Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Laboratory 3 Ckt1
Hochgeladen von
Rennel Mallari0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
13 Ansichten3 SeitenECE Laboratory
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenECE Laboratory
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
13 Ansichten3 SeitenLaboratory 3 Ckt1
Hochgeladen von
Rennel MallariECE Laboratory
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
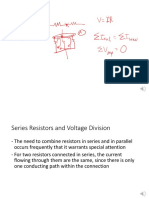
The total voltage is equal
to the sum of the drops.
V
T
= V
1
+ V
2
+ V
3
+ V
4
+ V
5
V
1
V
2
V
3
V
4
V
5
V
T
This is known as
Kirchhoffs voltage law (KVL).
The total voltage is equal
to the sum of the drops.
V
T
= V
1
+ V
2
+ V
3
+ V
4
+ V
5
V
1
V
2
V
3
V
4
V
5
V
T
V
1
V
2
V
3
V
4
V
5
V
T
This is known as
Kirchhoffs voltage law (KVL).
LABORATORY 3: VERIFICATION OF OHMS LAW and KVL in SERIES CIRCUITS
Name: _________________ Date: ________________
Course/Sec: ____________ Rating: _______________
Laboratory Objectives:
1. In this lab the student will analyze, construct, and test a simple circuit to verify Kirchoffs Voltage Law
and OHMs Law
2. To provide the students with hands-on experience in breadboarding resistive circuits.
3. To understand the characteristics of series circuits.
Laboratory Materials:
Analog/Digital Multimeter
Resistors
Power Supply
Connecting Wires
Breadboard
Key Concepts:
Kirchoffs Voltage Law- The IR drops must add to equal the applied voltage (KVL).
Characteristics of a Series Circuit
The current is the same everywhere in a series circuit.
The total resistance is equal to the sum of the individual resistance values.
The total voltage is equal to the sum of the IR voltage drops across the individual
resistances.
The total power is equal to the sum of the power dissipated by each resistance.
Current is the movement of electric charge between two points, produced by the
applied voltage.
The free electrons moving away from one point are continuously replaced by free
electrons flowing from an adjacent point in the series circuit.
All electrons have the same speed as those leaving the voltage source.
Therefore, I is the same in all parts of a series circuit.
Laboratory Procedure:
1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram.
2. Check your connections before switch on the supply.
3. Vary the regulated supply.
4. Measure the current using ammeter.
5. Note the readings in the tabulation.
6. Compare the observation reading to theoretical value.
Circuit Diagram 1.
Resistor
Value
Measured
Voltage
Theoretical
Voltage
Measured
Current
Theoretical
Current
R1
R2
R3
R4
R5
Circuit Diagram 2.
Resistor
Value
Measured
Voltage
Theoretical
Voltage
Measured
Current
Theoretical
Current
R1
R2
R3
R4
Circuit Diagram 3.
Resistor
Value
Measured
Voltage
Theoretical
Voltage
Measured
Current
Theoretical
Current
R1
R2
R3
R4
R5
R6
Circuit Diagram 4.
Resistor
Value
Measured
Voltage
Theoretical
Voltage
Measured
Current
Theoretical
Current
R1
R2
R3
LABORATORY OBSERVATION AND CONCLUSION:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- IECEP InvitationDokument1 SeiteIECEP InvitationRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 1 Midterm Logic Circuits and Switching TheoryDokument1 SeiteQuiz 1 Midterm Logic Circuits and Switching TheoryRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra2 - Exam - AnswerDokument1 SeiteAlgebra2 - Exam - AnswerRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument2 SeitenTrigonometryRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MatsciDokument1 SeiteMatsciRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra1 - Exam - AnswerDokument1 SeiteAlgebra1 - Exam - AnswerRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candidacy Declaration: Institute of Electronics Engineers of The Philippines, Inc. (Iecep) Pampanga ChapterDokument3 SeitenCandidacy Declaration: Institute of Electronics Engineers of The Philippines, Inc. (Iecep) Pampanga ChapterRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marcotting and BuddingDokument3 SeitenMarcotting and BuddingRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry Trigonometry Trigonometry Trigonometry Trigonometry Trigonometry TrigonometryDokument1 SeiteTrigonometry Trigonometry Trigonometry Trigonometry Trigonometry Trigonometry TrigonometryRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Get Unlimited Downloads With A MembershipDokument1 SeiteGet Unlimited Downloads With A MembershipRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sorry, This Document Was A Duplicate of A Document Already On ScribdDokument2 SeitenSorry, This Document Was A Duplicate of A Document Already On ScribdRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Verification Code May Take Up To 10 Minutes To Be Delivered. If You Do Not Receive Your Code, You CanDokument1 SeiteThe Verification Code May Take Up To 10 Minutes To Be Delivered. If You Do Not Receive Your Code, You CanRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Let Review 2015Dokument92 SeitenEnglish Let Review 2015Rennel Mallari89% (9)
