Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Financial Analysis Ratios
Hochgeladen von
Mahima Raju0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten4 SeitenExamples
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenExamples
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten4 SeitenFinancial Analysis Ratios
Hochgeladen von
Mahima RajuExamples
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
1
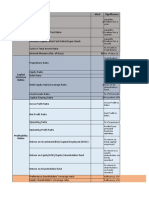
1. Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio:
Selling, general and administrative expenses, Interest on term loans may be broadly treated as
fixed costs of the company as they do not bear a direct relation with generating revenue.
Gross- profit being also the contribution from continuing operation.
2012 2011 2010
British Airways: Revenue (m) 10,827 9,987 7,994
Direct Cost of revenue ((m) 4,337 3,789 2,877
Gross profit (m) 6,490 6,198 5,117
Administrative expenses (m) 5,750 5,244 5,058
Selling costs (m) 466 436 290
Interest payable (m) 173 161 157
Total fixed costs (m) 6,389 5,841 5,505
Fixed charges cover ratio 1.01 times 1.06 times 0.92 times
Ryanair: Revenue (m) 4,390 3,629 2,988
Direct cost of revenue (m) 1,698 1,321 980
Gross profit (m) 2,692 2,308 2,008
Administrative expenses (m) 1,829 1,665 1,461
Selling costs (m) 180 155 145
Interest payable (m) 109 93 72
Total fixed costs (m) 2,118 1,913 1,678
Fixed charges cover ratio 1.27 times 1.20 times 1.19 times
(Direct cost of revenue = Fuel and oil costs + Maintenance, materials and repairs)
(Selling cost = Marketing costs)
(Administrative Expenses = Total cost of revenue- Direct cost of revenue)
(Interest payable = Finance Costs)
(Fixed charges cover ratio= Gross profit/Total fixed costs)
2
2. Return on Capital Ratio.
British Airways:
2012 2011 2010
Net profit after tax and interest (m) (100) 672 (425)
Average Capital & reserves ((m) 2,770 2,591 2,400
Return on capital ratio (%) n/a 25.93 n/a
Ryanair:
Net profit after tax and interest (m) 530 375 305
Average Capital & reserves ((m) 3,130 2,901 2,849
Return on capital ratio (%) 16.93 12.92 10.70
(Average Capital & reserves = opening equity + closing equity/2)
(Return on capital ratio= Net profit after tax and interest/Average Capital & reserves)
3. Debt Coverage Ratio:
Debt Coverage Ratio= Net profit after tax+ Depreciation + Non-Cash expenses/Loan
Installments payable during the year.
Since Fixed Loan Installments payable is not always easily obtainable from the published
accounts, for the time being this ratio analysis, we can keep it pending.
4. Days Sales in inventory ratio
Since an airlines final output (seat- kilometres) cannot be stored, this ratio is not relevant to
airline industry.
Days Sales = Total credit sales/365
3
5. Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio:
Average collection period = Trade Debtors / (Credit Sales/365)
Ideally, it should be in terms of the number of days credit sales, but this information is rarely
available from the financial statements, So total operating revenues is used.
Average Collection period in days 2012 2011 2010
British Airways 16 days 17 days 17 days
Ryanair 4 days 5 days 5 days
Trade debtors
British Airways(m) 488 460 384
Ryanair(m) 52 51 44
Total Sales
British Airways (m) 10,827 9,987 7,994
Ryanair(m) 4,390 3,629 2,988
Credit sales/day (m)
British Airways (m) 29.66 27.36 21.9
Ryanair(m) 12.02 9.94 8.18
The outstanding debtors are seen to bear the following proportions to respective sales.
British Airways 0.045 0.046 0.048
Ryanair 0.011 0.014 0.014
The Collection period is:-
British Air ways 0.045*365=16 days 0.046*365=17 days 0.048*365=17 days
Ryanair 0.011*365=4 days 0.014*365=5 days 0.014*365=5 days
Source: Published Airline Reports
(Average collection period in days= day sales in receivables)
4
Since the Statement of Cash flows is not available from the published airline reports, following
ratios are not calculated. These are all supplementary ratios, not belongs to any key financial
ratios.
