Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Carbon 20 Compounds 20 With 20 Lipids 1
Hochgeladen von
api-260690009Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Carbon 20 Compounds 20 With 20 Lipids 1
Hochgeladen von
api-260690009Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
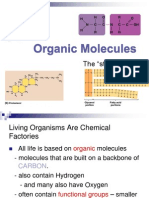
Carbon Compounds
Biology
K. Beris
Carbon Bonding and Functional Groups
Carbon atoms have 4 electrons in its outer shell
They can bond with four different elements
Functional groups
Clusters of atoms
The structural building block that determines
the characteristics of a compound
-OH, the hydroxyl group, is important to living
things
Large Carbon Molecules
In carbon compounds, molecules are built up
from smaller, simpler molecules
Monomerssimple molecules that bonds during
condensation reactions
Polymersmonomers that are bound together
Each releases OH
-
and H
+
which combine to form
water
Hydrolysisreversal of condensation reaction
Needs the addition of water to occur
Energy Currency
Life requires a constant supply of energy
ATP is a compound that contains large
amounts of energy in its overall structure
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are organic compounds composed of carbon,
hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of about 2 H atoms to 1 O
atom
Monosaccharidesa monomer of a carbohydrate
Simple sugar
Contains C, H, and O in a ratio of 1:2:1. Most common monosaccharides
are:
Glucosemain source of energy for the cell
Fructosefound in fruits
galactosefound in milk
These sugars are isomers same chemical formula but
different structural forms
Disaccharides and Polysaccharides
When 2 monosaccharides combine to form a
disaccharide
Examples: (write these in on your notes)
Sucrose
Maltose
Lactose
When 2 or more disaccharides combine, they
will form a polysaccharide
Animals store glucose in the form of glycogen
Plants store glucose as starches
Cellulose is another polysaccharide found in plant cell
walls
Proteins
Organic compounds composed of C, H, O, and N
Formed by the linkage of monomers
Skin and muscles of animals and many of the catalysts
found in plants and animals are made of proteins
Amino acidsthe 20 amino acids are the monomer building blocks for
proteins
They share a basic structure
A central carbon atom covalently bonded to a hydrogen atom
A carboxyl group, -COOH
An amino group, -NH2
A group that varies from amino acid to amino acid
Dipeptides and polypeptides
Dipeptide2 amino acids bond to each other, one at a
time to form a dipeptide
Polypeptideamino acids can bond to each other one at
a time forming a very long chain
Enzymeenzyme reactions depend on a physical fit
between the enzyme molecule and its substrate, the
reactant being catalyzed
An enzyme may fail to work if its environment is changed
pH or temperature change can change the shape of the
enzyme or substrate
Lipids
Lipids are large nonpolar organic molecules that do not
dissolve in water
Have a higher ratio of C and H to O atoms than
carbohydrates do
Fatty acidsunbranched carbon chains that make up
most lipids
Two ends have very different properties
Hydrophilicwater lovingattracted to water molecules
Hydrophobicwater fearingdoes not interact with water
Lipids
Complex lipids
Triglyceridesmade up of 3 molecules of fatty acids
joined to one molecule of alcohol glycerol
Phospholipidshave three fatty acids joined by a
molecule of glycerol
2 layers make up the cell membrane
Waxa long fatty acid chain joined to a long alcohol
chain
Highly waterproof
In plants, forms a protective coating on the outer surfaces
In animals forms protective layers
Lipids, cont.
