokument21 SeitenElitmus Papersanon_879320987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Evaluation of Circular MicrostripDokument14 SeitenPerformance Evaluation of Circular MicrostripIAEME PublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- FinalDokument19 SeitenFinalkluNoch keine Bewertungen
- On the possible mathematical connections between some “solutions of the Born–Infeld constraints corresponding to the cubic Curves”, some Ramanujan formulas, the κ formula regarding the Riemann Zeta Function and some expressions concerning the Supersymmetry BreakingDokument110 SeitenOn the possible mathematical connections between some “solutions of the Born–Infeld constraints corresponding to the cubic Curves”, some Ramanujan formulas, the κ formula regarding the Riemann Zeta Function and some expressions concerning the Supersymmetry BreakingMichele NardelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Exact Solution of The Cylindrical WaveDokument13 SeitenAn Exact Solution of The Cylindrical WavekrejishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of The Most Effective Method For Minimizing The Fading and Sep AnalyDokument5 SeitenDesign of The Most Effective Method For Minimizing The Fading and Sep AnalyIAEME PublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hamilton2013hexagonal 1Dokument9 SeitenHamilton2013hexagonal 1Tg WallasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nguyễn Quốc An (BKC18348) - Assignment 3 lần 2 - Discrete Math - C01K10T 1Dokument7 SeitenNguyễn Quốc An (BKC18348) - Assignment 3 lần 2 - Discrete Math - C01K10T 1KatonguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparative Study On Multicast Routing Using Dijkstra's, Prims and Ant Colony SystemsDokument10 SeitenA Comparative Study On Multicast Routing Using Dijkstra's, Prims and Ant Colony SystemsIAEME PublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDokument16 SeitenUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelSherlock Wesley ConanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inverse Sqaure Law For Gamma RadiationDokument7 SeitenInverse Sqaure Law For Gamma RadiationAhmedAmer1100% (2)
- Fast Calculations of Dyadic Green's Functions For Electromagnetic Scattering in A Multilayered MediumDokument21 SeitenFast Calculations of Dyadic Green's Functions For Electromagnetic Scattering in A Multilayered MediumMohammad Arif SaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accurate Computation of Vector Potentials in Lossy MediaDokument21 SeitenAccurate Computation of Vector Potentials in Lossy MediabeckliesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fuze Doppler Echo Algorithm of Near-Field Electromagnetic Scattering ModelDokument5 SeitenThe Fuze Doppler Echo Algorithm of Near-Field Electromagnetic Scattering Modelتپل خستهNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generate level set functions from STL filesDokument8 SeitenGenerate level set functions from STL filesTung DangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expert Lecture On GPS at UIET, CSJMU KanpurDokument57 SeitenExpert Lecture On GPS at UIET, CSJMU KanpurSuddhasheel Basabi GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA3004 Part 3: Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) : Martin SkoteDokument46 SeitenMA3004 Part 3: Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) : Martin SkotedavidbehNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Vector Line Integral: A Project ReportDokument13 SeitenTo Vector Line Integral: A Project ReportRamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Parallel Algorithm For Solving The 3d SCHR Odinger EquationDokument19 SeitenA Parallel Algorithm For Solving The 3d SCHR Odinger EquationSamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weighted Graphs Dijkstra's AlgorithmDokument7 SeitenWeighted Graphs Dijkstra's AlgorithmSyed MobashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 3 With SolutionsDokument5 SeitenMath 3 With SolutionsDiane BasilioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 - 12 Class X - Ag-3 (Cbse)Dokument6 Seiten01 - 12 Class X - Ag-3 (Cbse)Umesh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics: Center of Gravity & CentroidDokument13 SeitenEngineering Mechanics: Center of Gravity & CentroidIan Ark E. ColarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficient Hydraulic SectionDokument7 SeitenEfficient Hydraulic SectionSambhav PoddarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mse 2183 Assignment 3Dokument22 SeitenMse 2183 Assignment 3MarkusNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE AMaths Y13 SP 1Dokument16 SeitenIGCSE AMaths Y13 SP 1Michelle HsiehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit Jee 2005 MatDokument7 SeitenIit Jee 2005 MatLokesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus 1 Prelim to Midterm ReviewDokument14 SeitenCalculus 1 Prelim to Midterm Reviewnek ocinrocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficient Stripmap SAR Raw Data Generation Taking Into Account Sensor Trajectory DeviationsDokument5 SeitenEfficient Stripmap SAR Raw Data Generation Taking Into Account Sensor Trajectory Deviationsmani567Noch keine Bewertungen
- Outage Analysis and Optimal Power Allocation For Cooperative Communication SystemsDokument5 SeitenOutage Analysis and Optimal Power Allocation For Cooperative Communication SystemsballmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- s4 - 0606 - Sa1 2014 - All PaperDokument30 Seitens4 - 0606 - Sa1 2014 - All Paperapi-233271416Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Manual EMFTDokument99 SeitenMatlab Manual EMFTpratheep100% (1)
