Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Anatomy and Physiology
Hochgeladen von
Robin Tolentino100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
451 Ansichten9 SeitenThis document is a quiz for a anatomy and physiology lecture. It contains 21 multiple choice questions about topics like physiology, homeostasis, cell structure and function, and mitosis. The questions assess understanding of topics like the levels of organization of the body, positive and negative feedback mechanisms, and the roles and structures of organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus and lysosomes.
Originalbeschreibung:
sample examination anatomy medicine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document is a quiz for a anatomy and physiology lecture. It contains 21 multiple choice questions about topics like physiology, homeostasis, cell structure and function, and mitosis. The questions assess understanding of topics like the levels of organization of the body, positive and negative feedback mechanisms, and the roles and structures of organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus and lysosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
451 Ansichten9 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology
Hochgeladen von
Robin TolentinoThis document is a quiz for a anatomy and physiology lecture. It contains 21 multiple choice questions about topics like physiology, homeostasis, cell structure and function, and mitosis. The questions assess understanding of topics like the levels of organization of the body, positive and negative feedback mechanisms, and the roles and structures of organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus and lysosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 9
Page 1 of 9 | Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
QUIZ 1
Name: _____________________________________ Section: __________________ Date:___________
DIRECTION: Read the questions carefully. Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice
on the space before each number.
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
1. Physiology
A. Deals with the processes or functions of living things
B. Is the scientific discipline that investigates the bodys structure
C. Is concerned with organisms and does not deal with different levels of organization such
as cells and systems
D. Recognizes the unchanging (as opposed to dynamic) nature of living things
2. The basic living unit of all organisms is the
A. Organelle
B. Cell
C. Tissue
D. Organ
3. An organ is
A. A small structure within a cell that carries out a specific function
B. At a lower level of organization than a cell
C. Two or more tissues that perform a common function
D. A group of cells with a similar structure and function
4. Given these levels of organization: 1. Cell, 2. Chemical, 3. Organelle, 4. Organ, 5. Tissue. Choose
the arrangement that lists the levels of organization in the correct order from smallest to
largest.
A. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B. 2, 3, 1, 5, 4
C. 3, 2, 1, 4, 5
D. 4, 1, 3, 2, 5
5. Homeostasis is an example of which of the following characteristics of life?
A. Organization
B. Metabolism
C. Responsiveness
D. Differentiation
6. Homeostatic mechanisms
A. Keep variables exactly at the set point
B. Help to keep a relatively constant internal environment in the body
C. Act to keep values out of the normal range
D. Usually operate by positive feedback
7. Negative-feedback mechanisms
A. Are not homeostatic
B. Are rare in healthy individuals
C. Respond by making deviations from normal even larger
D. May have a receptor, a control center, and an effector
8. Which of these conditions indicate positive feedback has occurred?
A. Blood pressure decreases greatly; blood flow to the heart is inadequate, and blood
pressure decreases
B. Hot temperatures increase your body temperature above normal; you sweat.
C. Cold temperatures decrease your body temperature below normal; you shiver.
D. Blood pressure decreases; as a result, your heart rate increases.
Page 2 of 9 | Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
9. The systems that are most important in the regulation or control of the other systems of the
body are the
A. Circulatory and muscular systems
B. Circulatory and endocrine systems
C. Nervous and muscular systems
D. Nervous and endocrine systems
10. Body temperatures were measured during an experiment. On the graph below at point A, the
subject moved from a cool room into a hot office. As a result, body temperature increased to
point B.
Graphed below are two possible responses to the increase in body temperature.
Which of the responses graphed above represents a negative-feedback mechanism?
A. Response 1
B. Response 2
11. Which of these statements concerning body regions is correct?
A. The trunk region between the thorax and pelvis is the abdomen.
B. The leg extends from the hip to the ankle.
C. The forearm extends from the shoulder to the wrist.
D. The thorax is often subdivided superficially into four quadrants.
12. The thoracic cavity is divided into two parts by the
A. Mediastinum
B. Pleural cavity
C. Diaphragm
D. Peritoneal membranes
13. Serous membranes
A. Line body cavities that open to the outside
B. Produce a lubricating film of fluid
C. Are found only on the walls of the thoracic cavity
D. Separate the abdominal cavity from the pelvic cavity
14. The serous membrane on the surface of the lungs is called
A. Parietal pericardium
B. Visceral pericardium
C. Parietal pleura
D. Visceral pleura
Page 3 of 9 | Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
Identify whether the condition belongs to positive or negative feedback mechanism. Write A for Positive
feedback and B for Negative feedback.
