Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
SPM Linear Law
Hochgeladen von
Ng Yievia0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
233 Ansichten5 SeitenThe document discusses how to transform nonlinear graphs into linear graphs by changing the variables plotted on the x and y axes. Some examples of nonlinear relationships include y=ax^n, y=a/x, y=ab^x, and y=ax^b. By plotting alternative variables such as log(y), y^2, 1/x, or log(x) instead of x and y, the relationships can be linearized so they can be represented by an equation in the form of y=mx+c, which is a straight line. Six methods for linearizing common nonlinear relationships are described through examples and graphs. The document concludes by listing examples of nonlinear relationships and their linearized forms.
Originalbeschreibung:
热锅
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document discusses how to transform nonlinear graphs into linear graphs by changing the variables plotted on the x and y axes. Some examples of nonlinear relationships include y=ax^n, y=a/x, y=ab^x, and y=ax^b. By plotting alternative variables such as log(y), y^2, 1/x, or log(x) instead of x and y, the relationships can be linearized so they can be represented by an equation in the form of y=mx+c, which is a straight line. Six methods for linearizing common nonlinear relationships are described through examples and graphs. The document concludes by listing examples of nonlinear relationships and their linearized forms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
233 Ansichten5 SeitenSPM Linear Law
Hochgeladen von
Ng YieviaThe document discusses how to transform nonlinear graphs into linear graphs by changing the variables plotted on the x and y axes. Some examples of nonlinear relationships include y=ax^n, y=a/x, y=ab^x, and y=ax^b. By plotting alternative variables such as log(y), y^2, 1/x, or log(x) instead of x and y, the relationships can be linearized so they can be represented by an equation in the form of y=mx+c, which is a straight line. Six methods for linearizing common nonlinear relationships are described through examples and graphs. The document concludes by listing examples of nonlinear relationships and their linearized forms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
1 | P a g e
SPM Additional Mathematics- by KBJIM - jimmigmig@yahoo.com
The Linear Law
1. When you plot a linear graph (straight line graph), y=mx +c, you should expect to be able to draw a
straight line through all the given points. However, in experimental work, many data collected do not fit
exactly onto the linear graph.
x
x
x
x x
x
x
x x
x
x x
x
line of best fit not able to draw line of best fit.
2. We then draw the line of best fit. The line of best fit is a straight line that passes through most of
the plotted points. If the line of best fit can be drawn from the plotted points, then we say such a law of
the form y =mx +c does exist for the given data.
3. From the straight line drawn, we can then find an approximate linear law for the given data.
Assignment: Now try to plot straight line graphs and answer those questions given in your text book..
Changing non-linear graphs to linear
y y
b
x x
2
0 0
y = ax
2
+b y = aX +b
y = 5x
2
+8 y = 5X +8
1. The graph y = ax
2
+ b is a curve graph if we plot y vs x. To change it to a linear form, we plot y
vs x
2
. When we plot y vs x
2
, we let X =x
2
so that the graph has a linear equation y = aX + b
which is a straight line graph.
2 | P a g e
y y
b
x 1/x
0 0
y = a/x +b y = aX +b
y = 5/x +8 y = 5X +8
2. The graph y = a/x + b is a curve graph if we plot y vs x. To change it to a linear form, we plot y
vs 1/x. When we plot y vs 1/x , we let X =1/x so that the graph has a linear equation y = aX + b
which is a straight line graph.
y y
2
b
x x
0 0
y
2
= ax +b Y = ax +b
y
2
= 5x +8 Y = 5x +8
3. The graph y
2
= ax + b is a curve graph if we plot y vs x. To change it to a linear form, we plot y
2
vs x. When we plot y
2
vs x , we let Y =y
2
so that the graph has a linear equation Y = ax + b which
is a straight line graph.
y y
2
x 1/x
0 1 0
y
2
x = a Y = aX
y
2
x = 2 Y = 2X ( y
2
=2/x)
4. The graph y
2
x = a is a curve graph if we plot y vs x. To change it to a linear form, we plot y
2
vs
1/x. When we plot y
2
vs 1/x , we let Y =y
2
and X = 1/x so that the graph has a linear equation
Y = aX which is a straight line graph.
