Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
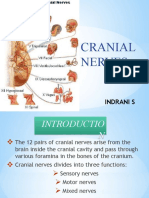
Cranial Nerves Nerve Function Test Extra Notes I. Olfactory
Hochgeladen von
lindsayparvessOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cranial Nerves Nerve Function Test Extra Notes I. Olfactory
Hochgeladen von
lindsayparvessCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
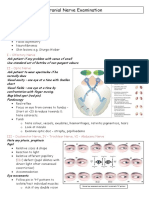
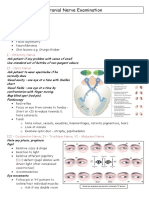
CRANIAL NERVES
NERVE
FUNCTION TEST EXTRA NOTES
I. Olfactory Sense of smell (sensory) Alcohol swab
Food
Not often done
II. Optic Visual pathway (sensory) Cotton wool test
Obstacle course
In conjunction with other parts of neuros not in isolation
Menace reflex:
o Afferent: visual pathway
o Efferent: CN vii ! CN vii (facial) innervates
orbicularis oculi (eyelids) ! Facial nerve paralysis if
lack of blink response
Fixating reflex:
o Afferent: visual pathway
o Efferent: eye movement; CN iii, iv, vi
Pupillary light reflex:
o Afferent: CN ii ! visual tract to optic tract
o Efferent: CN iii ! direct response; parasympathetic
(miosis)
Pupil size & symmetry:
o Mydriasis: sympathetic stimulation / lack of CN iii
(parasympathetic)
o Miosis: excessive parasympathetic / loss of
sympathetic
Horners syndrome:
lesion in sympathetic
supply to the eye
o Miosis
o Ptosis
o Protruding 3
rd
eyelid
o Enopthalmos
Test: Topical application of
phenylepherine into Rt
eye: miosis resolved
rapidly indicating a 3
rd
order lesion in the Rt eye.
III. Oculomotor Parasympathetic to pupillo-
constrictors
Motor to eye muscles
Pupillary light reflex:
o Loss on affected side
o Strabismus: down & out
IV. Trochlear Motor function ! muscles
of the eye
Position of the eyeball:
o Strabismus: dorsomedial
V. Trigeminal 1. Opthalmic branch:
Sensory (cornea, dorsal
nose, forehead)
2. Maxillary branch:
Sensory (face, maxilliary
teeth, palate, nose)
3. Mandibular:
Sensory (lower lip,
mandibualr teeth, tongue)
Motor to muscles of
mastication
Facial sensation:
o Pinching/haemostat
Corneal reflex:
o Blow on eye
o Sensory (V)
o Motor ! blink (VII)
Jaw tone = bilateral = Dropped jaw
Temporal / masseter muscle atrophy
VI. Abducent Motor: lateral rectus muscle
of the eye & retractor bulbi
muscle
Damage: medial strabismus & inability to retract the bulb
Not usually in isolation
VII. Facial Motor to small muscles of
facial expression
Parasympathetic salivary
and lacrimal gland
Sensory (tongue)
Menace reflex:
o Afferent: visual pathway
o Efferent: CN vii ! CN vii (facial) innervates
orbicularis oculi (eyelids) ! Facial nerve paralysis if
lack of blink response
Corneal reflex:
o Blow on eye
o Sensory (V)
o Motor ! blink (VII)
Facial sensation:
o Pinching/haemostat
o Sensory Trigeminal (V)
o Motor Facial (VII)
VIII. Vestibulocochlear Cochlear nerve: hearing
Vestibular nerve:
equilibrium
Cochlear nerve:
o Hand clap
o BAER
Vestibular nerve:
o Nystagmus
o Head tilt
o Circling towards lesion
o Ataxia
Vestibular syndrome:
o Central vs. peripheral
o Is the vestibular
affected in the
brainstem or closer to
the efferent i.e. ears?
*See slides for table?
