Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
WASTEH20 MBR Process Design PDF
Hochgeladen von
David Lambert0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
402 Ansichten23 SeitenMBR-process-design
Originaltitel
WASTEH20-MBR-process-design.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMBR-process-design
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
402 Ansichten23 SeitenWASTEH20 MBR Process Design PDF
Hochgeladen von
David LambertMBR-process-design
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 23
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
1
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Membrane Bioreactor Technology
Basic engineering design
Technical presentation for WWE Sdn Bhd
Kuala Lumpur November 7, 2003
Professor Zaini Ujang
Ph.D., C.Eng.(UK), C.W.E.M. (UK), PPT
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
2
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Presentation outline
Objectives
Which membrane systems?
Configurations
Aeration techniques
Activated sludge microbial populations
Biomass separation
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
3
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Objectives?
Organic removal
Organic removal and nitrification
Organic, nitrogen removal & water recycling
Organic and nutrient removal & water recycling
Persistent organic removal & water recycling
High strength waste management
Cleaner production
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
4
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Objectives & systems
Objectives MBR Conventional
1 Not recommended WSP, CAS, RBC etc
2 Not recommended CAS, EA, RBC etc
3 Recommended AS + RO
4 Recommended AS + RO
5 Recommended (Hybrid MBR) AS + RO + GAC
6 Recommended (Hybrid MBR) Hybrid
7 Recommended (Hybrid MBR) Hybrid
1=Organic removal, 2=Organic removal and nitrification, 3=Organic, nitrogen removal
& water recycling 4=Organic and nutrient removal & water recycling, 5=Persistent
organic removal & water recycling, 6=High strength waste, 7 =Cleaner production
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
5
MBR Basic Engineering Design
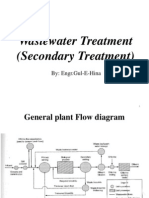
MBR processes
Membrane separation
bioreactors
Membrane aeration
bioreactors
Extractive membrane
bioreactors
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
6
MBR Basic Engineering Design
MBR processes
Membrane separation bioreactors Submerged
Effluent
Bioreactor
Influent
Activated Sludge-Based Membrane System
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
7
MBR Basic Engineering Design
MBR processes
Membrane separation bioreactors Side-stream
Effluent
Sludge
Return sludge
Primary clarifier Membrane Unit
Bioreactor
Sludge
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
8
MBR Basic Engineering Design
MBR Technology
Membrane separation bioreactors
Advantages Disadvantages
-Small footprint -Aeration limitation
-Complete solid removal -Membrane fouling
-Effluent disinfection -Membrane costs
-Removal of organic, nutrient & solid
-High loading rate capability
-Low/zero sludge production
-Rapid start up
-Sludge bulking not a problem
-Modular/retrofit
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
9
MBR Basic Engineering Design
MBR processes
Membrane aeration bioreactors
Effluent
Bioreactor
Influent
Oxygen
Bubbleless O transfer
Hollow fiber membrane
Gas Separation-Based Membrane System
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
10
MBR Basic Engineering Design
MBR Technology
Membrane aeration bioreactors
Advantages Disadvantages
-High oxygen utilization -Membrane fouling
-Highly efficient energy utilization -High capital cost
-Small foot print -Unproven at full scale
-Feed-forward control of O demand -Process complexity
-Modular/retrofit
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
11
MBR Basic Engineering Design
MBR processes
Membrane extractive bioreactors
Effluent
Bioreactor
Gas Separation-Based Membrane System
Influent/Polluted materials
For recycling
Hollow fiber membrane
Treated wastewater
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
12
MBR Basic Engineering Design
MBR Technology
Extractive membrane bioreactors
Advantages Disadvantages
-Treatment of toxic industrial effluents -High capital cost
-Small effluents -Process complexity
-Modular/retrofit -Unproven at full scale
-Isolation of bacteria from wastewater
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
13
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Performance comparison between activated
