Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mec525 - Mechanics of Metal Forming
Hochgeladen von
sunilsharma853380Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mec525 - Mechanics of Metal Forming
Hochgeladen von
sunilsharma853380Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
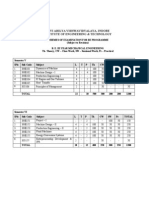
Lovely Professional University, Punjab
Course Code Course Title Course Planner Lectures Tutorials Practicals Credits
MEC525 MECHANICS OF METAL FORMING 15854::Jasvinder Singh 2.0 0.0 0.0 2.0
Course Category Courses with Numerical focus
TextBooks
Sr No Title Author Edition Year Publisher Name
T-1 MECHANICAL METALLURGY GEORGE E. DIETER 3rd 2013 M. G.HILLS
Reference Books
Sr No Title Author Edition Year Publisher Name
R-1 TECHNOLOGY OF METAL
FORMING PROCESSES
SURENDER KUMAR 1st PHI (PRETICE HALL INDIA)
Relevant Websites
Sr No (Web address) (only if relevant to the course) Salient Features
RW-1 http://thelibraryofmanufacturing.com/forming_basics.html Information and description related to Forming
RW-2 http://www.efunda.com/formulae/solid_mechanics/mat_mechanics/calc_principal_stres
s.cfm
Stress calculator
RW-3 http://www.google.co.in/url?
sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&cad=rja&ved=0CDUQFjAB&url=http
%3A%2F%2Facademic.uprm.edu%2Fpcaceres%2FCourses%2FMMII%2FIMoM-
5A.pdf&ei=kWeEUsu1I4nGrAeRpIHoAw&usg=AFQjCNHo0WGreYWWXV-
AGAgOx-PkhkQ4Yg&sig2=-2SOFiKHB7XaBE3R4hinjQ&bvm=bv.56343320,d.bmk
Principal stresses ans calculation
Week
Number
Lecture
Number
Broad Topic(Sub Topic) Chapters/Sections of
Text/reference
books
Other Readings,
Relevant Websites,
Audio Visual Aids,
software and Virtual
Labs
Lecture Description Learning Outcomes Pedagogical Tool
Demonstration/
Case Study /
Images /
animation / ppt
etc. Planned
Live Examples
Detailed Plan For Lectures
LTP week distribution: (LTP Weeks)
Weeks before MTE 7
Weeks After MTE 7
Spill Over 2
Week 1 Lecture 1 Introduction and state of
stresses(Cold,hot and warm
forming and types of
stresses)
R-1:1.2 and 1.3 Basic introductory part
of the course and
knowledge about
forming process related
with temperature
Basic understanding
of
different type of
Forming processes
Figures of Forging
processes
Making of rod
and tubes
Introduction and state of
stresses(Components and
principle stresses)
R-1:2.2 Different components of
stresses.
Basic understanding
of
different components
of stresses.
Rectangular block
representing
stresses
stress produce
during work
Lecture 2 Introduction and state of
stresses(Experiments and
bulk deformation processes)
T-1:18.1
R-1:1.6 and 1.7
Different types of
deformation processes
like Extrusion, Drawing
and rolling
Working of metal
deforming processes.
Figures of different
metal deformation
processes
Introduction and state of
stresses(Temperature and
crack formation)
R-1:1.7 Relation between
temperature and
cracking in deformation
processes.
Effect of temperature
on cracking in
deformation
processes
Figures of different
metal deformation
processes
cracks of plastic
when put in to
sun light ,
braking of glass
due to hot water
Week 2 Lecture 3 Stress and strain
relationships and Elastic
behaviours(Description of
stress at a point)
T-1:2.2 Component of stresses Different type of
stresses (normal and
shear stresses)
Figure of stresses
acting cube.
