Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
LESSON9.2 Electronics
Hochgeladen von
Thiyaku Marutha0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten27 Seitenphysic notes electronics
Originaltitel
LESSON9.2 electronics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenphysic notes electronics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten27 SeitenLESSON9.2 Electronics
Hochgeladen von
Thiyaku Maruthaphysic notes electronics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 27
LESSON 2-
Understanding semiconductor diodes.
Semiconductor Materials
Semiconductors are materials which conduct electricity better than insulator, but no so well as ordinary
conductors.
The following table shows the comparison between insulator, conductor and semiconductor:
Insulator Semiconductor Conductor
Example material Glass,
ceramic,
polythene
Silicon,
germanium,
selenium
Copper,
aluminium,
iron
Charge carrier No free electrons Free electrons
and holes
Free electrons
Resistance High Between insulator and
conductor
Low
Conductivity Decrease
when the temperature
Increase when the temperature
increase.
Also increase when light shines
on it or with presence of
impurities
Decrease when the
temperature
Charge carriers in semiconductors
In a pure crystal of a semiconductor( intrinsic semiconductor) such as silicon, each atom of silicon has
four electrons in outermost orbit that are involved in covalent bonding.
The vibrations of atoms causes some electrons to break free the bonds.
When an electron is removed from a covalent bond, it leaves behind a vacancy and is called a hole in
the bonding . Free electrons( negatively charged) and holes (positively charged) are known as charge
carriers .
Conduction in a semiconductor is by means of a movement of free electrons and holes in opposite
direction.
Semiconductors cannot conduct electricity as well as metals because they have smaller numbers of free
electrons and holes. The conductivity of the semiconductors can be increased by a process is called
doping
Doping of Semiconductors
Doping is a process of adding a small amount of impurities into the pure crystal of semiconductor (intrinsic
semiconductor).
Atoms of the impurities added should have almost the same size as the atoms of the intrinsic
semiconductor.
Type of Semiconductors Material
Different kinds of impurities are added produce different types of semiconductor ; the p-type and the n-type.
(i) p-type semiconductor
A p-type semiconductor is produced when trivalent atoms are added to intrinsic semiconductor atoms.
Only fhree of the four bonds formed by the trivalent atoms are complete. The vacancy is a hole with
positive charge.
The holes are now the majority charge carriers in the p-type semiconductor since there are more
holes than free electrons.
Examples of trivalent atoms are Indium,Boron and Gallium and called acceptor atoms.
(ii) n-type semiconductor
A n-type semiconductor is produced when pentavalent atoms are added to intrinsic semiconductor
atoms.
Each pentavalent atom donate a free electron ,because there will be one extra electron.
The electrons are now the majority charge carriers in the n-type semiconductor since there are more
free electrons than holes.
Examples of pentavalent atoms are Arsenic,Phosporus and Antimony and called donor atoms.
Comparison between p-type semiconductor and n-type semiconductor
p-type
semiconductor
n-type
semiconductor
Pure
Semiconduktor
Silicon,
Germanium
Silicon,
Germanium
Doping
substance
Indium,Boron,
Gallium
Phosporus,
Antimony,
Arsenic
Function of
doping
substance
Aceptor atom Donor atom
Valency of
doping
substance
Pentavalent Trivalent
Majority charge
carrier
Hole Electron
Minority charge
carrier
Electron Hole
Semiconductor Diode
A diode is a component (device) that allows electric current to flow in one direction only.
A diode acts like a one-way valve to electric current.
The structure and the symbol of a semiconductor diode
A semiconductor diode can be made by joining pieces of n-type and p-type semiconductor.
The semiconductor diode is also called p-n junction diode.
The following figure shows structure and the symbol of a semiconductor diode :
How does the p-n junction diode work?
When p-type semiconductor material in contact
with n-type semiconductor material , a layer called the depletion layer is formed in the middle.
At this junction , electrons from n-type material drifts across the junction to fill in the holes in p-type.
The holes from p-type material drift in the opposite direction to unite with free electrons in the n-type
material. As a result a depletion layer is a very narrow region which has lost all its available free electrons
and holes and thus behaves almost like pure silicon,i.e with high resistivity.
Any further movement of charges across the boundry in the depletion layer will be repelled by the charges
in the layer.
