Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Critical Power Supplies
Hochgeladen von
Rohit SachanCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Critical Power Supplies
Hochgeladen von
Rohit SachanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Critical Power Supplies has pleasure in bringing you this guide on how UPSSystems work.
An uninterruptible power supply, also uninterruptible power source, UPS orbattery / flywheel backup, is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the
input power source, typically the utility mains, fails.
A UPS differs from an auxiliary or emergency power system or standby generator in that it will provide instantaneous or near-instantaneous protection from input power interruptions
by means of one or more attached batteries and associated electronic circuitry for low power users, and or by means ofdiesel generators and flywheels for high power users. The on-
battery runtime of most uninterruptible power sources is relatively short515 minutes being typical for smaller unitsbut sufficient to allow time to bring an auxiliary power source
on line, or to properly shut down the protected equipment.
While not limited to protecting any particular type of equipment, a UPS is typically used to protect computers, data centers, telecommunication equipment or other electrical
equipment where an unexpected power disruption could cause injuries, fatalities, serious business disruption and/or data loss. UPS units range in size from units designed to protect
a single computer without a video monitor (around 200 VA rating) to large units powering entire data centers (>1MVA), buildings (>300kVA), or manufacturing processes.
Different types of UPS design.
the general categories of modern UPS systems are on-line, line-interactive or standby.
A standby (off-line) UPS system the load is powered directly by the input power and the backup power circuitry is only invoked when the utility power fails. Most UPS below 1 kVA
are of the line-interactive or standby variety which are usually less expensive.
A line-interactive UPS maintains the inverter in line and redirects the batterys DC current path from the normal charging mode to supplying current when power is lost.
A on-line UPS uses a double conversion method of accepting AC input, rectifying to DC for passing through the rechargeable battery (or battery strings), then inverting back to
120V/240V AC for powering the protected equipment.
For large power units, dynamic uninterruptible power supplies are sometimes used. A synchronous motor/alternator is connected on the mains via a choke. Energy is stored in a
flywheel. When the mains power fails, an Eddy-current regulation maintains the power on the load. DUPS are sometimes combined or integrated with a diesel-generator[clarification
needed], forming a diesel rotary uninterruptible power supply, or DRUPS.
A fuel cell UPS has been developed in recent years using hydrogen and a fuel cell as a power source, potentially providing long run times in a small space.
Off-line UPS design
The Offline / Standby UPS system (SPS) offers only the most basic features, providing surge protection and battery backup. With this type of UPS, a users equipment is normally
connected directly to incoming utility power with the same voltage transient clamping devices used in a common surge protected plug strip connected across the power line. When
the incoming utility voltage falls below a predetermined level the SPS turns on its internal DC-AC inverter circuitry, which is powered from an internal storage battery. The SPS then
mechanically switches the connected equipment on to its DC-AC inverter output. The switchover time can be as long as 25 milliseconds depending on the amount of time it takes the
Standby UPS to detect the lost utility voltage. Generally speaking, dependent on the size of UPS connected load and the sensitivity of the connected equipment to voltage variation,
the UPS will be designed and/or offered (specification wise) to cover certain ranges of equipment, i.e. Personal Computer, without any obvious dip or brownout to that device.
Line-interactive UPS design
This type of UPS is able to tolerate continuous undervoltage brownouts and overvoltage surges without consuming the limited reserve battery power. It instead compensates by auto-
selecting different power taps on the autotransformer. Changing the autotransformer tap can cause a very brief output power disruption,[citation needed] so the UPS may chirp for a
moment, as it briefly switches to battery before changing the selected power tap.[dubious discuss]
This has become popular even in the cheapest UPS because it takes advantage of components already included. The main 50/60 Hz transformer used to convert between line voltage
and battery voltage needs to provide two slightly different turns ratios: one to convert the battery output voltage (typically a multiple of 12 V) to line voltage, and a second one to
convert the line voltage to a slightly higher battery charging voltage (such as a multiple of 14 V). Further, it is easier to do the switching on the line-voltage side of the transformer
because of the lower currents on that side.
To gain the buck/boost feature, all that is required is two separate switches so that the AC input can be connected to one of the two primary taps, while the load is connected to
the other, thus using the main transformers primary windings as an autotransformer. Note that the battery can still be charged while bucking an overvoltage, but while
boosting an undervoltage, the transformer output is too low to charge the batteries.