Stress and strain
relationships and Elastic
behaviours(state of stress in
two and three dimensions)
T-1:2.3 and 2.5 Plane stresses in two
and three dimensions
Calculation of
stresses in two and
three dimensions
Figure of stresses
on oblique plane
Lecture 4 Stress and strain
relationships and Elastic
behaviours(state of stress in
two and three dimensions)
T-1:2.3 and 2.5 Plane stresses in two
and three dimensions
Calculation of
stresses in two and
three dimensions
Figure of stresses
on oblique plane
Week 3 Lecture 5 Stress and strain
relationships and Elastic
behaviours(Mohr's circle of
stress- two dimension and
three dimension)
T-1:2.4 and 2.7
R-1:2.7
Formation of mohr's
circle
calculation of stresses
with the help of
mohr's circle
Figure of mohr's
circle
Lecture 6 Stress and strain
relationships and Elastic
behaviours(Hydrostatics and
Deviator components of
stress)
T-1:2.10 Role of Hydrostatics and
Deviator components of
stress
Effect of stress
components
figure of
hydrostatic stresses
Stress and strain
relationships and Elastic
behaviours(Elastic stress
strain relations)
T-1:2.11 Stress strain relation Knowledge about
stress strain
relationship
Hooke's law elastic and
plastic body
Week 4 Lecture 7 Stress and strain
relationships and Elastic
behaviours(Calculations of
stresses from elastic strains)
T-1:2.12 Stress strain relation Knowledge about
stress strain
relationship
Numerical relates
to stress strain
relation.
Lecture 8 Test1
Week 5 Lecture 10 Yield criteria and flow rules
(Yield criteria of ductile
metals)
T-1:3.4 Von Mises or
Distortion-energy
Criterion
Calculation of
stresses for ductile
materials
Equations of Von
Mises
Lecture 9 Yield criteria and flow rules
(Introduction)
T-1:3.1 Introduction about
theory of plasticity
Knowledge about
stress-strain curves
Figure of Stress-
strain curves of
different materials
Yield criteria and flow rules
(The flow curve)
T-1:3.2 Description of flow
curve
Knowledge about
flow curve
Idealized flow
curve
Yield criteria and flow rules
(True stress and true strain)
T-1:3.3 Relation between true
stress and true strain
Knowledge about
stress-strain
equations
Equations of
stress-strain
relation
deformation of
object
Week 6 Lecture 11 Yield criteria and flow rules
(Combined stress test)
Spill Over Spill Over Spill Over
Lecture 12 Yield criteria and flow rules
(Yield locus)
T-1:3.5 and 3.6 Combined stress test and
Yield locus
Calculations of
stresses
Figure of Yield
criteria for plane
stresses
Yield criteria and flow rules
(Anistropy in yielding)
T-1:3.7 Anistropy in yielding Calculations of
stresses
Demonstration by
Faculty
Yield criteria and flow rules
(Yield surface and
normality)
T-1:3.7 Yield surface and
normality
Yield surface for Von
Mises criterion
Figures of Yield
Locus
Week 7 Lecture 13 Yield criteria and flow rules
(Octahedral shear stress and
shear strain)
T-1:3.9 shear stress and shear
strain in Octahedral
condition
Knowledge about the
calculation of stress
and strain
Demonstration by
Faculty
Yield criteria and flow rules
(Levy Mises equation)
T-1:3.11 Plastic stress-strain
relation
Levy Mises equation Demonstration by
Faculty
Yield criteria and flow rules
(Prandtl Reuss equation)
T-1:3.11 Plastic stress-strain
relation
Prandtl Reuss
equation
Equations of
Prandtl Reuss
Lecture 14 Yield criteria and flow rules
(Slip line field theory)
T-1:3.12 Two - Dimensional
plastic flow - Slip line
field theory
Methods of
developing plastic
constraint
Figure of mohr's
circle
MID-TERM
Week 8 Lecture 15 Forging and rolling of
metals(Classification of
forging process)
T-1:16.1 Different types of
forging processes
Uses of forging
processes
Figure of different
types of forging
processes
Manufacturing
of object by
blacksmith
Forging and rolling of
metals(Equipments)
T-1:16.2 Different types of
forging equipments
Uses of forging
equipments
Figure of different
types of forging
equipments
Forging and rolling of
metals(Forging plain strain)
T-1:16.3 Calculation of forces in
forging
Knowledge about
different forces in
forging
Figure of stress
distribution
Lecture 16 Forging and rolling of
metals(Open die and close
die forging)
T-1:16.4 and 16.5 Description of open and
closed die forging.
Knowledge about
different types of
forging dies
Figures of open
and closed die
forging.
