Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
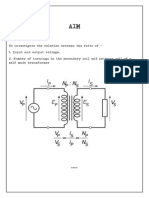
6 Electricity - Transmission
Hochgeladen von
Mohamad IskandarOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
6 Electricity - Transmission
Hochgeladen von
Mohamad IskandarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
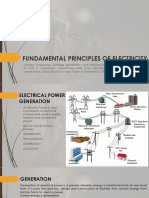
Power Plant
Step Up
Transformer
Step Down
Transformer
Step Down
Transformer
Distribution
Lines
Transmission
Lines
Residence
Whether it is fueled
by water, uranium
(nuclear), coal, wind,
natural gas, solar,
biomass, combined
cycle, geothermal
or landfll gas, power
plants use the fuel to
spin a turbine which
in turn produces
electricity. Most of
Cowlitz PUDs electrical
power is purchased
from Bonneville Power
Administration (BPA).
The electricity we
purchase from BPA
is made up of the
following (fuel mix):
Hydro 91.55%
Nuclear 4.79%
Coal 2.28%
Natural Gas .70%
Biomass 0.13%
Waste 0.04%
Petroleum 0.02%
Landfll Gases 0.01%
Other* 0.01%
*Includes the following fuel types - biomass,
landfll gas, petroleum and waste incineration.
As electricity leaves
the power plant it will
probably go through
a step up transformer
to increase its voltage.
This transformer may be
located in a substation.
A transformer is a piece
of electrical equipment
that has a two-sided
core. Each side has
copper wire wound
around it several times.
Between the sides an
electromagnetic feld
is created. In the case
of a step up transformer
the wire has fewer
winds on the side the
electricity comes in and
more winds on the side
it goes out. The ratio of
winds from one side to
the other determines
how much additional
voltage appears on
the side of the step up
transformer on which
the power goes out.
Transmission lines
carry electricity from
the power plant to
locations that can
be far away. While
traveling, electricity
loses voltage or
strength, in the form
of heat. Transformers
along the way help
boost the voltage to
make up for losses. The
high-power transmission
lines move from tower
to tower until they
reach a substation
in your area. The
electricity on these
lines typically runs at
115,000, 230,000 or
500,000 volts
Stepping it down
makes it more
economic to distribute
to the customers (i.e.
smaller equipment,
poles, wires, insulators,
transformers, etc.) A
step-down tranformer
takes care of this by
reversing what the
step up transformer did
earlier.
The electricity goes
through more winds
on the side it goes in, is
transferred across the
electromagnetic feld
to fewer winds on the
side it comes out. This
reduces the voltage
allowing it to move
over distribution lines.
Although the voltage
is much less than the
transmission lines it is still
very dangerous.
Distribution lines carry
the electricity from a
substation to your home
or business. They may
be overhead (as shown
in the above diagram)
or underground.
Electricity traveling on
distribution lines is at
14,270 volts.
Most of the time when
a power outage occurs
it happens between this
point and your home.
ALWAYS STAY AWAY
FROM POWER LINES
ESPECIALLY WHEN THEY
ARE ON THE GROUND!
Transformers are often
seen on distribution
lines as well. They look
a bit like a big can way
up on a power pole.
Before the electricity
enters your home
it must be stepped
down again to make
it work with the
appliances in your
home. The electricity
is transformed from
14,270 volts down to
240 volts and 120 volts.
These transformers can
be on the power poles
or on the ground in
your neighborhood. It
is a good rule-of-thumb
to stay away from these
transformers.
At the point electricity
enters your home it
goes through a meter
which determines
how much electricity
your household uses.
This meter is read
monthly either by a
person looking at your
actual meter or by
someone reading your
meter remotely with a
computer. The meter
reading continues from
one month to the next.
The difference between
the last reading and
the most current one is
your usage.
Electricity powers
your lights, washer
and dryer, television,
computer, ipod,
heater, air conditioner,
garage door and many
other things. Isnt it nice
to have electricity at
your disposal?