15. Maintains homeostasis by resisting or reducing any deviation from the set point
16. When a deviation from a normal value occurs, the response is to make the deviation
even greater
17. Medical therapy seeks to overcome illness by aiding this type of feedback
18. Increases heart rate in response to a decrease in blood pressure
19. Decreases the ability of the heart to pump following blood loss
20. Stretch of the uterus causes uterine contractions during delivery
TERMINOLOGIES
1. 9.
2. 10.
3. 11.
4. 12.
5. 13.
6. 14.
7. 15.
8.
1
2
3
4
6
15
13
10
9
5
7
8
11
12
14
Page 4 of 9 | Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
16. The stomach is located ____________________ to the diaphragm.
17. The nails are ____________________ to the wrist.
18. The scapulae are situated ____________________ to the spinal column.
19. The heart is found ____________________ to the ribs.
20. The skull is positioned ____________________ relative to the brain.
21. The pubic area of the abdomen can also be referred to as the lower, or ____________________
region.
22. The region inferior to the right lumbar region is the right inguinal region, or the
____________________ region.
23. The area superior to the right lumbar region is the ____________________ region.
24. A ____________________ is a horizontal cut that divides the body into upper and lower parts.
25. A ____________________ divides the body into two, not necessarily equal left and right parts.
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
1. The function of the cytoskeleton is most similar to the function of what other cellular structure?
A. Peroxisome
B. Plasma membrane
C. Cytoplasm
D. Mitochondria
2. Molecules done being processed in the endoplasmic reticulum are often transported to which
structure?
A. Peroxisomes
B. Mitochondria
C. Golgi apparatus
D. Vacuoles
3. Which of the following organelles is primarily responsible for cellular digestion?
A. Nucleus
B. Lysosome
C. Mitochondria
D. Golgi apparatus
4. Peroxisomes are able to convert toxic substances such as hydrogen peroxide into non-toxic
substances due to the action of:
A. Lipase
B. Catalase
C. Peroxilase
D. Hydrolase
5. The endoplasmic reticulum plays a major role in the processing of which of the following
biological molecules?
A. Carbohydrates
B. Proteins
C. Adenosine triphosphate
D. DNA
6. Which of the following shows the correct sequence of the cell cycle?
A. Cytokinesis mitosis G1 S G2
B. S G1 G2 mitosis cytokinesis
C. G1 S G2 mitosis cytokinesis
D. Mitosis G1 S G2 cytokinesis
Page 5 of 9 | Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
7. Membrane proteins can perform each of the following functions except:
A. Serve as carriers during transport
B. Function as enzymes
C. Determine the fluidity of the membrane
D. Act as receptors for hormones
8. One function of agranular endoplasmic reticulum is to:
A. Store iron in bone marrow cells
B. Synthesize proteins which are to be exported from secretory cells
C. Synthesize lipids in intestinal epithelial cells
D. Store glycogen in liver cells
9. Lysosomes are cell organelles which:
A. Modify and sort proteins which are to be exported from the cell
B. Produce hydrogen peroxide
C. Can digest proteins ingested by phagocytosis
D. Contain the enzymes of the Krebs cycle
10. Ribosomal RNA is synthesized in the:
A. Centromere
B. Centrosome
C. Centriole
D. Nucleolus
11. Which of the following structures is responsible for putting proteins together with RNA to make
ribosomal subunits?
A. Endoplasmic reticulum
B. Nucleolus
C. Golgi apparatus
D. None, they assemble spontaneously in the cytoplasm
12. Which of the following structures has the largest percentage of ribonucleic acid as a structural
component?
A. Ribosome
B. Nucleus
C. Nucleolus
D. Golgi apparatus
13. Which of the following structures contains the enzymes required for oxidative production of
adenosine triphosphate?
