Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lesson 3 - Understanding Transistors
Hochgeladen von
Thiyaku MaruthaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lesson 3 - Understanding Transistors
Hochgeladen von
Thiyaku MaruthaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
LESSON 3
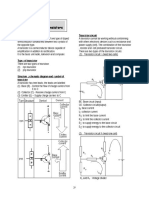
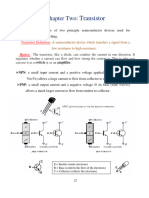
Understanding transistors
Introduction
A transistor consists of a crystal of one type of doped semiconductor sandwiched between two crystals of
the opposite type.
A transistor is a semiconductor device capable of amplification in addition to rectification.
It is the basic unit radio, television and computer.
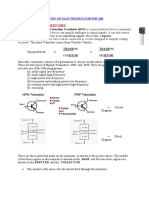
Types of transistor
There are two types of transistor
(1) npn transistor
(2) pnp transistor
Structure ,schematic diagram and symbol of transistor
A transistor has tree leads; the leads are labelled
(1) Base (B) - Control the flow of charge carriers from
E to C
(2) Collector (C) - Receive charge carriers from E
(3) Emitter (E) Supply charge carriers to C
Transistor circuit
A transistor cannot be working without combinining with others electronic devices such as resistance and
power supply (cell). The combination of thre transistor , resistor and cell produced transistor circuit.
There are two types of the transistor circuits:
(1) Transistor circuit I (need two cells)
BE: Base circuit (input)
CE: Collector circuitl(output)
Ib: base current
Ic: collector current
R1: to limit the base current
R2: to limit the collector current
E1: to supply energy to the base circuit
E2: to supply energy to the collector circuit
(2) Transistor circuit II (need one cell)
Rx and RY : Voltage divider
VRx = Rx x V
( Rx + Ry)
VRY = Ry x V
( Rx + Ry)
Example 1
The figure shows a transistor circuit. Resistor P has a resistance of 10 k. In order to light the bulb , the
potential difference across resistor P must be at least 2V.
What is the maximum value of resistor Q when the bulb lights?
Solution
Working principle of a transistor
(1) The base current is very small (in A) when it
compare with the collector current (in mA).
( Ib <<< Ic )
Current amplification = Ic
Ib
(2) A small change in base current, Ib will cause a big change in the collector current, Ic
( Ib <<< Ic)
(3) Ie = Ib + Ic
From the working principles above , we conclude that a transistor functions as a current amplifier by
allowing a small current to control a larger current.
(4) When R1 = 0 , the base voltage VR1 = 0. The base current does not flow and the
collector current als does not flow.
Ib = 0 and IC = 0
(5) When the resistance of R1 is increased, the base voltage will increase until the base
voltage exceeds a certain minimum value, the base current flows and cause a large collector
current flows.
From the working principles above , we conclude that a transistor functions as an automatic switch,so
that the transistor turned ON or OFF.
(6) When there is no Ic flowing in the collector circuit , Ib still flows in the collector
circuit.
(Ic = 0 hence Ib 0 )
(7) A transistor has not its own energy. The energy in a transistor is supplied by the
power supply , such as cell.
Applications of transistors
(1) The transistor as an amplifier
When a person speaks into a microphone, sound waves are converted into an alternating current .
The small changes in the base circuits cause the base current flows.
A small change in base current, will cause a big change in the collector current.
The earphone thus receives a large alternating current from the collector circuit and converts it into a
loud sound.
The capacitor blocks a steady current (direct current) from flowing into the transistor and microphone.
(2) The transistor as a light controlled switch
In bright light, the light-dependent resistor(LDR) has a very low resistance. Therefore the potential
diference across LDR is low and hence the potential difference across resistor R is high. The base
current flows
and cause a large collector current flows. The bulb lights up
In darkness , the light-dependent resistor(LDR) has a very high resistance. Therefore the potential
diference across LDR is high and hence the potential difference across resistor R is low. The base current
does not flow and cause the collector current does not flow. The bulb not lights up.
If the positions of the LDR and R are interchanged, the bulb is switched on in the dark and off in the bright
light.
(3) The transistor as a tempearture controlled switch
When the thermistor is cold, it has a larger resistance than R. Therefore the potential diference across
thermistor is high and hence the potential difference across resistor R is low. The base current does not
flow and cause the collector current does not flow.
The bulb not lights up.
When the temperature rises,the resistance of thermistor falls and the bulb lights up.
TUTORIAL 3
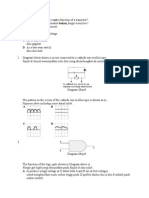
1 The figure shows the symbol for a npn transistor.
Which of the following show the correct names of the electrodes P,Q and R?
