Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Design and Fabrication of Puller FOR Valve Guide.: Assignment No: 04
Hochgeladen von
DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATEOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Design and Fabrication of Puller FOR Valve Guide.: Assignment No: 04
Hochgeladen von
DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATECopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
V .J .T.
I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
ASSIGNMENT NO: 04
DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF PULLER
FOR
VALVE GUIDE.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 86
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Design and fabrication of puller
Need for puller: -
Exhaust valve
position Cylinder head
of Engine
Valve guide to
be remove
Exhaust valve guide to
be remove.
Exhaust
valve.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 87
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
There are 24 valve guides which are forcibly inserted in to the head of the
cylinder of the engine and exhaust valve. There are four valve guides from which
two for intake valve and two for exhaust valve. The valve guide for intake is fitted
inside the body of the cylinder head of engine. And the valve guide for the exhaust
valve is fitted inside the assembly of the exhaust valve. The exhaust valve is set
with the exhaust valve cage and is easy for disassembly and maintenance. In order
to get a better heat resisting characteristic, the face the face of the valve is stelite
fuse plated. These valve guides are removing during the overhauling of the engine.
The main role of the valve guide in engine is in the assembly of the valve.
It works as the guider for the valve during the operation. The engine has the
720rpm for the load of 600 to 700KW. Therefore the valve guide has 130rpm. If in
the case the valve guide is not used then there is the possibility of ware out the
cylinder head and exhaust valve body due to the friction and energy generate. The
design of valve guide, intake and exhaust valve is made such that the work take
place smoothly without any damage and reduce the friction.
The valve guide is made up of special cast; the cylinder head is made up
of high grade cast iron of sufficient strength and the exhaust valve body is made of
mushroom type of heat resisting steel. They are forcibly fitted with each other and
remains in contact during operation. During the working high temperature and
presence of carbon rusted from inside in between head and guide made the contact
rigid and power full.
The old process for removing and assembling the valve guide is by
hammer and long rod as shown in fig. The rod having small outer diameter than
that of valve guide so it can easily go inside the hole made for the guide in head
and exhaust valve body. The rod have step like structure so that some part go
inside and reaming part engage with the valve guide. This process of removing the
guide take more time as the guide is press fitted. Also the guide can not be reused
as the hammering action damage the guide and the opening get shear out due to
the jerk given by the hammer. And also the formation of burr take place due to
which the problem arise in assembling the valve guide again. It may possible that
at the end guide get through out with speed and harm any workman standing near.
Also there is the possibility of slip of hammer and injure the workman.
During the assembly the guide is kept into the freezer for some time so
that it get shrink and reduce in outer diameter. Then the seat is fitted inside the
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 88
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
hole given on engine head and exhaust body. Then it get to the original shape after
short time and it get fitted.
The traditional way of removing and assembling the valve guide is by rod
and hammer. But by this process valve guide, head and exhaust valve body get
damage due to the sharp cut made by the hammer. So this process damage head,
exhaust valve body, guide and also hazardous to workman. So there was a need to
deign a puller which can pull and push the guide without causing any defect.
Old process of
removing intake Hammer
valve guide.
Rod use
for removing guide.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 89
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Hamme
r
Rod use
for
removing
guide.
Old process of
removing
Exhaust valve guide.
Old
process of
inserting
valve
guide of
exhaust.
Hammer
Rod
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 90
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Old process
Of
inserting
valve guide of
intake.
Hammer
The main concept for design of puller and pusher: -
i) The difficulties and hazard in the previous or old process that is trouble
shouting during the study of engine and seeing defect in previous process.
ii) Study of engine head and exhaust valve in deep and getting more
information form engineer and workman.
iii) The overall structure and dimension of intake and exhaust valve
guide.
iv) The overall structure and rough dimension of head and exhaust
valve.
v) The material of valve guide (special cast).
vi) Area that is available for supporting the puller around the intake valve
guide and exhaust valve guide.
vii) The force required to pull the guide out by traditional way.
viii) Total number of valve guide present.
ix) Area of contact between the guide and rod for pulling up.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 91
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
x) Both intake and exhaust guide must get remove and assembled
in single puller and by same action.
Main concept for Designing of puller: -
I have to develop the concept which can be used for assembly as well as
disassembled the guide of intake and exhaust valve. The main task is that the valve
guides of both are at deep from other side. The rod used for pulling must not get
bound certain limit as it has to pass through the hole that made for the guide that is
31mm diameter. So I can not increase the pulling rod size beyond certain limit.