1. Cash Reinvestment Ratio
2. Cash flows to revenue ratio
3. Cash flows per share ratio
4. Cash return on assets ratio
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Minimum Equipment ListDokument31 SeitenMinimum Equipment ListMahima RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benefits of Nuts: Walnuts: Inflammation FightersDokument3 SeitenBenefits of Nuts: Walnuts: Inflammation FightersMahima Raju100% (1)
- References: Theory of Goal Setting and Task Motivation: A 35-Year Odyssey. (Diagram)Dokument8 SeitenReferences: Theory of Goal Setting and Task Motivation: A 35-Year Odyssey. (Diagram)Mahima RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coventry University Harvard Reference Style GuideDokument0 SeitenCoventry University Harvard Reference Style GuideMahima RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Treasury Operation in Islamic BanksDokument17 SeitenTreasury Operation in Islamic BanksAnonymous f7wV1lQKRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hershey Company - Form - 10-Q (June-30-2021)Dokument96 SeitenHershey Company - Form - 10-Q (June-30-2021)Mince 0607qqNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBoe Options Expiration Calendar 2019Dokument1 SeiteCBoe Options Expiration Calendar 2019Xay Tonus100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Financial Analysis With Microsoft Excel 7th EditionDokument9 SeitenSolution Manual For Financial Analysis With Microsoft Excel 7th EditionToni Johnston100% (28)
- Accounting TaskDokument10 SeitenAccounting TaskSamuel Amon OkumuNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDP)Dokument2 SeitenEDP)02 - CM Ankita AdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SFM PDFDokument328 SeitenSFM PDFZainNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSV Stock Analyzer Sample VCD2aDokument20 SeitenOSV Stock Analyzer Sample VCD2aPrince AdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Exit Strategy - 1Dokument2 SeitenBusiness Exit Strategy - 1SUBRATA MODAKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio AnalysisDokument26 SeitenRatio AnalysisDeep KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Paper 2 Strategic Financial Management Chapter 2 Part 4 CA. Anurag SingalDokument54 SeitenFinal Paper 2 Strategic Financial Management Chapter 2 Part 4 CA. Anurag SingalPrasanni RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case - Assessing Martin Manufacturing's Current Financial PositionDokument3 SeitenCase - Assessing Martin Manufacturing's Current Financial PositionM B Hossain Raju100% (4)
- CementDokument7 SeitenCementannisa lahjieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap016 Financial Reporting AnalysisDokument15 SeitenChap016 Financial Reporting AnalysisThalia SandersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxonomy of Finance TheoriesDokument16 SeitenTaxonomy of Finance TheoriesDr. Vernon T Cox0% (1)
- Guide To TX3 (Version 1.0.0)Dokument44 SeitenGuide To TX3 (Version 1.0.0)arhagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Valuation ModelsDokument24 Seiten01 Valuation ModelsMarinaGorobeţchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 Cash Flow Estimation and Risk Analysis PDFDokument80 SeitenChapter 11 Cash Flow Estimation and Risk Analysis PDFGelyn Cruz100% (1)
- Bilbliography FinalDokument4 SeitenBilbliography Finalpoojagopwani3413Noch keine Bewertungen
- PAAPlus3 6KJOHNDEMDokument8 SeitenPAAPlus3 6KJOHNDEMMoktar Pandarat Maca-arabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Part1IA2.Docx 1Dokument73 SeitenReview Part1IA2.Docx 1HAZELMAE JEMINEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internship Saudi Pak Investment CompanyDokument39 SeitenInternship Saudi Pak Investment Companyikhan5100% (2)
- Faysal Active Principal Preservation Plan: OctoberDokument17 SeitenFaysal Active Principal Preservation Plan: OctoberKhanMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Chapter 2Dokument8 SeitenSolutions Chapter 2Vân Anh Đỗ LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Equity Analysis - SPI Index - The Top 100 Companies of The Swiss Performance IndexDokument205 SeitenFundamental Equity Analysis - SPI Index - The Top 100 Companies of The Swiss Performance IndexQ.M.S Advisors LLCNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 11648 J Ajtab 20150102 13 PDFDokument5 Seiten10 11648 J Ajtab 20150102 13 PDFAruddy AruddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review SalmanDokument3 SeitenLiterature Review SalmanvdocxNoch keine Bewertungen
- TradingsDokument2 SeitenTradingsMonish JayasuriyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indofood CBP Sukses Makmur - Bilingual - 31 - Mar - 21Dokument129 SeitenIndofood CBP Sukses Makmur - Bilingual - 31 - Mar - 21NicoleNoch keine Bewertungen