A. Mitochondrion
B. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
C. Cell membrane
D. Cytoplasm
14. Which of the following structures does not contain microtubules?
A. Microvilli
B. Cilia
C. Flagella
D. Mitotic spindle
15. Which of the following subcellular structures is not covered or composed of a membrane?
A. Golgi apparatus
B. Secretory vesicles
C. Endoplasmic reticulum
D. Centrioles
Page 6 of 9 | Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
16. Which structure is most likely responsible for autolysis?
A. Mitochondrion
B. Peroxisome
C. Secretory vesicle
D. Lysosome
17. Which of the following events do not occur in prophase of mitosis?
A. DNA condenses to form chromosomes
B. Nuclear membrane breaks down
C. Nucleolus breaks down
D. Chromosomes are replicated
18. A spindle fiber is a specialized form of:
A. Microtubule
B. Centrosome
C. Centriole
D. Chromosome
19. As a result of mitosis, each of the two new cells produced from the parent cell during
cytokinesis:
A. Receives a few chromosomes from the parent cell
B. Receives an exact copy of all the chromosomes present in the parent cell
C. Donates a chromosome to the parent cell
D. Receives exactly half the chromosome from the parent cell
20. Normal cells become cancer cells when
A. Regulation of cell growth and division occurs
B. Cells respond to control mechanisms
C. Cells pass through G1
D. Cells do not respond to checkpoints
21. Simple diffusion is defined as the movement of:
A. Molecules from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration
B. Molecules from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration
C. Water molecules across a membrane
D. Gas molecules across a membrane
22. When sugar is mixed with water, equilibrium is reached when:
A. Molecules of sugar stop moving
B. Water and sugar molecules are moving at the same speed
C. The dissolved sugar molecules are evenly distributed throughout the solution
D. There are he same number of water molecules as dissolved sugar molecules
23. The sodium potassium pump function to pump:
A. Sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell
B. Sodium ions into the cell and potassium ions out of the cell
C. Sodium and potassium ions into the cell
D. Sodium and potassium ions in both directions across the cell membrane
24. Osmosis is best defined as the movement of:
A. Molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
B. Molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration
C. Water molecules across a membrane from an area of low water to an area of higher
concentration
D. Water molecules across a membrane from an area of high water concentration to an
area of lower concentration
Page 7 of 9 | Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
25. Active transport moves a solute:
A. Up its concentration gradient, that is, from a low concentration to a high one
B. Up its concentration gradient, that it, from a high concentration to a low one
C. Down its concentration gradient, that is, from a low concentration to a high one
D. Down its concentration gradient, that is, from a high concentration to a low one
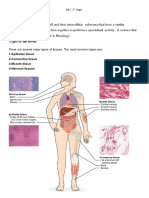
TISSUES, GLANDS AND MEMBRANES
1. Tall, thin epithelial cells that have the appearance of two or more layers, but with all cells
touching the basement membrane is:
A. Simple squamous epithelium
B. Simple columnar epithelium
C. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
D. Transitional epithelium
2. Epithelial cells that can stretch from a cuboidal or columnar shape to a squamous shape are
called:
A. Simple cuboidal epithelium
B. Simple columnar epithelium
C. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
D. Transitional epithelium
3. In which of these locations would pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium intermixed with
goblet cells be found?
A. Lining of blood vessels
B. Lining of nasal cavity and trachea
C. Lining of serous membranes
D. Lining of small intestine
E. Surface of the skin
4. Which of these cell connections attaches epithelial cells to the basement membrane?
A. Desmosomes
B. Gap junctions
C. Hemidesmosomes
D. Tight junctions
5. Which of these is NOT a part of connective tissue?
A. Ground substance
B. Basement membrane
C. Protein fibers
D. Fluid
6. Connective tissue cells that produce the extracellular matrix are called:
A. Blast cells
B. Cyte cells
C. Clast cells
D. Mast cells
7. A tissue with collagen fibers, proteoglycans, and chrondrocytes is:
A. Adipose
B. Blood
C. Bone
D. Cartilage
8. Which of these tissues has cells located in lacunae?
A. Blood
B. Bone
C. Cartilage
D. Both B and D
9. Given these characteristics: matrix composed almost entirely of collagen fibers, fibers can all be
oriented in the same direction or in many different directions, and able to withstand great
pulling forces in the direction of fiber orientation. Which of these tissues is described?
A. Loose (areolar) connective tissue
B. Bone
C. Cartilage
D. Dense connective tissue
Page 8 of 9 | Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
10. Fibrocartilage is found in
A. The costal cartilages
B. Joints, covering the ends of bones
C. The external ear
D. Disks between the vertebrae
11. Given these characteristics: cells cylindrical in shape, striated, usually one nucleus per cell, often
branched and connected by intercalated disks, and under involuntary control. Which tissue
possesses all of these characteristics?