The rod that used for pulling action is 2 foot long and 1½ foot rod come in stress.
So the rod must be hardened to withstand the pulling force. The same fixture is
going too used for pulling and pushing so I can not increase the pushing rod size
beyond certain limit. The contact between the guide and rod is 2 to 3mm around
21mm diameter.
This was the main part where I have to work in deep because I have to go
for pulling and pushing action at the same fixture. Once I made the design and
given to manufacture I invest my time and money both so I must be very perfect
and good in my design. As I was successful in previous puller I got same but little
different concept for this puller also. I found following thing very important
during the puller design to be effective.
i) How can I pull as well as push the guide from same structure or
design.
ii) How to make maximum contact between the pulling and pushing rod
with the guide to apply more and more force. As we get 2 to 3mm contact for
pulling after passing through 200mm distance and for pushing I have to use
the part which can act as connecting because the valve guide is cylindrical in
shape so my pushing rod must not damage it during the assembly of the
guide.
iii) How to get maximum support for pulling as well as pushing action so
that the body can withstand that force applied for pulling and pushing the
guide.
iv) How to select the body that support for pulling and pushing action is
long in up as guide is 175mm long.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 92
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
v) I can not used the outer diameter and internal diameter of supporting
body large as during assembly it may possible to get bend and get off center
and tailed position if I apply the force then it will not work at all.
vi) How to develop connecting part between the guide and pushing rod.
The other advantage of this part is to center the force and apply it uniform all
over the body.
vii) How to clamp the supporting body during pushing .For action during
pushing we can used the two threaded hole made previously on the head as
well as exhaust valve these hole have same size as well as at same distance
from the center of the guide that is why we do not required the two separate
clamping devise or arrangement for clamping. The clamping device is not of
flange type structure as there is obstacle presents like rod and studs.
Designing of puller: -
I started collecting data from visual study also the different concepts form
my colleague and workers. And then finally I select the following puller or pusher
design: -
a) The basic concept behind the puller is by the concept of nut and bolt
rd
that means by Newton’s 3 law of motion “every action there is always an
equal and opposite reaction.”
b) When we apply force on the guide that is fitted inside the cylinder head
or exhaust valve body that will apply equal and opposite force on the puller.
The puller nut is rotated by means of spanner that rotating force is given to
the bolt get converted in to the linear force by thread and bolt move upward
with the guide which is get engage with rod.
c) In the case of pusher the bolt is rotated by spanner that moves down
with respect to the thread provided to the supporting body. The bolt pushes
the connecting piece that will push the guide downward direction.
d) The required support is provide with the help of cylindrical pipe close at
one end with the round plate having centered hole having thread same as that
of pushing bolt. The round structure has flange type at the bottom to clamp
with the engine head or exhaust valve body. The round pipe is selected to get
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 93
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
maximum contact area and we can apply maximum force on it. The upper
plate is think in up to withstand at higher or extreme force.
e) In puller the valve guide and rod gripped by means of head given or step
given to rod at one end. In case of pusher the valve guide and rod gripped by
means of connecting piece that is shown in drawing afterward this piece is
used so that the threaded rod can not damage the inner and outer surface of
the of guide and to apply uniform force.
f) In case of the puller the rod is inserted from the downward so when
come up the supporting body is placed on it and clamp with the head or with
the exhaust valve body then the washer is placed on the supporting body then
the nut is inserted and tighten so that the rod is come out with the guide.
g) In case of pusher the guide is hold on the guide hole of head or exhaust
valve and then the connecting piece is inserted then the supporting body is
inserted on it and clamp with the head or exhaust valve body then the pushing
rod is rotated by the spanner and the force is apply on guide so that it get
press fitted inside the position of it.
Selection of material: -
The different part of the puller and there material is selected with respect
to there function and type of work that do also the type of stress that come on that
part: -
1. Supporting body: -
The main function of this part is to apply force on the head and valve
body and also absorb the force in pushing condition. This part must withstand at
maximum force and not get bend at maximum or peak force. This must have
sufficient allowable bending and tensile stress.
Material used: - EN-12 (Harden).
2. Bolt : -
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 94
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
The main work of the bolt is to pull out the guide out of the hole provided
and that of push is to push the guide inside the hole provided on the head and
exhaust valve body. Therefore the bolt must be hard so that it do not get affected
by the sharp edges of the main body and not get damage due to the stress develop
due to pulling and pushing action. In pulling the tensile stress develop that lead to
stress and in pushing the compressive stress develop that lead to bend.
Material used: - EN-24 (Harden).