Manufacturing
of object by
blacksmith
Forging and rolling of
metals(Calculation of
Forging)
T-1:16.6 Calculation of Forging
loads in closed-die
forging
Calculation of loads Figure of slab
Week 9 Lecture 17 Forging and rolling of
metals(Hot rolling and cold
rolling)
T-1:17.3 and 17.4 Hot and cold rolling Different types of
rolling
Figures of Rolling
mill
Manufacturing
of object by
blacksmith
Forging and rolling of
metals(Rolling of bar and
shapes)
T-1:17.5 Methods of rolling Different types of
rolling
Figures of Rolling
mill
similar process
as sugar cane
Forging and rolling of
metals(Forces and
geometrical relationship in
rolling)
T-1:17.3 and 17.4 Geometric relationship
in rolling
Calculations related
to rolling
Figures of forces
acting during
rolling
Lecture 18 Forging and rolling of
metals(Analysis of rolling
load)
T-1:17.7 Analysis of rolling loads Knowledge about the
calculation of rolling
lodes
Figures used to
define the rolling
loads
Week 10 Lecture 19 Test2
Lecture 20 Extrusion and Drawing
(Classification o f Extrusion
process)
T-1:18.1 Different types of
extrusion processes
Knowledge about
extrusion processes
Figure of extrusion
processes
making of sheets
at jindal
aluminum
factory
Extrusion and Drawing
(Deformation lubrication
and Defects in extrusion)
T-1:18.4 Different types of
lubrication and defects
in extrusion processes
Knowledge about
lubrication and
defects in extrusion
processes
Figure of extrusion
processes
Extrusion and Drawing
(Analysis of extrusion
process)
T-1:18.5 Analysis of extrusion
process
Knowledge about
different forces in
extrusion
Figure of stress-
strain distribution
in partial tube
Week 11 Lecture 21 Extrusion and Drawing
(Hydrostatic extrusion)
T-1:18.7 Use of hydro pressure in
extrusion
Role of hydrostatic
pressure in extrusion
Figures of
extrusion processes
Extrusion and Drawing(Rod
and wire drawing)
T-1:19.2 Different types of
drawing processes
Use and working of
drawing process
equipments
Figures of different
drawing processes
Extrusion and Drawing
(Analysis of wire drawing)
T-1:19.3 Analysis of forces acting
during process
Knowledge related
forces in wire
drawing
Figures of wire
drawing processes
Lecture 22 Extrusion and Drawing
(Tube drawing process)
T-1:19.4 Types of tube drawing
processes
Knowledge about
tube drawing
Figure of tube
drawing processes
Extrusion and Drawing
(Analysis of tube drawing)
T-1:19.5 Analysis of forces acting
during process
Knowledge related
forces in tube
drawing
Figure of tube
drawing processes
Week 12 Lecture 23 Test3
Lecture 24 Sheet metal Forming and
Lubrication mechanisms
(Forming methods)
T-1:20.1 and 20.2 Introduction and
methods of forming
processes
Different types of
forming processes
Figures of different
forming processes
Sheet metal Forming and
Lubrication mechanisms
(Shearing and Blanking)
T-1:20.3 Introduction and
methods of shearing and
blanking processes
Different types of
shearing and blanking
processes
Figures of different
shearing and
blanking processes
Manufacturing
of object by
blacksmith
Week 13 Lecture 25 Sheet metal Forming and
Lubrication mechanisms
(Bending)
T-1:20.4 Definition of terms used
in bending
Springback in
bending
Different types of
bending processes
Manufacturing
of object by
blacksmith
Sheet metal Forming and
Lubrication mechanisms
(Stretch forming)
T-1:20.5 Stretch forming
operation
Variation of necking Figures of
stretching
processes
Lecture 26 Sheet metal Forming and
Lubrication mechanisms
(Deep drawing)
T-1:20.6 Description of Deep
drawing
Analysis of deep
drawing process
figures of different
drawing processes
making of tube
Sheet metal Forming and
Lubrication mechanisms
(Forming limit criteria)
T-1:20.7 Description forming
limit
Analysis of forming
limit
Forming limit
diagram
Week 14 Lecture 27 Sheet metal Forming and
Lubrication mechanisms
(Lubrication principle and
mechanism)
R-1:7.2 and 7.3 Lubrication principals
and mechanism
Knowledge about
lubrication
mechanism
Figure of three
regimes of
lubrication
Sheet metal Forming and
Lubrication mechanisms
(Lubrication need and their
components and cost
selection)
R-1:7.4 and 7.5 Need of lubrication in
industries
Knowledge about
costs of lubrication
Different
components of
costs in lubrication
Lecture 28 Sheet metal Forming and
Lubrication mechanisms
(Chemical characteristics
and solid lubrication)
R-1:7.10 and 7.11 Chemical characteristics
values and categories of
solid lubrication
Types of solid
lubrication