The layer of the negative charge in the p-type region will prevent the majority charge carriers from the n-
type region(the electrons) from crossing the boundary. Similarly , the positive charge layer in the n-type
region will prevent the majority charge carriers from the p-type region(the holes) from crossing the boundry
in the opposite direction. Thus, a potential difference ,known as the junction voltage.In its normal state a p-
n junction delivers no current since the charges are in equilibrium.
The effect of this junction voltage is to prevent charge carriers from drifting across the junction.
The junction voltages for germanium and silicon are approximately 0.1 V and 0.6 V respectively.
In order for electric current to flow through the diode, the voltage applied across the diode must exceed the
junction voltage.
When the in forward-biased arrangement, the cell voltage greater than the junction voltage. The depletion
layer is narrow , and the resistance of diode decreases. Hence a large current flows through the diode.
When the in reverse-biased arrangement, the cell voltage lower than the junction voltage. The depletion
layer is wide , and the resistance of diode increases. Hence only a very small current (leakage current)
flows through the diode.
Graph of current, I against voltage V for p-n jenis silicon dan germanium diode
Experiment to show a semiconductor diode flows current in one direction only.
Figure(a) Figure(b)
The diode is connected to the cell in the forward-biased arrangement as shown in Figure(a).
The bulb light up.
The experiment is repeated with the reverse-biased arrangement as shown in Figure (b)
The bulb does not light up.
The experiment shows that a diode allow the current in one direction only when the diode in the forward-
biased arrangement.
Diode as a Rectifier
A diode can act as a rectifier because it can convert alternating current(a.c.) into direct current(d.c).
The process of converting a.c. to d.c. is called rectification.
There are two types of rectification process :
(1) Half -wave rectification
(2) Full - wave rectification
Half- wave rectification
For half of the cycle, A is more positive than B ,the diode conducts.
For the other half cycle, A is more negative than B , no current can flow.
Full-wave rectification
For half of the cycle, A is more positive than B ,the diode conducts and the current flows through the
resistance.
For the other half cycle, A is more negative than B ,
the current flows through the resistance in the same direction as before.
Capacitor
A capasitor is device which can
(1) store electric charge
(2) smooth out waveform in the rectified output
(3) separate the a.c and d.c (as a filter)
Smoothing output wave by a capacitor
By connecting a capacitor parallel to the resistance , the half-wave and the full-wave rectified waveform
could be partially smoothed out.
For half of the cycle, the capacitor is charged up. Energy is stored in the capacitor.
For the other half cycle, the capacitor releases its charge (discharges)
So the capacitor can produced a steady output or output is stablised.
TUTORIAL 2
1 Which of the statements on semiconductor material is not true?
A not obey the Ohms law
B the charge carriers are holes
C Silion and Germanium are two examples of pure semiconductor material
D conduct electricity better than insulator but no so well as ordinary conductors.
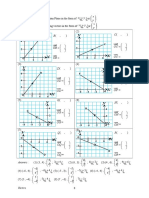
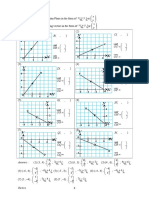
2 Which of the flowing graph resistance, R against temperature, T is correct for a pure
semiconductor material?
3 The process of adding a trivalent atom to a pure silicon crystal is known as
A doping
B donating
C excitation
D polarization
4 Which of the following is not a doping substance.
A antimony B germanium
C indium D gallium
5 Which of the following pairs characteristics are true?
n-type
semiconduktor
p-type
semiconduktor
A Doping antimony gallium
substance
B Funtion of
doping
substance
aceptor atom donor atom
C Valency
of doping
substance
trivalent pentavalent
D Majority
charge
carrier
hole electron
6 An n-type semiconductor is produced when some of the germanium atoms are replaced
with
A divalent atoms
B trivalent atoms
C tetravalent atoms
D pentavalent atoms
7 Which of the following diagrams is an n-type
semiconductor?
8 Which of the following pairs atoms can act as an impurity to produce an n-type
semiconductor when doped into a pure semiconductor?
A Boron and phosphorus
B Arsenic and antimony
C Antimony and gallium
D Indium and gallium
9 Which of the following is true according to a
p-type semiconductor?