sludge and MBR (Cicek et al., 1999)
Parameters Activated sludge MBR
Sludge age (d) 20 30
COD removal (%) 94.5 99
DOC removal (%) 92.7 97
TSS removal (%) 60.9 99.9
A-N removal 98.9 99.2
Total P removal (%) 88.5 96.6
Slude production
(kg VSS/COD.d)
0.22 0.27
Mean floc size (m) 20 3.5
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
14
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Design criteria MBR
Parameters
Design values
Loading rates (for >90% organic
removal)
1.2 to 3.2 kg COD/m
3
.d
0.05 to 0.66 kg BOD/m
3
.d
Loading rates for complete
nitrification
0.05 to 0.66 kg BOD/m
3
.d
Sludge age 10 to 50 d
Loading rate for complete nitrogen
removal
4 kg NH
4
-N/m
3
.d
5 kg NO
3
-N/m
3
.d
MLSS 10,000 to 20,000 mg/l
Flux 5 to 300 L/m
2
.h
Specific flux 20 to 200 L/ m
2
h bar
Design flux (Kubota, of 0.4 m) 0.5 m
3
/m
2
.d
(specific flux 125-175 L/ m
2
h bar)
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
15
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Aerobic MBR
Examples of design criteria
Wastewater Type V
(m
3
)
HRT
(h)
(d) Organic
load
(kg/m
3
d)
MLSS
(kg)
Sludge
yield (d)
Air
(m
3
/h)
Raw sewage (Ueda&
Hata, 1999)
HF/S/
PE
3.12 13.4 72 0.245 12.9 - 18
Municipal
(Cote et al., 1997)
HF/S 1 4.8 - 2.3 26 0.2 0.5-1.5
Raw sewage (Ueda
et al, 1999)
HF/S 21.4 13 120 0.315 12 - 42
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
16
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Aerobic MBR configurations
Examples of specific fluxes
Configurations Specific fluxes References
Submerged HF 50 to 65 L/m
2
.h.bar
Gunder & Krauth, 1998
Flat plate 115 L/m
2
.h.bar
Gunder & Krauth, 1998
Tubular side-stream 40 to 60 L/m
2
.h.bar
Le Clechet al., 1999
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
17
MBR Basic Engineering Design
MBR technology
Materials and pore size
Pore size Materials
UF and MF
submerged
0.02 to 0.5 m Polyethylene, polypropylene,
polysulphone etc
UF and MF
Side-stream
0.02 to 0.5 m Ceramics (MF), polyethylene,
polypropylene, polysulphone etc
NF submerged <0.02 m Polyethylene, polypropylene,
polysulphoneetc
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
18
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Aerobic MBR: Energy consumption
Pumping influent, recycling retente, permeate suction & aeration
Energy requirement References
MF submerged 0.2 to 0.4 kW.h/m
3
Cote et al., 1998
MF side-stream 2 to 10 kW.h/m
3
Cote et al., 1998
MF hollow fibre
submerged
0.3 kW.h/m
3
(0.28 for aeration)
Cote et al., 1997
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
19
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Anaerobic MBR technology
Membrane separation bioreactors Side-stream
Effluent
Sludge
Return sludge
Primary clarifier Membrane Unit
Anaerobic digester
Sludge
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
20
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Anaerobic MBR
Loading rates
Parameters Values References
Side-stream MBR -Loading
rates (acidogenic)
54 kg COD/m
3
.d
Anderson et al., 1986
Side-stream MBR - Loading
rates (methanogenic)
12.2 kg COD/m
3
.d
Anderson et al., 1986
Submerged MBR- Loading
rates
15 kg COD/m
3
.d
Li et al, 1985;
Kayawakeet al., 1991
HRT 67 h - POME
124 h - maize waste
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
21
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Typical values for the design parameters for
activated sludge processes
Process ,
d
F/M,
lb BOD/ lb
MLVSS.d
Volumetric
loading,
lb BOD / 10
3
ft
3
.d
MLSS,
mg/l
V/Q,
h
Q
r
/Q
Conventional
plug flow
3-15 0.2-0.6 20-40 1000-3000 4-8 0.25-0.75
Complete mix 0.75-
15
0.2-1.0 50-120 800-6500 3.5 0.25-1.0
Step feed 3-15 0.2-0.5 40-60 1500-3500 3-5 0.25-0.75
Single-stage
nitrification
8-12 0.10-0.2 5-20 1500-3500 6-15 0.5-1.5
Separate-stage
nitrification
15-100 0.05-0.2 3-9 1500-3500 3-6 0.5-2
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
22
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Typical values for the design parameters
for activated sludge processes
Process ,
d
F/M,
lb BOD/ lb
MLVSS.d
Volumetric
loading,
lb BOD / 10
3
ft
3
.d
MLSS,
mg/l
V/Q,
h
Q
r
/Q
Contact
stabilization
5-15 0.2-0.6 60-70 1000-3000 0.5-1 0.5-1.5
Extended
aeration
20-40 0.04-0.1 5-15 2000-8000 18-36 0.5-1.5
Oxidation
ditch
15-30 0.04-0.1 5-15 2000-8000 8-36 0.5-1.5
Intermittent
decanted EA
12-25 0.04-
0.08
5-15 2000-8000 20-40 NA
Sequencing
batch reactor
10-30 0.04-0.1 5-15 2000-8000 12-50 NA
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
Institute of Environmental & Water Resource Management
23