3. Connecting piece: -
The main work of this part is to transmit the applied force from the bolt to
the guide so that we can move down the guide to get it assembled to its position.
As it come between the guide and the pushing bolt soothe compressive stress are
develop inside it and not get damage itself as well as guide.
Material used: -EN-24 (Harden).
4. Nut: -
The main work of this is to transmit the rotary force into the linear force
by means of threads. The thread must be hardened as it may possible come in
contact with supporting body and possible of damage. This must withstand at the
applied force by spanner.
Material used: -Mild steel.
5. Clamping bolt: -
This bolt has the main work to clamp the supporting body flange with the
cylinder head or with the exhaust valve body. This bolt is taken standard.
Material used: -EN-8(Hardness 55-60Rc).
6. Washer: -
This is the part that was useful in pulling action as the diameter of the
pulling rod is less than the pushing rod. If we not use the washer then it may
possible that the rotation of spanner pull the bolt to ward out side and damage the
threads of the supporting body as well as that of the bolt itself. So we insert the
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 95
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
collar washer that helps to prevent to get damage. And also not make any affect of
it on the supporting action. This part must have in up compressive stress as it come
in between the supporting body and nut.
Material used: -EN-12(Harden).
Manufacturing Sequence: -
A) Supporting body: -
i) Raw material: - For all supporting components EN-12 is the material: -
1) Pipe of: Internal diameter 48mm.
Outer diameter73mm.
Length 223mm.
2) Plate of: Diameter 73mm.
Thickness 27mm.
3) Clamping plate: Diameter 165mm.
Thickness 15mm.
ii) First for pipe: -
1) Turn the pipe to the required dimension as shown in drawing.
2) Make the one slot of 90mm length X 20mm width having round
type end of 10mm diameter.
iii) Plate: -
1) Turn the plate to the required dimension as shown in drawing.
2) Drill the through hole of 24mm diameter
3) Then turn the threads of M26X1.5mm.
iv) Clamping plate: -
1) Turn the plate to the required dimension as shown in drawing.
2) Drill the two hole of 16mm diameter of at PCD of 122mm diameter.
3) Then turn the big hole of 70mm at center.
4) Cut the plate in opposite end having final width of plate 80mm form
both side.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 96
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
v) Join the three component that is pipe, plate and clamping plate as
shown in drawing by means of welding and finish its outer edges by
polishing.
vi) Heat treats the component to get hardness of 40Rc.
B) Connecting piece:-
i) Raw material: - EN-24 of 32mm diameter X 40mm length.
ii) Turn the job to the required dimension as shown in the drawing.
iii) Turn the step of 30mm diameter for 10mm length and 20mm diameter
for 25mm length.
iv) Make the counter shrink type hole for 3mm length on 30mm diameter
as shown in drawing.
v) Heat treats the component to 40Rc.
C) Nut: -
i) Raw material: - EN-24 of hexagonal size of 32mm flat to flat size and
75mm in length.
ii) Shape to the required dimension as shown in drawing.
iii) Drill the hole of 18mm diameter X 25mm length.
iv) Turn the threads of M20X1.5mm X 25mm length.
v) Repeat the procedure for producing nut of M20X1.5 X 20mm length and
two in numbers.
vi) Heat treats all components to 40Rc.
D) Clamping bolt: -
i) Raw material: - EN-8
ii) These two bolts are taken standard of size 19 mm hexagonal sizes and
M20X2mm from market.
E) Washer: -
i) Raw material: - EN-12 of 72mm diameter X 25mm length.
ii) Turn the plate to the required dimension as per drawing.
iii) Make the step of 70mm diameterX8mm length and 28mm diameter X
10mm length.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 97
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
iv) Drill the through hole of 22mm diameter.
v) Heat treats the four nuts till the hardness of 40Rc.
Method of operating the puller
Required material during operation: -
Puller set, two spanners of 32 and 19, hammer, diesel, oil, cotton rages.
Procedure for pulling action: -
1) First clean the guide with diesel and cotton rages to remove the carbon
that gets stuck on the body of the guide and also at gripping area.
2) Disassembled the puller in to its parts.
3) Give lubrication to the valve guide.
4) Insert the rod in to the valve guide from opposite side so it comes out
from another side.
5) Place the supporting body on the rod come from another side then clamps
the supporting body to the cylinder head or exhaust valve by bolt of
M20X2mm and 19mm hexagonal size.
6) Then put the washer on the supporting body.
7) Turn the nut of M20X1.5 by means of spanner of 32.
8) Apply the sufficient torque on the spanner so that the valve guide comes
out.