A Thedoping substance is trivalent atoms
B The majority charge carrier is free electrons
C The conductivity decreases when temperature is increased
10 Which of the following graph current,I against potential difference,V for a semiconductor
diode?
11 A function of a diode is as F
A Amplifier
B Rectifier
C Smoother
12 The diagram shows a circuit consisting of a diode and a bulb. When the switch is on, the
bulb does not light up.
What needs to be done to light up the bulb?
A Replace with a new bulb
B Reverse the diode connection
C Increase the number of dry cells
D Connect a resistor parallel to the bulb
13 The diagram shows a circuit containing bulbs X, Y and Z.
Which bulb in the circuit will light up when the switch is on?
A Z only
B X and Y only
C Y and Z only
D X,Y and Z
14 Which of the following circuit causes only a bulb is lighted up?
15 The diagram shows a circuit containing diode D, resistor R and a.c. power supply
is applied at terminal PQ. The waveform of the a.c. supply is shown in the diagram.
Which of the following waveform output is formed at CRO screen?
16 Which of the following waveform has been rectified?
17 The diagram shows a circuit containing two diodes , a resistance is connected to a.c.
voltage.
Which of the following waveform formed on the
CRO screen?
.
18 The diagram shows a rectification circuit which uses four diodes K,L,M and N
and resistor, R.
Which of the following is the direction of the current flowing?
A K N M L
B L M N R
C L R N
D M R N
19 The diagram shows a rectification circuit which uses four diode , a resistor and a battery.
Which of the following is the direction of the
current flowing?
A U S NOQ RT M L
B U S TMNO Q M L
C L M NOQR T S U
D L T SQR ON M U
20 The diagram shows a rectification circuit which uses four diodes and three resistors P ,
Q and R.
Which of the following resistor is only the
direct current flow?
A P B Q
C R D P ,Q and R
21
The function of the capacitor in fhe figure above as
A a rectifier
B an amplifier
C a current filter
D a voltage smoother
22
Based on the circuit above, which of the following waveform is formed on the CRO screen?
23 Which of the following circuit does the bulb not light up
24 The diagram shows the structure of a
semiconductor material.
(a) Based on the diagram above,
(i) name the type of the semiconductor material.
.........................................................
(ii) what is the function of the Boron atom?
.........................................................
(iii) name the majority charge carrier in the semiconductor material.
.........................................................
(b) At 0 K , a pure semiconductor material has very high resistance. Explain why?
....................................................................
...
(c) The diagram shows a p-type semiconductor is joined to an n-type semiconductor.
Later the combination of the semiconductor materials are connected to a bulb and a battery.
(i) Name the line X.
....................................................................
(ii) Give the name and the function of voltage at X .
....................................................................
(d) What happens to the bulb when the battery connection is reversed. Explain why?
.............................................................................
.............................................................................
.............................................................................
.............................................................................
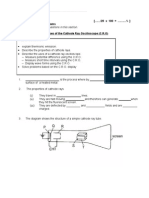
25 (a) Figure (a) shows an arrangement of
apparatus to study the conductivity of semiconductor diode by a student.
When the switch is closed by the student the bulb does not light up.
Figure (a)
(i) In the space below draw a circuit diagram for Figure (a)
(ii) State the characteristic of the diode
causes the bulb does not light up?
..
.
.
(iii) State the correction should be done to the connection of the circuit in Figure (a)
to make the bulb is lighted up.
..
.
..
(b) Figure (b) shows circuit X is connected to a transformer , resistor R and a cathode-
ray oscilloscope. When the switch is opened the waveform as shown in Figure (b) is formed on
the CRO screen.
Figure (b)
(i) In the space below draw a circuit diagram for circuit X.
(ii) In the space below draw a waveform
is produced in the CRO screen when a capacitor is connected parallel to resistor R.
(iii) Give the reason for your answer in
b(ii).
.
.
26 The diagram shows a rectification circuit which uses four diodes W ,X, Yand Z and resistor
R.
(a) What does the word rectification mean?
.............................................................................
(b) Draw the waveform formed on the CRO screen.
(c) By using the letters A,B,C,D,E,F,G and H in the figure above state the direction of
the current flows when at half of the cycle, A is more positive than B.
....................................................................
(d) What happen to the direction of the current flows in resistor R compared to the your answer in
(c) when at the other half cycle, A is more negative than B.