MBR Basic Engineering Design
Design procedure for submerged MBR
Steps V/Q,
h
Q
r
/Q
Wastewater characterization, and
flow rate
0.5-1 0.5-1.5
Objectives? 18-36 0.5-1.5
Oxidation ditch 8-36 0.5-1.5
Intermittent decanted EA 20-40 NA
Sequencing batch reactor 12-50 NA
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Rotating Biological ContactorDokument17 SeitenRotating Biological Contactormikelycan100% (2)
- Membrane Bioreactors Potential for Wastewater TreatmentDokument25 SeitenMembrane Bioreactors Potential for Wastewater TreatmentAgus WitonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shortcut Nitrogen Removal-Nitrite Shunt and DeammonificationVon EverandShortcut Nitrogen Removal-Nitrite Shunt and DeammonificationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) : Pilot Plant Process Modelling and Scale-UpDokument15 SeitenMembrane Bioreactor (MBR) : Pilot Plant Process Modelling and Scale-UpEswaramoorthi Sellappa Gounder100% (7)
- Training Manual MBBRDokument84 SeitenTraining Manual MBBRTahirJabbar100% (3)
- Modeling of Activated Sludge With ASM1 Model, Case Study On Wastewater Treatment Plant of South of IsfahanDokument10 SeitenModeling of Activated Sludge With ASM1 Model, Case Study On Wastewater Treatment Plant of South of IsfahanAnish GhimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kubota SMU General Information PDFDokument6 SeitenKubota SMU General Information PDFJulio TovarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 - Biological WWTP II - Moving Bed Biofilm ReactorDokument45 Seiten02 - Biological WWTP II - Moving Bed Biofilm ReactorAquasoul CoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBR V Conv ComparisonDokument10 SeitenMBR V Conv ComparisonJayakrishnan RadhakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membrane Bio Reactors ExplainedDokument16 SeitenMembrane Bio Reactors Explainedvvrckumar100% (1)
- 2 05MasteringMBBRprocessdesignforcarbonandnitrogenabatementDokument65 Seiten2 05MasteringMBBRprocessdesignforcarbonandnitrogenabatementYên BìnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Biofilm MBR For Municipal Wastewater TreatmentDokument133 SeitenApplication of Biofilm MBR For Municipal Wastewater Treatmentsulihah12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Process UASB GuideDokument18 SeitenUpflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Process UASB GuideKhang TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - Activated Sludge PDFDokument12 SeitenChapter 8 - Activated Sludge PDFRieskaYuniarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pptonfab MBBR 130616081952 Phpapp01Dokument18 SeitenPptonfab MBBR 130616081952 Phpapp01TAREK ALMAHDY100% (3)
- MBR Wastewater Treatment: Membrane Bioreactors ExplainedDokument16 SeitenMBR Wastewater Treatment: Membrane Bioreactors ExplainedAgus WitonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBBR MediaDokument2 SeitenMBBR MediaAseem Vivek Masih100% (2)
- Biological Treatment of WastewaterDokument15 SeitenBiological Treatment of WastewaterAyomideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment of Industrial Waste Water and Process Water With Membrane Processes and Membrane Bio ReactorsDokument52 SeitenTreatment of Industrial Waste Water and Process Water With Membrane Processes and Membrane Bio ReactorsturtlemethodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyna SandDokument4 SeitenDyna SandMaximilianoRodrigoCabestrero100% (1)
- Modeling Nitrogen ReomovalDokument307 SeitenModeling Nitrogen ReomovalenviroashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activated Sludge ProcessDokument28 SeitenActivated Sludge Processusmansherdin100% (2)
- Biological Nutrient RemovalDokument30 SeitenBiological Nutrient Removalsurajp333Noch keine Bewertungen
- Efficiency Comparison of Sewage Treatment Plants in BangaloreDokument36 SeitenEfficiency Comparison of Sewage Treatment Plants in BangalorePRETTY MARY100% (1)
- BV Webinar SlidesDokument64 SeitenBV Webinar SlidessuinsasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ActivateSludgeVS Membrane Reactor SLIDEDokument36 SeitenActivateSludgeVS Membrane Reactor SLIDEsebascian100% (1)
- MBR - Industrial WW AE 02Dokument12 SeitenMBR - Industrial WW AE 02transilvanpopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biowin ProjectDokument110 SeitenBiowin ProjectAnonymous e7NLhgTmzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report of Membrane Bioreactor System (MBR) For Wastewater TreatmentDokument10 SeitenReport of Membrane Bioreactor System (MBR) For Wastewater TreatmentJulie MahadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBBR Vs SBRDokument25 SeitenMBBR Vs SBRDileep C Dileep100% (2)