- Matlab ManualElectromagnetics IDokument99 SeitenMatlab ManualElectromagnetics IAnonymous JnvCyu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Distance Between Two Points Formula - Definition & ExamplesDokument11 SeitenDistance Between Two Points Formula - Definition & Examplesnarinder kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dijkstra's Algorithm Mathematical ModelDokument27 SeitenDijkstra's Algorithm Mathematical ModelMontenegro Roi VincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multimodal Phase Velocity-Frequency Dispersion ImaDokument36 SeitenMultimodal Phase Velocity-Frequency Dispersion Imapublio gallicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of A Rectangular Waveguide Using Finite Element MethodDokument9 SeitenAnalysis of A Rectangular Waveguide Using Finite Element MethodV'nod Rathode BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Geometry Manifold of Toeplitz Hermitian Positive Definite Covariance Matrices: Mostow/Berger Fibration and Berezin Quantization of Cartan-Siegel DomainsDokument11 SeitenInformation Geometry Manifold of Toeplitz Hermitian Positive Definite Covariance Matrices: Mostow/Berger Fibration and Berezin Quantization of Cartan-Siegel DomainsInternational Journal of Emerging Trends in Signal Processing (IJETSP)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Michele Nardelli: Sezione Filosofia - Scholar of Theoretical PhilosophyDokument137 SeitenMichele Nardelli: Sezione Filosofia - Scholar of Theoretical PhilosophyMichele NardelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCS VnaDokument12 SeitenRCS VnaMarius CheroiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- G N O M - A Program Package For Small-Angle Scattering Data ProcessingDokument4 SeitenG N O M - A Program Package For Small-Angle Scattering Data ProcessingAnne DiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2d and 3d Array AntennaDokument5 Seiten2d and 3d Array AntennaKurtish VenkatiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aterramento Freeware Grounding System DesignDokument4 SeitenAterramento Freeware Grounding System DesignWisller JeffersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework #5: Numerical Differentiation and IntegrationDokument5 SeitenHomework #5: Numerical Differentiation and IntegrationAndres MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEC130A: Practice Problems For Midterm 2: Instructor: Xiaoguang "Leo" Liu (Lxgliu@ucdavis - Edu) Updated: Mar. 6 2012Dokument11 SeitenEEC130A: Practice Problems For Midterm 2: Instructor: Xiaoguang "Leo" Liu (Lxgliu@ucdavis - Edu) Updated: Mar. 6 2012M Erizky SyaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Examination - April 23, 2013. MATH1014: Name: Surname: Student Number: SignatureDokument17 SeitenFinal Examination - April 23, 2013. MATH1014: Name: Surname: Student Number: SignatureexamkillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cs 3422872295Dokument9 SeitenCs 3422872295IJMERNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Optimization of Dijkstra's AlgorithmDokument5 SeitenOn The Optimization of Dijkstra's AlgorithmKimlong NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whole Digital Communication PPT-libreDokument319 SeitenWhole Digital Communication PPT-librePiyush GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithm To Construct Super Vertex Magic Total Labeling of Complete GraphsDokument5 SeitenAlgorithm To Construct Super Vertex Magic Total Labeling of Complete GraphsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijmet: ©iaemeDokument10 SeitenIjmet: ©iaemeIAEME PublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee Advance 2014 Phy I Questions SolutionsDokument9 SeitenJee Advance 2014 Phy I Questions SolutionsMohammed Aftab AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Optimal Design of Microstrip Sensors: P.W. WebbDokument9 SeitenAnalysis and Optimal Design of Microstrip Sensors: P.W. WebbRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series Fed Antena ArrayDokument4 SeitenSeries Fed Antena ArrayRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series Fed Antena ArrayDokument4 SeitenSeries Fed Antena ArrayRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series Fed Antena ArrayDokument4 SeitenSeries Fed Antena ArrayRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiation Damage Studies of Silicon Microstrip Sensors: B. Stugu4, R. Takashima', K. Tanizaki', S - Terada2, Y. Unno2Dokument7 SeitenRadiation Damage Studies of Silicon Microstrip Sensors: B. Stugu4, R. Takashima', K. Tanizaki', S - Terada2, Y. Unno2Ravindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFID Coverage Extension Using Microstrip-Patch Antenna ArrayDokument7 SeitenRFID Coverage Extension Using Microstrip-Patch Antenna ArrayRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiation Damage Studies of Silicon Microstrip Sensors: B. Stugu4, R. Takashima', K. Tanizaki', S - Terada2, Y. Unno2Dokument7 SeitenRadiation Damage Studies of Silicon Microstrip Sensors: B. Stugu4, R. Takashima', K. Tanizaki', S - Terada2, Y. Unno2Ravindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Optimal Design of Microstrip Sensors: P.W. WebbDokument9 SeitenAnalysis and Optimal Design of Microstrip Sensors: P.W. WebbRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFID Coverage Extension Using Microstrip-Patch Antenna ArrayDokument7 SeitenRFID Coverage Extension Using Microstrip-Patch Antenna ArrayRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Circuits and Systems Mid Semester ExamDokument1 SeiteDigital Circuits and Systems Mid Semester ExamRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preamble of Our ConstitutionDokument5 SeitenPreamble of Our ConstitutionRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Preamble and Essence of the Indian