Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A Business Review of E-COMMERCE in India: Research Papers
Hochgeladen von
Kr PrajapatOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A Business Review of E-COMMERCE in India: Research Papers
Hochgeladen von
Kr PrajapatCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Vol.1,Issue.VII/April; 12pp.
1-4
ReviewOf Research
ROR (1),
Key words:, E-business, , Electronic Card
(debit,credit), E-payment, E-data interchange,
Electronic funds, E-services, E-trade,
1. Introduction
E-commerce stands for electronic
commerce. It means dealing in goods and services
through the electronic media and internet. As a
result of globalization and revolutionized
technology and in many ways its feature, the term
e-commerce represents the edge of success in this
modern age computers and technology On the
Internet, it relates to a website of the vendor, who
sell products or services directly to the customer
from the portal using a digital shopping cart or
digital shopping basket system and allows
payment through credit card, debit card or EFT
payments. E-commerce involves carrying on a
business with thehelp of the internet and by using
the information technology like Electronic
DataInterchange. In general words, Electronic
commerce is the activity of buying and selling of
the goods and services across the world through
the World Wide Web.
2. Need of the Study
Growth of E-Business in India is
tremendous but still has lot of barriers which are
the obstacles in the way of E business. It needs a
focus and should be prioritize to make the country
in the lines of E-Business. We should look into
these barriers and steps should be taken to address
them.In this paper I describe the definitions and
understanding of E-business, the differences
between E-Commerce and E-Business, its
advantages over traditional commerce, types, E-
Business in India. In this paper I present you list of
the factors and the reasons behind these factors
which affect the growth of E-business, proposed
solutions for some of these factors. Proposed
model address some of the problems faced by
enabling the traders, farmers and buyers can sell
and purchase their products respectively like
fruits, vegetables in quantities of metric tonnes
regularly which is not possible in existing B2B,
B2C, C2C websites. These programs must be
conducted by government organizations which
eliminates the need of brokers, commission
Research Papers
Abstract
Future of ecommerce is very innovative in India with even the stock exchanges coming online
providing a online stock portfolio and status with a fifteen minute delay in prices. . Now country growing
awareness among the business community in India about the opportunities offered by Ecommerce. The main
factor of E-Commerce is adopting in India and the result of the study shows that the major problems facing E-
commerce in India. E-commerce stands for electronic commerce. E-commerce is improving standard among the
business community in worlds, about the opportunities offered by E-commerce. And its trading in goods and
services through the electronic medium. There are the issues of security and citizen's income and therefore the
implementation of sophisticated security measures could make a difference and change in Indian's mentality
about E-Commerce. E-Commerce has unleashed yet another revolution, which is changing the way businesses
buy and sell products and services. India is showing tremendous growth in the Ecommerce so now a day, low cost
of the PC and the growing use of the Internet.
Prof .Waghmare G .T.
ISSN:-2249-894X
A Business Review of E-COMMERCE in India
R
R
Prof .Waghmare G .T.
Department of Commerce
Yeshwant Mahavidyalaya,
Nanded
Vol.1,Issue.VII/April 2012;
ROR (2),
agents, and intermediaries and infuses trust in the
participants get into E-business.
3. External Global trends;-
Business models across the world also
continue to change drastically with the advent of
ecommerce and this change is not just restricted to
USA. Amongst emerging economies, China's
ecommerce presence continues to expand. With
384 million internet users, China's online shopping
sales rose to $36.6 billion in 2009 and one of the
reasons behind the huge growth has been the
improved trust level for shoppers. Other countries
are also contributing to the growth of ecommerce.
For example, the United Kingdom has the biggest
e-commerce market in the world when measured
by the amount spent per capita, even higher than
the USA. The internet economy in UK is likely to
grow by 12% between 2010 to 2016.
4.Types of E-Commerce:
B2B E-Commerce: Companies doing business
with each other such as manufacturers selling to
distributors and Wholesalers selling to retailers.
Pricing is based on quantity of order and is often
negotiable.