- Aeration Tank Blower Calcns Package - US UnitsDokument19 SeitenAeration Tank Blower Calcns Package - US UnitsAqua tech chemicals officesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBBR System for Wastewater TreatmentDokument3 SeitenMBBR System for Wastewater TreatmentdainguyenlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trickling Filters: Biological Wastewater Treatment Using Porous MediaDokument7 SeitenTrickling Filters: Biological Wastewater Treatment Using Porous MediaTasirmistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculations Used in Daily Operations of An EtpDokument9 SeitenCalculations Used in Daily Operations of An Etpnguyen an100% (1)
- Cost Analysis of Activated Sludge ProcessDokument19 SeitenCost Analysis of Activated Sludge ProcessDevendra Sharma100% (1)
- Modeling Oxidation Ditches Wastewater TreatmentDokument19 SeitenModeling Oxidation Ditches Wastewater Treatmentashok100% (1)
- Activated Sludge Calculations Excel CourseDokument22 SeitenActivated Sludge Calculations Excel CoursesahatNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is MBBR, and How Does It WorkDokument8 SeitenWhat Is MBBR, and How Does It WorkManuel AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anoxic TankDokument12 SeitenAnoxic TankpragatheeskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)Dokument13 SeitenMembrane Bioreactor (MBR)Hasriyani HafidNoch keine Bewertungen
- UASB-Process Design For Various Types of WastewatersDokument21 SeitenUASB-Process Design For Various Types of WastewatersapitbhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ozone Based Waste Water TreatmentDokument10 SeitenOzone Based Waste Water TreatmentZafar BukhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Next Generation of MBBR TechnologyDokument48 SeitenNext Generation of MBBR TechnologyLouay Mansour100% (1)
- Laundry Wastewater Treatment Using Coagulation and Membrane FiltrationDokument20 SeitenLaundry Wastewater Treatment Using Coagulation and Membrane FiltrationAnggy de Rincon100% (1)
- AOPs A Critical Review PDFDokument54 SeitenAOPs A Critical Review PDFM S MahtabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sequencing Batch Reactor Technology For Biological Wastewater Treatment: A ReviewDokument9 SeitenSequencing Batch Reactor Technology For Biological Wastewater Treatment: A ReviewDiliptiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 - Biological WWTP III - Membrane BioreactorDokument26 Seiten02 - Biological WWTP III - Membrane BioreactorAhmed100% (1)
- Equipment Design: Aeration Tank TitleDokument6 SeitenEquipment Design: Aeration Tank TitleKENGERALDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Zero DischargeDokument4 SeitenConcept of Zero DischargeShesharam Chouhan67% (3)
- MBR-C1 Fundamentals of MBRDokument36 SeitenMBR-C1 Fundamentals of MBRAlfonso José García Laguna100% (3)
- DAF DGF SeparatorsDokument8 SeitenDAF DGF SeparatorsDylan RamasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBRDokument9 SeitenMBRAuspicious MuthuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBBRDokument4 SeitenMBBRmudit03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro-Flo Technologies, Inc.: Chemical Name Acid - Typical Project Name XX-XXXXDokument4 SeitenHydro-Flo Technologies, Inc.: Chemical Name Acid - Typical Project Name XX-XXXXPutra TatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBR Presentation LatestDokument12 SeitenMBR Presentation LatestRuchi GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPA Lagoon Design Manual - Paul Krauft Utah State PDFDokument79 SeitenEPA Lagoon Design Manual - Paul Krauft Utah State PDFNataliaKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activated SludgeDokument27 SeitenActivated SludgeMukesh JagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CalculationDokument5 SeitenCalculationalok_rajpoot786100% (2)
- Clarifier Gear Drive Torque ValuesDokument4 SeitenClarifier Gear Drive Torque ValuesDavid Lambert100% (4)
- Cyclone DesignDokument1 SeiteCyclone DesignDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAFDokument1 SeiteDAFDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Booster Pump RequiredDokument6 SeitenBooster Pump RequiredDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Produksi WOOD PELLLETDokument3 SeitenProcess Produksi WOOD PELLLETDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grease Trap SizingDokument9 SeitenGrease Trap SizingEngFaisal Alrai100% (2)