Steroidssteroid molecules are composed of
4 fused C rings with various functional
groups attached to them
Make up animal hormones and cholesterol
Nucleic Acids
Very large and complex organic molecules that store
information in the cell
2 types
DNAcontains information that is essential for almost all cell
activities
RNAstores and transfers information that is essential for
the manufacturing of proteins
Both DNA and RNA are polymers, composed of
thousands of linked monomers
Nucleotides are made of a phosphate group, a five-
carbon sugar, and a ring-shaped nitrogenous base
Name of
Macromolecule
Carbohydrate Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids
Picture of the
molecule
Elements in the
molecule
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Sulfur
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Categories or
buildinblocks
Table sugar
Malt Sugar
Milk sugar
Monosaccharides
Disaccharides
Sucrose=glucose+ fructose
Maltose=glucose+ glucose
Lactose=glucose+ galactose
Amino acids glycerol and fatty
acids
Nucleotides
Examples Glucose, fructose, lactose,
galactose, glycogen, starch,
cellulose
Hair, skin, spider
webs, feathers,
turtle shells,
fingernails, bones
Cell membranes
Waxes
Oils
Cholesterol
DNA and RNA
Examples of
food sources
Sugar, cake, pie, breads,
pasta, rice, potatoes, candy,
soda pop
Peanut butter,
meat, beans
Vegetable oil
Peanut oil
Lard
butter
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 4Dokument62 SeitenChapter 4Eva NatashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument60 SeitenChapter 5EhazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein PDFDokument36 SeitenProtein PDF2d HoehoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Structure and Function of MacromoleculesDokument44 SeitenThe Structure and Function of MacromoleculesSerap BayramNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Structure and Function of MacromoleculesDokument50 SeitenThe Structure and Function of MacromoleculesVeronica P. CapoteNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP BIO MACROMOLECULES Chapter 5 ReviewDokument35 SeitenAP BIO MACROMOLECULES Chapter 5 Reviewrina muliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio MoleculesDokument47 SeitenBio MoleculesVivaMapwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP BIO MACROMOLECULES Chapter 5 ReviewDokument35 SeitenAP BIO MACROMOLECULES Chapter 5 Reviewsheila may valiao-de asisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of Cells: Chapter 2, Section 3Dokument40 SeitenChemistry of Cells: Chapter 2, Section 3idreesnazimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 ChemicalDokument4 SeitenChapter 2 ChemicalAya GhanamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2Dokument53 SeitenModule 2Andrian SiscarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Life?Dokument39 SeitenWhat Is Life?Kristel AbbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macromolecules: - Most Are Polymers - PolymerDokument37 SeitenMacromolecules: - Most Are Polymers - PolymerElvis wuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemicals of LifeDokument26 SeitenChemicals of LifeDenise CampuedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio EnergeticsDokument107 SeitenBio Energeticstiaria.wilson24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Human Systems Chapter 8 - DigestionDokument125 SeitenHuman Systems Chapter 8 - Digestionallie3dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Molecules: Chapter 2-3Dokument33 SeitenOrganic Molecules: Chapter 2-3Gissele AbolucionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Basis of Life Organic Compounds: By: Ej R. Agsalda Bsbio-1Dokument15 SeitenChemical Basis of Life Organic Compounds: By: Ej R. Agsalda Bsbio-1Ej AgsaldaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Molecules of LifeDokument175 SeitenThe Molecules of LifeTiffany BheaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 9Dokument29 SeitenModule 9Andrew Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating and Breaking Down Polymers:: Inability To Digest The Sugar in MilkDokument3 SeitenCreating and Breaking Down Polymers:: Inability To Digest The Sugar in MilkJessa Dela Cruz - RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemical Building Blocks of Life (Chapter 3) Nucleic Acids, Lipids and CarbohydratesDokument29 SeitenThe Chemical Building Blocks of Life (Chapter 3) Nucleic Acids, Lipids and Carbohydratesashakiobrien0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biomolecules: Lynnette A. EjemDokument103 SeitenBiomolecules: Lynnette A. EjemAirene Mae SupilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Humans in The World of Biology Humans in The World of BiologyDokument32 SeitenHumans in The World of Biology Humans in The World of BiologyJEANNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2. Biological MoleculesDokument6 Seiten2.2. Biological Moleculesstu.suman-iftikharNoch keine Bewertungen