Demonstration by
Faculty
Sheet metal Forming and
Lubrication mechanisms
(classification of lubricants
and use in forming process)
R-1:7.7 and 7.8 classification of
lubricants
Use of lubrication in
forming process
Demonstration by
Faculty
SPILL OVER
Week 15 Lecture 29 Spill Over
Lecture 30 Spill Over
Scheme for CA:
Component Frequency Out Of Each Marks Total Marks
Test 2 3 10 20
Total :- 10 20
Details of Academic Task(s)
AT No. Objective Topic of the Academic Task Nature of Academic Task
(group/individuals/field
work
Evaluation Mode Allottment /
submission Week
Test1 To check student's
ability to understand
subject matter
through written test
Unit 1 and Unit 2 Individual Answers should be
to the point and
problems should be
solved step wise.
3 / 4
Test2 To check the
understanding of
students about the
topics done in class
Unit : 4 Individual Answers should be
to the point and
problems should be
solved step wise.
9 / 10
Test3 To test the
knowledge of the
student
Unit : 5 Individual Answers should be
to the point and
problems should be
solved step wise.
11 / 12
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Course Code Course Title Course Planner Lectures Tutorials Practicals CreditsDokument7 SeitenCourse Code Course Title Course Planner Lectures Tutorials Practicals CreditsqwertyNoch keine Bewertungen
- P.h.y-200 Material ScienceDokument7 SeitenP.h.y-200 Material ScienceArpit BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationVon EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Mechanics of SolidDokument7 SeitenAdvance Mechanics of Solidrjrahul25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue NotesDokument70 SeitenFatigue NotesNirmalya MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes MFP-III-II MEDokument112 SeitenLecture Notes MFP-III-II MEMahmoud AttallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lectures On Metal FormingDokument122 SeitenLectures On Metal FormingRRR180Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Fatigue Analysis TechnologiesDokument38 SeitenAdvances in Fatigue Analysis TechnologiesMarcelino Pereira Do NascimentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of MaterialsDokument3 SeitenStrength of Materialsvp0209198825% (4)
- BTech MECHANICALJuly05 2011 PDFDokument52 SeitenBTech MECHANICALJuly05 2011 PDFappannusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mse 212Dokument6 SeitenMse 212Ana Emily PrentissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityDhaval PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Description: CH 101 - Applied Chemistry (2-0-2)Dokument20 SeitenCourse Description: CH 101 - Applied Chemistry (2-0-2)Nomi GraciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Description: CH 101 - Applied Chemistry (2-0-2)Dokument20 SeitenCourse Description: CH 101 - Applied Chemistry (2-0-2)Nomi GraciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCMT 4304-Mechanical Working and Testing of MaterialsDokument126 SeitenPCMT 4304-Mechanical Working and Testing of MaterialsSubhasishNathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machine Elements 2Dokument8 SeitenDesign of Machine Elements 2Sameer WaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academic Plan For Vth-Semester Mae (2011-12) : Subject: Microprocessor and Applications Subject Code: ETME-301Dokument5 SeitenAcademic Plan For Vth-Semester Mae (2011-12) : Subject: Microprocessor and Applications Subject Code: ETME-301Jayesh KatariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S. E. Mech. Engg. June 2013 PDFDokument34 SeitenS. E. Mech. Engg. June 2013 PDFDinesh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials (9024)Dokument6 SeitenStrength of Materials (9024)rajyamgarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparative Study of The Forming-Limit Diagram Next Term Models For Sheet SteelsDokument8 SeitenA Comparative Study of The Forming-Limit Diagram Next Term Models For Sheet SteelsRaghav KhajuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diploma Ii Year Mechanical Engineering: 2011-2012 SubjectsDokument31 SeitenDiploma Ii Year Mechanical Engineering: 2011-2012 SubjectsAjay GahlotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bài Tập Nhóm Môn Kỹ Thuật Chế TạoDokument8 SeitenBài Tập Nhóm Môn Kỹ Thuật Chế TạotranngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument26 SeitenChapter 4Lana AlakhrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, I Dore I Stitute of E Gi Eeri G & Tech OlogyDokument20 SeitenDevi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, I Dore I Stitute of E Gi Eeri G & Tech OlogySonal MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial TribologyDokument10 SeitenIndustrial TribologySurya Pratap Singh Parmar100% (1)