Electricity - Transmission (how electricity moves)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 02 Parallel-Lines-Angles Practice With AnswersDokument5 Seiten02 Parallel-Lines-Angles Practice With AnswersvkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Power System - Engineering Books PDFDokument2 SeitenPower System - Engineering Books PDFEswar ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methodology For Grid Stations& T.LDokument51 SeitenMethodology For Grid Stations& T.LiftikharNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2Von EverandA Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Levitation AbstractDokument6 SeitenMagnetic Levitation Abstractkkkoundi0% (1)
- Former DARPADoD Scientist On Neuro-AI Mind-Control Virus Weapons On Ignorant Humanity 2019Dokument35 SeitenFormer DARPADoD Scientist On Neuro-AI Mind-Control Virus Weapons On Ignorant Humanity 2019withtheflowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Howard Gardner Multiple IntelligenceDokument17 SeitenHoward Gardner Multiple IntelligenceMohamad IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railway ProjectDokument38 SeitenRailway Projectalankar123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Distribution SubstationDokument31 SeitenDistribution SubstationAadya100% (1)
- Four Paths of Influence Kenneth LeithwoodDokument28 SeitenFour Paths of Influence Kenneth LeithwoodMohamad IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transient Over VoltagesDokument38 SeitenTransient Over Voltagesraghav4life8724Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power PlantDokument33 SeitenThermal Power PlantManoj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm C581Dokument5 SeitenAstm C581Phan Linh100% (1)
- Listening Vocabulary Cambridge 10 To 18Dokument90 SeitenListening Vocabulary Cambridge 10 To 18Emon Rahman100% (1)
- Astm C 642-97 PDFDokument3 SeitenAstm C 642-97 PDFVasco Sorte100% (1)
- POWERPLANTDokument2 SeitenPOWERPLANTHi HiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AR 4.5 Building Services - IiDokument23 SeitenAR 4.5 Building Services - IiDarshini AmalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity PrintDokument14 SeitenElectricity PrintSirna Santosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Household CircuitDokument5 SeitenWhat Is Household CircuitAten AzharNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACTIVIDAD 6 How A Home Electrical System Work2Dokument7 SeitenACTIVIDAD 6 How A Home Electrical System Work2JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batangas State University Main Campus II Alangilan, Batangas CityDokument8 SeitenBatangas State University Main Campus II Alangilan, Batangas CityedeweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generation and TransmissionDokument9 SeitenGeneration and TransmissionAzat OnkolNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Power StationDokument2 SeitenWhat Is Power StationSajeed chocolateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical GenerationDokument14 SeitenElectrical GenerationRevati shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electrical Generation and DistributionDokument54 SeitenFundamentals of Electrical Generation and DistributionbhaskarjalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Electricity Delivers EnergyDokument6 SeitenHow Electricity Delivers EnergyAishwarya ChaudhryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 ElectricityDokument13 Seiten01 ElectricityAtharv PoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity: Electricity at A Glance, 2009Dokument7 SeitenElectricity: Electricity at A Glance, 2009Amos OkechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generation: The Power PlantDokument6 SeitenGeneration: The Power PlantElkay Rebel-Ikons MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Enter Post Title Here) : Power SystemDokument3 Seiten(Enter Post Title Here) : Power SystemElectric TechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Transformer in PowersystemsDokument19 SeitenRole of Transformer in PowersystemsDebojyotiMukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion Ecm433Dokument2 SeitenDiscussion Ecm433Nina WalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers9 21 11 PDFDokument16 SeitenTransformers9 21 11 PDFosanebiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architectural Building TechnologyDokument15 SeitenArchitectural Building TechnologyJuan Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- AR-307 Assignment-3: Electricals Q.1.: Aakarshit JainDokument10 SeitenAR-307 Assignment-3: Electricals Q.1.: Aakarshit JainAakarshit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black Decker The Complete Guide To Wiring, Updated 8th Edition Current With 2020-2023 Electrical Codes (Editors