A. Smooth muscle
B. Nervous tissue
C. Cardiac muscle
D. Skeletal muscle
12. In nerve cells, the ___________ contains the nucleus and is the site of general cell functions.
A. Axon
B. Cell body
C. Dendrite
D. Neuroglia
13. Inflammation of the serous membranes associated with the abdominopelvic cavity is called:
A. Pericarditis
B. Peritonitis
C. Pleurisy
D. Rhinitis
14. Which of these is NOT a chemical mediator of inflammation?
A. Histamine
B. Kinin
C. Leukotriene
D. Neutrophils
15. Which of these cells are labile cells, and continue to divide throughout life?
A. Liver cells
B. Skeletal muscle cells
C. Neurons
D. Skin cells
16. Given these characteristics:
i. Capable of contraction
ii. Covers all free body surfaces
iii. Lacks blood vessels
iv. Comprises various glands
v. Anchored to connective tissue by a basement membrane
Which of these are characteristics of epithelial tissue?
A. i, ii, iii
B. ii, iii, v
C. iii, iv, v
D. i, ii, iii, iv
E. ii, iii, iv, v
17. Chemical mediators of inflammation:
A. Stimulate nerve endings to produce the symptom of pain
B. Increase the permeability of blood vessels
C. Are released into or activated in tissues following injury
D. Cause dilation (expansion) of blood vessels
E. All of the above
Match these terms with the correct statement or definition. Write your answers on the space provided
before each number.
Dilation Neutrophils Increased permeability
Mediators of inflammation Edema
Disturbance of function Pain
18. Chemical substances that are released or activated in the injured tissues and
adjacent blood vessels.
Page 9 of 9 | Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
19. Two changes that occur in blood vessels that result in symptoms of redness,
heat, and swelling.
20.
21. Swelling of tissues when proteins and water from blood enter tissues.
22. Phagocytic white blood cells that fight infection; dead cells in pus.
23. Result of direct damage, mediators, and edema stimulating nerve cell endings.
24. Limitations produced by edema, tissue destruction, and pain.
Using the terms provided, complete these statements:
Fibrin Scab
Granulation tissue Scar
Macrophage Wound contracture
When the edges of a wound are close together, the wound fills with blood and a clot forms. The clot
contains a threadlike protein, ____(25)___, which binds the edges of the wound together and stops any
bleeding. The surface of the clot dries to form a ____(26)_____, which seals the wound. Neutrophils
enter the tissue from the blood. After the epithelium is repaired, the scab is shed, and a second type of
phagocytic cell, called a ____(27)_____ removes dead neutrophils, cellular debris, and the decomposing
clot. The clot is replaced by a delicate connective tissue called ____(28)_____, which consists of
fibroblasts, collagen, and capillaries. Sometimes a large amount of granulation tissue persists as a
____(29)_____, which at first is bright red because of the vascularization of the tissue. Repair takes
longer if the wound edges are far apart. Much more granulation tissue forms, and ____(30)_____ occurs
when fibroblasts pull the edges of the wound closer together. This can lead to disfiguring and
debilitating scars.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
GOD BLESS!