9) Repeat the procedure for removing other guides also.
Procedure for pushing action: -
1) This procedure is carried out after the cleaning, lapping and polishing.
2) Disassembled the puller into its parts.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 98
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
3) The guide to be insert must be shrink by keeping it into freezer for 2 to
2½ hours so its outer diameter get reduce.
4) Then hold it at the hole made for it inserts the connecting piece at the
upper part of the guide.
5) Then assemble the pusher on it clamp it to the body of head or exhaust
valve by M20X2mm and 19mm hexagonal bolt.
6) Then insert the pushing rod in the supporting body by rotating it with
32mm spanner.
7) The pushing rod get engage with supporting body threads and apply the
force on the guide through connecting piece and help to assemble it to its
required position.
8) Repeat the same procedure for assembling other guides.
Direction
of applied
torque.
Spanner
During operation
hold the exhaust
valve in to jaw.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 99
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Direction
of applied
torque.
Spanner
Pulling action by spanner and puller.
Direction
of applied
torque.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 100
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Spanner
Direction of applied
torque.
Pushing action by spanner and puller.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 101
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 102
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Supporting body
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 103
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Supporting body parts
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 104
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Supporting body part
NUT QUTY: - 3
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 105
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Connecting Piece.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 106
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Washer
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 107
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Pushing Rod.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 108
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Pulling Rod.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 109
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
Supporting
Body
Connectin
g piece washe Pushing
Nut
r Rod
RESULT AND DISCUSSIONS
The major project that was allotted to me while working in DG/AC
department Pulling
was to supervise the overhauling of the engine no.1 and 4 which was
to be dissembled for maintenance purpose almost after 10 years i.e. after 1997
Rod
when it was first overhauled after installing it in the year 1984. my skill laid in
how efficiently I get the parts dissembled without damaging them and if necessary
design some fixtures and pullers to make thee job easy. Also the clearance of
various parts had to be checked and if found beyond standard limits then those
parts must be replaced with new ones.
At one stage, when the cylinder heads were removed, there were 12
valve seats around the intake valve and 24 valve guides, two valve seats around
each intake valve and 4 valve guides (two for intake valve and two for exhaust
valve). Now removing these valve seats and guide both made of special cast, from
the frame of an engine cylinder head made up of high grade cast iron, was a tough
job to accomplish. Though these valve seats and guides were press fitted into the
frame, the rusting of the frame made these parts as good as one. Now this was the
stage where my engineering knowledge helped me, as I successfully designed a
puller to pull out these valve seats and valve guide easily from the frame without
causing any defect on it and also assemble the valve guide to its position. Also
getting it manufactured was a great challenge, as I had to get it done within the
specified time and with the desired precision. The Godrej supplier brought my
design to life, as the accuracy was very important in this design.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 110
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
During all this process I got to know the actual operation of an engine
got an opportunity to see and feel different parts of engine their properties and
could reason out why a specific material is used for a specific part. Major plus
point that the engine was and so were its components. So I got to see all its details
of various parts. Next I got the knowledge about various gauges like regarding the
way to use them, the steadiness required to get the approximate readings of the
parts and then manipulate to get the wear of that part and then comparing with the
standard wear limit.
Also while designing the puller I got the knowledge about the
standards used in the design and how the limits, fits and tolerances play an
important role in a design which helps during manufacturing the designed
component. Got to know how crucial the material selection process is as the
material selected has to specify the functional aspects of the designed parts and the
importance of hardening the parts.
As there are 6 diesel generators which are accompanied with 6
engines, and after every 2 years one or the other is being scheduled for major
overhauling. So the next time overhauled my project work can be used as a
reference for conducting various measurements. Also the puller developed can be
used for changing the valve seats and valve guides of that engine and if in any case
the puller gets damaged or lost then it need not be redesigned as my project has
got all the necessary details regarding the puller design and fabrication.
Apart from that I also got the knowledge about the air compressor as
well as about the centralize air conditionings unit. Apart from this, I got to
experience the human relations in an organization like how the communication
flows from top to bottom and vice versa, how to handle the personals below and
above ones designation, how the meetings go on and how to express our views,
new recruitments and retirements, the work pressure when the boss is present and
when the boss is absent, etc.
Overall I had a good experience during my tenure at GODREJ &
BOYCE Mfg. Co. Ltd. and I am glad that I got an opportunity to work with such a
big and renowned organization.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 111
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
CONCLUSION
In the overhauling of the diesel generator’s engine different parts
like the cylinder head, piston, liner, piston and oil rings, bearings, timing gear,
tappets, fuel oil injection pump, lubricating oil pump and cooler, pressure relief
valve and lubricating oil filter are successfully measured and inspected by
different gauges and the parts that had worn beyond the standard limits are
replaced by the new parts. These new parts are also measured and inspected and if
they had sufficient clearance only then they were used in assembly of the engine.
