Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hormones Endocrine Gland: (Clipart Edited From Corel Presentations 8)
Hochgeladen von
Zheena S. JaroOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hormones Endocrine Gland: (Clipart Edited From Corel Presentations 8)
Hochgeladen von
Zheena S. JaroCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture
http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio105/endocrin.htm
Endocrine System
The nervous system sends electrical messages to control and coordinate the
body. The endocrine system has a similar job, but uses chemicals to
communicate. These chemicals are known as hormones. A hormone is a
specific messenger molecule synthesized and secreted by a group of specialized
cells called an endocrine gland.
The major human endocrine glands include:
(clipart edited from Corel Presentations 8)
1. the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
The pituitary gland is called the master gland but it is under the control
of the hypothalamus. Together, they control many other endocrine
functions. They secrete a number of hormones, especially several which
are important to the female menstural cycle, pregnancy, birth, and
lactation (milk production). These include follicle-stimulating
hormone (FSH), which stimulates development and maturation of a
follicle in one of a womans ovaries, and leutinizing hormone (LH),
which causes the bursting of that follicle (= ovulation) and the formation
of a corpus luteum from the remains of the follicle.
There are a number of other hypothalamus and pituitary hormones which
affect various target organs.
Another group of non-sex hormones that many people have heard of is
the endorphins, which belong to the category of chemicals known
as opiates and serve to deaden our pain receptors. Endorphins, which are
chemically related to morphine, are produced in response to pain. The
natural response to rub an injured area, such as a pinched finger, helps to
release endorphins in that area. People who exercise a lot and push their
bodies until it hurts thereby stimulate the production of endorphins. It
is thought that some people who constantly over-exercise and push
themselves too much may actually be addicted to their own endorphins
which that severe exercise regime releases.
2. the thyroid gland
Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, therefore body temperature
and weight. The thyroid hormones contain iodine, which the thyroid
needs in order to manufacture these hormones. If a person lacks iodine in
his/her diet, the thyroid cannot make the hormones, causing a deficiency.
In response to the bodys feedback loops calling for more thyroid
hormones, the thyroid gland then enlarges to attempt to compensate (The
bodys plan here is if its bigger it can make more, but that doesnt help
if there isnt enough iodine.). This disorder is called goiter.
3. the pancreas
This organ has two functions. It serves as a ducted gland, secreting
digestive enzymes into the small intestine. The pancreas also serves as a
ductless gland in that the islets of
Langerhans secrete insulin and glucagon to regulate the blood sugar
level. The -islet cells secrete glucagon, which tells the liver to take
carbohydrate out of storage to raise a low blood sugar level. The -islet
cells secrete insulin to tell the liver to take excess glucose out of
circulation to lower a blood sugar level thats too high. If a persons
body does not make enough insulin (and/or there is a reduced response
of the target cells in the liver), the blood sugar rises, perhaps out of
control, and we say that the person has diabetes mellitus.
4. the adrenal glands
These sit on top of the kidneys. They consist of two parts, the
outer cortex and the inner medulla. The medulla
secretes epinephrine (= adrenaline) and other similar hormones in
response to stressors such as fright, anger, caffeine, or low blood sugar.
The cortex secretes corticosteroids such as cortisone. Corticosteroids
are well-known as being anti-inflammatory, thus are prescribed for a
number of conditions. However, these are powerful regulators that
should be used with caution
5. the gonads or sex organs
In addition to producing gametes, the female ovaries and
male testes (singular = testis) also secrete hormones. Therefore, these
hormones are called sex hormones. The secretion of sex hormones by
the gonads is controlled by pituitary gland hormones such as FSH and
LH. While both sexes make some of each of the hormones, typically
male testes secrete primarily androgens including testosterone. Female
ovaries make estrogen and progesterone in varying amounts depending
on where in her cycle a woman is. In a pregnant woman, the babys
placenta also secretes hormones to maintain the pregnancy.
6. the pineal gland
This gland is located near the center of the brain in humans, and is
stimulated by nerves from the eyes. In some other animals, the pineal
gland is closer to the skin and directly stimulated by light (some lizards
even have a third eye). The pineal gland secreted melatonin at night
when its dark, thus secretes more in winter when the nights are longer.
Melatonin promotes sleep (makes you feel sleepy). It also affects
reproductive functions by depressing the activity of the gonads.
