Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture - 2
Hochgeladen von
Adnan ChowdhuryCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture - 2
Hochgeladen von
Adnan ChowdhuryCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Unit 1 Notes
Adnan Chowdhury 4
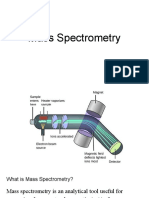
Mass Spectrometer:
The mass spectrometer can be used to determine relative atomic mass, relative molecular mass,
relative isotopic abundance, molecular structure, etc.
There are 5 things that happen when a sample is injected into a mass spectrometer:
1. Vaporisation: If the sample is a solid or liquid, it is vaporised (turned into a gas) using an
electric heater.
2. Ionisation: The gas particles are bombarded with high energy electrons from a filament wire (by
thermionic emission) to ionise them. Electrons are knocked out and positive ions are formed.
A(g) + e
-
A
+
(g) + 2e
-
A = an atom
M(g) + e
-
M
+
(g) + 2e
-
M = a molecule.
3. Acceleration: The positive ions are accelerated by an electric field
4. Deflection: The positive ions are deflected using a magnetic field. Lighter ions with greater
charge have less momentum and are deflected more compared to heavier ones with less charge.
For a given magnetic field, only ions with a particular mass/charge (m/z) ratio can make it to
the detector. Ions with greater mass/charge ratio will deflect more.
5. Detection: The magnetic field strength is slowly increased. This changes the mass/charge ratio
of ions that can reach the detector. A mass spectrum is produced.
Unit 1 Notes
Adnan Chowdhury 5
Problem:
Calculate the relative atomic mass of Magnesium.
Problem:
Calculate the relative atomic mass of Neon.
Problem:
Unit 1 Notes
Adnan Chowdhury 6
Chlorine has two isotopes Cl-35 and Cl-37. Identify the species responsible for the peaks.
Problem:
Bromine has two isotopes Br-79 and Br-81.
a. Identify the particles responsible for the peaks.
b. Deduce the relative abundance of the two isotopes.
c. Write a chemical equation to show the formation of the species at m/z = 160.
Problem:
Carbon has three isotopes C-12, C-13 and C-14. Chlorine has two isotopes Cl-35 and Cl-37. Calculate the
maximum and minimum mass of CCl4.
Problem:
The relative atomic mass of copper is 63.5. Calculate the relative abundance of the two copper isotopes
with relative isotopic masses of 63 and 65.
Problem:
The mass spectrum of a chloride of phosphorus, PClx, shows three main group of lines, The m/z values
of which are given in the table below:
m/z
I 66, 68
II 101, 103, 105
III 136, 138, 140, 142
a. Identify the species responsible for the peaks.
b. Deduce the value of x.
Bombarding with electrons makes some molecules break up into fragments. These all show up in
the mass spectrum making a fragmentation pattern.
The fragment with the greatest relative abundance is called the base peak.
The fragment with the highest m/z value is called the molecular ion (M
+
) peak.
For organic compounds, the M
+
peak has the second highest m/z value and the highest m/z value
is for the (M+1)
+
peak. This happens due to Carbon-13 isotope.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sheikh Shakib Ahsan: Batch: BBA (Management) - 2016 Phone: +8801946361500 +8801626784751 E-MailDokument3 SeitenSheikh Shakib Ahsan: Batch: BBA (Management) - 2016 Phone: +8801946361500 +8801626784751 E-MailAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.4 Transition Metals - Complex IonsDokument12 Seiten5.4 Transition Metals - Complex IonsAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 87793Dokument2 Seiten87793Adnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photo Description Price: QTY Requir EdDokument9 SeitenPhoto Description Price: QTY Requir EdAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balancing Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsDokument28 SeitenBalancing Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae: Name: Adnan ChowdhuryDokument3 SeitenCurriculum Vitae: Name: Adnan ChowdhuryAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projectiles Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Dokument6 SeitenProjectiles Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Adnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry QuestionsDokument40 SeitenChemistry Questionskaotao1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4.10 - 4.11 Organic Synthesis and Structure Determination MSDokument30 Seiten4.10 - 4.11 Organic Synthesis and Structure Determination MSAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ItemsDokument44 SeitenLab ItemsAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2013 QP - Unit 4 AQA ChemistryDokument20 SeitenJune 2013 QP - Unit 4 AQA ChemistryAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- CUP IBChemistry c01 It MolesDokument53 SeitenCUP IBChemistry c01 It MolesAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.06 - 4.07 Aromatic Chemistry and Amines MSDokument20 Seiten4.06 - 4.07 Aromatic Chemistry and Amines MSAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- CUP IBChemistry c02 It Atomic StructureDokument30 SeitenCUP IBChemistry c02 It Atomic StructureAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- CUP IBChemistry c06 It Rates of ReactionsDokument33 SeitenCUP IBChemistry c06 It Rates of ReactionsAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqa Chem4 QP Jun12Dokument24 SeitenAqa Chem4 QP Jun12Adnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- CUP IBChemistry c04 It Periodic TableDokument37 SeitenCUP IBChemistry c04 It Periodic TableAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- CUP IBChemistry c01 It MolesDokument53 SeitenCUP IBChemistry c01 It MolesAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- CUP