- I Never Realized So Many Board Games Existed! I'm Hooked!!! I Never Realized So Many Board Games Existed! I'm Hooked!!!Dokument1 SeiteI Never Realized So Many Board Games Existed! I'm Hooked!!! I Never Realized So Many Board Games Existed! I'm Hooked!!!Rennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kto12 Education SystemDokument1 SeiteKto12 Education SystemRennel MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Antenna Effect: Guideline StandardsDokument9 SeitenAntenna Effect: Guideline StandardssrajeceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yashvardhan - EEC Micro Project ReportDokument15 SeitenYashvardhan - EEC Micro Project Report166CMYashvardhan Shinde75% (4)
- Technical SpecificationsDokument56 SeitenTechnical SpecificationsTrajkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infineon Thyristors and Diodes2009Dokument48 SeitenInfineon Thyristors and Diodes2009LeonardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistanc Ewelding HandbookDokument9 SeitenResistanc Ewelding Handbooksarath_srkNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRS4 Series PCB Power RelaysDokument3 SeitenHRS4 Series PCB Power Relayscyber_nauticaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nexans - 1051841 - MCCC 4X10mm2 XLPE PVC+E10mm2 PVCDokument2 SeitenNexans - 1051841 - MCCC 4X10mm2 XLPE PVC+E10mm2 PVCKAREEEMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 1Dokument28 SeitenSolid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 1Yawar KhurshidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saudi Aramco Test ReportDokument8 SeitenSaudi Aramco Test Reportkarthi51289Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test Equipment TE 98 01Dokument23 SeitenTest Equipment TE 98 01Carlos GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 163224Dokument8 Seiten163224p09el860Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.4 Lecture Slides For Chenming Hu Book: Modern Semiconductor Devices For ICsDokument79 SeitenCh.4 Lecture Slides For Chenming Hu Book: Modern Semiconductor Devices For ICsChenming Hu100% (1)
- Internship Report: Noman DilberDokument42 SeitenInternship Report: Noman Dilberfarhan9125Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4.2.2 Short-Circuit Test IEC TR 61901 - 2016Dokument6 Seiten4.2.2 Short-Circuit Test IEC TR 61901 - 2016sajuaanalsa100% (1)
- Portable Mobile ChargerDokument9 SeitenPortable Mobile Chargermohamed AasisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philips 3C85 Ferrite MaterialDokument9 SeitenPhilips 3C85 Ferrite Materialcatalin0827Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee231 Lec 1C PDFDokument33 SeitenEe231 Lec 1C PDFPaolo Josemari ZafraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ds2 Series User Manual: Ac Servo SystemDokument167 SeitenDs2 Series User Manual: Ac Servo SystemricardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Com 223 Basic Hardware Maintenance TheoryDokument83 SeitenCom 223 Basic Hardware Maintenance TheoryProsper EmonenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department Of: ACADEMIC YEAR:2021-2022 II Year/Iii SemesterDokument8 SeitenDepartment Of: ACADEMIC YEAR:2021-2022 II Year/Iii SemesternagendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 DH-DV Catalog March 2015Dokument40 Seiten01 DH-DV Catalog March 2015BNCHNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE8311 Electrical Machines Lab - 1 Manual PDFDokument67 SeitenEE8311 Electrical Machines Lab - 1 Manual PDFkrishnandrk100% (2)
- (3Cx25+1Cx25) Bare SHASWAT CABLEDokument16 Seiten(3Cx25+1Cx25) Bare SHASWAT CABLEGaurav KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Science Mid Term PaperDokument6 Seiten10 Science Mid Term PaperAnishika100% (1)
- Heat Loss in Bare and Lagged Pipes PDFDokument13 SeitenHeat Loss in Bare and Lagged Pipes PDFjamaiiica100% (1)
- ModulanteDokument23 SeitenModulanteVBPNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparison Between Maximum Torque/Ampere and Maximum Efficiency Control Strategies in IPM Synchronous MachinesDokument8 SeitenA Comparison Between Maximum Torque/Ampere and Maximum Efficiency Control Strategies in IPM Synchronous Machinesreddy venkata krishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9702 w18 QP 12Dokument20 Seiten9702 w18 QP 12poojaNoch keine Bewertungen