Additionally, it affects thyroid and adrenal cortex functions. In some
animals, melatonin affects skin pigmentation. Because melatonin
production is affected by the amount of light to which a person is
exposed, this is tied to circadian rhythm (having an activity cycle of
about 24 hours), annual cycles, and biological clock functions.
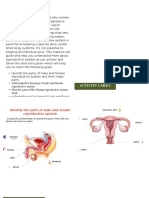
Assignment: Be able to locate/identify the endocrine glands in the body.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Types of SpeechesDokument9 SeitenTypes of Speecheskiratuz1998Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reported SpeechesDokument9 SeitenReported SpeechesLê TràNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accent Training Module 160Dokument132 SeitenAccent Training Module 160hismileguyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Great SpeechesDokument168 SeitenGreat Speechesraks0701Noch keine Bewertungen
- Debate SpeechesDokument2 SeitenDebate Speechesrandihcap2017Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of SpeechesDokument9 SeitenTypes of Speechesjho_olisNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Information Management: Boonyarat Phadermrod, Richard M. Crowder, Gary B. WillsDokument10 SeitenInternational Journal of Information Management: Boonyarat Phadermrod, Richard M. Crowder, Gary B. WillsgilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opening SpeechesDokument6 SeitenOpening Speechesapi-264416360Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine System: Dr. Alisha Noreen Lecturer Iqra UniversityDokument25 SeitenThe Endocrine System: Dr. Alisha Noreen Lecturer Iqra UniversitypashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Training Report Citigroup Transaction Services (M) SDN BHDDokument27 SeitenIndustrial Training Report Citigroup Transaction Services (M) SDN BHDhisyamstarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Speeches of Public SpeakingDokument11 SeitenSample Speeches of Public SpeakingRenaline TrinidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Report 2013Dokument22 SeitenFinal Report 2013Ahmad HazaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSS Medical College ProspectusDokument42 SeitenJSS Medical College ProspectusMota ChashmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Finance and Central Banking: Renard A. SottoDokument16 SeitenIntroduction To Finance and Central Banking: Renard A. SottoShiena Jane BayleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Aquatic Plants Phytoremediators As Green Technology Treatment in Polluted Urban Lakes EcologyDokument8 SeitenApplication of Aquatic Plants Phytoremediators As Green Technology Treatment in Polluted Urban Lakes EcologythesijNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accent Neutralization ProgramDokument21 SeitenAccent Neutralization ProgramISamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Removal of PhenolDokument16 SeitenRemoval of PhenolVinit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM EssaysDokument8 SeitenSPM EssaysWnhannan Mohamad100% (2)
- Descriptive Analysis of The Sensory Properties of Beverages and Gelatins Containing Sucrose or Synthetic Sweeteners'Dokument5 SeitenDescriptive Analysis of The Sensory Properties of Beverages and Gelatins Containing Sucrose or Synthetic Sweeteners'Elson TavaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Building Toward Construction Sustainability: Energy Efficiency With Material and Design AspectsDokument11 SeitenGreen Building Toward Construction Sustainability: Energy Efficiency With Material and Design AspectsghchgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspirational SpeechDokument9 SeitenInspirational SpeechPauloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Removal of Congo Red by Using Adsorption Onto Palm Oil WasteDokument55 SeitenRemoval of Congo Red by Using Adsorption Onto Palm Oil Wastedamnchemaddicted100% (1)
- Writing Essays U8 Upstream AdvancedDokument5 SeitenWriting Essays U8 Upstream AdvancedMonica BalteanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organization Profile: 1.1 Description of The OrganizationDokument23 SeitenOrganization Profile: 1.1 Description of The OrganizationEklo NewarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Check Your English Vocabulary For MedicineDokument66 SeitenCheck Your English Vocabulary For MedicineCamiru ValenzuelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing 3 - Short EssayDokument26 SeitenWriting 3 - Short EssayCậu Bé Bút Chì100% (1)
- The Help of Mass Media New NewDokument14 SeitenThe Help of Mass Media New NewEry BustamanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- CATTI 三级汉英真题 讲解Dokument53 SeitenCATTI 三级汉英真题 讲解serina bianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phonetics and Phonology PDFDokument22 SeitenPhonetics and Phonology PDFsarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 (Week 1)Dokument5 SeitenUnit 1 (Week 1)bobzmark100% (1)