P Q R
A Base Emitter Colletor
B Base Colletor Emitter
C Colletor Base Emitter
D Emitter Base Colletor
2 Which of the following show the correct symbol of the pnp transistor?
3 The diagram shows the symbol for a transistor.
Which of the following shows the correct name of the electrode P and the type of the transistor?
Electrode P Type of transistor
A Emitter pnp
B Collector pnp
C Emitter npn
D Collector npn
4 The figure shows a transistor circuit.
Which of the following components are required to place in box P and Q?
P Q
A Bulb Bulb
B Dry cell Bulb
C Resistor Dry cell
D Bulb Resistor
5 Which of the following circuits can function?
6 In which one of the circuits will the lamp light?
7 In which circuit will the light-emitting diode (LED) light up when the switch is on?
8 The diagram shows a transistor circuit.
Which of the following is true?
A Ie > Ic >Ib B Ie > Ib >Ic
C Ic > Ie >Ib D Ic > Ib >Ie
9 The diagram shows the symbol of an npn transistor.
What is the value of Ie?
A 24 mA B 115 mA
C 125 mA D 600 mA
E 1000 mA
10 Which of the following is not a function of a
transistor?
A As a rectifier
B As an amplifier
C As a light controlled switch
D As a tempearture controlled switch
11 The diagram shows a circuit using a transistor.
What is the function of transistor?
A Switch
B Rectifier
C Amplifier
D Voltage divider
12 The diagram shows an amplifier circuit.
What is the function of the capacitor in the diagram?
A To amplify the sound signal
B To change electrical signal to sound wave
C To change sound signal to electrical signal
D To block the direct current from the cell from flowing into the transistor and
microphone
13 How does the resistance of a thermistor and the resistance of a light-dependent resistor
change when their surroundings become hotter and darker?
Resistance of Resistance of thermistor light-
dependent
as it gets hotter resistor as it gets
darker
A Decreases Decreases
B Decreases Increases
C Increases Decreases
B Increases Increases
14 The diagram shows a transistor circuit.
What is the function of the transistor T?
A Switch
B Heater
C Amplifier
D Voltage divider
15 Which of the following circuit is the bulb lights up when the LDR is illuminated by bright
light?
16 The diagram shows a transistor circuit.
The bulb will light up when the circuit in
A bright light
B a dark room
C low temperature
D high temperaure
17 The figure shows a transistor circuit. Resistor P has a resistance of 10 k. In order to
light the bulb , the potential difference across resistor P must be at least 2V.
What is the maximum value of resistor S when the bulb lights?
A 10 k B 40 k
C 50 k D 60 k
E 100 k
18 Figure shows a light dependent resistor (LDR) , resistors R and S, a light emmiting diode
(LED) , a transistor and a battery that will be connected to form a circuit. The LED emmits lights when
it is in a bright surroundings.
(a) (i) State one function of a transistor.
..
(ii) Complete the circuit in the diagram above so that the LED emits light in a bright
surroundings.
(iii) Give one reason why LED emmits light in a bright surroundings.
..
.
(b) What modification is required to the circuit so that the LED will emmits light when the
surroundings become dark?
.
(c) An alarm is needed which emmits sound when there is a fire. Two modifications have to be
made to the circuit in (a)(ii) by replacing electronic components.
(i) State one electronic component which needs to be replaced . Give a reason for
your answer.
.
.
(ii) Name two electronic components that are needed to replace the unsuitable
components.
.
.
(iii) In the space below, draw a circuit diagram to show the new circuit.
19 The diagram shows a transistor circuit.
In order to trigger alarm X , the potential difference across NO must be at least 1V.
(a) What is the potential difference across
MO ?
(b) When the resistance of resistors P and Q are 500 respectively,
(i) what is the potential diference across MN?
(ii) what happens to alarm X?
............................................................
..
(c) When the resistance of resistor Q is 500 and the resistance of resistor P is 4000 ,
determine the potential difference across the resistor Q to show that alarm X is not triggered.
(d) The table shows the variations of the resistance of a thermostat , T with
temperature.
Temperature /
o
C
Thermostat resistance
/
200 1750
100 3500
55 5000
30 6000
When resistor P is replaced by thermostat
T , what is
(i) the resistance of resistor Q if alarm X is triggered at 200o C.
(ii) the temperature is required to trigger alarm X ,when the resistance of resistor is
1000.
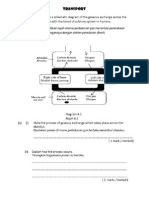
20 The diagram shows a transistor circuit. The circuit is used to automatically switch on the
blb at night.
