Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cathode-Ray Oscilloscopes
Hochgeladen von
Sreejith VaneryOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cathode-Ray Oscilloscopes
Hochgeladen von
Sreejith VaneryCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Thouheed/ece/10
Cathode-Ray Oscilloscopes
Introduction
The oscilloscope is the basic instrument for the study of all
types of waveforms.
It can be employed to measure such quantities as peak
voltage, frequency, phase difference, pulse width, delay time, rise time, and
fall time.
An oscilloscope consists of a cathode-ray tube (!T" and its
associated control and input circuitry.
In the !T, electrons generated at a heated cathode are shaped
into a fine beam and accelerated toward a fluorescent screen.
The screen glows at the point at which the electrons strike.
The electron beam is easily deflected vertically and
hori#ontally by voltages applied to deflecting plates.
$sually, the beam is swept hori#ontally across the screen by a
ramp voltage generated by a lime base circuit, and the waveform to be
investigated is applied to deflect the beam vertically.
This results in a voltage-versus-time display of the input
waveform.
%ost oscilloscopes are dual-trace (or multitrace" instruments
capable of displaying two or more waveforms simultaneously.
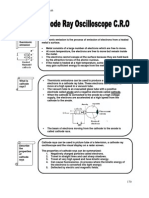
CATHODE-RAY TUBE
Operation
The basic construction and biasing of a cathode-ray tube are
shown in &igure '.
The filament heats the cathode, which emits electrons.
The triode section of the tube consists of a cathode, a grid, and
an anode.
The cathode is typically held at appro(imately -) k*, and the
grid potential is ad+ustable from appro(imately -),,, * to -),-, *.
The grid-cathode potential controls the electron flow from the
cathode and thus controls the number of electrons directed to the screen.
'
Thouheed/ece/10
A large number of electrons striking one point will cause the
screen to glow brightly. a small number will produce a dim glow.
Therefore, the grid potential control is a brightness control.
The grid voltage controls the flow of electrons to anodes A',
A), and A/ which focus the beam to a fine point at the screen.
The focusing electrodes A', A), and A/ are sometimes
referred to as an electron lens.
The function of the electron lens is to focus the electrons to a
fine point on the screen of the tube.
*oltages applied to the vertical and hori#ontal deflecting
plates move the electron beam around the screen.
A beam of electrons is generated by the cathode and directed
to the screen, causing the phosphor coating on the screen to glow where
the electrons strike.
The electron beam is deflected vertically and hori#ontally by
e(ternally applied voltages.
&igure '. 0asic cathode-ray tube construction.
)
Thouheed/ece/10
/
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sicx1003 Unit 5Dokument29 SeitenSicx1003 Unit 5SimranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-III (Topic - 3)Dokument61 SeitenUnit-III (Topic - 3)vsresika20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrodynamic Waves: Wireless Transmission Through Air, Metals, Water and the Human BodyVon EverandElectrodynamic Waves: Wireless Transmission Through Air, Metals, Water and the Human BodyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.3introduction To CRO - Cathode Ray Oscilloscope: Block DiagramDokument12 Seiten3.3introduction To CRO - Cathode Ray Oscilloscope: Block DiagramAddisu Safo BoseraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 37 Cathode Rays and Cathode Ray TubeDokument30 Seiten37 Cathode Rays and Cathode Ray TubeASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode Ray OscillioscopeDokument27 SeitenCathode Ray Oscillioscopeayoubt2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physic 4.1 Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDokument25 SeitenPhysic 4.1 Cathode Ray OscilloscopeSascha WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit1croppt 141013124117 Conversion Gate02Dokument25 SeitenUnit1croppt 141013124117 Conversion Gate02Rahul ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A CRO (Cathode Ray Oscilloscope) & Its WorkingDokument4 SeitenWhat Is A CRO (Cathode Ray Oscilloscope) & Its WorkingRai Mudassar IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A CRO (Cathode Ray Oscilloscope) & Its WorkingDokument4 SeitenWhat Is A CRO (Cathode Ray Oscilloscope) & Its WorkingRai Mudassar IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscilloscopes: Electronic Instrumentation 15EC35Dokument26 SeitenOscilloscopes: Electronic Instrumentation 15EC35Darshan rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRODokument59 SeitenCRONaman SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Oscilloscope: Cathode Ray Tube and Other Internal ComponentsDokument19 SeitenThe Oscilloscope: Cathode Ray Tube and Other Internal ComponentsParag NikhraNoch keine Bewertungen
- M Systems: ScilloscopesDokument6 SeitenM Systems: ScilloscopesAnkit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cro Saravana SelviDokument25 SeitenCro Saravana SelviIndranil KutheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDokument17 SeitenCathode Ray OscilloscopeLochan DhayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 21,22,23Dokument136 SeitenChap 21,22,23Tejas SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRO-A.K. Sawhney (2012)Dokument42 SeitenCRO-A.K. Sawhney (2012)jeet174tNoch keine Bewertungen