- The "Stuff" of LifeDokument46 SeitenThe "Stuff" of LifeMarcela UrbnNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biochemistry Crash CourseDokument18 SeitenThe Biochemistry Crash CourseJassel DurdenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci9 M 2 3 - Carbon CompoundsDokument35 SeitenSci9 M 2 3 - Carbon Compoundsredox franciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMD Topic 1 - Organic Compounds and EnzymesDokument51 SeitenRMD Topic 1 - Organic Compounds and Enzymesz4g4v7gkzjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio G11 Unit 2 PPXDokument65 SeitenBio G11 Unit 2 PPXBereket NetsanetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomolecules: Dr. Vishwajeet S. GhorpadeDokument49 SeitenBiomolecules: Dr. Vishwajeet S. GhorpadeVishwajeet GhorpadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 - Biological Macromolecules - HandoutDokument9 SeitenLecture 3 - Biological Macromolecules - HandoutJayson Llamasares0% (1)
- CH 4Dokument26 SeitenCH 4Samantha Shane P. ConumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biotech NotesDokument15 SeitenBiotech NotesJadeal28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science-Finals ReviewerDokument18 SeitenPhysical Science-Finals ReviewerPrecious Miracle Lucas SacataniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 BayoDokument10 SeitenChapter 5 BayoWee-Weh HamjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemistry of LifeDokument32 SeitenThe Chemistry of LifeHaniel David BesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2. Molecules and MembranesDokument49 SeitenUnit 2. Molecules and MembranesArio AhmadieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Compounds (From Google)Dokument27 SeitenCarbon Compounds (From Google)Luzel AnferneeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Importance of Organic Compound: Represented By: Moawiz Gondal Reg: Bsen02203018 Course: BiologyDokument13 SeitenBiological Importance of Organic Compound: Represented By: Moawiz Gondal Reg: Bsen02203018 Course: BiologyMoawiz GondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 101 - Integrated Principles of Zoology 18th Edition (Summary of Chapter 2)Dokument10 SeitenBio 101 - Integrated Principles of Zoology 18th Edition (Summary of Chapter 2)Kaeya's asscheeksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 Complete Study GuideDokument38 SeitenTopic 2 Complete Study GuidechalihflNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Basis of Living OrganismsDokument20 SeitenChemical Basis of Living Organismsapi-320180050Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session 1 Biomolecules Part 1Dokument47 SeitenSession 1 Biomolecules Part 1Clemence Marie FuentesNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiomoleculesDokument28 SeitenBiomoleculesprincessmagpatocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Part 1 复习资料2Dokument4 SeitenBio Part 1 复习资料2Tianjia MaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Elements of Life: TB-BA-2: 18-4-2022Dokument5 SeitenEssential Elements of Life: TB-BA-2: 18-4-2022Khánh NhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Organic CompoundsDokument27 SeitenStructure of Organic CompoundsBetty Weiss100% (1)
- BiochemistryDokument73 SeitenBiochemistrylujainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2. Biological MoleculesDokument5 Seiten2.2. Biological MoleculesChung Pui SzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4Dokument27 SeitenCH 4Aubry DurangparangNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Brief Review of Chemistry: Positively ChargedDokument50 SeitenA Brief Review of Chemistry: Positively ChargedElijah PunzalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical Molecules Unit 2 G 11Dokument9 SeitenBiochemical Molecules Unit 2 G 11eyosiyas tekleweyinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 Lipids ProteinsDokument21 SeitenWeek 3 Lipids Proteinssabeera.ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Function of MacromoleculesDokument19 SeitenStructure and Function of MacromoleculesMaretaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological MoleculesDokument98 SeitenBiological MoleculesSuyashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walang MakakaseethisDokument3 SeitenWalang MakakaseethisAlissa YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science Lesson 4 - Structure and Function of BiomoleculesDokument38 SeitenPhysical Science Lesson 4 - Structure and Function of Biomoleculesrainjarrenperegrino13298Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson: 2.2 Carbon Based Molecules Week 6Dokument3 SeitenLesson: 2.2 Carbon Based Molecules Week 6Menna FouadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsVon EverandAnatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic Basis of Inheritance-FinalPDFDokument16 SeitenGenetic Basis of Inheritance-FinalPDFknlsinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrolysis of Intact ProteinDokument4 SeitenHydrolysis of Intact ProteinChloe Valena67% (3)