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1Von EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology - ExamDokument9 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology - ExamQoppppNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology-A ReviewDokument38 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology-A Reviewjava_biscocho1229100% (4)
- Final Exam in Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument6 SeitenFinal Exam in Anatomy and PhysiologyKeanu Ribs100% (2)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument7 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyFreeNursingNotes0% (1)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology SyllabusDokument6 SeitenHuman Anatomy and Physiology Syllabusapi-275510930Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3-4 Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument27 SeitenChapter 3-4 Anatomy and PhysiologyOregon190100% (6)
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Practice TestDokument13 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Practice TestDani AnyikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology TestDokument5 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology TestPao ParelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology LectrueDokument76 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology LectrueButch Dumdum73% (15)
- Outline of Anatomy and Physiology (Prelim-Midterm)Dokument11 SeitenOutline of Anatomy and Physiology (Prelim-Midterm)Jhason John J. Cabigon100% (3)
- Quiz Urinary Reproductive 20Dokument5 SeitenQuiz Urinary Reproductive 20estherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seeley's: Chapter 1 Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument41 SeitenSeeley's: Chapter 1 Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyThea Mallari67% (3)
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument5 SeitenHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyAngela Alcantara100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Exam 2011-12Dokument3 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Midterm Exam 2011-12cstavrop18100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology Exam CompilationsDokument7 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Exam CompilationsRomeo Rivera100% (4)
- Anatomy and Physiology Terms: Brief Definitions, Roots & Morphology; An Abecedary; Vol 2-Planes & DirectionsVon EverandAnatomy and Physiology Terms: Brief Definitions, Roots & Morphology; An Abecedary; Vol 2-Planes & DirectionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Room LectureDokument12 SeitenOperating Room LectureMARY GRACE SABAL100% (1)
- Muscular QuizDokument4 SeitenMuscular QuizMaria MoscaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC 1 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY MidtermDokument12 SeitenMC 1 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY MidtermNicole Sheen EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument140 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyNaveen Eldose100% (3)
- Answers Chapter 10 and 11 ExamDokument7 SeitenAnswers Chapter 10 and 11 ExamMara Romanoff75% (4)
- Activity 2B Integumentary System LOPEZ 1.0Dokument3 SeitenActivity 2B Integumentary System LOPEZ 1.0Ma. Joanna Catherine LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Musculoskeletal QuestionsDokument4 SeitenMusculoskeletal QuestionsJen Del Mundo100% (1)
- Muscular SystemDokument8 SeitenMuscular SystemJoannah Marie100% (2)
- CH 5 AnswersDokument22 SeitenCH 5 AnswersYhormmie Harjeinifujah100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology Course SyllabusDokument5 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Course SyllabusDanna ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology, Laboratory ManualDokument28 SeitenPhysiology, Laboratory ManualSherwan R Shal100% (2)
- Year One Anatomy and Physiology Study NotesDokument94 SeitenYear One Anatomy and Physiology Study Notescoolpinkgurl100% (8)
- Anatomy and Physiology I SyllabusDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology I SyllabusDharshini Muniandy100% (2)
- Biochemistry ExamDokument4 SeitenBiochemistry ExamKyle Broflovski100% (1)
- TBDokument163 SeitenTBBlaquevagabond0% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology Mid-Semster Study Notes PDFDokument32 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology Mid-Semster Study Notes PDFsimone dumbrell100% (10)
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument51 SeitenHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyMa Ruth Parel86% (7)
- Skeletal System ReviewerDokument3 SeitenSkeletal System ReviewerBea AbellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument25 Seiten1 Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDani AnyikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIDokument33 SeitenReproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIlhayes1234100% (5)
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument123 SeitenHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyWilliamMindoro100% (1)
- Final Practice TestDokument113 SeitenFinal Practice TestDylanCollins0% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Facial BonesDokument12 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of Facial BonesAubrey Unique Evangelista100% (2)
