Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Gross Anatomy Urinary System
Hochgeladen von
May LacdaoOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Gross Anatomy Urinary System
Hochgeladen von
May LacdaoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Figure 18.
1Urinary Sysstem
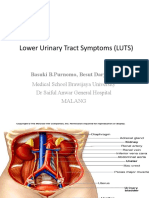
URINARY SYSTEM
- Excretory System
- composed of organs that
excrete water and waste
products in the form of
urine
ORGANS:
1. Kidneys
2. Ureter
3. Urinary Bladder
4. Urethra
URINARY SYSTEM
FUNCTIONS:
1. Excretion of unwanted
substances i.e. waste products
from cell metabolism, excess
salts and toxins
2. Maintenance of water balance
3. Regulation of acid-base balance
4. Production of hormones i.e.
renin
Kidney
- paired, reddish brown,
retroperitoneal bean-
shaped organ in superior
lumbar region
- extends from vertebral
levels T12 superiorly and
L3 inferiorly
Structures related to the anterior surface of each kidney.
Structures related to the posterior surface of each kidney.
Kidney
Coverings:
1. Renal capsule
2. perirenal fat (perinephric fat)
3. renal fascia (gerotas fascia)
4. Pararenal (paranephric fat)
2 parts:
1. cortex - outer
2. medulla
inner
- contains tubes that
collect urine
- these form a number of
cone shaped structures
called renal pyramids
- in between the pyramids
are the renal columns of
Bertini
- The tips of the
pyramids are
surrounded by cup
like structures
collecting urine
called minor calyces
- 2 or 3 minor calyces
would unite to form
the major calyces
- The major calyces
unite to form the
Renal Pelvis
Nephron
- Structural and functional unit of the kidney
- 1 million nephron each kidney
Consists of the ff:
A. Renal(Malphigian) Corpuscle
1. glomerulus
2. Bowmans capsule
B. Tubules
1. Proximal convoluted tubule
2. Loop of Henle(descending/ascending)
3. Distal convoluted tubule
4. Collecting tubules
Figure 18.4
Ureter
- 10 inches long muscular tube
- 3 anatomical constrictions:
1. at the uretero-pelvic junction
2. where iliac vessels cross the
ureter
3. where it joins the urinary
bladder
Urinary bladder
Hollow muscular
organ
Wall consist of
detrussor muscle
Inner- trigone
occupied by
ureteral orifices
and urethral orifice
Apex and Base
3 surfaces: 1 Superior
and 2 infero-lateral
Surfaces and base
are triangular in
outline, slightly convex
and separated by
blunt borders
The base and infero-
lateral surfaces meet
at the neck and is
continous with the
urethra
Parts of Urinary Bladder
Male Urethra
1. Male 20 cm
- both sperm and
urine passes
a. prostatic
- widest, most dilatable
b. membranous
- traverses urogenital
diaphragm, shortest
and least dilatable
c. penile
- longest, traverses
corpus spongiosum
Female Urethra
- tubes extending from
bladder to the outside
- Female urethra
- About 4 cm long
- Urethral opening is
located in front of
vaginal opening in the
vestibule
THE END
Thank you!
Henedina Eva Casis-Barilea MD;DTM&H; FPSA
Associate Professor 1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Icrc - War Surgery 2Dokument640 SeitenIcrc - War Surgery 2Florina PopaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper LimbDokument31 SeitenUpper LimbNandhana Kattuparambil SunojNoch keine Bewertungen
- VASCULAR - Abdominal Aorta Duplex ScanDokument24 SeitenVASCULAR - Abdominal Aorta Duplex ScanSophia Elinor MenesesNoch keine Bewertungen
- GYNE UltrasoundgyneDokument11 SeitenGYNE UltrasoundgyneMara AbantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: Giulio Del Popolo Donatella Pistolesi Vincenzo Li MarziDokument189 SeitenMale Stress Urinary Incontinence: Giulio Del Popolo Donatella Pistolesi Vincenzo Li MarziVeronika AtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imaging in Genitourinary SystemDokument77 SeitenImaging in Genitourinary SystemIrvan R. Loho100% (1)
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDokument105 SeitenMale and Female Reproductive Systemjanmic100% (3)
- Gestroresectional SyndromesDokument18 SeitenGestroresectional SyndromesAna CotomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scrotal SwellingDokument40 SeitenScrotal Swellingeirene simbolonNoch keine Bewertungen
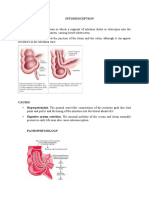
- INTUSSUSCEPTIONDokument3 SeitenINTUSSUSCEPTIONS GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Anatomy of The Esophagus and StomachDokument82 SeitenClinical Anatomy of The Esophagus and StomachmackieccNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The GITDokument66 SeitenBlood Supply of The GITgtaha80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomi AbdomenDokument36 SeitenAnatomi Abdomenari naNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periampullary CarcinomaDokument35 SeitenPeriampullary Carcinomaminnalesri100% (2)
- EXPT. 2 LAB REPORT Extraction and Characterization of Proteins Group 2Dokument11 SeitenEXPT. 2 LAB REPORT Extraction and Characterization of Proteins Group 2May Lacdao57% (7)
- Embryology and Anatomy of The Gastrointestinal TractDokument58 SeitenEmbryology and Anatomy of The Gastrointestinal TractYitancloudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Neonatal SurgeryDokument44 SeitenPrinciples of Neonatal Surgerykbmed2003100% (2)