IBChemistry c03 It BondingDokument59 SeitenCUP IBChemistry c03 It BondingAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqa Chem5 QP Jun14Dokument24 SeitenAqa Chem5 QP Jun14Adnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equation Name of Mechanism Mechanism: 4.8, 4.9 Exam Questions Ms 1Dokument9 SeitenEquation Name of Mechanism Mechanism: 4.8, 4.9 Exam Questions Ms 1Adnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.08 - 4.09 Amino Acids and PolymersDokument16 Seiten4.08 - 4.09 Amino Acids and PolymersAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.06 - 4.07 Aromatic Chemistry and AminesDokument30 Seiten4.06 - 4.07 Aromatic Chemistry and AminesAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3 Exam QuestionsDokument52 Seiten4.3 Exam QuestionsRegirocksNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.03 Acid and Bases MSDokument24 Seiten4.03 Acid and Bases MSAdnan ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Caffeine Is A Widely UsedDokument5 SeitenCaffeine Is A Widely UsedHarry HopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- J. J. Thomson and The Electron: 1897-1899 An IntroductionDokument42 SeitenJ. J. Thomson and The Electron: 1897-1899 An IntroductionJBNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Edexcel 1Dokument6 Seiten1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Edexcel 1Tasveer AcademyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quinoa Saponins Analysis and Preliminary InvestigationsDokument12 SeitenQuinoa Saponins Analysis and Preliminary InvestigationsAndreaPaloCardenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass SpectrometryDokument4 SeitenMass SpectrometryCarlton GrantNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Physics C E&M Unit 3 1. Magnetic Field and Force HandoutDokument28 SeitenAP Physics C E&M Unit 3 1. Magnetic Field and Force HandoutmoonidiveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Guide Unit 1Dokument76 SeitenRevision Guide Unit 1Amie PorterNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE-504 Lecture 4 Basics of Mass Spectrometery by Dr. Charu C. PantDokument13 SeitenCHE-504 Lecture 4 Basics of Mass Spectrometery by Dr. Charu C. PantAbhishek Singh ChandelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-1: Thomson Cathode Ray Tube Experiment: Electron Gun Negative Phosphor ScreenDokument2 Seiten1-1: Thomson Cathode Ray Tube Experiment: Electron Gun Negative Phosphor ScreenEliana Hwang100% (3)
- Red Cabbage Anthocyanins Profile, Isolation, Identification, and Antioxidant ActivityDokument7 SeitenRed Cabbage Anthocyanins Profile, Isolation, Identification, and Antioxidant ActivityIan Ai No Kami CasvitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q MsmplusDokument1 SeiteQ MsmplusKhondokar TarakkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Compound Identification ReportDokument3 SeitenQualitative Compound Identification ReportKartik RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification and Quantification of A Marker Compound For Pepper PDFDokument8 SeitenIdentification and Quantification of A Marker Compound For Pepper PDFciborg1978Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 - RscmodifiedDokument59 SeitenChapter 13 - RscmodifiedVivek SagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijms 23 08810Dokument19 SeitenIjms 23 08810Ojan Arifin MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 222 Lab Report Electron Charge To Mass RatioDokument6 SeitenPhysics 222 Lab Report Electron Charge To Mass RatioEmily Gatlin100% (14)
- Review of Laser-Driven Ion Sources and Their Applications PDFDokument72 SeitenReview of Laser-Driven Ion Sources and Their Applications PDFAjit UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 1 Revision Guide Atomic Structure Aqa PDFDokument9 Seiten1 1 Revision Guide Atomic Structure Aqa PDFItai Nigel ZembeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ujian Akhir Semester Elusiasi Struktur (Senyawa Organik) T.A: 2019-2020 GenapDokument11 SeitenUjian Akhir Semester Elusiasi Struktur (Senyawa Organik) T.A: 2019-2020 GenapArianto UmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Guide: Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry - Example Questions and AnswersDokument8 SeitenStudent Guide: Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry - Example Questions and AnswersPlayer mineNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Atomic Structure EXAMPRODokument36 Seiten1.1 Atomic Structure EXAMPROamandasparkle100% (1)
- 4101-A - Application of Mass Spectrometry To Inorganic CompoundsDokument9 Seiten4101-A - Application of Mass Spectrometry To Inorganic CompoundsGuRi JassalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaur 2004Dokument10 SeitenKaur 2004Unni KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 000152883Dokument301 Seiten000152883Yuwono WibowoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPE Mass Spectrometry Workshop PresentationDokument36 SeitenCAPE Mass Spectrometry Workshop PresentationDelano PeteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass SpectrometryDokument19 SeitenMass SpectrometryArchieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Notes SEBAGABO 4Dokument332 SeitenChemistry Notes SEBAGABO 4CHRISTOPHER NSENGIYUMVA100% (2)
- Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue On Nanocrystalline TiO2Dokument7 SeitenPhotocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue On Nanocrystalline TiO2Michel G. RahalNoch keine Bewertungen
- O MegatronDokument12 SeitenO MegatronIvan ArnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fragmenttaion-Halides To Learning ResourcesDokument11 SeitenFragmenttaion-Halides To Learning ResourcesShinu DiazNoch keine Bewertungen