B2C E-Commerce: Businesses selling to the
general public typically through cataloes utilizing
shopping cart software. By dollar volume, B2B
takes the prize, however B2C is really what the
average Joe has in mind with regards to
ecommer ce as a whol e. f or exampl e
indiatimes.com
C2C E-Commerce: There are many sites offering
free classifieds, auctions, and forums where
individuals can buy and sell thanks to online
payment systems like PayPal where people can
send and receive money online with ease. eBay's
auction service is a great example of where
customer-to-customer transactions take place
every day.
G2G (Government-to-Government), G2E
(Government-to-Employee), G2B (Government-
to-Business), B2G (Business-to-Government),
G2C (Government-to-Citizen), C2G (Citizen-to-
Government) this all are forms of ecommerce that
involve transactions with the government--from
procurement to filing taxes to business
registrations to renewing licenses.
5. E-commerce Status and Utilisation in India.
Today E-commerce is a backbone in Indian
society and it has become an integral part of our
daily life. There are websites providing any
number of goods and services. Then there are
those, which provide a specific productalong with
its allied services Multi-product e-commerce-
A Business Review of E-COMMERCE in India
These Indian E-commerce portals provide goods
and services in a variety of categories, for
example:
1) Stocks and shares and e-commerce- In India
today, we can even deal in stocks and shares
through e-commerce. Some of the services offered
to registered members are: Online buying/selling
of stocks and shares, Market analysis and research,
Company information, Comparison of companies,
Research on Equity and Mutual Funds.
2) Real estate and e-commerce- They provide
information on new properties as well as
properties for resale. One can deal directly with
developer through consultant. Allied services:
Housing Finance, Insurance companies,
Architects & Interior Designers, NRI services,
Packers &Movers.
3) Hobbies and e-commerce- The most popular
hobbies from time immemorial are reading, music
and films. The books cover a wide range of topics
like Business, Art, Cookery, Engineering,
Children's Stories, Health, Medicine, Biographies,
Horror, Home & Garden, etc.
4) Employment and e-commerce- Two major
portals like www.Monsterindia.com and
www.naukri.com (meaning job.com in Hindi) are
instrumental in providing job seekers with suitable
employment at the click of a mouse. The service
for job seekers is free and for Employers they
charge a nominal fee. Jobs are available online in
fields ranging from secretarial to software
development, and from real estate to education.
5) Travel & tourism and e-commerce- India has
a rich history and heritage and e-commerce is
instrumental, to a large extent, in selling India as a
product, encouraging Indians as well as foreigners
to see its multifaceted culture and beauty. The
tourist destination sites are categorized according
to themes like: Adventure - trekking, mountain
climbing etc, Eco-Themes pertains to jungles,
flora and fauna.
6. International Authorities for E-trade
Regulation ;-
There is also Asia Pacific Economic
Cooperation (APEC) was established in 1989 with
the vision of achieving stability, security and
prosperity for the region through free and open
trade and investment. APEC has an Electronic
Commerce Staring Group as well as working on
common privacy regulations throughout the APEC
region. Internationally there is the International
Consumer Protection and Enforcement Network
(ICPEN), which was formed in 1991 from an
informal network of government customer fair
ReviewOf Research
Vol.1,Issue.VII/April 2012;
ROR (3),
trade organisations. The purpose was stated as
being to find ways of co-operating on tackling
consumer problems connected with cross-border
transactions in both goods and services, and to help
ensure exchanges of information among the
participants for mutual benefit and understanding.
7. Benefits of E-Commerce to Businesses.
There is a growing awareness among the
business community in India about the
opportunities offered by e-Commerce. Safe and
secure payment modes are crucial too along with
the need to invent and popularize innovations such
as Mobile Commerce. The other reports available
on India Reports are on retail, outsourcing,
tourism, food and other emerging sectors in India.
1.Unlimited shelf place for products and services
2.The young population find online transactions
much easier
3.Easy reach to a fast growing online community
4.Improved fraud prevention technologies that
offer a safe and secure business environment and
help prevent credit card frauds, identity thefts and
phishing
5.Bigger web presence of SME's and Corporate
because of lower marketing and infrastructure
costs.
6.Fuse the global geographical and time zone
boundaries
7.Rapidly increasing Internet user base
8.Technology advancements such as VOIP
(Voiceover-IP) have bridged the gap between
buyers and sellers online
9.The emergence of blogs as an avenue for
information dissemination and two-way
communication for online retailers and E-
commerce vendors
There are various user of E-Commerce in
Businesses.