....................................................................
....................................................................
(e) What happen to the output waveform when
(i) the terminals of diodes X and Y are reversed
............................................................
(ii) only the terminals diode Y are reversed
..
(iii) the terminals of diodes W, X, Y and Z are reversed.
............................................................
(f) Draw the waveform formed when a capacitor is connected parallel to resistor R in the
figure above.
27 Abu wants to power a ticker timer and a transistor radio. The ticker timer requires an
input voltage of 12 V a.c. and the transistor radio requires an input voltage 12 V d.c. The power
supply at Abus school is 240 V a.c.
(a) Abu used a transformer as shown in Figure (a) to power the ticker timer.
Figure (a)
(i) Name the type of the transformer is used.
............................................................
(ii) Give one reason why the soft-iron core is used in the transformer?
..
(iii) The number of turns in the primary coil is 2000. Calculate the number of turns in
the secondary coil.
[ Assume that the transformer is
an ideal transformer ]
(b) The transformer in Figure (a) is not suitable to power the radio. A modification is
required before the radio is used.
(i) Explain why the transformer is not suitable to use?
............................................................
............................................................
(ii) Name two electronic components that are needed to use.
...................................
..
(c) Figure (b) shows a circuit that can be modified to produce a full-wave rectification
and smoothing output wave
Figure (b)
Complete the circuit in the dotted box by adding the electronic components in b(ii)
28 (a) Figure (a) shows circuits J, K, L, M and N
each containing an ideal transformer. Diodes in the circuits are used for the purpose of
rectification.
Figure (a)
Key :
Np = Number of turns in primary coil
Ns = Number of turns in secondary coil
(i) What is meant by rectification ?
(ii) Explain the working principle of a transformer.
(iii) You are asked to make a 12 V battery charger . Study the circuits, J, K ,L, M
and N in Figure (a) and consider the following aspects:
- type of transformer
- ratio of the number of turns in primary coil to secondary coil
- type of rectification
- characteristic of output current
(b) Figure (b) shows a circuit consisting of a transformer, an ammeter and two
light bulbs. The ammeter reading is 0.5 A and both bulbs light up with normal brightness.
Figure (b)
(i) What is the output voltage of the transformer?
(ii) Calculate the efficiency of the transformer.
28
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Xiyj Xiyj: Answers: (1) (3, 4)Dokument2 SeitenXiyj Xiyj: Answers: (1) (3, 4)Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 I Graphs of Functions IIDokument24 SeitenChapter 2 I Graphs of Functions IIThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 Maths F4Dokument3 SeitenTest 1 Maths F4Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 Form 5 MathsDokument5 SeitenTest 1 Form 5 MathsThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Standard FormDokument14 SeitenChapter 1 Standard FormThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 I Number BasesDokument18 SeitenChapter 1 I Number BasesThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 2Dokument23 SeitenBiology Form 4 Chapter 2Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Vectors in Cartesian PlaneDokument2 Seiten3.1 Vectors in Cartesian PlaneThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Dokument18 SeitenAdd Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Functions (Paper 2) : (KEDAH 2013)Dokument2 SeitenTrigonometric Functions (Paper 2) : (KEDAH 2013)Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 - Understanding TransistorsDokument19 SeitenLesson 3 - Understanding TransistorsThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Math p2 Trial SPM SSC 2011Dokument11 SeitenAdd Math p2 Trial SPM SSC 2011Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minda Bestari: Pusat Motivasi Dan TuisyenDokument4 SeitenMinda Bestari: Pusat Motivasi Dan TuisyenThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Form 4 Test 1Dokument4 SeitenPhysics Form 4 Test 1Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON9.4 ElectronicsDokument27 SeitenLESSON9.4 ElectronicsThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assestment Form 4 2012Dokument10 SeitenAssestment Form 4 2012Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Maths Form 4 Paper 1 2012 2Dokument15 SeitenAdd Maths Form 4 Paper 1 2012 2Thiyaku Marutha100% (2)