- Planthormones 141025004114 Conversion Gate02 PDFDokument75 SeitenPlanthormones 141025004114 Conversion Gate02 PDFSaiTimmarao100% (1)
- Phytoremediation of Bamboo Reinforced SunflowerDokument13 SeitenPhytoremediation of Bamboo Reinforced SunflowerGerome CausapinNoch keine Bewertungen
- University Technology Mara: Puan Nurul Ain Binti Muhammad RafiaiDokument34 SeitenUniversity Technology Mara: Puan Nurul Ain Binti Muhammad RafiaiQistina ShahrilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Final 10th Grade Road To Ielts Third Term Workshop 2019Dokument9 SeitenAc Final 10th Grade Road To Ielts Third Term Workshop 2019taric rosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health Benefits of Physical ActivityDokument8 SeitenMental Health Benefits of Physical Activityapi-315842258Noch keine Bewertungen
- Language and ThoughtDokument6 SeitenLanguage and ThoughtPeter ThairuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParticipleDokument2 SeitenParticipleAsiale AlmoceraNoch keine Bewertungen
- English PhoneticsDokument9 SeitenEnglish PhoneticsAna GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Absorption: - Absorption Is The Process byDokument57 SeitenDrug Absorption: - Absorption Is The Process byccccccc1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Adventure SportsDokument12 SeitenAdvantages and Disadvantages of Adventure SportsKevin C. AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.-NURSES-ACT-1950-2 MalaysiaDokument22 Seiten2.-NURSES-ACT-1950-2 Malaysiakoyote73Noch keine Bewertungen
- Malaysian University English TestDokument22 SeitenMalaysian University English Testruzana100% (1)
- Lesson Plan For Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument7 SeitenLesson Plan For Anatomy and PhysiologyJamie Bagundol100% (1)
- Ms. Cynthia Bea: ProfessorDokument22 SeitenMs. Cynthia Bea: ProfessorJohn Cedric Vale CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- V3 Unit 9B - Human Regulation and ReproductionDokument16 SeitenV3 Unit 9B - Human Regulation and ReproductionNellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormones in The BodyDokument9 SeitenHormones in The BodySherry SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- HAPL4 - HUMAN ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY - MODULE 4 & 5Dokument47 SeitenHAPL4 - HUMAN ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY - MODULE 4 & 5welpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology WithDokument14 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology WithDonita Meña LaroyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Anatomy - Module 1 & 2 - Final TermDokument46 SeitenHuman Anatomy - Module 1 & 2 - Final TermwelpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grow Taller: © Dr. Laura de Giorgio All Rights ReservedDokument12 SeitenGrow Taller: © Dr. Laura de Giorgio All Rights ReservednepplutoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument14 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyDonita Meña LaroyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Module On Human Body: Lesson V: The Endocrine SystemDokument8 SeitenA Module On Human Body: Lesson V: The Endocrine Systemapi-3731377Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine SystemDokument8 SeitenThe Endocrine SystemVictoria VintuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument6 SeitenEndocrine SystemChechan AmbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EndocrineDokument15 SeitenEndocrineapi-200177496Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho Physiology of SepsisDokument5 SeitenPa Tho Physiology of SepsisMikee Ann ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine System: Exocrine GlandsDokument5 SeitenThe Endocrine System: Exocrine GlandsahmedfikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System PresentationDokument29 SeitenEndocrine System PresentationTanayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument58 SeitenEndocrine SystemBeBs jai SelasorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endochrine SystemDokument6 SeitenEndochrine Systemskitz0frenicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Point Perspective DrawingDokument7 Seiten3 Point Perspective DrawingZheena S. JaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ang Konsepto NG BayaniDokument15 SeitenAng Konsepto NG BayaniZheena S. Jaro67% (3)
- Dasma, Cavite CLUPDokument283 SeitenDasma, Cavite CLUPZheena S. Jaro67% (3)