Also I got the knowledge about the air compressor as well as about the centralize
air conditionings unit.
Also, successfully designed and fabricated the puller which was
needed to remove valve seats and valve guides of engine cylinder head. This
replaced the traditional method of removing the valve seats and valve guides by
screw driver and hammer which would sometimes develop a defect on them
causing them for rejection and replacing with new one, as a result, this process of
replacing these valve seats and valve guides was to costly.
FUTURE SCOPE
Diesel generators from a part of every company, especially in a
country like India where power cutoffs are very often and to compensate these
power cutoffs, diesel generators play an important role by generating the power
and keep the firm running. And wherever these generators are present their
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 112
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
maintenance is must. Also air compressor and centralize air conditioning present
in every firm.
There are 6 diesel generators at GODREJ & BOYCE Mfg. Ltd. and
the major overhauling is under process for one or the other engine, hence my work
can be used as a reference. Also the puller will be very useful for removing the
valve seats and valve guides of engines.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. “Daihatsu Diesel Engine Instruction Book”
–By Daihatsu Diesel Mfg. Co. Ltd, Japan.
2. “A Course In Internal Combustion Engine”
–By M. L. Mathur and R. P. Sharma.
Dhanpat Rai & Sons.
3. “Design Data Book”
–By PSG College of Engg. and Tech., Coimbatore.
4. “Material Selection In Mechanical Design”
–By Michael Ashby.
Butterworth Heinemann.
5. “Basic Refrigeration And Air Conditioning”
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 113
V .J .T. I, MATUNGA INPLANT TRAINING REPORT
– By P. N. Ananthanarayanan.
TATA McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Ltd, New Delhi, 2000.
6. http://www.globalspec.com/newsletter
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Page 114
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Plymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceVon EverandPlymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Fabrication of Puller FOR Valve Seat.: Assignment No: 03Dokument20 SeitenDesign and Fabrication of Puller FOR Valve Seat.: Assignment No: 03DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- GV500 Series Winch Manual PDFDokument41 SeitenGV500 Series Winch Manual PDFĐại Hùng100% (2)
- D200 Cap 08 (Trasmissione)Dokument18 SeitenD200 Cap 08 (Trasmissione)Wylk BeserraNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument4 SeitenUntitledFluke RanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bangla CAT Report01Dokument25 SeitenBangla CAT Report01Nashik IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual Rgd/Rgs Series Index Drives Models 350RGD/RGS, 500RGD/RGS & 600RGD/RGSDokument16 SeitenService Manual Rgd/Rgs Series Index Drives Models 350RGD/RGS, 500RGD/RGS & 600RGD/RGSSuhas KODRENoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB Manifolds Sub Group 1Dokument6 SeitenLAB Manifolds Sub Group 1MALIK MUHAMMAD HAMZA FAROOQ MALIK MUHAMMAD FAROOQNoch keine Bewertungen
- DTA - Dynamic Torque Anchor Technical DatasheetDokument5 SeitenDTA - Dynamic Torque Anchor Technical DatasheetEvolution Oil ToolsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tier 4 I E E A I Manual C4.4 To C 7.1 Industrial Products TPD1726E1Dokument29 SeitenTier 4 I E E A I Manual C4.4 To C 7.1 Industrial Products TPD1726E1EduardoCastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Downhole Motors PDFDokument15 SeitenDownhole Motors PDFarasquare100% (1)
- The Technicals of DL135 Power Swivel - Augustus Zhang From Dongying Robust Company ChinaDokument31 SeitenThe Technicals of DL135 Power Swivel - Augustus Zhang From Dongying Robust Company ChinayelmustafaaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- MB308 1Dokument11 SeitenMB308 1Amanz MKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valve LappingDokument8 SeitenValve LappingSumeet Khachane100% (1)
- 6.38 10M EH Single Shear Seal BOPDokument19 Seiten6.38 10M EH Single Shear Seal BOPpramodptvpm_65797156Noch keine Bewertungen
- SureShade Instructions Replacing Small ATF Extending Tube 052020Dokument4 SeitenSureShade Instructions Replacing Small ATF Extending Tube 052020Davor GiaconiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Del Swivel SL225Dokument9 SeitenManual Del Swivel SL225Jean Aguilar100% (1)
