Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
MOLARITY
Hochgeladen von
Adam FrenchOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MOLARITY
Hochgeladen von
Adam FrenchCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MOLARITY
I. Introduction
Knowing the concentration of a solution can help chemists to precisely mix and remix
substances to create a solution using the Molarity of that solution. In daily life, knowing the
Molarity can be helpful in mundane tasks as using laundry detergent, or as important as
knowing the dosage of a drug to take.
II. Discussion
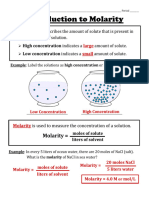
The concentration of a solute in a solution is expressed as its Molarity. It tells you how
much of a solute is present. Molarity is the moles of solute in a solution divided by the liters of
solution.
Molarity (M) = Moles of solute / Liters of solution
There are three steps to converting grams of a substance to moles. (If given the number of
grams of solute present instead of the number of moles of solute)
1. Determine how many grams are given in the problem.
2. Calculate the molar mass of the substance.
3. Divide step one by step two.
* To determine the mass of a molecule, simply add up all of the atomic masses for the atoms
that make up the molecule.
Examples:
1. 4.35 moles of KMnO
4
are dissolved in enough water to give 750mL of solution.
Determine the molarity of the solution. (1L = 1000mL)
Given: 4.35 moles of KMnO
4
, 750mL .750L
Find: Molarity
Solution: M= (moles)/ (L)
M= 4.35 moles KMnO
4
.750 L solution
Molarity = 5.80 moles KMnO
4
/ L solution
2. Calcuate the molarity when 75.0 grams of MgCl
2
is dissolved in 500.0 mL of solution.
3. 49.8 grams of KI is dissolved in enough water to make 1.00 L of solution. What is the
molarity?
OSMOLARITY
I. Introduction
Osmolarity is a concept that allows you to determine if water will move from one side of a
membrane to the other side. That is: will Osmosis occur? Water will always move across a
membrane into the solution with the higher osmolarity.
II. Discussion
Osmolarity is the product of a solutions molarity and the number of particles produced per
formula unit if the solute dissociates. The equation for osmolarity is
Osmolarity = molarity x i
i represents the number of particles produced from the dissociation of one formula unit of
solute.
* The units of osmolarity are osmols (osm).
Examples:
1. Determine the osmolarity of 2M CaCl
2
Given: 2M, 3 = i
*the value of i is 3 because three ions are produced from the dissociation of one
CaCl
2
formula unit.
CaCl
2
Ca
2+
+ 2Cl
-
Find: Osmolarity
Solution: Osmolarity = Molarity x i
= 2M x 3
Osmolarity = 6 osmol
2. Calculate the osmolarity (osmol) of the following solutions.
a) 5.2 M Na
2
CO
3
Given: 5.2M, 3 = i ( Na
1+
+ CO
2+
)
Find : Osmolarity
Solution: Osmolarity = Molarity x i
= 5.2M x 3
Osmolarity = 15.6 osmol
b) 0.15 M Al(NO
3
)
3
Given: .15M, 4 = i (Al
3+
+ NO
3
1+
)
Find: Osmolarity
Solution: Osmolarity = Molarity x i
= 0.15M x 4
Osmolarity = 0.6 osmol
III. Reference
http://www.chemteam.info/Solutions/Molarity-problems-answers.html
http://www.fordhamprep.org/gcurran/sho/sho/lessons/lesson56.htm
http://fog.ccsf.cc.ca.us/pherrman/documents/OsmolarityS10.pdf
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chemistry Concepts Stoichiometry Water SDokument50 SeitenChemistry Concepts Stoichiometry Water SJoseph DakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moles Conversion NotesDokument26 SeitenMoles Conversion Notesapi-449002661Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Calculations IV - Solution Stoichiometry.Dokument13 SeitenChemical Calculations IV - Solution Stoichiometry.Phi NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concepts, Molarity, Solutions and DilutionsDokument54 SeitenBasic Concepts, Molarity, Solutions and DilutionsMuhammed Shafi Tk100% (1)
- TOPIC 10. CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS IV - Solution StoichiometryDokument15 SeitenTOPIC 10. CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS IV - Solution StoichiometryArlane M. AbenojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 The MoleDokument48 Seiten5 The MoleCas AndersNoch keine Bewertungen
- LU2 Stoichiometry CalculationDokument67 SeitenLU2 Stoichiometry CalculationCarina JL100% (1)