3 | P a g e
y log y
1 c
x x
0 0
y = ab
x
Y = mx +c (log y =x log b +log a)
y = 3(2
x
) Y = 0.3x +0.48 ( log y =x log 2 +log 3)
5. The graph y = ab
x
is a curve graph if we plot y vs x. To change it to a linear form, we plot log y
vs x. When we plot log y vs x , we let Y =log y and the graph has a linear equation Y = mx + c
which is a straight line graph.
y log y
b
x log x
0 0
y = ax
n
Y = mX +c ( log y = n log x + log a )
y = 3x
2
Y = 2X +0.48 (log y =2 log x +log 3)
6. The graph y = ax
b
is a curve graph if we plot y vs x. To change it to a linear form, we plot log y vs
log x. When we plot log y vs log x , we let Y =log y and X =log x then the graph has a linear
equation Y = mX + c which is a straight line graph.
y y
x x
2
0 0
y = ax
n
y = mx +c
y = 3x
2
y = 3X
you could also plot y against x
2
4 | P a g e
Exampl e G.1: Reduce the follow types of variations to a linear relationship:
(a) y =ax
n
(b) xy =2 (c) y =3x
2
+8 (d) y
2
=5x +8 (e) y =x
2
+2x (f) y =2x + 3
x
(g) y
2
= 1/x +8 (h) 2x
2
+y
2
=8x (i) y =ab
x
(j) pv =k
Solution:
(a) y =ax
n
(b) xy =2
log y = n log x +log a y =2/x
Let Y =log y , X =log x and c =log a Let X =1/ x
Then Y =nX + c then y =2X
(c) y =3x
2
+8
(d) y
2
=5x +8
Let X =x
2
Let Y =y
2
Then y =3X +8 then Y =5x +8
(e) y =x
2
+2x
(f) y =2x +3
x
y =x +2 yx =2x +3
x
Let y =Y
Let Y =yx
x
Then Y =x +2 then Y =2x +3
(g) y
2
=1/x
+8
(h) 2x
2
+y
2
=8x
Let Y
=y
2
and X =1/x
2x +y
2
= 8
x
Then Y =X +8 Let Y =y
2
, then Y =8 2x
x
(i) y =ab
x
(j) pv =k
log y =x log b +log a p =k/v
Let log y =Y
, m =log b and c =log a
Let V =1/v
Then Y =mx +c then p =kV
5 | P a g e
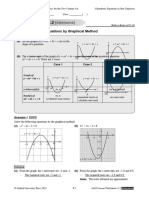
Exampl e G.2: The figure shows a linear rel ationshi p that has been reduced.
Find (a) the original graph relationshi p (b) the value of x when y =4
Solution:
log y
(a) gradient of graph, m = 2
2
linear equation: Y =2X +2
log y =2 log x + 2
log y =log x
2
+log 100 log x
1
hence y =100x
2
(b) when y =4 , x =0.2
Exampl e G.3: The figure shows a linear rel ationshi p that has been reduced from y = ka
x
.
Find the val ue of a and k.
Solution:
log y
(a) gradient of graph, m = 2.66 2.4 =0.026 (10, 2.66)
10
linear equation: Y =0.026x +2.4
log y = x log a +log k
m =log a =0.026 and log k =2.4 2.4
hence a =1.061 and k =251 x
0
Author says..........
If you wish to have a personal tuition class on Physi cs, Chemistry or
Add. Maths, kindly contact me at 012-4599768 (Penang Island Onl y)
( Correspondence Tuition courses can be arranged for outstation students ).
You may save or copy this topic. Pass it to your schoolmates if you like. The website is
www.webfunpage.com
.........................................then click on item No.1......................................................
