Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Scribed PhyOlevel Chap1
Hochgeladen von
Foong YenyeeCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Scribed PhyOlevel Chap1
Hochgeladen von
Foong YenyeeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
www.duzhongxueku.
com Physics
Chapter1
Physical Quantities
- a quantity that can be measured.
- consists of a numerical magnitude and a unit.
International System of Units (SI unit)
Physical quantities are quantities that can be measured. They can be classified into:
(i) Base quantities
A base quantities is a quantity that cannot beexpressed in terms of other quantities.
(ii) Derived quantities
A derived quantity is a quantity that is a combination of base quantities by meant of
multiplication, division or both.
To make working with units easier, some derived units are given special names.
Prefix and standard form
-A prefix is a letter placed before a unit of measurement to act as the multiplier of the unit
- their symbols and the multipliers they represent are as follows:
www.duzhongxueku.com Physics
Scalar Quantities : quantity which has only magnitude or size [eg. Mass, length, speed,
volume]
Vector quantities: quantity which has magnitude or size and direction [ eg. Velocity, force,
displacement and acceleration]
Length:
A rule (ruler) is used to measure length for distances between 1mm and 1meter; the SI unit
for length is the meter (m)
To find out the volume of a regular object, you can use a mathematical formula, you just
need to make a couple of length measurements.
To measure the volume of an irregular object you have to put the object into measuring
cylinder with water. When you add the object it displaces the water, making the water level
rise. Measure this rise. This is the volume of your object.
Time:
An interval of time is measured using clocks, the SI unit for time is the second(s)
To find the amount of time it takes a pendulum to make a spin, time ~25 circles and then
divide by the same number as the number of circles.
Oscillation: each complete to-and- fro motion is one oscillation
Period: time take for one complete oscillation
Precision
- the smallest unit an instrument can measure
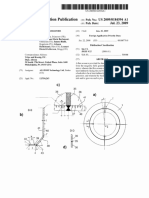
Place your eye directly above the markings to avoid PARALLAX ERRORS.
Precision of metre rule is 0.1cm or 1mm.
Precision of vernier calipers is 0.01cm.
Precision of micrometer screw gauge is 0.01mm.
Accuracy and consistency in measurements
1. Accuracy : the ability of an instrument to measure nearest to the actual value
2. Consistency: the ability of an instrument to measure consistently with little or no
relative deviation among readings
www.duzhongxueku.com Physics
3. Sensitivity: the ability of an instrument to detect small change in the quantity
measured
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankVon EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Quantities and MeasurementsDokument12 SeitenPhysical Quantities and Measurementsaahil.9277Noch keine Bewertungen
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (10)
- 1 - Quantities, Units, MeasurementsDokument47 Seiten1 - Quantities, Units, MeasurementsAushia Tanzih Al-HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringVon EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- LP4 Facilitator SlidesDokument231 SeitenLP4 Facilitator SlidesSumayya LimbadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and Experimentation Class 9 IcseDokument28 SeitenMeasurement and Experimentation Class 9 Icseabhishek_sinha100% (2)
- General Physics BlockDokument43 SeitenGeneral Physics Blockmdridomd15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement & Significant FiguresDokument65 SeitenMeasurement & Significant FiguresJim Marco100% (1)
- Measurement PPDokument14 SeitenMeasurement PPmohd razif ibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Meeting-1Dokument7 SeitenSummary of Meeting-1Nihad ƏhmədovNoch keine Bewertungen
- P6 (W1)Dokument32 SeitenP6 (W1)Ace CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vernier and Micrometer Caliper-DoneDokument4 SeitenVernier and Micrometer Caliper-DoneJAMEL DENYSE FERNANDEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units of MeasurementDokument8 SeitenUnits of MeasurementLiney Carrillo ContrerasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miss Saima Presentation MeasurementDokument38 SeitenMiss Saima Presentation MeasurementAdeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Notes Chapter OneDokument15 SeitenPhysics Notes Chapter Onemanoj sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 1Dokument60 SeitenGroup 1Adriel MarasiganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement & QuantitiesDokument5 SeitenMeasurement & QuantitiesBearnesia IndonesiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and Statistical Tasks 1Dokument8 SeitenMeasurement and Statistical Tasks 1Agum GhifariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examen Final - Idioma TecnicoDokument30 SeitenExamen Final - Idioma Tecnicosamuel rojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement-Grade 7Dokument26 SeitenMeasurement-Grade 7a.gayle1998Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 1 PhysicsDokument6 SeitenLab Report 1 PhysicsAzam Aziz100% (3)