8. Ecommerce Barriers are most follow in
India.
Some of the infrastructural barriers
responsible for slow growth of ecommerce in India
are as follows. Some of these even present new
business opportunities.
A. Payment Cash And Collection: When get paid
by net banking one has to end up giving a
significant share of revenue (4% or more) even
with a business of thin margin. This effectively
A Business Review of E-COMMERCE in India
means y parting away with almost half of profits.
Fraudulent charges, charge backs etc. all become
merchant's responsibility and hence to be
accounted for in the business model.
B. Vendor Management: However advanced
system may be, vendor will have to come down
and deal in an inefficient system for inventory
management. This will slow down drastically.
Most of them won't carry any digital data for their
products. No nice looking photographs, no digital
data sheet, no mechanism to check for daily prices,
availability to keep your site updated.
C. Taxation: Octroi, entry tax, VAT and lots of
state specific forms which accompany them. This
can be confusing at times with lots of exceptions
and special rules.
D. Logistics: You have to deliver the product, safe
and secure, in the hands of the right guy in right
time frame. Regular post doesn't offer an
acceptable service level; couriers have high
charges and limited reach. Initially, you might
have to take insurance for high value shipped
articles increasing the cost.
E. Multiple issues of trust and lack of payment
gateways: privacy of personal and business data
connected over the Internet not assured; security
and confidentiality of data not in place.
F. Multiple gaps in the current legal and regulatory
framework.
G. Multiple gaps in the current legal and regulatory
framework.
H. Limited Internet access among customers and
SMEs.
I. Poor telecom and infrastructure for reliable
connectivity.
9. Impact on markets and retailers.
Economists have theorized that e-
commerce ought to lead to intensified price
competition, as it increases consumers' ability to
gather information about products and prices.
Research by four economists at the University of
Chicago has found that the growth of online
shopping has also affected industry structure in
two areas that have seen significant growth in e-
commerce, bookshops and travel agencies.
Generally, larger firms have grown at the expense
of smaller ones, as they are able to use economies
of scale and offer lower prices. The lone exception
to this pattern has been the very smallest category
of bookseller, shops with between one and four
employees, which appear to have withstood the
trend.
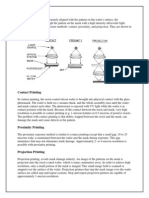
10. Various roll of Ecommerce in India.
Today, we are talking about e-commerce
ReviewOf Research
Wholesaler
Manufacturer
Organization
Trader
Seller
Buyer
Online
Exchange
Program
Are Using
In Business
Vol.1,Issue.VI/March 2012;
ROR (4),
progress level of India, the seventh-largest by
geographical area, the second-most populous
country, and the most populous democracy in the
world. Indian E-commerce space percentage is
getting higher as more and more online retailers
enter the market. Although this level of entry in the
e-commerce market is good from a long term
perspective, the challenge is that most
entrepreneurs don't have the resources or capital to
wait for years before they can get profits. The past
3 years have seen a rise in the number of
companies' embracing e-commerce technologies
and the Internet in India. Most E-commerce sites
have been targeted towards the NRI's with Gift
del i ver y s er vi ces , books , Audi o and
videocassettes. Major Indian portal sites have also
shifted towards E-commerce instead of depending
on advertising revenue. The web communities
built around these portal sites with content have
been effectively targeted to sell everything from
event and movie tickets the grocery and
computers. This is not to say that the E-commerce
scenario has been bad in India as highly successful
E-business like baba bazaar and India mart have
proved. Indian Banks too have been very
successful in adapting EC and EDI Technologies
to provide customers with real time account status,
transfer of funds between current and checking
accounts, stop payment facilities. ICICI Bank,
AND UTI-Bank also have put their electronic
banking over the internet facilities in place for the
upcoming e-commerce market speed post also
plain to clone the federal express story with online
package status at any moment in time.The day
cannot be far when with RBI regulations will able
to see stock transfer and sale over the Net with
specialized services.