- Molarity QuestionsDokument9 SeitenMolarity QuestionsNur MahammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoic Hi o MetricDokument13 SeitenStoic Hi o Metricdeep_singh234Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM 12 Chapter 3Dokument24 SeitenCHEM 12 Chapter 3ryankyleacostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Notes On Ana Chem Lecture 4Dokument6 SeitenImportant Notes On Ana Chem Lecture 4Eliza Loren PalleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating Molarity and Molality Concentration - Video & Lesson TranscriptDokument9 SeitenCalculating Molarity and Molality Concentration - Video & Lesson TranscriptAbi AbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Atoms 1st Chapter 13 SlidesDokument51 SeitenChemistry Atoms 1st Chapter 13 Slideszarwalz1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concentration of Solutions and Molarity: What We Need Is A Way of Quantifying The Concentration of A Solution!Dokument32 SeitenConcentration of Solutions and Molarity: What We Need Is A Way of Quantifying The Concentration of A Solution!MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 Chem LabDokument8 SeitenModule 5 Chem LabAivan NovillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument57 SeitenChapter 1alex tomsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 73 Solutions Molarity KEYDokument2 Seiten73 Solutions Molarity KEYGlennica Joyce AbenesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MolalityDokument6 SeitenMolalityDien AuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Chem M8Dokument9 SeitenGen Chem M8Daniela MadelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - CHE 218 - 2021.2022Dokument7 SeitenModule 1 - CHE 218 - 2021.2022Emmy OlabosipoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ways of Expressing Solution Concentration: For General Chemistry 2/grade 12-STEM Quarter 3/week 2.c-dDokument17 SeitenWays of Expressing Solution Concentration: For General Chemistry 2/grade 12-STEM Quarter 3/week 2.c-daeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument4 SeitenChapter 3Zaw Min TunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoichiometry & Titration: Submitted byDokument14 SeitenStoichiometry & Titration: Submitted byGezem GigantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note-4 SolutionsDokument64 SeitenNote-4 SolutionsIra AgcaoiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concentration Units, Mole Fractions, and Molality PDFDokument6 SeitenConcentration Units, Mole Fractions, and Molality PDFpie50% (2)
- 07 SolutionDokument72 Seiten07 SolutionsyammyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Basic ChemistryDokument80 SeitenReview Basic ChemistryEko PamungkasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molarity and Molality ANSWERSDokument3 SeitenMolarity and Molality ANSWERSNarayanRajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 Learning Guide Name: InstructionsDokument12 SeitenUnit 7 Learning Guide Name: InstructionsDimitri ModvalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Envi SciDokument17 SeitenEnvi SciPatrick LozaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Molarity: High Concentration Indicates A Low Concentration Indicates ADokument10 SeitenIntroduction To Molarity: High Concentration Indicates A Low Concentration Indicates AGrace BatlleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Physical 2018Dokument23 SeitenChapter 3 Physical 2018api-376382598Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problems Chapter 3Dokument3 SeitenProblems Chapter 3Amith BangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keyws12 2Dokument4 SeitenKeyws12 2Rea RevillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemQuest 39-41answersDokument8 SeitenChemQuest 39-41answersejNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 PowerpointDokument39 SeitenChapter 16 PowerpointsuhailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument36 SeitenChapter 1maya 1DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aim: Doing Calculations Using The Molarity Formula: Do Now: Get Ready For QuizDokument12 SeitenAim: Doing Calculations Using The Molarity Formula: Do Now: Get Ready For QuizZaid YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CopperDokument8 SeitenCopperMehul Sethaliya GajjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolutionsDokument4 SeitenSolutionsYasmin Abigail AseriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 20 Final Review Solutions Checklist: KnowledgeDokument8 SeitenChemistry 20 Final Review Solutions Checklist: KnowledgeRahill SafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GLT 121 TOPICS 1aDokument7 SeitenGLT 121 TOPICS 1ablessingNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolutionDokument6 SeitenSolutionLexiaYapNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE121 Lec8 SP120Dokument52 SeitenCHE121 Lec8 SP120djpsychoscientzNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS 10.8 Worksheet On Solution ConcentrationsDokument3 SeitenWS 10.8 Worksheet On Solution ConcentrationsJia HuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1201 ConcDokument18 Seiten1201 ConcManni Piyush SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Percent by Mass:: Notable Concentration Units FormulaDokument1 SeitePercent by Mass:: Notable Concentration Units FormulaCharles Dion MilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry II OBODODokument50 SeitenChemistry II OBODOpalmer okiemuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molarity and Polarity Report ChemistryDokument23 SeitenMolarity and Polarity Report ChemistryLydia Mae S. Ela100% (1)