- Chapter 2 MeasurementsDokument5 SeitenChapter 2 MeasurementsChristian Guimmayen ArizoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument11 SeitenChapter 2api-298420434Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 - 2 Instrumentation and Measurement. International System of UnitsDokument48 SeitenTopic 1 - 2 Instrumentation and Measurement. International System of UnitsCristina CurasovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and UnitsDokument10 SeitenMeasurement and UnitsHanan MdSomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Physical Quantities and Measurement Dbs1012Dokument24 SeitenChapter 1 - Physical Quantities and Measurement Dbs1012佳壕Noch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Physics MeasurementsDokument15 Seiten01 Physics MeasurementsAli SalamehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 01 Notes Physics PDFDokument5 SeitenChapter 01 Notes Physics PDFOmer FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Notes (Physics)Dokument65 SeitenChapter 1 Notes (Physics)ronniego100% (2)
- MarkellaDokument23 SeitenMarkellamimoakal24Noch keine Bewertungen
- DGD RQZ9 U XMPHRJ EDx FDsDokument5 SeitenDGD RQZ9 U XMPHRJ EDx FDsvedant72930Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 1: Intro Ductio NDokument44 SeitenGeneral Physics 1: Intro Ductio Npalitpa moreNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Phy Quant 2 (Length & Time) (9jan8)Dokument26 Seiten01 Phy Quant 2 (Length & Time) (9jan8)Sagar JathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT1 Physical Quantities & Measurements NOTESDokument9 SeitenUNIT1 Physical Quantities & Measurements NOTESWahaj RehanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH1103 Practical 02Dokument23 SeitenPH1103 Practical 02jegubenjamin12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1.1 (PPT) Units - Measurements Grade 10 PhysicsDokument93 SeitenTopic 1.1 (PPT) Units - Measurements Grade 10 PhysicsLaw PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOP CH.1 MeasurementDokument211 SeitenFOP CH.1 MeasurementKristine Joyce RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline 2-1Dokument28 SeitenOutline 2-1api-294483847Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 1 IntroDokument22 SeitenGeneral Physics 1 IntroJayhanne CuerdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Quantities Measurements & UnitsDokument35 SeitenPhysical Quantities Measurements & UnitsSajayanKSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Grade MeasurementDokument27 Seiten3rd Grade MeasurementkhrysssyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units and Measurements OfflineDokument25 SeitenUnits and Measurements OfflineASHOK KUMAR RANANoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2 Sec 1 Measurement-PowerpointDokument23 SeitenCH 2 Sec 1 Measurement-Powerpointapi-294483847100% (2)
- Lecture 1 Physics 1Dokument42 SeitenLecture 1 Physics 1nicole quisiquisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantities, Units, and MeasurementDokument8 SeitenQuantities, Units, and MeasurementTriacute80% (5)
- Wk01 - Lec01 Physical QuantitiesDokument23 SeitenWk01 - Lec01 Physical QuantitiesYouCan SpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- TenthClass Content EM Physics 01-MeasurementOfLengthDokument10 SeitenTenthClass Content EM Physics 01-MeasurementOfLengthArindam GuhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1. Physical Quantities 2017-18Dokument9 SeitenUnit 1. Physical Quantities 2017-18SHANNIE CARRIEDONoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-1: TypesDokument4 SeitenChapter-1: TypesPIETDS1 aeronauticalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using A MicrometerDokument4 SeitenUsing A MicrometerXielalah Sai SoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Outcomes: MeasurementDokument37 SeitenLearning Outcomes: MeasurementLely WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement: Physical QuantitiesDokument31 SeitenMeasurement: Physical QuantitiesHaris GondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Notes Units and DimensionsDokument53 SeitenPhysics Notes Units and DimensionsThota RevanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement & CalibrationDokument32 SeitenMeasurement & CalibrationArun ShishodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fisbing - Tugas - 3Dokument18 SeitenFisbing - Tugas - 3ummysalmahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screenshot 2023-09-20 at 12.32.56 AMDokument34 SeitenScreenshot 2023-09-20 at 12.32.56 AMSiya ParmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- RevisionDokument6 SeitenRevisionSaleh AlgdaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gimbi Poly Technic College Basic Electrical/Electronic Equipment Servicing NTQF Level - I Learning Guide-28Dokument38 SeitenGimbi Poly Technic College Basic Electrical/Electronic Equipment Servicing NTQF Level - I Learning Guide-28Lemmi GutetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics G7 Week 1 B1 Ch.13 MeasurementsDokument32 SeitenPhysics G7 Week 1 B1 Ch.13 MeasurementsAyesha DuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traceable Temperatures - Temp. Measurement and Calibration 2nd Ed.Dokument435 SeitenTraceable Temperatures - Temp. Measurement and Calibration 2nd Ed.jupoc90% (10)
- T SC 2550160 Ks2 Year 5 Properties and Changes of Materials Revision Activity Mat Ver 4Dokument6 SeitenT SC 2550160 Ks2 Year 5 Properties and Changes of Materials Revision Activity Mat Ver 4khushbakhtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Chapter 9 1st 25 PagesDokument25 SeitenPhysics Chapter 9 1st 25 PagesAdrie CRNoch keine Bewertungen