- Venting DesignDokument1 SeiteVenting DesignDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pekerjaan Plumbing Main Equipment: Bill No 3 Project: Coca-Cola Bulan Baru, Surabaya Services: PlumbingDokument34 SeitenPekerjaan Plumbing Main Equipment: Bill No 3 Project: Coca-Cola Bulan Baru, Surabaya Services: PlumbingDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pekerjaan Plumbing Main Equipment: Bill No 3 Project: Coca-Cola Bulan Baru, Surabaya Services: PlumbingDokument34 SeitenPekerjaan Plumbing Main Equipment: Bill No 3 Project: Coca-Cola Bulan Baru, Surabaya Services: PlumbingDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Drop CalculationDokument8 SeitenPressure Drop CalculationDavid Lambert100% (1)
- Booster Pump RequiredDokument6 SeitenBooster Pump RequiredDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAFDokument1 SeiteDAFDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commissioning Procedure Air Pre HeaterDokument15 SeitenCommissioning Procedure Air Pre HeaterDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selecting of Booster Pump For BuildingDokument7 SeitenSelecting of Booster Pump For BuildingDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gambar ProsesDokument1 SeiteGambar ProsesDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matchday Hari IniDokument2 SeitenMatchday Hari IniDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Price List With Breakdown & Unit PriceDokument1 SeitePrice List With Breakdown & Unit PriceDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- PyrolysisDokument1 SeitePyrolysisDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load FactorDokument4 SeitenLoad FactorDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFD WTP PDFDokument1 SeitePFD WTP PDFDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perhitungan Natural DraftDokument2 SeitenPerhitungan Natural DraftDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sizing ScrubberDokument62 SeitenSizing ScrubberindahazhrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleaching Tank PT. Gurita Mandala No. Deskripsi KeteranganDokument1 SeiteBleaching Tank PT. Gurita Mandala No. Deskripsi KeteranganDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load FactorDokument4 SeitenLoad FactorDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Control Panel Sheet-5Dokument1 SeiteLocal Control Panel Sheet-5David LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wiring Diagram DC IIDokument2 SeitenWiring Diagram DC IIDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konversi Besi Tulangan Ke Wire MeshDokument1 SeiteKonversi Besi Tulangan Ke Wire MeshDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBBR OM Manual-250Dokument42 SeitenMBBR OM Manual-250senthil2002100% (3)
- Layout Line Checking Part (Front View) Revisi-1Dokument1 SeiteLayout Line Checking Part (Front View) Revisi-1David LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Form WWTPDokument35 SeitenTechnical Form WWTPDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrology, 2009, Madan Mohan Das, Mimi Das Saikia, 8120337077, 9788120337077, PHI Learning Pvt. LTD., 2009Dokument18 SeitenHydrology, 2009, Madan Mohan Das, Mimi Das Saikia, 8120337077, 9788120337077, PHI Learning Pvt. LTD., 2009pjpilot123Noch keine Bewertungen
- WHAT IS HYDROGRAPHY - NOAA Hydro Training 2009Dokument32 SeitenWHAT IS HYDROGRAPHY - NOAA Hydro Training 2009Tony ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water TariffDokument625 SeitenWater TariffLlucifer ImpulseNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 Water TurbineDokument40 SeitenL1 Water TurbineJamal M. DaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Time Frame: 9 Hours: Learning ModuleDokument13 SeitenTopic Time Frame: 9 Hours: Learning ModuleJea Escabal MosenabreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D 5640 Standard Guide For Selection of Weirs and Flumes For Open Channel Flow Measurement of WaterDokument7 SeitenAstm D 5640 Standard Guide For Selection of Weirs and Flumes For Open Channel Flow Measurement of WatergedebhaskoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fish passage experience at small-scale hydropower plants in FranceDokument12 SeitenFish passage experience at small-scale hydropower plants in Franceflanker100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flexim Case Study Anastasia Island Wastwater Treatment Plant With Air inDokument14 SeitenFlexim Case Study Anastasia Island Wastwater Treatment Plant With