Autotransformers can be engineered to cover a wide range of varying input voltages, but this requires more taps and increases complexity, and expense of the UPS. It is common for
the autotransformer to only cover a range from about 90 V to 140 V for 120 V power, and then switch to battery if the voltage goes much higher or lower than that range.
In low-voltage conditions the UPS will use more current than normal so it may need a higher current circuit than a normal device. For example to power a 1000 watt device at 120
volts, the UPS will draw 8.32 amps. If a brownout occurs and the voltage drops to 100 volts, the UPS will draw 10 amps to compensate. This also works in reverse, so that in an
overvoltage condition, the UPS will need fewer amps of current.
On-Line UPS Design
The online UPS is ideal for environments where electrical isolation is necessary or for equipment that is very sensitive to power fluctuations. Although once previously reserved for
very large installations of 10 kW or more, advances in technology have permitted it to now be available as a common consumer device, supplying 500 watts or less. The online UPS is
generally more expensive but may be necessary when the power environment is noisy such as in industrial settings, for larger equipment loads like data centers, or when operation
from an extended-run backup generator is necessary.
The basic technology of the online UPS is the same as in a standby or Line-Interactive UPS. However it typically costs much more, due to it having a much greater current AC-to-DC
battery-charger/rectifier, and with the rectifier and inverter designed to run continuously with improved cooling systems. It is called a Double-Conversion UPS due to the rectifier
directly driving the inverter, even when powered from normal AC current.
In an online UPS the batteries are always connected to the inverter, so that no power transfer switches are necessary. When power loss occurs, the rectifier simply drops out of the
circuit and the batteries keep the power steady and unchanged. When power is restored, the rectifier resumes carrying most of the load and begins charging the batteries, though
the charging current may be limited to prevent the high-power rectifier from overheating the batteries and boiling off the electrolyte.
The main advantage to the on-line UPS is its ability to provide an electrical firewall between the incoming utility power and sensitive electronic equipment. While the standby and
Line-Interactive UPS merely filter the input utility power, the Double-Conversion UPS provides a layer of insulation from power quality problems. It allows control of output voltage
and frequency regardless of input voltage and frequency.
A second major advantage is the inbuilt bypass circuit in on-line UPS which ensures should any problems occur with the UPS or batteries as long as their is mains power the load will
be powered. The bypass is either automatic or a combination of manual and automatic depending on the model / manufacturer.
The working principle of UPS
The working principle of UPS
From basic principles in terms of application, UPS is a device that contains stored energy in order to inverter as the main component, regulated stable frequency output power
protection equipment. Mainly by the rectifier, batteries, power inverters and static switch of several components.
1) rectifier: rectifier is a rectifier device, simply means that the exchange of (AC) into direct current (DC) devices. It has two main functions: First, the alternating current (AC)
into direct current (DC), through the supply of filtered load, or the supply inverter; second, to provide battery charging voltage. Therefore, it is also play a role in charger.
2) Battery: UPS battery is used as a storage energy device, which consists of several cells in series, with a capacity to maintain its size determines the discharge (supply) time.
Its main function is: When the electricity is normal, the energy converted into chemical energy stored in the battery internal; when the electricity fails, the chemical energy into
electrical energy provided to the inverter or the load.
3) Inverter: popular speaking, the inverter is a DC (DC) into alternating current (AC) device. It consists of inverter bridge control logic and filter circuit.
4) Static Switch: static switch also known as static switch, which is a non-contact switch, is to use two SCR (SCR) reverse parallel composition of a communication switch, its
closed and disconnected from the logic controller control. Conversion and the model is divided into two kinds of type and. Conversion-type switch is mainly used for two-way
power supply system, its role is to achieve all the way to another road from the automatic switching; and model switch is mainly used for parallel inverters with electricity or
more inverter.
UPS's matching
Generally based on facilities in the electricity environment, and want to achieve power conservation purposes, select the appropriate UPS. For example: built-in switching power
supply for low-power devices typically can choose Off-line UPS; in the electrical environment to poor areas should use on-line interactive type or on-line UPS; while the right does
not allow the time or times required intermittent sine wave AC equipment that can only use on-line UPS. But also based on your device to select the general ordinary PC, or the
IPC's power in the 200W or so; Apple machine is around 300W; server between 300W and 600W, other equipment, the power values refer to the device's instructions.