IX. Glossopharyngeal Sensory to pharynx and
tongue
Motor (with Vagus X) to
pharynx
Parasympathetic to parotid
Gag reflex
Damage: dysphagia
X. Vagus Sensory: Thoracic and
abdominal viscera
Parasympathetic: Thoracic
and abdominal organs
Motor: Pharynx
Moto & sensory: larynx,
trachea, oesophagus
Gag reflex
Cough reflex
Oculo-cardiac reflex (heart rate slows down with pressure
on the eyeball)
Auscultate: borborygmi, tachycardia
XI. Accessory Motor to neck muscles No tests
Atrophy
XII. Hypoglossal Motor to tongue Tongue tone & symmetry
Usually combined with other caudal stem abnormalities
Cranial nerve evaluation:
In clinical practice cranial nerves can be evaluated in groups:
Vision and pupillary light response (II, III, VII)
Palpebral fissure and 3
rd
eyelid symmetry (III, V, sympathetic nerves)
Eyeball position and movement (III, IV, VI, VII)
Vestibular function (VIII)
Facial and trigeminal nerves (V, VII)
Tongue and laryngeal-pharyngeal function (IX, X, XII)
Test in groups/specific signs:
Eyes (Vision, Strabismus, Anisocoria (unequal pupil size), PLR)
Sensation
Movement & position
Swallowing
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Oncology DrugsDokument6 SeitenOncology DrugslindsayparvessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Facial MusclesDokument26 SeitenFacial MusclesAdel Yousef JaffalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurology NotesDokument31 SeitenNeurology NotesArif Setyawan75% (4)
- Oral Pathology Mnemonics for NBDE First Aid: RememberologyVon EverandOral Pathology Mnemonics for NBDE First Aid: RememberologyBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (7)
- Bell's Palsy Facial Nerve ParalysisDokument37 SeitenBell's Palsy Facial Nerve Paralysiswahyu_sitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- .Nervus Cranialis 1-6Dokument30 Seiten.Nervus Cranialis 1-6meiliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Nervous System: Checklist PMPF Checklist PMPFDokument2 SeitenCentral Nervous System: Checklist PMPF Checklist PMPFsalsabeel100% (1)
- Neuro Ophthalmology For Med Student - 2016Dokument120 SeitenNeuro Ophthalmology For Med Student - 2016Surat Tanprawate100% (3)
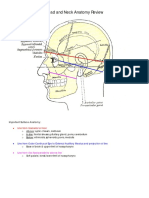
- 1 - Head and Neck Anatomy Review LiteDokument34 Seiten1 - Head and Neck Anatomy Review LiteDiana MitreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRANIALDokument11 SeitenCRANIALDemianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical Incisions: STJ - Dr. Aylin Mert 0902110019Dokument22 SeitenSurgical Incisions: STJ - Dr. Aylin Mert 0902110019NiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chest RadiologyDokument129 SeitenChest RadiologyNadiya SafitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthesia in Day Care SurgeryDokument143 SeitenAnesthesia in Day Care SurgeryGmkmcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modifiers-Table 122015 2Dokument25 SeitenModifiers-Table 122015 2khatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Taking Proforma - Central Nervous SystemDokument8 SeitenCase Taking Proforma - Central Nervous SystemK Haynes Raja95% (37)
- Caesarean SectionDokument23 SeitenCaesarean SectionNurul Fahmiza TumiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurologic Examination English Class2011 1Dokument79 SeitenNeurologic Examination English Class2011 1HieLdaJanuariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A History of MedicineDokument63 SeitenA History of MedicineITZAMNA ALVAREZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Teaching ErcpDokument8 SeitenClinical Teaching ErcpDeep Kaur100% (1)
- Uro MCQDokument12 SeitenUro MCQLouisa Abigail D'Cruz100% (4)
- Medicine Colloquium Exam - 2014 ADokument40 SeitenMedicine Colloquium Exam - 2014 ArachaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination of The Cranial NervesDokument28 SeitenExamination of The Cranial NervesTiara MustikadewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuorlogical Assessment-1Dokument52 SeitenNeuorlogical Assessment-1Salman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNExam PDFDokument3 SeitenCNExam PDFRachel RajkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerve Examination: Prepare PatientDokument3 SeitenCranial Nerve Examination: Prepare PatientLemuel S. JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves ExamDokument58 SeitenCranial Nerves ExamTom JenyonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves Examination Complete PDFDokument41 SeitenCranial Nerves Examination Complete PDFJulie SianquitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurologic Examination: Muhammad Iqbal BasriDokument79 SeitenNeurologic Examination: Muhammad Iqbal Basribima sarewoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerve Examination 341Dokument29 SeitenCranial Nerve Examination 341Chanu HandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cavernous Sinus ThrombosisDokument6 SeitenCavernous Sinus ThrombosismcwnotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial NervesDokument40 SeitenCranial NervesugochukwuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurologic Examination: Based On Demyer'S "The Neurologic Examination, A Programed Text, 6 Edition"Dokument40 SeitenNeurologic Examination: Based On Demyer'S "The Neurologic Examination, A Programed Text, 6 Edition"Michaella MaralitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerve Examination: A Step-by-Step GuideDokument45 SeitenCranial Nerve Examination: A Step-by-Step GuideTanat AsavisanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing The Stroke Patient Boudreaux 2013Dokument25 SeitenAssessing The Stroke Patient Boudreaux 2013wahyu dian ekoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNS ExaminationDokument59 SeitenCNS ExaminationSania ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves: (I) Olfactory (II) OpticDokument1 SeiteCranial Nerves: (I) Olfactory (II) OpticLeahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerve Examination Part IDokument91 SeitenCranial Nerve Examination Part IAARYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Peripheral Nervous System & Autonomic Nervous SystemDokument28 SeitenPeripheral Nervous System & Autonomic Nervous Systemobsgynunair januari18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro Exam - 20 HO-1Dokument96 SeitenNeuro Exam - 20 HO-1cpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latest Dr. Saleh Facial Nerve Applied 16.5.23Dokument85 SeitenLatest Dr. Saleh Facial Nerve Applied 16.5.23Saleh Mohammad ShoaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerve PEDokument22 SeitenCranial Nerve PELoiNingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bells PalsyDokument28 SeitenBells PalsyshadiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP Kelumpuhan Nervus Fasialis Perifer 2Dokument28 SeitenPP Kelumpuhan Nervus Fasialis Perifer 2Just MahasiswaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stroke Infark: Laporan KasusDokument29 SeitenStroke Infark: Laporan KasusNuzulut FianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerve Assessment: Nerve Name Function Test IDokument9 SeitenCranial Nerve Assessment: Nerve Name Function Test IBecky Mariñas ReducaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerve 1 To 6Dokument30 SeitenCranial Nerve 1 To 6Angetile KasangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Approach To The Neuro Exam Feb 2011Dokument35 Seiten2 Approach To The Neuro Exam Feb 2011suaqaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3665 Kelumpuhan Nervus FascialisDokument28 Seiten3665 Kelumpuhan Nervus FascialismardiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial NervesDokument58 SeitenCranial NervesinduNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Minute Neurological Exam: Dr. Al Jin November 17, 2015Dokument14 Seiten5 Minute Neurological Exam: Dr. Al Jin November 17, 2015Shitaljit IromNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNS Examination: Done by DR/ Abdullah Mohd. Jan MBBS, InternDokument37 SeitenCNS Examination: Done by DR/ Abdullah Mohd. Jan MBBS, InternBrajesh MouryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves and Reflexes AssessmentDokument46 SeitenCranial Nerves and Reflexes AssessmentNina KristianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnatomyDokument8 SeitenAnatomystuffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bell'S Palsy: DR Ika Rosdiana, SPRMDokument24 SeitenBell'S Palsy: DR Ika Rosdiana, SPRMMartvera SusilawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerve I - Olfactory NerveDokument6 SeitenCranial Nerve I - Olfactory NerveAysha AishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves 1 6 05122022 124013pmDokument68 SeitenCranial Nerves 1 6 05122022 124013pmHira KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves Guide for NursesDokument4 SeitenCranial Nerves Guide for NursesNatalia OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1cranial NervesDokument48 Seiten1cranial NervesKaarthigan RamaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head, Eyes, Ears, Nose and Throat Exam GuideDokument9 SeitenHead, Eyes, Ears, Nose and Throat Exam GuideironNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head and NeckDokument103 SeitenHead and NeckChester VergilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial NerveDokument3 SeitenCranial NerveBilal SaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves LesionsDokument43 SeitenCranial Nerves LesionsAdilah RadziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurological Exam: H.Khorrami PH.DDokument89 SeitenNeurological Exam: H.Khorrami PH.DHossein KhorramiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro Ophthalmology PDFDokument70 SeitenNeuro Ophthalmology PDFSurat Tanprawate100% (4)