- Biological PsychologyDokument1 SeiteBiological PsychologyZheena S. JaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Awakenings - Reaction PaperDokument1 SeiteAwakenings - Reaction PaperZheena S. JaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Andrology Lecture 3 Male Reprod Organs ScrotumDokument23 SeitenAndrology Lecture 3 Male Reprod Organs ScrotumgnpobsNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level Teacher Learning Areas Teaching Dates and Time Quarter Week 9Dokument7 SeitenGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level Teacher Learning Areas Teaching Dates and Time Quarter Week 9Jelbah AapsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 108 Health Care Ethics MidtermDokument70 SeitenNCM 108 Health Care Ethics MidtermMaria Arlyn Lacuña SagosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 GYNE 7 - EndometriosisDokument6 Seiten1 GYNE 7 - EndometriosisIrene FranzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Celebrity Focus: Helping You Through Pregnancy, Birth and BeyondDokument84 SeitenCelebrity Focus: Helping You Through Pregnancy, Birth and BeyondNickie EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block 2.2 Safe Motherhood and NeonatesDokument17 SeitenBlock 2.2 Safe Motherhood and Neonatesanon_55864979Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9.diagnosis and Initial Management of Dysmenorrhea PDFDokument6 Seiten9.diagnosis and Initial Management of Dysmenorrhea PDFMubdi AfdhalNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCOS and Infertility - Causes and TreatmentDokument42 SeitenPCOS and Infertility - Causes and TreatmentlouloucheNoch keine Bewertungen
- FPPackDokument25 SeitenFPPackPrashantMBhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2Dokument78 Seiten2api-3744136Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Tissue CultureDokument28 SeitenPlant Tissue CultureMuhammad Irshad80% (5)
- b1 ChecklistDokument2 Seitenb1 ChecklistRoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Northwestern Medicine Fertility Reproductive Ivf Brochure PDFDokument8 SeitenNorthwestern Medicine Fertility Reproductive Ivf Brochure PDFHafid JuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infertility Management in Women With PolycysticDokument7 SeitenInfertility Management in Women With PolycysticCarolina SidabutarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemuliaan Tanaman Nilam (Progestemon Cablin) Lokal Melalui Perkembangbiakan VegetatifDokument8 SeitenPemuliaan Tanaman Nilam (Progestemon Cablin) Lokal Melalui Perkembangbiakan Vegetatifarmadanti shafiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal CareDokument13 SeitenMaternal CareHannan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Genitile Mutilation RPDokument8 SeitenFemale Genitile Mutilation RPPalak GroverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Sheets (Parasitology Lab)Dokument7 SeitenReport Sheets (Parasitology Lab)billhaddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gary Crompton's Fight Against Prostate CancerDokument21 SeitenGary Crompton's Fight Against Prostate Cancerramskill2982100% (2)
- Part Test For Aipmt 2016Dokument18 SeitenPart Test For Aipmt 2016Apex InstituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Prepared by Mr. Abhay Shripad Joshi Yash Institute of Pharmacy AurangabadDokument18 SeitenIntroduction To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Prepared by Mr. Abhay Shripad Joshi Yash Institute of Pharmacy AurangabadMourian AmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uterine Inversion: Liu Soo Kiun Lau Fui Yii NG Chiat HawDokument12 SeitenUterine Inversion: Liu Soo Kiun Lau Fui Yii NG Chiat HawElvis NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogens in The Environment: - Viruses and Prions - Bacteria and Rickettsiae - Fungi and Algae - Protozoans - HelminthsDokument34 SeitenPathogens in The Environment: - Viruses and Prions - Bacteria and Rickettsiae - Fungi and Algae - Protozoans - HelminthsEnaANoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive System SIMDokument9 SeitenReproductive System SIMandz100% (7)
- Varicocele Embolization Is Becoming The Treatment of Choice For Many Patients and Their PhysiciansDokument15 SeitenVaricocele Embolization Is Becoming The Treatment of Choice For Many Patients and Their Physiciansdwyane0033Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cloning in Plants Applications of Genetic Engineering: Mam Iqra IqbalDokument56 SeitenCloning in Plants Applications of Genetic Engineering: Mam Iqra Iqbalsaba anwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phylum MesozoaDokument25 SeitenPhylum Mesozoatapas kundu100% (3)
- Lesson Three - Puberty and Body PartsDokument6 SeitenLesson Three - Puberty and Body PartsBrianMarBeltranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Reproductive Technology945Dokument35 SeitenAssisted Reproductive Technology945Praluki HerliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test 2.2Dokument7 SeitenSummative Test 2.2jellyB RafaelNoch keine Bewertungen