of Cool Springs Press)Dokument1.207 SeitenBlack Decker The Complete Guide To Wiring, Updated 8th Edition Current With 2020-2023 Electrical Codes (Editors of Cool Springs Press)Luis Felipe Alcantara PiñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Question Explain The Power Transmission To Distribution With Neat Diagram. SolutionDokument11 SeitenAssignment Question Explain The Power Transmission To Distribution With Neat Diagram. SolutionSwaroopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One 1.0 Background of The StudyDokument50 SeitenChapter One 1.0 Background of The StudyNduka GodwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Does Electricity Get To Your HomeDokument3 SeitenHow Does Electricity Get To Your HomeAinaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Lines and TransformersDokument4 SeitenPower Lines and TransformersUkash Adan FaditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trinning FileDokument32 SeitenTrinning FileelsayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC / Ac Inverter: Name: Mustafa Khader Abdel Abbas. Stage: (Morning)Dokument7 SeitenDC / Ac Inverter: Name: Mustafa Khader Abdel Abbas. Stage: (Morning)مصطفى الجبوريNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of Overhead Distribution SystemDokument9 SeitenComponents of Overhead Distribution SystemReginald L. CamineroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer XII Physics Investigatory ProjectDokument12 SeitenTransformer XII Physics Investigatory ProjectRudraksh SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Power SystemsDokument9 SeitenElectric Power SystemsAbdifatah mohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generation, Transmission DistributionDokument4 SeitenGeneration, Transmission Distributionmaverick arquilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Basic FundasDokument5 SeitenPower Basic FundasLalit Kumar ChetaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Transformer EasyDokument19 SeitenPresentation On Transformer EasyBensaron KadiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transporting Electricity InfosheetDokument1 SeiteTransporting Electricity Infosheetapi-222959505Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical WiringDomest 8310585Dokument20 SeitenElectrical WiringDomest 8310585Berry KasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAY 1 PresentationDokument28 SeitenDAY 1 PresentationEgbin TransmissionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Services 1Dokument8 SeitenBuilding Services 1Praveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 1 Sistemas Eléctricos de PotenciaDokument10 SeitenHomework 1 Sistemas Eléctricos de PotenciaSebastián TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Has High Efficiency. Fault Current Is Limited by The Inductor Output Short Circuit Current Is Easy To ImplementDokument6 SeitenHas High Efficiency. Fault Current Is Limited by The Inductor Output Short Circuit Current Is Easy To ImplementRajalakshmi ShivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Installation and MaintenanceDokument1 SeiteElectrical Installation and MaintenanceEarl Cris RiggsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Magnetic InductionDokument1 SeiteElectro Magnetic InductionTobi AboabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generation, Transmission and DistributionDokument8 SeitenGeneration, Transmission and DistributionCesar García MataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On: By-Er Rajinder Kumar Lecturer Electrical Engg. Govt Polytechnic College AmritsarDokument70 SeitenPresentation On: By-Er Rajinder Kumar Lecturer Electrical Engg. Govt Polytechnic College AmritsarAnonymous ExWAN2xjFJ100% (1)
- Eptd EEE FIFTH SEMESTER BY SUNUL SIRDokument15 SeitenEptd EEE FIFTH SEMESTER BY SUNUL SIRSolaiappan KtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Plans and How Electrical FlowsDokument10 SeitenPower Plans and How Electrical FlowsEugene OlidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Phase DistributionDokument3 Seiten3 Phase DistributionDodik NugrohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- En M Wikipedia Org Wiki Alternating CurrentDokument16 SeitenEn M Wikipedia Org Wiki Alternating CurrentMayurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generation Transmission and DistributionDokument18 SeitenGeneration Transmission and DistributionayazNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Power Grids WorkDokument14 SeitenHow Power Grids WorkPandey d'GunnerzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parameter Measurement Reliability of Supply Technical Losses Commercial Losses Collection Efficiency Billing Efficiency Employee CostDokument40 SeitenParameter Measurement Reliability of Supply Technical Losses Commercial