- Syllabus - BE Mech II Wef 2012-13 PDFDokument28 SeitenSyllabus - BE Mech II Wef 2012-13 PDFPavan KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mackerle2001 A BibliographyDokument10 SeitenMackerle2001 A BibliographyprofessorvasudevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SE Production SandwichDokument43 SeitenSE Production SandwichRohittitansinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- FSW Welding PresentationDokument56 SeitenFSW Welding PresentationMazharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btech 2Dokument17 SeitenBtech 2Divyesh SindhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal FormingDokument4 SeitenMetal Formingolyad ahmedinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Twist Springback Prediction After An Ahss Forming ProcessDokument12 SeitenEvaluation of Twist Springback Prediction After An Ahss Forming ProcessDVP EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mtech StructuresDokument27 SeitenMtech Structuresapi-293374101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument48 SeitenChapter 4Zhiyi HeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of Thick Walled Cylinders With HolesDokument47 SeitenDesign and Analysis of Thick Walled Cylinders With HolesKeryn Pelled-FeldmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Machine DesignDokument2 SeitenAdvanced Machine Designsamir0% (1)
- Friction Stir Welding PP TDokument56 SeitenFriction Stir Welding PP TSantosh V HiremathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Forming ProcessDokument5 SeitenMetal Forming ProcesstadeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Notes-2019Dokument16 SeitenChapter 2 - Notes-2019PraneethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lovely Professional University, Punjab: Detailed Plan For LecturesDokument5 SeitenLovely Professional University, Punjab: Detailed Plan For LecturesZain MirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials by G. G. Tawshikar PDFDokument912 SeitenStrength of Materials by G. G. Tawshikar PDFAmit R. Ghule100% (5)
- Paper Procesos Deformacion PlasticaDokument12 SeitenPaper Procesos Deformacion PlasticaJorge BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Construction and DesignDokument5 SeitenModule 3 Construction and DesignDhimas Surya Negara100% (1)
- Theory of Metal CuttingDokument7 SeitenTheory of Metal Cuttingrjrahul25100% (2)
- Chapter Three: Principles of Metal Forming Theory: Manufacture Engineering ProcessesDokument21 SeitenChapter Three: Principles of Metal Forming Theory: Manufacture Engineering ProcessesAshok Kumar UppariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tkundu@email - Arizona.edu: EM 508: Fracture MechanicsDokument2 SeitenTkundu@email - Arizona.edu: EM 508: Fracture MechanicsBakkiya RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout-8a-Metal Forming BasicDokument23 SeitenHandout-8a-Metal Forming BasicAmardhianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Instruction Division FIRST SEMESTER 2010-2011 Course Handout Part IIDokument3 SeitenBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Instruction Division FIRST SEMESTER 2010-2011 Course Handout Part IIGirish HanumaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue 2Dokument16 SeitenFatigue 2kalirajgurusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reliability Engineering (Mec663)Dokument7 SeitenReliability Engineering (Mec663)Arpit Goyal33% (3)
- Curriculum (B. TECH) : Undergraduate ProgrammeDokument43 SeitenCurriculum (B. TECH) : Undergraduate ProgrammeHarman Singh NagpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B Tech Mechanical Engineering Syllabus For Batch 2013-14Dokument30 SeitenB Tech Mechanical Engineering Syllabus For Batch 2013-14ra44993541Noch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical and Experimental Study of Frictional Behavior in Bending Under Tension TestDokument9 SeitenNumerical and Experimental Study of Frictional Behavior in Bending Under Tension Testsergio_rollaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Forming Technology 1601913164Dokument12 SeitenMetal Forming Technology 1601913164jesssepinkman03Noch keine Bewertungen