- II Yr EMI Unit 3Dokument10 SeitenII Yr EMI Unit 3Amazonas ManutençãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRT AssignmentDokument21 SeitenCRT AssignmentRittika RatawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - OscilloscopeDokument29 SeitenChapter 4 - OscilloscopeSYAFIQAH ISMAILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode - Ray - Oscilloscop First Year 1Dokument7 SeitenCathode - Ray - Oscilloscop First Year 1Tangent ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Physics Handout Unit 5Dokument21 SeitenGrade 10 Physics Handout Unit 5Milkias BerhanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- OscillioscopeDokument20 SeitenOscillioscopeAbhishek MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode RaysDokument55 SeitenCathode RaysAbarhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode Ray OscilloscopesDokument17 SeitenCathode Ray OscilloscopesiagooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eec 126Dokument51 SeitenEec 126Adam AdewaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory & Solved Exercise: Written/Composed By: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # 0313-5665666 WebsiteDokument6 SeitenTheory & Solved Exercise: Written/Composed By: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # 0313-5665666 WebsiteFatima ObaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRO (Cathode Ray Oscilloscope)Dokument126 SeitenCRO (Cathode Ray Oscilloscope)Bhavika jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.cro, Ad and Da ConvertersDokument25 Seiten11.cro, Ad and Da ConvertersmaniaxcaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medc 0503 2022-2023 Lab 2 - CroDokument10 SeitenMedc 0503 2022-2023 Lab 2 - CroLance ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit III NotesDokument27 SeitenUnit III NotesSwami Naidu GummadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRO Bs-3rdDokument44 SeitenCRO Bs-3rdAbdur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDokument24 SeitenCathode Ray OscilloscopeAntonovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding The Uses of C.R.O.Dokument24 SeitenUnderstanding The Uses of C.R.O.mydadawalfnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Static Deflection in CRTDokument43 SeitenElectro Static Deflection in CRTutadaneelimadeviutadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRO UpdateDokument59 SeitenCRO UpdaterfgfgtrtrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 CRTDokument11 Seiten1 CRTSuvesh nlnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cro ModifiedDokument34 SeitenCro Modifiedsatya_vanapalli3422Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDokument20 SeitenCathode Ray OscilloscopeVaishnavi PillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (Cro)Dokument25 SeitenCathode Ray Oscilloscope (Cro)Sai KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Beams and OscilloscopeDokument28 SeitenElectron Beams and OscilloscopeAkachukwu OguineNoch keine Bewertungen
- CroDokument10 SeitenCroSongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of CRO: Submitted By-Vikram Arya M.Sc-1 Semester Department of Physics D.S.B-Campus NainitalDokument21 SeitenStudy of CRO: Submitted By-Vikram Arya M.Sc-1 Semester Department of Physics D.S.B-Campus NainitalneerajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Lab ManualDokument17 SeitenPhysics Lab ManualindirabinuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode Ray Tube QRGDokument3 SeitenCathode Ray Tube QRGfatima benfrihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.4 Modern Physics Notes: Cathode RaysDokument21 SeitenS.4 Modern Physics Notes: Cathode RaysMwebaza JulianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 1 Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDokument14 Seiten9 1 Cathode Ray Oscilloscopesuemozac100% (5)
- 3 CroDokument25 Seiten3 CroMAHAMEGHA BAHANANoch keine Bewertungen
- Sir Chhotu Ram Institute of Engineering & Technology C C S University, Campus, MeerutDokument9 SeitenSir Chhotu Ram Institute of Engineering & Technology C C S University, Campus, Meerutitz me BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module Name: Biomedical Instrumentation Code: EEBT 05105Dokument36 SeitenModule Name: Biomedical Instrumentation Code: EEBT 05105jonathan stevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 16 Thermionic Emission CroDokument3 SeitenUnit 16 Thermionic Emission Croyusuke123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-5 4Dokument26 SeitenUnit-5 4kkkkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To RadTech - X-Ray ProductionDokument9 SeitenIntro To RadTech - X-Ray ProductionEzekiel MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDokument4 SeitenCathode Ray OscilloscopesushilNoch keine Bewertungen
- FSC Physics 2 Year: Chapter 14: ElectromagnetismDokument24 SeitenFSC Physics 2 Year: Chapter 14: ElectromagnetismAdeela UmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14Dokument15 SeitenChapter 14Gaurav SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planks ConstantDokument5 SeitenPlanks Constantprateekjain01100% (4)
- Engineering Mechanics ObjectiveDokument45 SeitenEngineering Mechanics ObjectiveSreejith Vanery100% (3)
- SurveyingDokument9 SeitenSurveyingSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- The OSI and TCPDokument8 SeitenThe OSI and TCPSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Infrastructure & Building ServicesDokument6 SeitenBasic Infrastructure & Building ServicesSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engineering ObjectiveDokument42 SeitenCivil Engineering ObjectiveSreejith Vanery80% (10)
- Coputer Programing CDokument81 SeitenCoputer Programing CSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnglishDokument2 SeitenEnglishSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi Media: InteractivityDokument3 SeitenMulti Media: InteractivitySreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam TurbineDokument42 SeitenSteam TurbineSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- I.C. Engines: (I) According To The Type of Fuel UsedDokument15 SeitenI.C. Engines: (I) According To The Type of Fuel UsedSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental of Power PlantDokument3 SeitenFundamental of Power PlantSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- SurveyingDokument9 SeitenSurveyingSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- RefrigerationDokument52 SeitenRefrigerationSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion Engines2Dokument92 SeitenInternal Combustion Engines2Rupinder Rp100% (1)
- RADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging)Dokument6 SeitenRADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging)Sreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extrusion ProcessesDokument6 SeitenExtrusion ProcessesSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- DigitalDokument2 SeitenDigitalSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lich King Chorus PDFDokument21 SeitenLich King Chorus PDFMacgy YeungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Media ReportDokument46 SeitenMedia ReportAndrew AB BurgoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- JKR SPJ 1988 Standard Specification of Road Works - Section 1 - GeneralDokument270 SeitenJKR SPJ 1988 Standard Specification of Road Works - Section 1 - GeneralYamie Rozman100% (1)
- Exchange Rates JBDokument9 SeitenExchange Rates JBboss9921Noch keine Bewertungen
- Telemeter-Electronic Brochure Flexible Heaters WebDokument12 SeitenTelemeter-Electronic Brochure Flexible Heaters WebXavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet: Permanent Magnet GeneratorDokument2 SeitenData Sheet: Permanent Magnet Generatordiegoadjgt100% (1)
- Gist of FIEO ServicesDokument1 SeiteGist of FIEO Servicessanjay patraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 48 Volt Parallel Battery System PSS-SOC - Step-By-Step VolvoDokument11 Seiten1 48 Volt Parallel Battery System PSS-SOC - Step-By-Step VolvoEyosyas NathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Definition Multimedia Interface SpecificationDokument51 SeitenHigh-Definition Multimedia Interface SpecificationwadrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergies To Cross-Reactive Plant Proteins: Takeshi YagamiDokument11 SeitenAllergies To Cross-Reactive Plant Proteins: Takeshi YagamisoylahijadeunvampiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caselet - LC: The Journey of The LCDokument5 SeitenCaselet - LC: The Journey of The LCAbhi JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- U-Blox Parameters Setting ProtocolsDokument2 SeitenU-Blox Parameters Setting Protocolspedrito perezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group H Macroeconomics Germany InflationDokument13 SeitenGroup H Macroeconomics Germany Inflationmani kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Layer 3 Managed 8 10G Port Switch Controller: RTL9303-CGDokument55 SeitenLayer 3 Managed 8 10G Port Switch Controller: RTL9303-CG박윤지100% (1)
- Alpine MRV f305Dokument2 SeitenAlpine MRV f305Luis RrNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fracture MechanicsDokument81 SeitenOn Fracture MechanicsDEEPAK100% (1)
- COST v. MMWD Complaint 8.20.19Dokument64 SeitenCOST v. MMWD Complaint 8.20.19Will HoustonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invidis Yearbook 2019Dokument51 SeitenInvidis Yearbook 2019Luis SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions & Answers On CountersDokument24 SeitenQuestions & Answers On Counterskibrom atsbha100% (2)
- Transport StrikeDokument9 SeitenTransport StrikeYsrael Von ArcillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lenovo Security ThinkShield-Solutions-Guide Ebook IDG NA HV DownloadDokument10 SeitenLenovo Security ThinkShield-Solutions-Guide Ebook IDG NA HV DownloadManeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- FGD MetallurgyDokument5 SeitenFGD MetallurgyrajivashishNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.traders Virtual Mag OTA July 2011 WebDokument68 Seiten11.traders Virtual Mag OTA July 2011 WebAde CollinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Juegos PPCDokument8 SeitenJuegos PPCikro995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fabric Technologist RoleDokument3 SeitenFabric Technologist RoleAnup Kumar DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- News/procurement-News: WWW - Sbi.co - inDokument15 SeitenNews/procurement-News: WWW - Sbi.co - inssat111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Facts PDFDokument18 SeitenEnergy Facts PDFvikas pandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Team Work in An OrganizationDokument10 SeitenImportance of Team Work in An OrganizationMohammad Sana Ur RabNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAA PUBLICATIONS May Be Purchased or Downloaded For FreeDokument4 SeitenFAA PUBLICATIONS May Be Purchased or Downloaded For FreeFlávio AlibertiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muhammad Safuan Othman (CD 4862)Dokument24 SeitenMuhammad Safuan Othman (CD 4862)Andy100% (1)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersVon Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosVon EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionVon EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (543)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tVon EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (27)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonVon EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesVon EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...Von EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionVon EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (15)
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsVon EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceVon EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeVon EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (10)
- Electronics All-in-One For Dummies, 3rd EditionVon EverandElectronics All-in-One For Dummies, 3rd EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialVon EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsVon EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationVon EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Diploma Interview Q&A: Career GuideVon EverandPower Electronics Diploma Interview Q&A: Career GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsVon EverandWearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsEdward SazonovNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeVon EverandA Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (53)
- Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldVon EverandEmpires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (87)