- Generator Rotor Removal PDFDokument8 SeitenGenerator Rotor Removal PDFMohamed Omar100% (1)
- Rukovodstvo Po Obsluzhivaniju Dvigatelej Hyundai D6a D8aDokument168 SeitenRukovodstvo Po Obsluzhivaniju Dvigatelej Hyundai D6a D8ajack comboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carter WCD ManualDokument35 SeitenCarter WCD ManualsvanellaautosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repair Instructions - Off Vehicle PDFDokument37 SeitenRepair Instructions - Off Vehicle PDFFernando OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- MK - @MSITStore - C - OCSI - QuickServe 2016 OfflineDVD InstalleDokument24 SeitenMK - @MSITStore - C - OCSI - QuickServe 2016 OfflineDVD InstalleTocxoan Tocxoan100% (2)
- Contents:: Choke Valve Installation & Maintenance ManualDokument10 SeitenContents:: Choke Valve Installation & Maintenance Manualimam susantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- D08 26 Oil CylinderDokument3 SeitenD08 26 Oil CylinderVăn Tuấn NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irjet-Fabrication of Automatic Hydraulic PDFDokument5 SeitenIrjet-Fabrication of Automatic Hydraulic PDFXaviour XaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valvula DireccionDokument8 SeitenValvula DireccionVictor Manuel Lozada ObessoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOW Annual Maintenance of Howden CompressorsDokument13 SeitenSOW Annual Maintenance of Howden CompressorsMasroor RasoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Valve Lapping Machine For Ic EngineDokument35 SeitenDesign of Valve Lapping Machine For Ic EngineIfa75% (4)
- John Deere 450CLC Excavator Service Repair Technical Manual (TM1925)Dokument14 SeitenJohn Deere 450CLC Excavator Service Repair Technical Manual (TM1925)laopaodunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series 4280: Motor Mounted Horizontal End Suction Pump Service Work InstructionsDokument4 SeitenSeries 4280: Motor Mounted Horizontal End Suction Pump Service Work InstructionsvimalmailbookNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.V. Manual (FC Type)Dokument20 SeitenG.V. Manual (FC Type)sambhajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daewo Matiz2Dokument54 SeitenDaewo Matiz2hipo84575% (4)
- Lab Report 4Dokument6 SeitenLab Report 4MALIK MUHAMMAD HAMZA FAROOQ MALIK MUHAMMAD FAROOQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating & Maintenance InstructionsDokument8 SeitenOperating & Maintenance InstructionsVAN VIET NGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Valve SpringDokument6 SeitenValve SpringSaddam LemuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volvo Penta 3.0 GS, 4.3 GL-GS-Gi, 5.0 GL-Gi, 5.7 GS-GSi, 7.4 Gi-GSi, 8.2 GSi Sez.8-9Dokument35 SeitenVolvo Penta 3.0 GS, 4.3 GL-GS-Gi, 5.0 GL-Gi, 5.7 GS-GSi, 7.4 Gi-GSi, 8.2 GSi Sez.8-9Luciano LiuzziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Process of Overhaul For Diesel Power Generating SetDokument4 SeitenBasic Process of Overhaul For Diesel Power Generating SetMarcos Fernandez100% (1)
- Well InterventionDokument21 SeitenWell InterventionCito Ali100% (1)
- Before Removal: Special Tools Description Part No. QtyDokument3 SeitenBefore Removal: Special Tools Description Part No. QtyPhomma Khinphommavong0% (1)
- Hyster H360-700C Transmission Service ManualDokument58 SeitenHyster H360-700C Transmission Service ManualArmando Orta100% (1)
- Detroit 8.2 v8Dokument25 SeitenDetroit 8.2 v8Jose Juan Davila100% (3)
- Ford Half ShaftDokument10 SeitenFord Half Shaftsuysuy00Noch keine Bewertungen
- SOP - Bob CatDokument37 SeitenSOP - Bob CatvozefjadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lord Barbutador de Moto para SuzukiDokument31 SeitenLord Barbutador de Moto para SuzukiJose Luis LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 40 90 Mechanical Seal Kits SWIDokument2 Seiten40 90 Mechanical Seal Kits SWIWong DaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuickServe Online - (4021531) QSB4.5 and QSB6.7 Operation and Maintenance ManualDokument7 SeitenQuickServe Online - (4021531) QSB4.5 and QSB6.7 Operation and Maintenance Manualibrahim salemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mud Pump Bomco LGF-1000 Operations ManualDokument26 SeitenMud Pump Bomco LGF-1000 Operations ManualWilliam Arturo AristizabalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propeller RemovalDokument10 SeitenPropeller RemovalMedha Jog Katdare100% (1)
- Hydraulic Cylinder Liner PullerDokument4 SeitenHydraulic Cylinder Liner PullerLogeshMech100% (5)