Losses Collection Efficiency Billing Efficiency Employee CostRishi MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument50 SeitenLecture 1Sardar A'amirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appraisal Techniques Used in Evaluating Capital Investments: Conventional Capital Budgeting and The Real Options ApproachDokument472 SeitenAppraisal Techniques Used in Evaluating Capital Investments: Conventional Capital Budgeting and The Real Options ApproachMohamad IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical & Non-Ethical: The DifferencesDokument10 SeitenEthical & Non-Ethical: The DifferencesMohamad IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kepimpinan Dalam Etika KaunselingDokument3 SeitenKepimpinan Dalam Etika KaunselingMohamad IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leaders Ethics and SchoolsDokument20 SeitenLeaders Ethics and SchoolsMohamad IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories of Learning and Student Development PDFDokument5 SeitenTheories of Learning and Student Development PDFMohamad IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teori Schlossberg Transition - Mattering & MarginalityDokument17 SeitenTeori Schlossberg Transition - Mattering & MarginalityMohamad Iskandar0% (1)
- Teori ChickeringDokument15 SeitenTeori ChickeringMohamad Iskandar100% (1)
- ChickeringDokument21 SeitenChickeringMohamad IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- OMC-116 Installation Manual: ObservatorDokument11 SeitenOMC-116 Installation Manual: ObservatorQasim JummaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mecanica de Materiales Cap 8Dokument15 SeitenMecanica de Materiales Cap 8Kevin ChicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy, Work and Power: PHY111: Mechanics and Thermo Properties of MatterDokument71 SeitenEnergy, Work and Power: PHY111: Mechanics and Thermo Properties of MatterStudent 365Noch keine Bewertungen
- Andrew HBX-6516DS-VTM SingleDokument3 SeitenAndrew HBX-6516DS-VTM SingleMarceloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computed Torque Control of The Stewart Platform WiDokument8 SeitenComputed Torque Control of The Stewart Platform WiJose ArhuiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Selection and Design For Delivery Drone PropellersDokument6 SeitenMaterial Selection and Design For Delivery Drone PropellersRicardo DíazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saving Energy in HomeDokument7 SeitenSaving Energy in HomeShubham PhadtareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide Rings: Fcs Fluoro Carbon Seals PVT LTDDokument2 SeitenGuide Rings: Fcs Fluoro Carbon Seals PVT LTDvikram velayuthamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uhpc 16703 NabizadehDokument3 SeitenUhpc 16703 NabizadehKY PengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research (Design of Water Tank-Appendix)Dokument19 SeitenResearch (Design of Water Tank-Appendix)Alyssa Mae GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 IntroductionDokument4 Seiten01 IntroductionChrispin MachilikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - 0 MC Destructive TestingDokument23 Seiten4 - 0 MC Destructive TestingRidho KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GAOTek SFP 202 PDFDokument7 SeitenGAOTek SFP 202 PDFইমরানুল শহীদ আলভীNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hitachi Oil-Flooded Screw CompressorsDokument11 SeitenHitachi Oil-Flooded Screw CompressorsBui Hoang DucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometri Ruang File 1Dokument4 SeitenGeometri Ruang File 1Muhammad Isna SumaatmajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireline: Product SpecificationDokument3 SeitenWireline: Product Specificationsatcom_77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tiempo KleinDokument43 SeitenTiempo KleinIxchéel PilónNoch keine Bewertungen
- 986AASDokument7 Seiten986AASteam engineerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rayan CarteDokument12 SeitenRayan CarteRadhika RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog of Cross Arm PDFDokument3 SeitenCatalog of Cross Arm PDFAhmed TahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-3 and Chapter-4 Thermoelectric Effect and Chemical Effect of Current - SA Sir PDFDokument30 SeitenChapter-3 and Chapter-4 Thermoelectric Effect and Chemical Effect of Current - SA Sir PDFKim MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 TH MathematicsDokument2 SeitenClass 10 TH MathematicsUmme AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAK 12403 - Exp 5 Head Loss Through FittingsDokument7 SeitenDAK 12403 - Exp 5 Head Loss Through FittingsMuiz UdinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic EngineeringDokument50 SeitenElectronic EngineeringShafiNoch keine Bewertungen