- Titration Calculations: Revision Summary: Number 59 WWW - Curriculumpress.co - UkDokument3 SeitenTitration Calculations: Revision Summary: Number 59 WWW - Curriculumpress.co - UksandalailaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Concentration - MolarityDokument9 SeitenSolution Concentration - MolarityMaki-Chan マキNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolutionChemistryLab8 8 12Dokument17 SeitenSolutionChemistryLab8 8 12Nadir BashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Unit One LabsDokument14 SeitenChemistry Unit One Labscarlissia wilkinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 11 Notes CompleteDokument55 SeitenCH 11 Notes CompleteeherrerahghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Solution PrepDokument15 SeitenLab Solution PrepRichardBrookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Chemistry of Polyelectrolyte SolutionsVon EverandPhysical Chemistry of Polyelectrolyte SolutionsMitsuru NagasawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Material Modeling in AbaqusDokument13 SeitenAdvanced Material Modeling in AbaqusUdhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- EenaduDokument2 SeitenEenaduAPPI NAIDUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid MensurationDokument5 SeitenSolid MensurationDelfin MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nalanda English Medium School: (Shewalwadi)Dokument18 SeitenNalanda English Medium School: (Shewalwadi)Dipanshu Gawde100% (1)
- Elems 05Dokument101 SeitenElems 05Reynald de VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SamponDokument2 SeitenSamponandreeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of MechanicsDokument21 SeitenFoundations of MechanicsUriel MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper: Physics Joint Entrance Screening Test (JEST - 2017)Dokument24 SeitenPaper: Physics Joint Entrance Screening Test (JEST - 2017)Rakesh PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- C 2 P 5Dokument9 SeitenC 2 P 5sundarmeenakshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExperimentDokument2 SeitenExperimentSarah Jean TraballoNoch keine Bewertungen
- G-EMPMD256 Kollidon Polyvinylpyrrolidone Excipients For The Pharmaceutical IndustryDokument1 SeiteG-EMPMD256 Kollidon Polyvinylpyrrolidone Excipients For The Pharmaceutical IndustryVõ Đức Trọng100% (1)
- ch09 PDFDokument132 Seitench09 PDFdaler12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - Mechanisms of Heat TransferDokument10 SeitenChapter 8 - Mechanisms of Heat TransferBảo Tín TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021exam 2013Dokument8 Seiten2021exam 2013Kamuel Ming WanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Universal Method For Preparing Nutrient Solutions of A Certain Desired CompositionDokument21 SeitenA Universal Method For Preparing Nutrient Solutions of A Certain Desired CompositionWilliamQuantrillNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM 1449 2006 Mathematics p2 BerjawapanDokument18 SeitenSPM 1449 2006 Mathematics p2 Berjawapanpss smk selandar71% (7)
- Grade 12 Physics 2nd Term Test Paper With Answers 2020 North Western ProvinceDokument58 SeitenGrade 12 Physics 2nd Term Test Paper With Answers 2020 North Western ProvinceDenethi panchaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Darcy S Law and The Field Equations of The Flow of Underground FluidsDokument38 SeitenDarcy S Law and The Field Equations of The Flow of Underground FluidsAnonymous BVbpSENoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Structures of Metals & CeramicsDokument61 SeitenChapter 3 - Structures of Metals & CeramicsNur Zahidah100% (1)
- Electromagnetism and Microwaves: Unit - IiDokument30 SeitenElectromagnetism and Microwaves: Unit - IiMukulKaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part IB - Quantum Mechanics: Based On Lectures by J. M. EvansDokument63 SeitenPart IB - Quantum Mechanics: Based On Lectures by J. M. EvansBob CrossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Corona DischargeDokument3 SeitenMechanism of Corona DischargemayureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ge8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFDokument8 SeitenGe8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFThamizh gomathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discovery of Electron: The Atomic StructureDokument3 SeitenDiscovery of Electron: The Atomic Structurejohn100% (1)
- Class XII Summer AssignmentDokument17 SeitenClass XII Summer AssignmentArumugam AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Melanin Physics by NEB HERUDokument72 SeitenMelanin Physics by NEB HERURobert MccrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naveen Kumar PPT On Projectile MotionDokument17 SeitenNaveen Kumar PPT On Projectile MotionBARUN SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasonic SolutionDokument46 SeitenUltrasonic Solutionsoumyadev86% (14)
- Physical Science ModuleDokument35 SeitenPhysical Science ModuleGajulin, April JoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3Dokument4 SeitenTutorial 3Dhivya NNoch keine Bewertungen