- Drive Axle, Speed Reducer, and Differential: J2.00-3.20XM (J40-60XM, J40-60XM) (A216) J2.00-3.20XM (J40-60Z) (A416)Dokument18 SeitenDrive Axle, Speed Reducer, and Differential: J2.00-3.20XM (J40-60XM, J40-60XM) (A216) J2.00-3.20XM (J40-60Z) (A416)InfoMecanicaTaller contactoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baoji Engineering YM-16IIF Hydraulic Cathead Operations ManualDokument22 SeitenBaoji Engineering YM-16IIF Hydraulic Cathead Operations ManualDhrubajyoti BoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumatic Actuators Series 92 93 TM en UsDokument10 SeitenPneumatic Actuators Series 92 93 TM en UsizoelsiregarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resealing The VE Injector PumpDokument20 SeitenResealing The VE Injector PumpFayez AlnamarnehNoch keine Bewertungen
- C70 Shift RemovalDokument57 SeitenC70 Shift RemovalIsi DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installing The Discharge Chute Adjusting The ConDokument1 SeiteInstalling The Discharge Chute Adjusting The ConKathryn O’ConnorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Ash Handling Operation & Maintenance PDFDokument64 SeitenBoiler Ash Handling Operation & Maintenance PDFdreamboy87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manual: Internal Gear PumpDokument16 SeitenInstruction Manual: Internal Gear PumpGrosu DanutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assembly and Disaassembly of PumpsDokument5 SeitenAssembly and Disaassembly of Pumpsshin deiru100% (1)
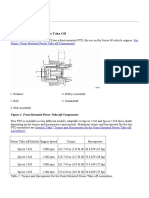
- Section 10 - Power Take-OffDokument19 SeitenSection 10 - Power Take-OffMiller Andres ArocaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CYBW Air Pump Manual-DeyuanDokument11 SeitenCYBW Air Pump Manual-DeyuanSew Chi Zhong0% (1)
- New File ListDokument2 SeitenNew File ListDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Aahan's BirthdayDokument22 SeitenAahan's BirthdayDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Educational Multimedia On Hydraulics and PneumaticsDokument89 SeitenEducational Multimedia On Hydraulics and PneumaticsDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Dipak Vinayak Shirbhate VSRDIJCSIT 3479 Research Communication June 2014Dokument4 SeitenDipak Vinayak Shirbhate VSRDIJCSIT 3479 Research Communication June 2014DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Girls Hostel FormDokument1 SeiteGirls Hostel FormDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Circles For Vikramshila StudentsDokument22 SeitenQuality Circles For Vikramshila StudentsDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Dipak Vinayak Shirbhate VSRDIJMCAPE 3631 Research Paper 4 8 August 2014Dokument8 Seiten2 Dipak Vinayak Shirbhate VSRDIJMCAPE 3631 Research Paper 4 8 August 2014DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Prospectus For 14-15Dokument44 SeitenProspectus For 14-15DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Circle A Case Study: Prof. D.V. Shirbhate Principal, Vikramshila Polytechnic DarapurDokument34 SeitenQuality Circle A Case Study: Prof. D.V. Shirbhate Principal, Vikramshila Polytechnic DarapurDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Domestic Water Heater PDFDokument39 SeitenDomestic Water Heater PDFDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Pramod Naik's Letter Director MsbteDokument1 SeitePramod Naik's Letter Director MsbteDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Salary Slip - May 2014Dokument5 SeitenSalary Slip - May 2014DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Boys Hostel FormDokument1 SeiteBoys Hostel FormDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (1)
- Prospectus For 13-14Dokument42 SeitenProspectus For 13-14DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of EnterprenuersDokument12 SeitenClassification of EnterprenuersDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (2)
- Creativity & The Business IdeaDokument12 SeitenCreativity & The Business IdeaDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Inplant TrainingDokument1 SeiteInplant TrainingDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Prospectus Data 2013-14Dokument12 SeitenProspectus Data 2013-14DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Leave ApplicationDokument2 SeitenLeave ApplicationDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (2)