Secondly, we should understand the UPS's rated power of representation: apparent power (in VA); the actual output power (in W). Due to the presence of reactive power it had
contributed to this difference, the conversion relationship between the two: Apparent Power * Power Factor = actual output power. Off-line, on-line interactive power factor
between 0.5 and 0.7, on-line power factor is generally 0.8. With UPS for equipment should pay attention to: The UPS output power to match the actual basis, and some dealers
intentionally or unintentionally, it will cause confusion (VA) and (W) the difference, which points to draw the user's attention.
Use of UPS
UPS should be noted that the use of items:
1) UPS's use of the environment should pay attention to well-ventilated, which will help heat and keep the environment clean.
2) Do not bring inductive load, such as the Counter, fluorescent lights, air-conditioning so as to avoid damage.
3) UPS's output load control is about 60% of the best, most reliable.
4) UPS with load is too light (for example, 1000VA, UPS with 100VA load) may cause the battery depth of discharge, will reduce the battery life, should be avoided.
5) Appropriate discharge, contribute to the activation of cells, such as the long-term non-stop electricity, every three months to be artificially cut off electricity to use UPS with a
load-discharge time, so you can extend battery life.
6) For most small UPS, to work to open UPS, with load at boot time to avoid startup, work should be shut down UPS; for network computer room UPS, because most of the
network is 24 hours, so UPS must also be running around the clock.
7) UPS charge promptly after discharge to prevent battery damage due to excessive self-discharge.
UPS maintenance and repair
The use of an uninterruptible power supply system in the process, people tend to one-sided view that is maintenance-free battery and not take this seriously. However, there are
data show that due to battery failure caused by the host UPS failure or an abnormal proportion of the work of about 1 / 3. Thus, to enhance the proper use of the UPS batteries
and maintenance, to extend the battery life, lower failure rate UPS systems, has become increasingly important. In addition to matching the regular brand batteries other than
the following aspects should be the proper use and maintenance of batteries:
1) Maintain the appropriate environmental temperature: an important factor affecting battery life is the ambient temperature, the general requirements of the battery
manufacturers the best ambient temperature is between 20 ~ 25 . Although the temperature of the battery discharge capacity has increased, but the cost is the battery life
significantly shortened. According to test the determination of the ambient temperature whenever they exceed 25 , is increased by 10 , the battery life should be cut by half.
UPS is currently used batteries are generally maintenance-free sealed lead-acid battery, universal design life is 5 years, which is required in battery manufacturers environment
can be achieved. Not reach specified environmental requirements, the length of their life there is a huge difference. In addition, the ambient temperature increase will lead to
increased chemical activity within the battery, resulting in a lot of heat, in turn prompted ambient temperature, this vicious cycle will accelerate to shorten battery life.
2) periodic charge-discharge: UPS power supply in the float voltage and discharge voltage, in the factory have to debug into the rating, while the size of the discharge current
increases as the load increases, the use of reasonable adjustments should be load, , such as controlling the use of computer and other electronic equipment, the number of units.
Under normal circumstances, the load should not exceed 60% of rated load UPS. In this context, the battery discharge current will not over-discharge.
UPS due to long-term and electricity connected, in the supply of high quality, rare use of mains power failure environment, the battery will be a long period of float charge state,
the course of time will cause the battery chemical energy and electrical energy conversion activity decreased with each other to accelerate the shorten the life of aging.