ConstitutionDokument32 SeitenThe Preamble and Essence of the Indian ConstitutionRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved ProblemsDokument10 SeitenSolved ProblemsRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chp4 Microwave FiltersDokument77 SeitenChp4 Microwave FiltersRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Circuits and Systems End Semester ExamDokument2 SeitenDigital Circuits and Systems End Semester ExamRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chp4 Microwave FiltersDokument77 SeitenChp4 Microwave FiltersRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Circuits Mid Semester ExamDokument1 SeiteDigital Circuits Mid Semester ExamRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Waves: Properties, Spectrum & ApplicationsDokument5 SeitenElectromagnetic Waves: Properties, Spectrum & ApplicationsRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endterm DCS 2017 SolDokument10 SeitenEndterm DCS 2017 SolRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Circuits Mid Semester Exam -2 QuestionsDokument1 SeiteDigital Circuits Mid Semester Exam -2 QuestionsRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Circuits and Systems End Semester ExamDokument2 SeitenDigital Circuits and Systems End Semester ExamRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM Mid Term-IDokument1 SeiteDIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM Mid Term-IRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shagun PrintDokument6 SeitenShagun PrintRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics and Communication Department The Lnmiit, Jaipur Digital Circuits and Systems (Code: DCS)Dokument4 SeitenElectronics and Communication Department The Lnmiit, Jaipur Digital Circuits and Systems (Code: DCS)Ravindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 9Dokument1 SeiteAssignment 9Ravindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPTU B.tech Integrated Circuits NEC-501 Sem 5 - 2015-16Dokument4 SeitenUPTU B.tech Integrated Circuits NEC-501 Sem 5 - 2015-16Ravindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequency and wavelength bands for electromagnetic radiationDokument4 SeitenFrequency and wavelength bands for electromagnetic radiationRavindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
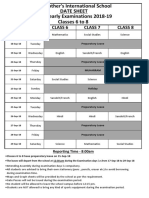
- Mother's International School Half Yearly Exam Date Sheet 2018-19 Classes 6-8Dokument1 SeiteMother's International School Half Yearly Exam Date Sheet 2018-19 Classes 6-8Ravindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- P2Dokument17 SeitenP2Ravindra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acid Isolation System: MolecularDokument6 SeitenNucleic Acid Isolation System: MolecularWarung Sehat Sukahati100% (1)
- Sampling Fundamentals ModifiedDokument45 SeitenSampling Fundamentals ModifiedArjun KhoslaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Make Pcbat Home PDFDokument15 SeitenHow To Make Pcbat Home PDFamareshwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merlin Gerin Medium VoltageDokument10 SeitenMerlin Gerin Medium VoltagekjfenNoch keine Bewertungen
- WSM 0000410 01Dokument64 SeitenWSM 0000410 01Viktor Sebastian Morales CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 63db2cf62042802 Budget Eco SurveyDokument125 Seiten63db2cf62042802 Budget Eco SurveyNehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 8 HW WS - B - Graphs & ChartsDokument6 SeitenWEEK 8 HW WS - B - Graphs & Chartsangela trioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scenemaster3 ManualDokument79 SeitenScenemaster3 ManualSeba Gomez LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pike River Case StudyDokument7 SeitenPike River Case StudyGale HawthorneNoch keine Bewertungen
- DX133 DX Zero Hair HRL Regular 200 ML SDS 16.04.2018 2023Dokument6 SeitenDX133 DX Zero Hair HRL Regular 200 ML SDS 16.04.2018 2023Welissa ChicanequissoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discount & Percentage Word Problems SolutionsDokument4 SeitenDiscount & Percentage Word Problems SolutionsrheNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATmega32 SummaryDokument18 SeitenATmega32 SummaryRajesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itec 3100 Student Response Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenItec 3100 Student Response Lesson Planapi-346174835Noch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist PBL 2Dokument3 SeitenChecklist PBL 2Hazrina AwangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Successful Organizational Change FactorsDokument13 SeitenSuccessful Organizational Change FactorsKenneth WhitfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- C J L F S: Vinod TiwariDokument21 SeitenC J L F S: Vinod TiwariVinod TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shri Siddheshwar Co-Operative BankDokument11 SeitenShri Siddheshwar Co-Operative BankPrabhu Mandewali50% (2)
- JRC Wind Energy Status Report 2016 EditionDokument62 SeitenJRC Wind Energy Status Report 2016 EditionByambaa BattulgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NVH Analysis in AutomobilesDokument30 SeitenNVH Analysis in AutomobilesTrishti RastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company's Profile Presentation (Mauritius Commercial Bank)Dokument23 SeitenCompany's Profile Presentation (Mauritius Commercial Bank)ashairways100% (2)
- ETP Research Proposal Group7 NewDokument12 SeitenETP Research Proposal Group7 NewlohNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 March CaravanDokument48 Seiten2014 March CaravanbahiashrineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mosaic Maker - Instructions PDFDokument4 SeitenMosaic Maker - Instructions PDFRoderickHenryNoch keine Bewertungen