- Inbound 2795149120147640433Dokument52 SeitenInbound 2795149120147640433elainemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuorlogical AssessmentDokument38 SeitenNeuorlogical AssessmentSalman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurologic Ass Faculty - 2023 1st Term-1Dokument29 SeitenNurologic Ass Faculty - 2023 1st Term-1cwley64Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerve Examination GuideDokument74 SeitenCranial Nerve Examination GuideDheeraj Kumar RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNEXAMDokument3 SeitenCNEXAMCabdi Kaafi Maxamad CumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP6 - 6 - Neurological System P2Dokument44 SeitenCP6 - 6 - Neurological System P2dafabc50Noch keine Bewertungen
- Forelimb: 1: Epiphysis of Supraglenoid Tubercle 3: Proximal Epiphysis of Humerus 5: Greater TubercleDokument13 SeitenForelimb: 1: Epiphysis of Supraglenoid Tubercle 3: Proximal Epiphysis of Humerus 5: Greater TuberclelindsayparvessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocular TherapeuticsDokument2 SeitenOcular TherapeuticslindsayparvessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fitness - May 2014 USADokument126 SeitenFitness - May 2014 USAlindsayparvessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells Involved in Acute InflammationDokument4 SeitenCells Involved in Acute InflammationlindsayparvessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aggravating Factors Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDokument4 SeitenAggravating Factors Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsJann ericka JaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tintinalli - Chapter 37 Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in AdultsDokument11 SeitenTintinalli - Chapter 37 Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in AdultsPgmee KimsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Koch AO Manual Chapter 2 2005Dokument45 SeitenKoch AO Manual Chapter 2 2005Juan Guillermo RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conium MaculatumDokument19 SeitenConium MaculatumVinod Kumar100% (1)
- Grace ResumeDokument2 SeitenGrace Resumeapi-486547216Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nabh Application Diagnostic Laboratories Imaging Centres PDFDokument35 SeitenNabh Application Diagnostic Laboratories Imaging Centres PDFPrateek ChaharNoch keine Bewertungen
- DFGHJKDokument3 SeitenDFGHJKcliffwinskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pelvic Planes Dimensions and ContractionTITLEDokument12 SeitenPelvic Planes Dimensions and ContractionTITLEDavid Eka PrasetyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WMed Residency Match 2023Dokument3 SeitenWMed Residency Match 2023WWMTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Carbetocin Vs OxytocinDokument23 SeitenThesis Carbetocin Vs OxytocinHimanshu SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Abstract SupplementDokument360 Seiten2010 Abstract SupplementcatatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology's Books in Departmental LibraryDokument5 SeitenPathology's Books in Departmental LibraryVedant RautelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icmr STS 2019Dokument26 SeitenIcmr STS 2019Kanthimathinathan KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colorectal Cancer: - Dr. Suneet KhuranaDokument36 SeitenColorectal Cancer: - Dr. Suneet KhuranaCarlo ToledooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver EnzymesDokument6 SeitenLiver EnzymesWande AyodeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marzo - Ped 2023Dokument3 SeitenMarzo - Ped 2023miriam arredondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breech Presentation: (English Case)Dokument56 SeitenBreech Presentation: (English Case)Heri FarnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- M Kaavya Sree Balaji Medical College and Hospital IndiaDokument33 SeitenM Kaavya Sree Balaji Medical College and Hospital IndiaNailahRahmahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Twin to twin transfusion syndrome الدكتور ماهر معايطةDokument7 SeitenTwin to twin transfusion syndrome الدكتور ماهر معايطةjordanmedicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biopsy Questions - RDDokument5 SeitenBiopsy Questions - RDTariq Khalid100% (1)
- Consolidated List of Casualties Treated in InfirmaryDokument9 SeitenConsolidated List of Casualties Treated in Infirmaryapi-293976957Noch keine Bewertungen