(a) (i) Name component Q
....................................................................
(ii) What is the function of component Q
....................................................................(b) What is the function of resistor R?
....................................................................
(c) (i) What happens to potential difference
Vp at night.
............................................................
(ii) Explain why the bulb is lighted up at night ?
............................................................
............................................................
............................................................
............................................................
............................................................
............................................................
(d) Bulb M is labelled 240 V,60 W starts to light up when Vp is 2.0 V and the
resistance of resistor P is 10 k.
Determine the maximum resistance of resistor S.
(e) What happens to the bulb when it is connected directly to the transistor
circuit without using the relay switch. Explain why?.
....................................................................
....................................................................
....................................................................
....................................................................
37
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Electronics Lab 14Dokument14 SeitenElectronics Lab 14Aruna KumarasiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Dokument18 SeitenAdd Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VB Tutorial-Connect VB Application With MS Access Through CodingDokument19 SeitenVB Tutorial-Connect VB Application With MS Access Through CodingBeschiAntonyD79% (19)
- Lesson 3 - Understanding Transistors: Transistor CircuitDokument9 SeitenLesson 3 - Understanding Transistors: Transistor CircuitSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nota TransistorDokument13 SeitenNota TransistorLokman HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Physics Sir Mas FaizDokument23 SeitenForm 5 Physics Sir Mas FaizNur Aina SofrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRANSISTORSDokument5 SeitenTRANSISTORSMuler MillsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mod 4 Book 2 Transistors Intergrated Circuits Printed Circuit BoardsDokument61 SeitenMod 4 Book 2 Transistors Intergrated Circuits Printed Circuit Boardsranjit prasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Then by using KCL: I = I +I (1) And I = βI Substituting the value of Ic in eq (1) I = (1+β) I (2) Solving equation (2) andDokument3 SeitenThen by using KCL: I = I +I (1) And I = βI Substituting the value of Ic in eq (1) I = (1+β) I (2) Solving equation (2) andDaniyal AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectronicsDokument9 SeitenElectronicsEstephen EdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 3 TransistorDokument9 Seiten9 3 Transistorsuemozac100% (1)
- Recap On CH - 11 of G - 11 With TGDokument5 SeitenRecap On CH - 11 of G - 11 With TGKhin Khin ThanNoch keine Bewertungen
- (L5) - (JLD 3.0) - Semiconductors - 31st DecDokument66 Seiten(L5) - (JLD 3.0) - Semiconductors - 31st DecAshfaq khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BJT PresentationDokument128 SeitenBJT PresentationMarcus FNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 1 Bipolar Junction Transistor Transistor Principle of OperationDokument45 SeitenChapter - 1 Bipolar Junction Transistor Transistor Principle of OperationDeepak SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXPERIMENT NO. 1: Verification of The Integrity of The Junctions of A BJT Transistor I. ObjectivesDokument6 SeitenEXPERIMENT NO. 1: Verification of The Integrity of The Junctions of A BJT Transistor I. ObjectivesschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication 12 4697 82Dokument9 SeitenPublication 12 4697 82Mariam AznabetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nzcee 3105: TransistorsDokument23 SeitenNzcee 3105: TransistorsPhilip ClagueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 NotesDokument19 SeitenModule 4 Notes4JN20ME039 - Sindhu H KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulae For: SemiconductorsDokument15 SeitenFormulae For: SemiconductorsTejas PagareNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 What Is Semiconductor? Semiconductor .Dokument12 Seiten1 What Is Semiconductor? Semiconductor .cyric wongNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRACTICLE NO 1 CTDokument3 SeitenPRACTICLE NO 1 CTAnb BajwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - BJTDokument102 SeitenChapter 3 - BJTFarish IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Does A Transistor Circuit WorksDokument30 SeitenHow Does A Transistor Circuit WorksJacob BrackettNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 DC Power SupplyDokument33 Seiten1 DC Power Supplyapolloroka33% (3)
- 2.1 Goals of This Lab 2.2 Diode V-I Characteristics: DVM 1k R +5VDokument4 Seiten2.1 Goals of This Lab 2.2 Diode V-I Characteristics: DVM 1k R +5VRMK BrothersNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3a BJT IntroductionDokument20 Seiten3a BJT IntroductionSyahmi AkmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5: Power Semiconductor DevicesDokument60 SeitenChapter 5: Power Semiconductor DevicesDipti GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEF 23903 - High Current Measurements PDFDokument39 SeitenBEF 23903 - High Current Measurements PDFblaze ember100% (1)