- PartB1 INTERCOHESIONDokument12 SeitenPartB1 INTERCOHESIONAhmet AydınNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hall Effect in GermaniumDokument12 SeitenThe Hall Effect in GermaniumSanele ZiqubuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH16: Adsorption and Ion ExchangeDokument5 SeitenCH16: Adsorption and Ion Exchangeangel matienzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flux Screen For GeneratorsDokument13 SeitenFlux Screen For GeneratorsMichal KowalczykNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Drop CalculatorDokument26 SeitenPressure Drop CalculatorAnonymous 6S9tcbhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equations For The Soil-Water Characteristic'curve: D.G. XingDokument12 SeitenEquations For The Soil-Water Characteristic'curve: D.G. XingburlandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 3 CH: 1 Electric Flux & Gauss's LawDokument2 SeitenWorksheet 3 CH: 1 Electric Flux & Gauss's LawJiya JithinNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXP - 8 - Determination of Venturimeter ConstantDokument6 SeitenEXP - 8 - Determination of Venturimeter Constantpratyush mishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Enhancement of Filtration Process With Filter Aids Diatomaceous Earth and Wood Pulp CelluloseDokument7 SeitenA Study On Enhancement of Filtration Process With Filter Aids Diatomaceous Earth and Wood Pulp CellulosegoldennanukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Reactive Power Compensation TechnologiesDokument79 SeitenReview of Reactive Power Compensation TechnologiesRadu BabauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro User Manual: DaltonicsDokument36 SeitenMicro User Manual: DaltonicsBromance H.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Course Structures & Evaluation Plan: MSC PhysicsDokument35 SeitenCourse Structures & Evaluation Plan: MSC PhysicsBikash SaikhomNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWS90 Ch05 ModalDokument24 SeitenAWS90 Ch05 ModalCinitha ANoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP 3 SolutionDokument1 SeiteDPP 3 SolutionOmprakash DhakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Test A: Teacher Notes and Answers Momentum and CollisionsDokument5 SeitenChapter Test A: Teacher Notes and Answers Momentum and CollisionsHans HenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGC2016 NortonStraw MattStraw PublicDokument27 SeitenSGC2016 NortonStraw MattStraw Publicpmr80_2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hsslive Xi Physics Notes Seema ElizabethDokument237 SeitenHsslive Xi Physics Notes Seema ElizabethJIJIN SASTHARAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Integrals Over Non-Rectangular RegionsDokument21 SeitenMultiple Integrals Over Non-Rectangular RegionsCodrutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic: Bioenergetics: Living OrganismsDokument9 SeitenTopic: Bioenergetics: Living OrganismsNaiomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body of Knowledge (Science)Dokument5 SeitenBody of Knowledge (Science)Putri HandayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDokument17 SeitenThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedUjjawal singhalNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review On Numerical and Experimental StudyDokument4 SeitenA Review On Numerical and Experimental StudyAbhijit GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gases: Grade 12 Rutherford - ThomsonDokument36 SeitenGases: Grade 12 Rutherford - ThomsonLennie ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Problems in Modern QuantumDokument9 SeitenSolutions To Problems in Modern QuantumFabrício MendesNoch keine Bewertungen
- T494Dokument10 SeitenT494Liliana Mejia HoyosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static Equilibrium - 7esDokument6 SeitenStatic Equilibrium - 7esEpay Castañares LascuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceVon EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (51)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyVon EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesVon EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2193)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayVon EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (125)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldVon EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (64)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidVon EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1396)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowVon EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (49)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldVon EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (60)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldVon EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (54)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessVon EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterVon EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (410)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Von EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (157)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingVon EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessVon EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (57)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeVon EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceVon EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- The Reality Revolution: The Mind-Blowing Movement to Hack Your RealityVon EverandThe Reality Revolution: The Mind-Blowing Movement to Hack Your RealityBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (19)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itVon EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (13)
- Transform Your Life And Save The World: Through The Dreamed Of Arrival Of The Rehabilitating Biological Explanation Of The Human ConditionVon EverandTransform Your Life And Save The World: Through The Dreamed Of Arrival Of The Rehabilitating Biological Explanation Of The Human ConditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeVon EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNoch keine Bewertungen