Air inAngel AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30.rain Water HarvestingDokument5 Seiten30.rain Water HarvestingmariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02-Pipe - FittingsDokument1 Seite02-Pipe - Fittingssopan kharcheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines 24x7 Water Supply Systems 1640325006Dokument118 SeitenGuidelines 24x7 Water Supply Systems 1640325006khajan singh rawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- BR363-Embankment Dam SafetyDokument112 SeitenBR363-Embankment Dam SafetyBart kaczynskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-1-8 Water Balance CalculationsDokument5 Seiten3-1-8 Water Balance CalculationskprasannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- METEOROLOGY - Mohamed ElgharibDokument17 SeitenMETEOROLOGY - Mohamed ElgharibmahmooodgaaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ground Water Extraction - Tubewell Technology Lecture 9Dokument16 SeitenGround Water Extraction - Tubewell Technology Lecture 9Snehasis MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Rainfall-Runoff Neuron Input Model With Artificial Neural Network For Simulation For Availability of Discharge at Bah Bolon WatershedDokument8 SeitenAnalysis of Rainfall-Runoff Neuron Input Model With Artificial Neural Network For Simulation For Availability of Discharge at Bah Bolon WatershedErvan KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kiswahili Phonetics and PhonologyDokument8 SeitenKiswahili Phonetics and Phonologyjeff omangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sewage Treatment Plant in Ahmedabad Baroda Surat Rajkot - Gujarat-IndiaDokument9 SeitenSewage Treatment Plant in Ahmedabad Baroda Surat Rajkot - Gujarat-IndiaShubham India - Sewage Treatment PlantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of EarthdamsDokument21 SeitenTypes of EarthdamsDilipKumarAkkaladeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taseko Mines New Prosperity Waste and Stockpile Preliminary DesignDokument144 SeitenTaseko Mines New Prosperity Waste and Stockpile Preliminary DesignAnonymous B7dF7CPTajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Revenue Water's Impact on Services, Environment and FinancesDokument16 SeitenNon-Revenue Water's Impact on Services, Environment and FinancesAkmalYahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Savannah Agar Life Science Grade 12 Maris Stella: Analysis of The Water Quality in The Umgeni RiverDokument30 SeitenSavannah Agar Life Science Grade 12 Maris Stella: Analysis of The Water Quality in The Umgeni RiverSavannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tunnel Type Silt EjectorDokument11 SeitenTunnel Type Silt EjectorHaseeb Uz Zaman33% (3)
- Water: Availability and Use: November 2016Dokument5 SeitenWater: Availability and Use: November 2016Jud Kevin Marlon T. AcainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minor Irrigation WorksDokument420 SeitenMinor Irrigation WorksRutuja BhawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science4 Water CycleDokument8 SeitenScience4 Water CycleJoy PartozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychrometric Chart: Normal Temperature 190 FEETDokument1 SeitePsychrometric Chart: Normal Temperature 190 FEETADITYA BANERJEENoch keine Bewertungen
- LECTURE 5-Measurement of Water Yield From WatershedDokument23 SeitenLECTURE 5-Measurement of Water Yield From WatershedChu DicksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CROPWAT Guide Estimates Irrigation NeedsDokument10 SeitenCROPWAT Guide Estimates Irrigation NeedsamityalwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planktonic ForaminiferaDokument22 SeitenPlanktonic ForaminiferaAli YücelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Confinement (Book #1 in the Love and Madness series)Von EverandConfinement (Book #1 in the Love and Madness series)Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Voice of God: Experience A Life Changing Relationship with the LordVon EverandThe Voice of God: Experience A Life Changing Relationship with the LordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Locked Away (Book #2 in the Love and Madness series)Von EverandLocked Away (Book #2 in the Love and Madness series)Noch keine Bewertungen
- From Raindrops to an Ocean: An Indian-American Oncologist Discovers Faith's Power From A PatientVon EverandFrom Raindrops to an Ocean: An Indian-American Oncologist Discovers Faith's Power From A PatientBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)