Therefore, generally every 2-3 months should be fully discharged once, discharge time can be battery capacity and load size of the set. After a full load discharge, according to
the provisions of recharge for more than 8 hours.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Ccna 1Dokument21 SeitenCcna 1Dinesh SrinivasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hindu Review For The Month of AugustDokument5 SeitenHindu Review For The Month of AugustNayakNareshNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Broadcast and Collision DomainDokument3 SeitenBroadcast and Collision DomainRohit SachanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Broadcast and Collision DomainDokument3 SeitenBroadcast and Collision DomainRohit SachanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Broadcast of A Programme From Source To Listener Involves Use of StudiosDokument3 SeitenThe Broadcast of A Programme From Source To Listener Involves Use of StudiosRohit SachanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Nasscom Nac Tech Sample Test 1 Part ADokument3 SeitenNasscom Nac Tech Sample Test 1 Part AkiruthikaveluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contactors and Contactor Assemblies: Contactors For Switching Motors SiriusDokument8 SeitenContactors and Contactor Assemblies: Contactors For Switching Motors SiriuschochoroyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- EloTrain CatalogDokument56 SeitenEloTrain CatalogAbdul Shokor Abd TalibNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Reyrolle Aux. RelaysDokument80 SeitenReyrolle Aux. RelaysHutama RezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Brushless Excitation SystemDokument26 SeitenBrushless Excitation SystemManish TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- Schematics and DiagramDokument67 SeitenSchematics and DiagramArgel Linard Francisco Mabaga100% (1)
- MC3PHACDokument36 SeitenMC3PHACBảo BìnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- ESC63C Series Speed Control Unit: Troubleshooting SpecificationsDokument1 SeiteESC63C Series Speed Control Unit: Troubleshooting Specificationsfaraidun100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
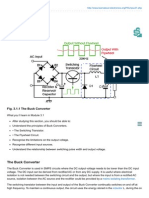
- Buck ConvertersDokument4 SeitenBuck ConvertersAbenav SankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Sai ReportDokument20 SeitenSai ReportGANESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Solar Storage Solution20180709 V3Dokument12 SeitenSolar Storage Solution20180709 V3SathishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Formulation and Calculation of Y-Bus Matrix Using MATLABDokument39 SeitenFormulation and Calculation of Y-Bus Matrix Using MATLABPrasanna UdataNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- APM100 Outdoor Power Supply System User Manual (V1.3)Dokument58 SeitenAPM100 Outdoor Power Supply System User Manual (V1.3)Stephane70Noch keine Bewertungen
- SYS-6010 Service Manul V2.0Dokument50 SeitenSYS-6010 Service Manul V2.0Ahsan Saleem100% (1)
- Automatic Railway Gate Control System Using Arduino Uno PresentationDokument20 SeitenAutomatic Railway Gate Control System Using Arduino Uno PresentationRio Martin100% (1)
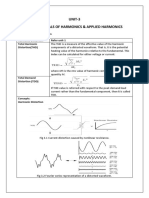
- UNIT-3 Fundamentals of Harmonics & Applied HarmonicsDokument14 SeitenUNIT-3 Fundamentals of Harmonics & Applied Harmonicslvb123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eja510-530 Gs01c31f01-01enDokument11 SeitenEja510-530 Gs01c31f01-01enpalebejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inverters For Grid Connected PV SystemsDokument26 SeitenInverters For Grid Connected PV SystemsDeepti GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Activity-Lab-2-The DC Shunt Generator and MotorDokument14 SeitenActivity-Lab-2-The DC Shunt Generator and MotorDiether PaderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report Group No. 23 ECEDokument8 SeitenProject Report Group No. 23 ECEArvind Gupta100% (1)
- Multi Tool Group (PEHJ0252-00)Dokument14 SeitenMulti Tool Group (PEHJ0252-00)Wilbort Encomenderos RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnet OfferDokument5 SeitenMagnet Offernaren1202Noch keine Bewertungen
- Excitation & AVRDokument16 SeitenExcitation & AVRRandhir Kumar100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Electrical Drives:: Unit - I Drive CharacteristicsDokument22 SeitenElectrical Drives:: Unit - I Drive CharacteristicsJegan8586100% (1)
- Sunny Island 5048 Installation Operation Manual PDFDokument224 SeitenSunny Island 5048 Installation Operation Manual PDFriadhi fairuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCM13/EV experiment board analysis DC, stepper motorsDokument1 SeiteMCM13/EV experiment board analysis DC, stepper motorsHema OkshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2033A ManualDokument52 Seiten2033A ManualfedysiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inductance Calculation Method of Synchronous Reluctance MotorDokument4 SeitenInductance Calculation Method of Synchronous Reluctance MotorAbhishek AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jesmi MiniProjectDokument31 SeitenJesmi MiniProjectAayush SthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JPX01 MDF Product DescriptionDokument33 SeitenJPX01 MDF Product DescriptionAbhishek Srivastava0% (1)
- Plasma Arc Voltage Torch Height Controller: Operation Manual Vision 1404Dokument23 SeitenPlasma Arc Voltage Torch Height Controller: Operation Manual Vision 1404BoroDragovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)