- 7.2 Gaseous Exchange in PlantsDokument17 Seiten7.2 Gaseous Exchange in PlantsTheresa IzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOCHEMISTRY BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS-answersDokument7 SeitenBIOCHEMISTRY BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS-answerschristinejoan100% (5)
- Biotechnology Principles & ProcessesDokument3 SeitenBiotechnology Principles & ProcessesKambaska Kumar BeheraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Theory of Evolution Throughout HistoryDokument18 SeitenThe Theory of Evolution Throughout HistoryTupu AdreNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5) Late Postmortem ChangesDokument34 Seiten5) Late Postmortem ChangesenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SchedulesDokument193 SeitenSchedulesSuresh ParamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haemin Crystals LabDokument6 SeitenHaemin Crystals LabNaiomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flowchart GaDokument1 SeiteFlowchart GaSidney Bruce ShikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Production of PenicillinDokument9 SeitenIndustrial Production of Penicillinssthakurleo100% (11)
- Taxonomy PDFDokument15 SeitenTaxonomy PDFSwarup MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam #1 KeyDokument9 SeitenExam #1 KeyCaitlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Metabolism: Dr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman Associate Professor Department of PharmacognosyDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Metabolism: Dr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman Associate Professor Department of PharmacognosyAnonymous TCbZigVqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.lymphatic SysDokument43 Seiten6.lymphatic SysMai Z HaniyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Biology SL - 2024 Prediction Exam - May 2024 Paper 1Dokument16 SeitenIB Biology SL - 2024 Prediction Exam - May 2024 Paper 1Christy HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISCED-f 2013 Detailed Field DescriptionsDokument96 SeitenISCED-f 2013 Detailed Field DescriptionsToni D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fetal Developmental MilestonesDokument28 SeitenFetal Developmental MilestonesShahad HakimuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbial DiversityDokument6 SeitenMicrobial DiversityDev AnandhNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlgaeDokument53 SeitenAlgaeDeepika KVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tobacco Etch Virus Protease: A Shortcut Across BiotechnologiesDokument16 SeitenTobacco Etch Virus Protease: A Shortcut Across BiotechnologiesNhật ThiệnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digeorge Syndrome: Rupesh Mohandas GR3Dokument18 SeitenDigeorge Syndrome: Rupesh Mohandas GR3Rupesh MohandasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Science SyllabusDokument5 SeitenEnvironmental Science Syllabusapi-262589183Noch keine Bewertungen
- GMOs - Environmental Concerns - Garden OrganicDokument1 SeiteGMOs - Environmental Concerns - Garden OrganicAndyPandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Domestication Genetics WheatDokument21 SeitenDomestication Genetics Wheatari novitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- NC-AhR Diminishes The Efficacy of Chemotherapy Via Suppressing STING Dependent Type-I Interferon in Bladder CancerDokument17 SeitenNC-AhR Diminishes The Efficacy of Chemotherapy Via Suppressing STING Dependent Type-I Interferon in Bladder Cancerzhe zhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Action of EpinephrineDokument5 SeitenMechanism of Action of EpinephrineKhalid HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rat DissectionDokument15 SeitenRat Dissectionapi-233187566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Studentdatainterp Sexual-SelectionDokument5 SeitenStudentdatainterp Sexual-SelectionParnoor SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wound Healing - Alternatives in Management PDFDokument68 SeitenWound Healing - Alternatives in Management PDFHealer MobeiusNoch keine Bewertungen