- Unit 12Dokument23 SeitenUnit 12Hello worldNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 BJTransistors pt1 Rev2.3 LectDokument37 Seiten3.1 BJTransistors pt1 Rev2.3 LectShudermawan JarumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Circuits and Electronics - by Josh Baruma @unitech PNGDokument12 SeitenNotes On Circuits and Electronics - by Josh Baruma @unitech PNGJosh BarumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Marks With Answers Collection 1Dokument19 Seiten2 Marks With Answers Collection 1Guna PriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Week 03Dokument54 SeitenLecture Week 03عبدالله قيس محمود الحيدريNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 A) Application of BJT As AmplifierDokument12 Seiten4 A) Application of BJT As AmplifierDharshan kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- VTU Notes Basic ElectronicsDokument22 SeitenVTU Notes Basic ElectronicsCicira BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 2.1Dokument85 SeitenChapter 3 2.1vipar snikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 TransistorDokument19 Seiten2.1 TransistorKshitij ParshettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- (L3) - Semiconductors - 22th DecDokument52 Seiten(L3) - Semiconductors - 22th DecShreshth GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2-BJT Applics and Feedback AmpliDokument37 SeitenChapter 2-BJT Applics and Feedback Ampliramya hegdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module2a BEEDokument16 SeitenModule2a BEEmd hasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Circuits: A - B - C - DDokument7 SeitenElectronic Circuits: A - B - C - DaravindhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics ExamDokument2 SeitenElectronics Examgettadd2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Bipolar Junction TransistorsDokument11 Seiten2 - Bipolar Junction TransistorsSainyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiDokument15 SeitenTransistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiPRANGHI80% (10)
- Lab.5 Power ElectronicsDokument7 SeitenLab.5 Power Electronicsbaig79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 3.6Dokument4 SeitenExercise 3.6ChewLee TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- الفصل 2tDokument23 Seitenالفصل 2tmustafaasaad020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edc Unit-3Dokument19 SeitenEdc Unit-3jeganece84Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.transistors FinalDokument43 Seiten3.transistors FinalSanjana HaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Atc IVDokument13 SeitenReview Atc IVArsenio MalapitNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectronicsDokument20 SeitenElectronicsMulugeta WoldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- RB6802B35Dokument25 SeitenRB6802B35MishtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 TransistorsDokument50 Seiten3 TransistorsUshan AdhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic ElectronicsDokument30 SeitenBasic ElectronicsMd. Mahamudul Hasan100% (1)
- Bipolar Junction Transistor Characteristics EELE101 LaboratoryDokument11 SeitenBipolar Junction Transistor Characteristics EELE101 LaboratoryHanieft NdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture5 (Analogue Electronics I)Dokument15 SeitenLecture5 (Analogue Electronics I)amash.emillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter3 Bipolar Junction Transistor PDFDokument28 SeitenChapter3 Bipolar Junction Transistor PDFJ VikasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Paper 1Dokument30 SeitenElectronic Paper 1maiyaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- INST200 x1 Mastery Version01Dokument9 SeitenINST200 x1 Mastery Version01KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Von EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 Form 5 MathsDokument5 SeitenTest 1 Form 5 MathsThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2Dokument11 SeitenSPM Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2kslpeter87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 Maths F4Dokument3 SeitenTest 1 Maths F4Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic Functions SeminarDokument5 SeitenQuadratic Functions SeminarThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 Maths F4Dokument3 SeitenTest 1 Maths F4Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Matter & The Atomic Structure ModulDokument43 Seiten1 Matter & The Atomic Structure Modulryder1man6433100% (1)
- Test 1 Form 5 MathsDokument5 SeitenTest 1 Form 5 MathsThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xiyj Xiyj: Answers: (1) (3, 4)Dokument2 SeitenXiyj Xiyj: Answers: (1) (3, 4)Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 I Graphs of Functions IIDokument24 SeitenChapter 2 I Graphs of Functions IIThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add MathsDokument40 SeitenAdd MathsJoseph TingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphs of Functions IIDokument21 SeitenGraphs of Functions IIThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 I Number BasesDokument18 SeitenChapter 1 I Number BasesThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Standard FormDokument14 SeitenChapter 1 Standard FormThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 II Matrices ENRICHDokument10 SeitenChapter 13 II Matrices ENRICHThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON9.4 ElectronicsDokument27 