- Physiology SyllabusDokument11 SeitenPhysiology SyllabusBarney Cordova100% (1)
- Anatomy Quiz - Digestive SystemDokument4 SeitenAnatomy Quiz - Digestive SystemHappy Happy LifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Anatomy and Physiology For NursesDokument48 SeitenHuman Anatomy and Physiology For NursesKelly J Wilson86% (21)
- 1700+ Review Questions - Anatomy & PhysiologyDokument129 Seiten1700+ Review Questions - Anatomy & PhysiologyHarun Mohamed100% (6)
- Anatomy & Physiology: Essentials ofDokument69 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology: Essentials ofclyde i am100% (1)
- Lecture Quiz On Muscular System: QuestionsDokument2 SeitenLecture Quiz On Muscular System: QuestionsCeline MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology With Lab: Learning Module No. 01Dokument227 SeitenCourse Title: Anatomy and Physiology With Lab: Learning Module No. 01Pecayo AlpayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Health Assessment and Pain (30 Items)Dokument17 SeitenNursing Health Assessment and Pain (30 Items)Ik-ik MiralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 15 Study QuestionsDokument18 SeitenChapter 15 Study Questionsashok_solanki_23100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/RationaleDokument16 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/Rationaleyachiru121Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology (Abridged) PDFDokument9 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology (Abridged) PDFJust IsaacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 The Integumentary SystemDokument25 SeitenChapter 5 The Integumentary Systemlolasparkle100% (2)
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument61 SeitenHuman Anatomy and Physiologymarn_shy100% (3)
- 3600+ - Review - Questions - Volume1 1Dokument133 Seiten3600+ - Review - Questions - Volume1 1kjjjjjkjkj100% (3)
- BIOLOGY II FBI1224 2022 Question Paper 1Dokument10 SeitenBIOLOGY II FBI1224 2022 Question Paper 1zoulzz0903Noch keine Bewertungen
- NSG QuizzesDokument10 SeitenNSG QuizzesLin LadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock Final ExamDokument15 SeitenMock Final ExamAryan PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. B. C. D. eDokument6 SeitenA. B. C. D. eEnixam ZulevtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument5 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology48pgcw62kkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amaltas - The Golden Shower TreeDokument1 SeiteAmaltas - The Golden Shower TreeRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex B-1 RR 11-2018 Sworn Statement of Declaration of Gross Sales and ReceiptsDokument1 SeiteAnnex B-1 RR 11-2018 Sworn Statement of Declaration of Gross Sales and ReceiptsEliza Corpuz Gadon89% (19)
- Creamy Carbonara RecipeDokument1 SeiteCreamy Carbonara RecipeRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunization Routine Table3 PDFDokument9 SeitenImmunization Routine Table3 PDFOwaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Manual For Free Range Chicken Production (Meat Type) : Emerson E. SiscarDokument14 SeitenBasic Manual For Free Range Chicken Production (Meat Type) : Emerson E. SiscarRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cassia Fistula Golden-Shower: Fact Sheet ST-127Dokument3 SeitenCassia Fistula Golden-Shower: Fact Sheet ST-127Robin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine IM Platinum-1Dokument357 SeitenMedicine IM Platinum-1Bom Tna67% (3)
- Heritage Chicken Breeds (Pure Breeds)Dokument3 SeitenHeritage Chicken Breeds (Pure Breeds)Robin Tolentino100% (3)
- Radio JournalDokument40 SeitenRadio JournalRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questionnaires For CONDUCTOR'S LICENSE EXAM APPLICANTS EDITEDDokument4 SeitenQuestionnaires For CONDUCTOR'S LICENSE EXAM APPLICANTS EDITEDJohn MagayanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Andits Laws in AnaesthesiaDokument111 SeitenPhysics Andits Laws in AnaesthesiaRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Face and ScalpDokument31 SeitenThe Face and ScalpRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Choral Works of Robert Delgado - SATB ScoreDokument48 SeitenThe Choral Works of Robert Delgado - SATB ScoreRobin Tolentino88% (16)
- Gen Anesthesia Medicine PhysiologgyDokument82 SeitenGen Anesthesia Medicine PhysiologgyRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohol by Dr. SibbalucaDokument4 SeitenAlcohol by Dr. SibbalucaRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Jayjay Song Ronda CatongaDokument6 SeitenThe Jayjay Song Ronda CatongaRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Anatomy and Physiology MedicineDokument73 SeitenLiver Anatomy and Physiology MedicineRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temporal and Infratemporal FossaeDokument29 SeitenTemporal and Infratemporal FossaeRobin Tolentino100% (1)
- Anatomic Structures: St. Paul University PhilippinesDokument6 SeitenAnatomic Structures: St. Paul University PhilippinesRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-4 Hemostasis, Surgical Bleeding and TransfusionDokument17 Seiten1-4 Hemostasis, Surgical Bleeding and TransfusionRobin Tolentino100% (3)