- TENSILE Lab SheetDokument4 SeitenTENSILE Lab SheetKerem Taha TekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysVon EverandMaterials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Mec339 - Rapid Prototyping and Reverse Engineering LaboratoryDokument3 SeitenMec339 - Rapid Prototyping and Reverse Engineering Laboratorysunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- R PT Timetable FacultyDokument1 SeiteR PT Timetable Facultysunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Lecture 5 Forming Analysis-SlabMethodDokument7 SeitenModule 2 Lecture 5 Forming Analysis-SlabMethodsunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technote Ra02Dokument2 SeitenTechnote Ra02sunilsharma853380100% (1)
- Microsoft PowerPoint - LECTURE3Dokument36 SeitenMicrosoft PowerPoint - LECTURE3Sugumar MuthusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test ScheduleDokument1 SeiteTest Schedulesunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Performance and Emission Characteristics of Straight Vegetable Oil-Ethanol Emulsion in A CompressionDokument6 SeitenPerformance and Emission Characteristics of Straight Vegetable Oil-Ethanol Emulsion in A Compressionsunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- New Technologies and Applications of Edm ProcessDokument4 SeitenNew Technologies and Applications of Edm Processsunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stanford University, Stanford, Galiji 94305, UsaDokument15 SeitenStanford University, Stanford, Galiji 94305, Usasunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Graphite-to-Diamond Transformation : Journal of Solid Statechemistry%, &Dokument7 SeitenThe Graphite-to-Diamond Transformation : Journal of Solid Statechemistry%, &sunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power Mixed Electric Discharge MachiningDokument14 SeitenPower Mixed Electric Discharge MachiningNimo NingthoujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Make A Line Graph Using Excel 2007Dokument7 SeitenHow To Make A Line Graph Using Excel 2007Mukesh Kumar BaliwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- JJ)Dokument1 SeiteJJ)sunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cassava, A Potential Biofuel Crop in ChinaDokument18 SeitenCassava, A Potential Biofuel Crop in Chinasunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mech 5th SemDokument16 SeitenMech 5th Semsunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- BTech P&I July05 2011Dokument51 SeitenBTech P&I July05 2011sunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prediction of Performance and Emission of Castor OilDokument3 SeitenPrediction of Performance and Emission of Castor Oilsunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laser and Its ApplicationsDokument50 SeitenLaser and Its ApplicationsmadangkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Guidelines For ProjectsDokument13 Seiten1 Guidelines For ProjectsSunil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc Welding Job 14Dokument3 SeitenArc Welding Job 14Sunil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Indian Army Advertisement 1Dokument1 Seite1 - Indian Army Advertisement 1sunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- 40 Non Conventional MachiningDokument20 Seiten40 Non Conventional MachiningPRASAD326100% (6)
- 43 - Press Release 7-1-13Dokument1 Seite43 - Press Release 7-1-13Sunil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument3 SeitenAssignmentsunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 D O M E: Workshops/Seminars OrganizedDokument3 Seiten2011 D O M E: Workshops/Seminars Organizedsunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advt Open MKT 2013Dokument11 SeitenAdvt Open MKT 2013Pawan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mec 442 Set ADokument1 SeiteMec 442 Set Asunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Testing of Welds - Part 2 - Heavy Engineering Research AssociationDokument2 SeitenMechanical Testing of Welds - Part 2 - Heavy Engineering Research Associationsunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- ISO - IsO Standards - IsO - TC 44 - SC 5 - Testing and Inspection of WeldsDokument4 SeitenISO - IsO Standards - IsO - TC 44 - SC 5 - Testing and Inspection of Weldssunilsharma853380Noch keine Bewertungen