11. Business applications use under E-
Commerce; There are some common
applications related to electronic commerce are
the following;
1. Document automation in supply chain and
logistics
2. Domestic and international payment
systems
3. Enterprise content management
4. Group buying
5. Automated online assistants
6. Instant messaging
7. Newsgroups
8. Online shopping and order tracking
9. Online banking
10. Online office suites
11. Shopping cart software
A Business Review of E-COMMERCE in India
12. Teleconferencing , Electronic tickets
12. Conclusion
A developing country can become
industrialized and modernized if it can extensively
apply IT to enhance productivity and international
competitiveness, develop ecommerce and e-
governance applications. An information-based
society or knowledge based society is composed of
IT products, IT applications in society
andeconomy as a whole. Many countries in Asia
are taking advantage of E-commerce through
opening of economies, which is essential for
promoting competition and diffusion of Internet
technologies. Large enough to have a critical mass
of 10 to 20 million users to be able to make an
impact on e-commerce and e-governance. In the
next 3 to 5 years, India will have 30 to 70 million
Internet users which will equal, if not surpass,
many of the developed countries. Internet
economy will then become moremeaningful in
India. With the rapid expansion of internet, E-
commerce, is set to play a very important role in
the 21st century, the new opportunities that will be
thrown open,will be accessible to both large
corporations and small companies. The role of
government is to provide a legal framework for E-
Commerce so that while domestic and
international trade are allowed to expand their
horizons, basic rights such as privacy, intellectual
property, prevention of fraud, consumer protection
etc are all taken care of.
13. References.
1. P T Joseph, text book on E-Commerce in India.
2. Electronic Banking Group of the Basel
Committee on Banking Supervision, Risk.
Management Principles for Electronic Banking,
July, 2003.
3. Electronic commerce from Wikipedia-the free
encyclopaedia.
4. Department of Electronics 1999, Information
technology Bill along with cyber laws,govt of
india.
5. Sinha (April 2009), Ecommerce in India The
Real Challenges
6. Kapurubandara, M. Arunatileka, S. Gnige
"Application of e-business strategies for SMEs in
developingcountries", 2004, International
conference on e-Commerce and e-Service
7. Rastogi, Rajiv; Country's report on E
Commerce Initiatives.
8. Zorayda Ruth Andam (2003) "e-Commerce and
e-Business" in e-ASEAN task force.
ReviewOf Research
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Emerging Trends of EcommerceDokument7 SeitenEmerging Trends of EcommercecronysaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of E-Commerce in India: Chapter-1Dokument11 SeitenStudy of E-Commerce in India: Chapter-1bikram prustyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of E-Commerce in The Indian EconomyDokument7 SeitenImpact of E-Commerce in The Indian EconomyrajisumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Commerce Services in India: Prospects and ProblemsDokument36 SeitenE-Commerce Services in India: Prospects and Problemsfida mohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future of E-Commerce For Development of Rural IndiaDokument8 SeitenFuture of E-Commerce For Development of Rural IndiaAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecommerce in IndiaDokument24 SeitenEcommerce in Indiaintellectarun100% (2)
- E-Commerce in India Future and Its Perspective: A StudyDokument7 SeitenE-Commerce in India Future and Its Perspective: A StudyInternational Journal of Scientific Research and Engineering StudiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem and Prospects of E-Commerce: Alka Raghunath & Murli Dhar PangaDokument10 SeitenProblem and Prospects of E-Commerce: Alka Raghunath & Murli Dhar Pangaवैभव शिरोडेNoch keine Bewertungen
- 218 1658150510Dokument11 Seiten218 1658150510Anand KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5thAICC Paper 45Dokument17 Seiten5thAICC Paper 45NoamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Executive SummaryDokument39 SeitenExecutive Summarytanisq10Noch keine Bewertungen
- E Business Notes For GgsipuDokument41 SeitenE Business Notes For GgsipubasantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecommerce in IndiaDokument78 SeitenEcommerce in IndiaArvind Sanu Misra100% (2)
- Emerging Trends of E-Commerce in India: An Empirical StudyDokument7 SeitenEmerging Trends of E-Commerce in India: An Empirical Studyinventionjournals100% (1)
- Research Paper On Ecommerce in India PDFDokument4 SeitenResearch Paper On Ecommerce in India PDFafnhemzabfueaa100% (1)