Personal tuition is also available to students who are taking G.C.E O l evel, A level, IBO, SAM,
STPM and HSC.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- OSM LessonWS 4A03 3.2 Intensive eDokument8 SeitenOSM LessonWS 4A03 3.2 Intensive es1501194Noch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Program Ver11Dokument13 SeitenLinear Program Ver11Ryan KoNoch keine Bewertungen
- App e Mathematics PDFDokument70 SeitenApp e Mathematics PDFmiguelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Practice Problems - Basic Calculus: Dy DX y X y X y X y X y X y X X y X y X X y X y y X y X X Ye Ye XDokument4 SeitenChapter Practice Problems - Basic Calculus: Dy DX y X y X y X y X y X y X X y X y X X y X y y X y X X Ye Ye XSajin SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pengamiran LatihanDokument2 SeitenPengamiran LatihanABDUL MANAF BIN CHE AMAT MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 1.2. Linear Functions: Chapter 1: Linear and Quadratic Functions With Applications To BusinessDokument3 SeitenSection 1.2. Linear Functions: Chapter 1: Linear and Quadratic Functions With Applications To BusinessJohn McCreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02-Linear Programming (Theory)Dokument7 Seiten02-Linear Programming (Theory)THE MULTIVERSENoch keine Bewertungen
- OSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a lv2 eDokument4 SeitenOSM ConsolEx 4A04 4a lv2 e林俊佑Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stresses On A PlaneDokument7 SeitenStresses On A PlaneKuan RickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEng6302 Lecture 4 Analysis of Stress and Strain ASM 2021Dokument25 SeitenMEng6302 Lecture 4 Analysis of Stress and Strain ASM 2021KKDhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1. Pembuktian SBB:: X y X yDokument10 Seiten2.1. Pembuktian SBB:: X y X yfauzanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 June - Quiz - Linear InequalitiesDokument7 Seiten02 June - Quiz - Linear InequalitiesimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Answers & Hints) : JEE Adv. Part Test - 1Dokument12 Seiten(Answers & Hints) : JEE Adv. Part Test - 1Mohammed Aftab AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sketching y X Transformations and Turning Point Form: Chapter 7 Parabolas and Other GraphsDokument1 SeiteSketching y X Transformations and Turning Point Form: Chapter 7 Parabolas and Other GraphsraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions InvestigationDokument10 SeitenFunctions InvestigationAmadi PARANAVITHANANoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Mechanics: OutlineDokument37 SeitenStructural Mechanics: OutlineZain ul HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 Geophysics-Vector - Operators - SDokument26 Seiten0 Geophysics-Vector - Operators - S鄭啟宏Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lista Modulo1Dokument32 SeitenLista Modulo1Enzo HaradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformations Of: Vertical Stretch/compressionDokument4 SeitenTransformations Of: Vertical Stretch/compressionMaher KamraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphs of Trigo FunctionsDokument5 SeitenGraphs of Trigo FunctionsWeteachNoch keine Bewertungen
- 033 SurbhiGole A1Dokument18 Seiten033 SurbhiGole A1Surbhi GoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - A Gallery of Graphs: Solutions To Exercise 4ADokument31 SeitenChapter 4 - A Gallery of Graphs: Solutions To Exercise 4AKim TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 PDFDokument5 SeitenChapter 8 PDFSHIVAS RAINANoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 1.1 - ContourLines, Level Curves and 3D Graphs)Dokument12 SeitenLecture Notes (Chapter 1.1 - ContourLines, Level Curves and 3D Graphs)Shaktivell Letchumanan100% (1)
- EquationofstraightlineDokument12 SeitenEquationofstraightlineomsaiboggala811Noch keine Bewertungen
- Handout01 State Variable ModelsDokument6 SeitenHandout01 State Variable ModelsRafael Pires BarbosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limits MultivariableDokument2 SeitenLimits MultivariablePedroNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA1505 1920S1 Part I Chapter 1Dokument19 SeitenMA1505 1920S1 Part I Chapter 1Jaehun JeongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Sys Linear Eqns IIDokument44 Seiten7 Sys Linear Eqns IINada EssamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 4B: 1 A For X 0Dokument2 SeitenExercise 4B: 1 A For X 0Calixto JaxonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Transformation and Rank Nullity Theorem 2 LecturesDokument32 SeitenLinear Transformation and Rank Nullity Theorem 2 Lecturespratyay gangulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 SummaryDokument6 SeitenChapter 5 Summarycha chaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Law NotesDokument3 SeitenLinear Law NotesSya SuhailaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Calculus HandoutsDokument11 SeitenDifferential Calculus HandoutsChristian AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polynomial End Behavior: DateDokument2 SeitenPolynomial End Behavior: DateRachide DaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 1102, Solved Problems On Multiple IntegralsDokument12 SeitenMath 1102, Solved Problems On Multiple IntegralsFaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphs: Inflection PointsDokument36 SeitenGraphs: Inflection PointsSamarjeet SalujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 1995 Paper 2Dokument9 SeitenMathematics 1995 Paper 2hungeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes 4Dokument9 SeitenNotes 4kv8nrv5kdzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 1271: Common Graphs & Transformations: Straight LinesDokument6 SeitenMath 1271: Common Graphs & Transformations: Straight LinesNguyễn Duy QuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Set - Week 1: Problem 1Dokument4 SeitenExercise Set - Week 1: Problem 1Mark HelouNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA2001 - Differential Calculus of Multivariable Functions 1314ADokument48 SeitenMA2001 - Differential Calculus of Multivariable Functions 1314AMatthew LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple RegressionDokument8 SeitenSimple RegressionDlo PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAT - Passport To Advanced Math Module - 7: Topic-Polynomials and Algebraic FractionsDokument9 SeitenSAT - Passport To Advanced Math Module - 7: Topic-Polynomials and Algebraic FractionsMadhav AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macromechanics of A LaminateDokument45 SeitenMacromechanics of A LaminateAvinash ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differentiation of Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDokument28 SeitenDifferentiation of Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsAudie T. MataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 The ParabolaDokument37 SeitenChapter 7 The ParabolaVihanga RuwanmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of The Integrals: Key Concept InvolvedDokument2 SeitenApplication of The Integrals: Key Concept InvolvedPrayag VaradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of LawsDokument6 SeitenDetermination of LawspundekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 35 - Polynomial and Rational Functions - Solving A Quadratic InequalityDokument4 Seiten35 - Polynomial and Rational Functions - Solving A Quadratic InequalityMarc FragosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Chapter 8 Maths Important FormulasDokument2 SeitenClass 12 Chapter 8 Maths Important FormulasVansh johariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module V Applications of IntegrationDokument21 SeitenModule V Applications of IntegrationShinTaxErrorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Orthogonal Structure in The Design Matrix: 8.1 Example: (Simple Linear Regression)Dokument2 Seiten8 Orthogonal Structure in The Design Matrix: 8.1 Example: (Simple Linear Regression)Noman ZahoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture NotesDokument90 SeitenLecture NotesSharad RaykhereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes 16 Torsion Prop PDFDokument17 SeitenNotes 16 Torsion Prop PDFKucinx GaronkNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIT2 25F13 Solution6.4 PDFDokument5 SeitenMIT2 25F13 Solution6.4 PDFfunk singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplementary Notes On Sketching Exponential and Logairthmic Functions PDFDokument6 SeitenSupplementary Notes On Sketching Exponential and Logairthmic Functions PDFShantoshCumarasurierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Von EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Von EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rental TenantDokument7 SeitenRental TenantNg YieviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermateability Microwave Journal PinoDokument5 SeitenIntermateability Microwave Journal Pinopredrag_miletic_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lean Daily Management SystemDokument8 SeitenLean Daily Management SystemNg Yievia100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind MapDokument1 SeiteChapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind MapNg YieviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procrastination Ebook FINALDokument21 SeitenProcrastination Ebook FINALNg Yievia100% (1)