- AME101 LectureNotesDokument142 SeitenAME101 LectureNotesNagarjunavarma GannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustic Emission March 2004 - Back To BasicsDokument16 SeitenAcoustic Emission March 2004 - Back To BasicsfndandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 UV VIS PhenylephrineDokument7 Seiten8 UV VIS PhenylephrineEdgard Mauricio OlascuagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemp Thermographic ReportDokument20 SeitenHemp Thermographic ReportEste BanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 734 Part2 EmulsionDokument28 Seiten734 Part2 EmulsionSuvin PsNoch keine Bewertungen
- GR 9 Eng BaselineDokument12 SeitenGR 9 Eng BaselineMalie SibisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Strength Tensile TestDokument3 SeitenLab Report Strength Tensile TestAbdul KarimNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRP-FT Maintenance ManualDokument20 SeitenGRP-FT Maintenance ManualSaleh EttehadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide To Better Geotextile Specifying US FABRICSDokument19 SeitenGuide To Better Geotextile Specifying US FABRICSOladunni AfolabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSS&C - PKundur - Cap06Dokument72 SeitenPSS&C - PKundur - Cap06Francisco GuerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guia para Expandido de TubosDokument3 SeitenGuia para Expandido de Tubosjafc986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thirteen Moons in MotionDokument41 SeitenThirteen Moons in MotionGalacticMaya100% (3)
- Reed Cog Psych 1972Dokument26 SeitenReed Cog Psych 1972Abhinav JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard S Ific Ion For: - !' N G :.. F.Ld'.Tita"Ilj.MDokument6 SeitenStandard S Ific Ion For: - !' N G :.. F.Ld'.Tita"Ilj.MIgnacio Hiram M RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Master Thesis Work CFD Pump Valve SystemDokument1 Seite2016 Master Thesis Work CFD Pump Valve SystemMohamedNihasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book 2: Chapter 4 - Fluid Flow: Application LimitationsDokument20 SeitenBook 2: Chapter 4 - Fluid Flow: Application LimitationsVaniya GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAMPLE PAPER-AT-2324-C-XII-PASS-AT+PCM-Paper-2Dokument24 SeitenSAMPLE PAPER-AT-2324-C-XII-PASS-AT+PCM-Paper-2Arijit DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Downloaded From Uva-Dare, The Institutional Repository of The University of Amsterdam (Uva)Dokument12 SeitenDownloaded From Uva-Dare, The Institutional Repository of The University of Amsterdam (Uva)Iqioo RedefiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- FS-l6S: Instruction ManualDokument25 SeitenFS-l6S: Instruction ManualFazrulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of VOltage and Power Interactions in Multi-Infeed HVDC SystemsDokument9 SeitenAnalysis of VOltage and Power Interactions in Multi-Infeed HVDC SystemstinazdrilicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thin-Walled Structures: Jovan Trajkovski, Jasenko Perenda, Robert Kunc TDokument7 SeitenThin-Walled Structures: Jovan Trajkovski, Jasenko Perenda, Robert Kunc TMohamed AmineNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASAP 2020: Accelerated Surface Area and Porosimetry SystemDokument462 SeitenASAP 2020: Accelerated Surface Area and Porosimetry SystemMargiani FortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Void Formers DesignDokument78 SeitenPlastic Void Formers DesignzadadazNoch keine Bewertungen
- AGI MiniSting ManualDokument108 SeitenAGI MiniSting ManualVvg ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Estimate Details With Reference To Approved Drawings. A Cable Shall Consist of 12 Nos 12.7mmDokument2 SeitenMaterial Estimate Details With Reference To Approved Drawings. A Cable Shall Consist of 12 Nos 12.7mmepe civil1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diagramas Momento CurvaturaDokument21 SeitenDiagramas Momento CurvaturaCarlosAlbertoBarriosnuevosPelaezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LambdaSpectroscopyBrochure PDFDokument18 SeitenLambdaSpectroscopyBrochure PDFAnastasia CrucicovschiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes 2Dokument65 SeitenNotes 2Aamir khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test-Ch 6 v2Dokument3 SeitenTest-Ch 6 v2api-188215664Noch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Mechanics and Out-of-Equilibrium Systems!Dokument15 SeitenStatistical Mechanics and Out-of-Equilibrium Systems!hrastburg100% (1)