- Autocad 2009 Tips and Tricks DVSDokument24 SeitenAutocad 2009 Tips and Tricks DVSDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal For New PolytechnicDokument7 SeitenProposal For New PolytechnicDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Diploma Education For Rural StudentsnnDokument55 SeitenImportance of Diploma Education For Rural Studentsnnvspd2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rule 3Dokument1 SeiteRule 3DIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENoch keine Bewertungen
- Nss Allotment Request Letter ModifiedDokument2 SeitenNss Allotment Request Letter ModifiedDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE75% (4)
- Catalogo Air Cooled Screw Chiller LGDokument42 SeitenCatalogo Air Cooled Screw Chiller LGgian ososNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table (4b) Actuator Dimensions (OM-2 To OM-3, OM-4 To OM-6) Table (4a) Actuator Dimensions (OM-1)Dokument5 SeitenTable (4b) Actuator Dimensions (OM-2 To OM-3, OM-4 To OM-6) Table (4a) Actuator Dimensions (OM-1)NaveenRajNoch keine Bewertungen
- V-Rings & V-Seals - Global O-Ring and Seal PDFDokument7 SeitenV-Rings & V-Seals - Global O-Ring and Seal PDFMAMI RAKOTOMAHANINANoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual 2008 EpicaDokument16 SeitenService Manual 2008 EpicaUmmes Ahmed100% (3)
- Engine Lombardini LDW1003Dokument56 SeitenEngine Lombardini LDW1003albert michaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic ClutchDokument12 SeitenHydraulic Clutchmrkadu_610% (1)
- Compressor, Main Parts, Types and Working Principle: PV NRT P TDokument6 SeitenCompressor, Main Parts, Types and Working Principle: PV NRT P TMuhammad Arslan AfzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Innovations Arrived From 1860Dokument2 SeitenThe Innovations Arrived From 1860NicolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qustion TestDokument3 SeitenQustion Testprabhu4321Noch keine Bewertungen
- HATZ-IM - Unidad DieselDokument33 SeitenHATZ-IM - Unidad DieselAdrian MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- EntireIndex2013 1-99Dokument100 SeitenEntireIndex2013 1-99foxxbatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minebea Stepper Motor Winding Wiring PinoutsDokument3 SeitenMinebea Stepper Motor Winding Wiring PinoutsBabobrillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Regulator Valve Kit: GM 6L45, 6L50, 6L80, 6L90Dokument2 SeitenPressure Regulator Valve Kit: GM 6L45, 6L50, 6L80, 6L90Mohamed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series BS: Compact Worm GearDokument60 SeitenSeries BS: Compact Worm GearPulithevan SrinivasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sandvik RD414 Training Material 2015Dokument19 SeitenSandvik RD414 Training Material 2015rolandNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAI Industries, Inc. - Catalog Polea de MotorDokument2 SeitenPAI Industries, Inc. - Catalog Polea de MotorAlexis ValleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deutz 2013 Automotive Specs PDFDokument2 SeitenDeutz 2013 Automotive Specs PDFY.EbadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraf Atp Index Transmission PDFDokument1.285 SeitenAircraf Atp Index Transmission PDFhebert perezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DK 1008-En 04.15 13 PDFDokument1 SeiteDK 1008-En 04.15 13 PDFIulia CostacheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue 2018: Automatic Transmission Fluid Coolant Concentrate Engine OilDokument34 SeitenCatalogue 2018: Automatic Transmission Fluid Coolant Concentrate Engine OilOne CarNoch keine Bewertungen
- W20845C V K3fah3b2000016 08062020Dokument931 SeitenW20845C V K3fah3b2000016 08062020eng samiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Twin Disc ManualDokument164 SeitenTwin Disc ManualDavid B100% (10)
- Testing & Commissioning ChecklistsDokument18 SeitenTesting & Commissioning Checklistsmoh khNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of RobotsDokument13 SeitenHistory of RobotsAiswar PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dgca Module 17 Part 2Dokument9 SeitenDgca Module 17 Part 2Amal Vinod100% (1)
- Mitsubishi Evo ECU PinoutsDokument2 SeitenMitsubishi Evo ECU PinoutsDavid AlanocaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Standard Part List Cone CrusherDokument2 SeitenGeneral Standard Part List Cone CrushermoddysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Tools & Equipment: Catalog #4Dokument68 SeitenAutomotive Tools & Equipment: Catalog #4Ptryzzia Aunne100% (1)
- Dgms Tech Circular No 2 of 2002 Accident Due To TipperDokument4 SeitenDgms Tech Circular No 2 of 2002 Accident Due To Tipperj subbaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- L 31190Dokument4 SeitenL 31190Jose ivan delgado UgaldeNoch keine Bewertungen