- Medicine Ball: Workout ChartDokument1 SeiteMedicine Ball: Workout ChartThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- DC Regulated Power SupplyDokument14 SeitenDC Regulated Power SupplyMegha Projects100% (2)
- Rfid Based Voting MachineDokument91 SeitenRfid Based Voting MachineRakesh kumar100% (1)
- Design of A High-Efficiency 2.45-Ghz Rectenna For Low-Input-Power Energy HarvestingDokument4 SeitenDesign of A High-Efficiency 2.45-Ghz Rectenna For Low-Input-Power Energy HarvestingMaritza NuñezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Implementation of GSM Based Industrial AutomationDokument8 SeitenDesign and Implementation of GSM Based Industrial AutomationPramillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day - 4 Custom Power Compensating DevicesDokument0 SeitenDay - 4 Custom Power Compensating Devicesbd9051Noch keine Bewertungen
- Secure Power Solution International Guide 2012 - 2013Dokument32 SeitenSecure Power Solution International Guide 2012 - 2013Abu ZubairNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPD 503 Service NotesDokument2 SeitenGPD 503 Service NotesArnauNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRM-PPT-EEE SRIDHAR VecDokument66 SeitenSRM-PPT-EEE SRIDHAR VecnikcsitNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETP48200-B2A1 Embedded Power User ManualDokument85 SeitenETP48200-B2A1 Embedded Power User ManualAlberto PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Meters (Analog Electromechanical Instruments)Dokument25 SeitenAnalog Meters (Analog Electromechanical Instruments)zemichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Train LightingDokument40 SeitenTrain LightingSrikanth Vsr75% (4)
- The Valve Wizard: How To Design Valve Guitar Amplifiers!Dokument3 SeitenThe Valve Wizard: How To Design Valve Guitar Amplifiers!Diego García Medina100% (1)
- Physics Chapter 4 Form 5Dokument11 SeitenPhysics Chapter 4 Form 5violetNoch keine Bewertungen
- RectifierDokument5 SeitenRectifierpreethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS - Cable Locator - CL 20 - BAUR - En-GbDokument3 SeitenDS - Cable Locator - CL 20 - BAUR - En-GbDaniel NgigiNoch keine Bewertungen
- XR500DDokument20 SeitenXR500DGabino Ubilio MurilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generation of High D.C. Voltages: Unit-IvDokument18 SeitenGeneration of High D.C. Voltages: Unit-IvsrilakshmisiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 KW Bi-Directional CLLC DC-DC Converter InfineonDokument55 Seiten11 KW Bi-Directional CLLC DC-DC Converter InfineonShri KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- LHF 630 & 800 File 0740 800 028Dokument34 SeitenLHF 630 & 800 File 0740 800 028Madalina Lazar100% (1)
- Electrician&Wireman: Under Craft Instructor Training Scheme (Cits) Two Semesters (One Year)Dokument20 SeitenElectrician&Wireman: Under Craft Instructor Training Scheme (Cits) Two Semesters (One Year)confirm@Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sanyo Microwave Oven Service Manual 2029Dokument26 SeitenSanyo Microwave Oven Service Manual 2029Bibiz999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Overspeed DetectionDokument67 SeitenOverspeed Detection20-403 TejashwiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Paper of Put Coin and Draw Power 2010Dokument9 SeitenFull Paper of Put Coin and Draw Power 2010Biswajit SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8Dokument9 SeitenChapter 8cheraziziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Flux Based Direct Power Control of Three-Phase PWM Rectifiers PDFDokument9 SeitenVirtual Flux Based Direct Power Control of Three-Phase PWM Rectifiers PDFbensumbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE430 - PO1 (Students Kit) - TORQUE-SPEED CHARACTERISTICSDokument19 SeitenEEE430 - PO1 (Students Kit) - TORQUE-SPEED CHARACTERISTICSMuzamer PuteraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Models For Design Electrical Calculations For Industrial PlantsDokument182 SeitenModels For Design Electrical Calculations For Industrial Plantsalex100% (1)
- Matrix Drives Reduce Energy Costs For Asphalt Transport SystemDokument4 SeitenMatrix Drives Reduce Energy Costs For Asphalt Transport SystemphysicudoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Puente Gbu6aDokument4 SeitenPuente Gbu6aJESSAMYN GUERRERO MONTOYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes and Effect of Harmonics in Power System IJSETR-VOL-3-IsSUE-2-214-220Dokument7 SeitenCauses and Effect of Harmonics in Power System IJSETR-VOL-3-IsSUE-2-214-220emmanuel akaNoch keine Bewertungen