- BreastDokument49 SeitenBreastcryphonexyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrolithiasis Case StudyDokument31 SeitenNephrolithiasis Case StudyL.a.Zumárraga67% (3)
- Anatomy of OesophagusDokument25 SeitenAnatomy of OesophagusRabi SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The Kidney & Ureter - NewDokument42 SeitenAnatomy of The Kidney & Ureter - NewHaider Nadhem AL-rubai0% (1)
- PCNL EhDokument38 SeitenPCNL EhIndra JayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HerniaDokument24 SeitenHerniaSalman HabeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryology of Urinary SystemDokument4 SeitenEmbryology of Urinary SystemZllison Mae Teodoro MangabatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Radiology Notes UrologyDokument106 SeitenMaster Radiology Notes UrologySafwan ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical Female Urogenital Anatomy - UpToDateDokument57 SeitenSurgical Female Urogenital Anatomy - UpToDateErickNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Anatomy of The KidneyDokument15 Seiten1 - Anatomy of The Kidneysara khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kod - S Guide On Final Professional Exam 1 PDFDokument31 SeitenKod - S Guide On Final Professional Exam 1 PDFHassanAbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy - KeyDokument18 SeitenAnatomy - KeyAnonymous MtKJkerbpUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vascular Diseases (1 of 3)Dokument4 SeitenVascular Diseases (1 of 3)Doctor GeneralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Male Female Catheterization Rle 30Dokument95 SeitenMale Female Catheterization Rle 30HoneylouAzOpondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toacs Surgical Trainees 2009 ADokument15 SeitenToacs Surgical Trainees 2009 AAnonymous bzHRfZzv100% (1)
- Atlas PCNLDokument19 SeitenAtlas PCNLaldillawrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Pelvic ExenterationDokument13 SeitenTotal Pelvic ExenterationRirin Wahyuni100% (1)
- Carcinoma Penis Management: Dr. Lilamani Rajthala MS Resident Moderator: Dr. Samir ShresthaDokument63 SeitenCarcinoma Penis Management: Dr. Lilamani Rajthala MS Resident Moderator: Dr. Samir ShresthaBibek GhimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Osteomyelitis: Presented by Group - GDokument20 SeitenAcute Osteomyelitis: Presented by Group - GSujan ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast Disorder: by DR - Wael MetwalyDokument7 SeitenBreast Disorder: by DR - Wael MetwalyhasebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FriS41700 PhlegmasiaCeruleaDolensisaLimbThreateningProblem BhendeDokument54 SeitenFriS41700 PhlegmasiaCeruleaDolensisaLimbThreateningProblem BhendeSuren VishvanathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Limb IschaemiaDokument32 SeitenAcute Limb IschaemiaAnonymous 9wHscM100% (1)
- LaryngoscopeDokument15 SeitenLaryngoscopeIhteshamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iontophoresis TENNIS ELBOW (Lateral Humeral Epicondylitis)Dokument2 SeitenIontophoresis TENNIS ELBOW (Lateral Humeral Epicondylitis)Ikre19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maniobras QuirurgicasDokument6 SeitenManiobras Quirurgicasyesmaster15100% (3)
- Powerpoint: Disorders of The EsophagusDokument65 SeitenPowerpoint: Disorders of The Esophagusj.doe.hex_8782% (11)
- Ultrasound - A GuideDokument9 SeitenUltrasound - A GuideDebasish KunduNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - General Complications of Fractures - d3Dokument27 Seiten1 - General Complications of Fractures - d3Jheng-Dao Yang100% (1)
- Final Exam in Topographical AnatomyDokument50 SeitenFinal Exam in Topographical Anatomytastyk100% (2)
- 1-Indroduction To EmbryologyDokument25 Seiten1-Indroduction To Embryologyselman P k100% (1)
- Ocular InjuryDokument46 SeitenOcular InjurysnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thoracotomy: Surgery For Lung ProblemsDokument14 SeitenThoracotomy: Surgery For Lung ProblemsPutri ChalqieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joints Anatomy PresentationDokument41 SeitenJoints Anatomy Presentationahmadnaveed99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne Case COCDokument37 SeitenGyne Case COCLian BaylosisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optic Nerve Disease, Papillaedema Optic Atropy, Visual FieldDokument31 SeitenOptic Nerve Disease, Papillaedema Optic Atropy, Visual FieldsamxtraNoch keine Bewertungen
- UTI On A Background of Obstructive NephropathyDokument26 SeitenUTI On A Background of Obstructive NephropathyAminath MeesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Surgery: Post-Operative Care and ManagementDokument9 SeitenGeneral Surgery: Post-Operative Care and ManagementMohammed Yousif AbdualjabbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of MicturitionDokument20 SeitenPhysiology of MicturitionSyedaNaveenBatool0% (1)