- 21BCS8135 (Shubham Kumar) Project Review Paper Semester 5Dokument7 Seiten21BCS8135 (Shubham Kumar) Project Review Paper Semester 5Xxx RecoverNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Comerce RuralDokument10 SeitenE-Comerce RuralGopi KhuntNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amoo Samuel BS4S14 A1Dokument24 SeitenAmoo Samuel BS4S14 A1Samuel AmooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ujjwal Singha MahapatraDokument16 SeitenUjjwal Singha MahapatraUjjwal MahapatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emerging Trends of E-Commerce in India: An Empirical StudyDokument7 SeitenEmerging Trends of E-Commerce in India: An Empirical StudyinventionjournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Tailing - A Promising Approach in Indian Retail Industry-FULL PAPERDokument12 SeitenE-Tailing - A Promising Approach in Indian Retail Industry-FULL PAPERgprakash_mNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Commerce Applications in India: An Empirical Study: NCRD's Sterling Institute of Management and StudiesDokument71 SeitenE-Commerce Applications in India: An Empirical Study: NCRD's Sterling Institute of Management and StudiesSubrat PatnaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trends in E-Commerce and Consumer Behaviour in Contemporary EraDokument9 SeitenTrends in E-Commerce and Consumer Behaviour in Contemporary EraDhaval LathiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of The Student Tabassum Parveen CU Registration No. CU University Roll NODokument24 SeitenName of The Student Tabassum Parveen CU Registration No. CU University Roll NOMD AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grand Project 141 - 150Dokument46 SeitenGrand Project 141 - 150Parth SanghviNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of E-Commerce in IndiaDokument5 SeitenHistory of E-Commerce in Indiakartheek_aldi67% (6)
- Project Report & Finance Under The University of Calcutta)Dokument22 SeitenProject Report & Finance Under The University of Calcutta)Sujit ChouhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian E-Commerce Industry Analysis PDFDokument11 SeitenIndian E-Commerce Industry Analysis PDFKetan Rathod100% (1)
- The Impact of E-Commerce in BangladeshDokument12 SeitenThe Impact of E-Commerce in BangladeshMd Ruhul AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of E-Commerce in Indian Economy: Related PapersDokument14 SeitenImpact of E-Commerce in Indian Economy: Related PapersxyzhjklNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Commerce and The Future of Modern BusinessDokument8 SeitenE-Commerce and The Future of Modern BusinessRitika RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Digital Marketing On E-Commerce - Questionnaire PendingDokument35 SeitenImpact of Digital Marketing On E-Commerce - Questionnaire PendingKinnari Singh0% (1)
- Sectorial Analysis IOTDokument16 SeitenSectorial Analysis IOTAneesh DugarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Material For Unit 1Dokument26 SeitenLearning Material For Unit 1shikha22bcom24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Analysis of Ecommerce Websites A Case StudyDokument13 SeitenComparative Analysis of Ecommerce Websites A Case Studyarcherselevators100% (3)
- Equalizaton Levy Under Income Tax ActDokument49 SeitenEqualizaton Levy Under Income Tax ActRAKESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting The Growth of E-Business in India and Importance of SmesDokument6 SeitenFactors Affecting The Growth of E-Business in India and Importance of SmesSeema PunjabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scope of Ecommerce in MaharashtraDokument13 SeitenScope of Ecommerce in MaharashtraKavita Koli0% (1)
- School of Commerce and Management Studies CIA 4 (Research)Dokument14 SeitenSchool of Commerce and Management Studies CIA 4 (Research)VighneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Business Impact of E-CommerceDokument8 SeitenThe Business Impact of E-CommerceVarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project ON E-Commerce in Global ScenarioDokument35 SeitenProject ON E-Commerce in Global ScenarioSandeep GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatin Nabihah 265302Dokument9 SeitenFatin Nabihah 265302FatinAzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Assignment 2Dokument7 SeitenManagement Assignment 2Adisu MasreshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E CommerceDokument21 SeitenE CommerceAyesh AyeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of E-Commerce in Indian Economy PDFDokument13 SeitenImpact of E-Commerce in Indian Economy PDFJayagokul SaravananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact-of-E-Commerce-in-Indian Economy Case Study PDFDokument13 SeitenImpact-of-E-Commerce-in-Indian Economy Case Study PDFakthaks14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Renin - Ecommerce ProjectDokument36 SeitenRenin - Ecommerce ProjectBOBBY THOMASNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Ecommerce Association of India InitiativeDokument20 SeitenAn Ecommerce Association of India InitiativeVipul SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Studay On Ecommerce WilsonkumarDokument5 SeitenA Studay On Ecommerce WilsonkumarThala WilsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study On Customer Satisfaction Regarding E-Commerce CompanyDokument65 SeitenStudy On Customer Satisfaction Regarding E-Commerce CompanyShweta RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- IN2263 Assignment Week2Dokument4 SeitenIN2263 Assignment Week2Jay KaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Hitesh Khurana Research Communication Sep 2011 PDFDokument8 Seiten7 Hitesh Khurana Research Communication Sep 2011 PDF॰अचूक॰ Milan SubediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of E-Commerce in Indian Economy: Kumar Anuj, Fahad Fayaz, Ms Namita KapoorDokument13 SeitenImpact of E-Commerce in Indian Economy: Kumar Anuj, Fahad Fayaz, Ms Namita KapoorAnilNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Synopsis: "E-Commerce Growth in International Market "Dokument10 SeitenA Synopsis: "E-Commerce Growth in International Market "Dee RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E - Commerce in IndiaDokument8 SeitenE - Commerce in IndiaAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Electronic Commerce On Business in Tenkasi AreaDokument5 SeitenThe Impact of Electronic Commerce On Business in Tenkasi Areafreak badNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Gold: Mastering E-Commerce Strategy for Maximum Business SuccessVon EverandDigital Gold: Mastering E-Commerce Strategy for Maximum Business SuccessNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-commerce Evolution : Navigating Trends and Innovations in Digital MarketingVon EverandE-commerce Evolution : Navigating Trends and Innovations in Digital MarketingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module2 1Dokument84 SeitenModule2 1Kr Prajapat100% (1)
- HDFC SipDokument4 SeitenHDFC SipKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec EngineeringDokument7 SeitenEc EngineeringVarunHvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tools & Resources Scheme Analysers: LoginDokument2 SeitenTools & Resources Scheme Analysers: LoginKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cavity Writeup ExpDokument7 SeitenCavity Writeup ExpKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- DmuxDokument6 SeitenDmuxKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 004Dokument35 SeitenChap 004Lokesh Ranjan KrishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus Deployment: S. NO. Topic As Per Blownup Syllabus Lect. No. Planned DAT E Actual Del. Date Reason For Deviati ONDokument12 SeitenSyllabus Deployment: S. NO. Topic As Per Blownup Syllabus Lect. No. Planned DAT E Actual Del. Date Reason For Deviati ONKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Report On Alumni LectureDokument1 SeiteA Report On Alumni LectureKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idea ExerciseDokument27 SeitenIdea ExerciseSamdarsh NirankariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sme Media Kit 2012Dokument8 SeitenSme Media Kit 2012KuldeepDesai007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Noise in Comm SystemDokument38 SeitenNoise in Comm SystemKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1: Introduction To TechnologiesDokument1 SeiteUnit-1: Introduction To TechnologiesKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Alone: A Handbook For Small BusinessDokument44 SeitenWorking Alone: A Handbook For Small BusinessKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Seminar Topics List1Dokument15 SeitenECE Seminar Topics List1Kr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10ksb Us BrochureDokument13 Seiten10ksb Us BrochureKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Exploratory Study On Electronic Retailing in IndiaDokument5 SeitenAn Exploratory Study On Electronic Retailing in IndiaKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investment Amount Calculation TableDokument1 SeiteInvestment Amount Calculation TableKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 010jan Vijay CaseDokument14 Seiten010jan Vijay CaseKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 010jan Vijay CaseDokument14 Seiten010jan Vijay CaseKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fact SheetviewDokument54 SeitenFact SheetviewKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Axis LT Fund PerformanceDokument6 SeitenAxis LT Fund PerformanceKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Seminar Topics List1Dokument15 SeitenECE Seminar Topics