- Solving AbsoluteDokument6 SeitenSolving AbsoluteNg YieviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple BarometerDokument11 SeitenSimple BarometerNg YieviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How I Met Myself Sample QuestionsDokument23 SeitenHow I Met Myself Sample QuestionsNg YieviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxford Fajar Companion WebsiteDokument1 SeiteOxford Fajar Companion WebsiteNg YieviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer All Questions: Chapter 21: Reproduction Chapter 22: GrowthDokument20 SeitenAnswer All Questions: Chapter 21: Reproduction Chapter 22: GrowthNg YieviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Declan Galbraith Tell Me WhyDokument1 SeiteDeclan Galbraith Tell Me WhyNg Yievia100% (1)
- Eclipse (Meyer Novel) : Plot SummaryDokument2 SeitenEclipse (Meyer Novel) : Plot SummaryNg YieviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math F311Dokument4 SeitenMath F311Shivam KediaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP Models Bom 1101Dokument86 SeitenLP Models Bom 1101Frances Mary BareñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibps RRB BookDokument554 SeitenIbps RRB Booksanat samantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asymptotic AnalysisDokument42 SeitenAsymptotic AnalysissonuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brockington College Mathematics Faculty Homework BookletDokument31 SeitenBrockington College Mathematics Faculty Homework BookletNayem Hossain HemuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Substitution & ApplnDokument5 SeitenMethods of Substitution & ApplnBoobalan RNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Sec Multiple ChoiceDokument3 SeitenC Sec Multiple ChoiceAngel FaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - IC Binary Trees SolutionsDokument34 SeitenAssignment - IC Binary Trees SolutionsDrKrishna Priya ChakireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transforms and Partial Differential Equation Questions Notes of m3, 3rd Semester NotesDokument52 SeitenTransforms and Partial Differential Equation Questions Notes of m3, 3rd Semester NotesBalaji Shanmugam100% (3)
- Maths Paper With AnswerDokument3 SeitenMaths Paper With AnswerNishanth M SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pointers GR 9Dokument1 SeitePointers GR 9Patricia Ann JacintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cse 551 - Foa - 2Dokument8 SeitenCse 551 - Foa - 2saisrinivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE/CS 559 - Neural Networks Lecture Notes #6: Learning: Erdem KoyuncuDokument13 SeitenECE/CS 559 - Neural Networks Lecture Notes #6: Learning: Erdem KoyuncuNihal Pratap GhanatheNoch keine Bewertungen
- 110.302 Differential Equations Professor Richard BrownDokument2 Seiten110.302 Differential Equations Professor Richard BrownLuis BaldassariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 77Dokument3 SeitenMath 77Pressy Leen LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid-Term Course Work CM1015 / Computational MathematicsDokument5 SeitenMid-Term Course Work CM1015 / Computational Mathematicspalpras9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Logarithmic Functions and Equations 2Dokument16 SeitenLogarithmic Functions and Equations 2Ruth BalitianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Topics SL Chapter Summaries PDFDokument6 SeitenCore Topics SL Chapter Summaries PDFsinbad SailorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Numbers (Exam Questions I) : Created by T. MadasDokument68 SeitenComplex Numbers (Exam Questions I) : Created by T. MadasHui Ni YamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigo Ratios & Identities-01 - TheoryDokument14 SeitenTrigo Ratios & Identities-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- FP1 Past Questions QPDokument16 SeitenFP1 Past Questions QPalekon323Noch keine Bewertungen
- BDT Cua Tran Quoc AnhDokument19 SeitenBDT Cua Tran Quoc AnhPhạm Quốc BảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- g9 3q Simplifying RadicalsDokument10 Seiteng9 3q Simplifying RadicalsDorothy Julia Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26-Matrices and Determinants - 01-TheoryDokument26 Seiten26-Matrices and Determinants - 01-TheoryRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Madura Coaching Centre: Madurai - 01.Ph: 7373007731, 8838037215Dokument2 SeitenMadura Coaching Centre: Madurai - 01.Ph: 7373007731, 8838037215SURESH KANNAN50% (2)
- DAG and DagittiDokument7 SeitenDAG and DagittiDani Yitu MedanituNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Mathematics Project WorkDokument10 SeitenAdditional Mathematics Project WorkQwin GanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fracciones Parciales - StewartDokument10 SeitenFracciones Parciales - StewartDaniel CastellamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- SumpartDokument1 SeiteSumpartDario RuysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijh (KKFKHZ Fkklahko Vius "Kcnksa Esa GH Mùkj Nsaa Mikar Ds Vad Iw - KKZD Ds - KSRD GsaaDokument2 SeitenIjh (KKFKHZ Fkklahko Vius "Kcnksa Esa GH Mùkj Nsaa Mikar Ds Vad Iw - KKZD Ds - KSRD GsaakumargauravNoch keine Bewertungen