- West Bengal University of Health Sciences: Name of The InstitutionDokument9 SeitenWest Bengal University of Health Sciences: Name of The InstitutionVarun Mohanakumaran RajambikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical Review On HypospadiasDokument30 SeitenSurgical Review On Hypospadiasbakukangtribe100% (1)
- Final MBBS FlyerDokument2 SeitenFinal MBBS FlyerAnonymous RxWzgONoch keine Bewertungen
- Sentinal Lymph Node BiopsyDokument12 SeitenSentinal Lymph Node BiopsySahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Maternal Anatomy WilliamsDokument60 SeitenChapter 2 Maternal Anatomy WilliamsDiskaAstariniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Urinary RetentionDokument26 SeitenAcute Urinary Retentionlukmankyubi100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Small and Large Intestines, Rectum and AnusDokument24 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of Small and Large Intestines, Rectum and AnusElmer PatrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of BladderDokument10 SeitenAnatomy of BladderKiran tyraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary System: Cytology, Histology, Cystoscopy, and RadiologyVon EverandUrinary System: Cytology, Histology, Cystoscopy, and RadiologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swollen Kidney, (Hydronephrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandSwollen Kidney, (Hydronephrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology ProtozoansDokument13 SeitenParasitology ProtozoansMay LacdaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM 40.1 Expt. 11Dokument3 SeitenCHEM 40.1 Expt. 11May Lacdao0% (1)
- Germination DiscussionDokument3 SeitenGermination DiscussionMay Lacdao100% (1)
- Bot 120 Exercise 4 Carbohydrate SynthesisDokument2 SeitenBot 120 Exercise 4 Carbohydrate SynthesisMay Lacdao0% (1)
- Antibacterial Activity of Two Common Garden WeedsDokument16 SeitenAntibacterial Activity of Two Common Garden WeedsMay LacdaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- State of Talent Supply and Demand in The PhilippinesDokument2 SeitenState of Talent Supply and Demand in The PhilippinesMay LacdaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal AnatomyDokument60 SeitenMaternal AnatomyRaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Examination of The 4 Genitourinary TractDokument12 SeitenPhysical Examination of The 4 Genitourinary TractrudybisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDokument22 SeitenBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaMc N Mi Kabiling100% (1)
- Emergensi Urologi UiiDokument83 SeitenEmergensi Urologi UiitrianaamaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urethral Injury in Penile FractureDokument6 SeitenUrethral Injury in Penile FractureBeno This isNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urethral StrictureDokument35 SeitenUrethral StrictureDoctors PodcastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) : Basuki B.Purnomo, Besut DaryantoDokument24 SeitenLower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) : Basuki B.Purnomo, Besut DaryantoDeviruchi GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomi Genitalia Pria WanitaDokument65 SeitenAnatomi Genitalia Pria WanitaTaufik Adi SNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 MerilDokument1 Seite3 MerilGuntur Aji PrasetyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary SystemDokument10 SeitenUrinary SystemMaruen RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncbi - Nlm.nih - Gov-Post-Op Urinary RetentionDokument9 SeitenNcbi - Nlm.nih - Gov-Post-Op Urinary RetentiondadupipaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chlamydia Vs GonorrhoeaDokument31 SeitenChlamydia Vs Gonorrhoeakyro draxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urology PDFDokument24 SeitenUrology PDFzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Pathophysiology of ProstrateDokument44 SeitenAnatomy and Pathophysiology of Prostraterajan kumar100% (3)
- Salinas2003 PDFDokument15 SeitenSalinas2003 PDFnatashiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Woody Got Wood Multiple TranslatedDokument3 SeitenWoody Got Wood Multiple TranslatedОлен БондарчукNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Urinary Disorders - 2012 - Small Animal Clinical Diagnosis by Laboratory Methods Fifth EditionDokument30 Seiten7 Urinary Disorders - 2012 - Small Animal Clinical Diagnosis by Laboratory Methods Fifth EditionNarvarte Hospital Veterinario de EspecialidadesNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Neobladder?Dokument2 SeitenWhat Is A Neobladder?WKYC.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- CatheterizationDokument3 SeitenCatheterizationLawrence Cada NofiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah Trauma Urologi - DR WibisonoDokument34 SeitenKuliah Trauma Urologi - DR WibisonoAgung Budi SuristioNoch keine Bewertungen
- VCUG Parent Resource Revised 1-27-10Dokument2 SeitenVCUG Parent Resource Revised 1-27-10NataliaMaedyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BACA Programme July 08Dokument30 SeitenBACA Programme July 08ready medicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carr 2018Dokument2 SeitenCarr 2018Brisbany AlcibarNoch keine Bewertungen