- Biochemistry of CarbohydratesDokument7 SeitenBiochemistry of CarbohydratesRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The EYEDokument115 SeitenAnatomy of The EYERobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Shoulder Joint - Chapter Summary - Anatomy of The Shoulder Joint by Snell Medicine LectureDokument76 Seiten3 Shoulder Joint - Chapter Summary - Anatomy of The Shoulder Joint by Snell Medicine LectureRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensives Summary Katzung PharmacologyDokument8 SeitenAntihypertensives Summary Katzung PharmacologyRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ikaw (Zamora)Dokument5 SeitenIkaw (Zamora)Robin Tolentino100% (5)
- Pathology, Lecture 2, Cell Injury (Slides)Dokument139 SeitenPathology, Lecture 2, Cell Injury (Slides)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (8)
- Cellular Responses To Stress and Toxic Insults: Adaptation, Injury, and DeathDokument81 SeitenCellular Responses To Stress and Toxic Insults: Adaptation, Injury, and DeathICE ADRIENNE OCAMPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3: Compartmentation: Cells and Tissues: Functional Compartments of The BodyDokument10 SeitenChapter 3: Compartmentation: Cells and Tissues: Functional Compartments of The BodyShivani RailowalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benign TumorsDokument78 SeitenBenign TumorsLavanya KalapalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 (Moving To 12)Dokument19 SeitenClass 11 (Moving To 12)crultimate18Noch keine Bewertungen
- NSEJS 2023 Exam Paper SolutionDokument21 SeitenNSEJS 2023 Exam Paper SolutionAaditya ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itutor Fortnightly Test Series: Subjective Test - 1 (H.A.)Dokument4 SeitenItutor Fortnightly Test Series: Subjective Test - 1 (H.A.)Debangsu GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testicular TumorsDokument14 SeitenTesticular TumorsJose SirittNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tissue (Biology) - Wikipedia PDFDokument37 SeitenTissue (Biology) - Wikipedia PDFKissa FrecNoch keine Bewertungen
- #04 Final Ntse Mat Test (17!08!2018)Dokument15 Seiten#04 Final Ntse Mat Test (17!08!2018)rahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- K1R3 - B1A019043 - PLATYHELMINTHES DAN MOLLUSCA - Muhammad Zikri Hazmi (Inggris)Dokument11 SeitenK1R3 - B1A019043 - PLATYHELMINTHES DAN MOLLUSCA - Muhammad Zikri Hazmi (Inggris)Muhammad HazmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal TissueDokument32 SeitenAnimal TissueIan Kerby Sollano100% (1)
- Anatomy Lab.2Dokument8 SeitenAnatomy Lab.2aminqasm111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fish Diseases (Jorge C. Eiras, Helmut Segner, Thomas Wahli Etc.) (Z-Library)Dokument1.327 SeitenFish Diseases (Jorge C. Eiras, Helmut Segner, Thomas Wahli Etc.) (Z-Library)Iryna ZapekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histologi Kepala Leher THTDokument38 SeitenHistologi Kepala Leher THTWidya ParamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Science-9 CombinedDokument20 SeitenChapter Science-9 CombinedAnushkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SST 6 Chapter 4 OutlineDokument13 SeitenSST 6 Chapter 4 OutlineGail AidNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Epithelial Basement MembraneDokument9 SeitenThe Epithelial Basement MembraneSitipradyta KasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Considerations 3.1 The Culture EnvironmentDokument4 SeitenBiological Considerations 3.1 The Culture EnvironmentPaavni SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Mucosal Embryology and HistologyDokument13 SeitenOral Mucosal Embryology and HistologyEner Orbegoso CollantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- @@@ Regenerating Tubular Epithelial Cells of The KidneyDokument8 Seiten@@@ Regenerating Tubular Epithelial Cells of The KidneyeullobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CelladhesionDokument51 SeitenCelladhesionNina Difla MuflikhahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Physiology PRACTICE SCENERIO QUESTIONDokument8 SeitenHuman Physiology PRACTICE SCENERIO QUESTIONThao NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- About Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Overview and TypesDokument9 SeitenAbout Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Overview and TypesJoelie-Ann NatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artemia:: Basic and Applied BiologyDokument297 SeitenArtemia:: Basic and Applied BiologyNiqh Rafiqah100% (1)
- Gen-Path-Oral-Path-Microbio-Complete (AutoRecovered)Dokument10 SeitenGen-Path-Oral-Path-Microbio-Complete (AutoRecovered)DENTAL REVIEWER ONLYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zoology Lab Manual Hard CoverDokument103 SeitenZoology Lab Manual Hard CoverMona Saad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid-Old Cells Are A Potential Target For Anti-Aging Interventions in The ElderlyDokument16 SeitenMid-Old Cells Are A Potential Target For Anti-Aging Interventions in The ElderlyecmelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cancer of LarynxDokument36 SeitenCancer of LarynxHealth Education Library for People50% (2)
- Lab Manual Human PhysiologyDokument84 SeitenLab Manual Human Physiologyaurelya nicoleNoch keine Bewertungen