List1Kr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 010jan Vijay AnsDokument7 Seiten010jan Vijay AnsKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Calendar With Event Planner v2Dokument51 Seiten2014 Calendar With Event Planner v2Kr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolation TecgniquesDokument2 SeitenIsolation TecgniquesKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference ProximityDokument1 SeiteDifference ProximityKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule For The Year 2012 With Regard To Various Cut-Off Dates For Services Pertaining To StudentsDokument1 SeiteSchedule For The Year 2012 With Regard To Various Cut-Off Dates For Services Pertaining To StudentsKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- CsDokument18 SeitenCsKr PrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Receivables An OverviewDokument69 SeitenOracle Receivables An OverviewmanukleoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impropriety of JudgesDokument8 SeitenImpropriety of JudgesPrincess Ruksan Lawi SucorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date Sheet For Pms in Service 02 2021Dokument1 SeiteDate Sheet For Pms in Service 02 2021Oceans AdvocateNoch keine Bewertungen
- California Child and Spousal Support Bench GuideDokument96 SeitenCalifornia Child and Spousal Support Bench GuideAnonymous oY5Dk8c5u100% (2)
- Tysiac V Poland WebDokument5 SeitenTysiac V Poland WebNina KakauridzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black MoneyDokument5 SeitenBlack MoneySaanvi GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP FICO Course Content by Archon Tech SolutionsDokument4 SeitenSAP FICO Course Content by Archon Tech SolutionsCorpsalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Contract CondoDokument7 Seiten1 Contract CondoABNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roman EmperorsDokument10 SeitenRoman EmperorsAbdurrahman Shaleh ReliubunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Memorial Drafting and Judgement Writing Competition 2022Dokument14 SeitenMemorial Drafting and Judgement Writing Competition 2022Naila JabeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Care Ethics Final 3Dokument10 SeitenHealth Care Ethics Final 3Allysa Kyle AlfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echavez v. Dozen Construction PDFDokument3 SeitenEchavez v. Dozen Construction PDFCathy BelgiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revidert Norwegian BlacklistDokument13 SeitenRevidert Norwegian Blacklistgauthams309Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Assignment Name: Matrix No: CompanyDokument20 SeitenSample Assignment Name: Matrix No: CompanynurainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case No. 83-3Dokument3 SeitenCase No. 83-3angelo macatangayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Docket - Larson v. Perry (Dorland) ("Bad Art Friend")Dokument20 SeitenCivil Docket - Larson v. Perry (Dorland) ("Bad Art Friend")x2478Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of IP AddressesDokument3 SeitenTypes of IP Addressesbekalu amenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MME Technical OverviewDokument568 SeitenMME Technical OverviewAndreea TrenteaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Law - Lecture Notes Definition of A "Company"Dokument105 SeitenCompany Law - Lecture Notes Definition of A "Company"namukuve aminaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reyes v. CA 216 SCRA 25 (1993)Dokument7 SeitenReyes v. CA 216 SCRA 25 (1993)Karla KanashiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rsi - ProfileDokument91 SeitenRsi - ProfileNhung TruongNoch keine Bewertungen
- CES-107-J Assembly and Test 21000 SeriesDokument13 SeitenCES-107-J Assembly and Test 21000 SeriesJorge SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benefits BookletDokument59 SeitenBenefits BookletThe QuadfatherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft Constitution of Made Men WorldwideDokument11 SeitenDraft Constitution of Made Men WorldwidebrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outbound Inbound Calls From External ToDokument3 SeitenOutbound Inbound Calls From External TorajueeguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serrano de Agbayani Vs PNB - DigestDokument2 SeitenSerrano de Agbayani Vs PNB - DigestG Ant Mgd100% (1)
- Discover Aes MsdsDokument17 SeitenDiscover Aes MsdsAkbar WildanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDIC, TIL, WarehouseDokument11 SeitenPDIC, TIL, WarehouseA.T.Comia100% (1)
- Admission Notice: Vallabhbhai University, MandiDokument1 SeiteAdmission Notice: Vallabhbhai University, Mandianonymous accountNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rosevelt ScottDokument3 SeitenRosevelt ScottsamtlevinNoch keine Bewertungen