SeitenLESSON9.4 ElectronicsThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 SimultaneousEquationsDokument2 Seiten4 SimultaneousEquationsTiffanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 2Dokument23 SeitenBiology Form 4 Chapter 2Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nota FungsiDokument8 SeitenNota Fungsirhythm_no1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Vectors in Cartesian PlaneDokument2 Seiten3.1 Vectors in Cartesian PlaneThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Functions (Paper 2) : (KEDAH 2013)Dokument2 SeitenTrigonometric Functions (Paper 2) : (KEDAH 2013)Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Maths Form 5 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Dokument20 SeitenAdd Maths Form 5 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Thiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TransportDokument7 SeitenTransportThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Maths Form 4 Paper 2 Midterm 2012Dokument12 SeitenAdd Maths Form 4 Paper 2 Midterm 2012Thiyaku Marutha100% (2)
- BM Perlis 09Dokument13 SeitenBM Perlis 09chuahcpkNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON9.4 ElectronicsDokument27 SeitenLESSON9.4 ElectronicsThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BM k12 Johor SPM 09Dokument35 SeitenBM k12 Johor SPM 09Cg IfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional MathematicsDokument19 SeitenAdditional MathematicsThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON9.2 ElectronicsDokument27 SeitenLESSON9.2 ElectronicsThiyaku MaruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Requirements An NtroductionDokument7 SeitenRequirements An NtroductionIcs MonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- QR Code PPT Grade 9Dokument9 SeitenQR Code PPT Grade 9Tarun PNoch keine Bewertungen
- CD 00158241Dokument81 SeitenCD 00158241hschoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differentiate Between App Controller & VMM 8Dokument13 SeitenDifferentiate Between App Controller & VMM 8Aniket SonaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- tms320f28p559sj q1Dokument268 Seitentms320f28p559sj q1heliosentricNoch keine Bewertungen
- 750T Hardware ServiceDokument248 Seiten750T Hardware ServiceJuan DominguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link OS v6.7ReleaseNotesDokument208 SeitenLink OS v6.7ReleaseNotesCristhian RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intelligent Lighting System For Railway PlatformsDokument3 SeitenIntelligent Lighting System For Railway PlatformsMahesh MahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS619 SRS Helping Material 3Dokument18 SeitenCS619 SRS Helping Material 3Hani HaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Phone: Service ManualDokument140 SeitenMobile Phone: Service ManualAlexandro Silva PinheiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ericsson For Sale From Powerstorm 4SP10291213Dokument4 SeitenEricsson For Sale From Powerstorm 4SP10291213nethouse123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Soc Design Methodology Soc Design MethodologyDokument25 SeitenSoc Design Methodology Soc Design MethodologyNguyen Van ToanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vishal Peddigari: Experience SummaryDokument4 SeitenVishal Peddigari: Experience SummaryScribe.coNoch keine Bewertungen
- Man Sicam Q100 UsDokument376 SeitenMan Sicam Q100 UsHuy Truong GiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi Instrument Automation Server InterfacesDokument31 SeitenMulti Instrument Automation Server InterfacesAmalia DyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charmouh Abdellah TP CALCULATRICEDokument34 SeitenCharmouh Abdellah TP CALCULATRICEalilovemaroc1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abhishek Resume PDFDokument4 SeitenAbhishek Resume PDFPrince AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systolic Arrays & Their ApplicationsDokument35 SeitenSystolic Arrays & Their ApplicationsSp SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- LG FlatronDokument13 SeitenLG FlatronAngel AlarasNoch keine Bewertungen
- KM 2050Dokument2 SeitenKM 2050Anonymous WD109Uaky0% (1)
- Asus Eeepc 1008ha - Rev 1.3gDokument50 SeitenAsus Eeepc 1008ha - Rev 1.3gS_sergNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pankaj Agarwal: - Internship at Iit Bombay - Moodle VPL ProjectDokument1 SeitePankaj Agarwal: - Internship at Iit Bombay - Moodle VPL ProjectPankaj AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Learn Pattern Printing Easily - GeeksforGeeksDokument13 SeitenHow To Learn Pattern Printing Easily - GeeksforGeeksVinnie TendereNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS207 Electronic Devices & CircuitsDokument3 SeitenCS207 Electronic Devices & Circuitsnisanth123Noch keine Bewertungen
- The PowerShell Scripting & Toolmaking Book, Forever EditionDokument548 SeitenThe PowerShell Scripting & Toolmaking Book, Forever EditionKherfallah KarimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide: Block DiagramDokument60 SeitenReference Guide: Block DiagrambestalfiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Report of The Basic Arithmetic Operations Using C++Dokument8 SeitenLaboratory Report of The Basic Arithmetic Operations Using C++Roschelle Eleda0% (1)
- How BIOS Works 4Dokument7 SeitenHow BIOS Works 4NafeesAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICx2272 Substation GatewayDokument6 SeitenICx2272 Substation GatewaybirinderNoch keine Bewertungen