Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Good Manufacturing Practices
Hochgeladen von
Shweta SaxenaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Good Manufacturing Practices
Hochgeladen von
Shweta SaxenaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Good manufacturing practice
Good manufacturing practices (GMP) refer to guidelines laid down by agencies which control
authorization and licensing for manufacture and sale of food, drug products , and active
pharmaceutical products. These guidelines are laid down with the intention of providing
minimum requirements that a pharmaceutical or a food product manufacturer must meet while
manufacturing drugs or food products ,which then assures that the products
manufactured/produced are of high quality and do not pose any risk to the consumer or public.
Good manufacturing practice guidelines provides guidance for manufacturing, testing, and
quality assurance in order to ensure that drug product is safe for human consumption. Many
countries have legislated that pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturer must follow
GMP procedures, and have created their own GMP guidelines that correspond with their
legislation. Basic concepts of all of these guidelines remain more or less similar to the ultimate
goals of safeguarding the health of patient as well as producing good quality medicine, medical
devices or active pharmaceutical products. In the U.S.A a drug may be deemed adulterated even
though it has passed all of the specifications tests and it is found to be manufactured in a facility
or condition which violates or do not comply with current good manufacturing guideline.
Therefore complying with GMP is a mandatory aspect in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Although there are a number of them, all guidelines follow a few basic principles:
Hygiene: Pharmaceutical manufacturing facility must maintain a clean and hygienic
manufacturing area.
Controlled environmental conditions in order to prevent cross contamination of drug
product from other drug or extraneous particulate matter which may render the drug
product unsafe for human consumption.
Manufacturing processes are clearly defined and controlled. All critical processes are
validated to ensure consistency and compliance with specifications.
Manufacturing processes are controlled, and any changes to the process are evaluated.
Changes that have an impact on the quality of the drug are validated as necessary.
Instructions and procedures are written in clear and unambiguous language. (Good
Documentation Practices)
Operators are trained to carry out and document procedures.
Records are made, manually or by instruments, during manufacture that demonstrate that
all the steps required by the defined procedures and instructions were in fact taken and
that the quantity and quality of the drug was as expected. Deviations are investigated and
documented.
Records of manufacture (including distribution) that enable the complete history of a
batch to be traced are retained in a comprehensible and accessible form.
The distribution of the drugs minimizes any risk to their quality.
A system is available for recalling any batch of drug from sale or supply.
Complaints about marketed drugs are examined, the causes of quality defects are
investigated, and appropriate measures are taken with respect to the defective drugs and
to prevent recurrence.
GMP guidelines are not prescriptive instructions on how to manufacture products. They are a
series of general principles that must be observed during manufacturing. When a company is
setting up its quality program and manufacturing process, there may be many ways it can fulfill
GMP requirements. It is the company's responsibility to determine the most effective and
efficient quality process.
Facts About Current Good Manufacturing
Practices (cGMPs)
Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) for human pharmaceuticals affect every American.
Consumers expect that each batch of medicines they take will meet quality standards so that they will
be safe and effective. Most people, however, are not aware of cGMPs, or how FDA assures that drug
manufacturing processes meet these basic objectives. Recently, FDA has announced a number of
regulatory actions taken against drug manufacturers based on the lack of cGMPs.
What are cGMPs?
cGMP refers to the Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations enforced by the US Food
and Drug Administration (FDA). cGMPs provide for systems that assure proper design,
monitoring, and control of manufacturing processes and facilities. Adherence to the cGMP
regulations assures the identity, strength, quality, and purity of drug products by requiring that
manufacturers of medications adequately control manufacturing operations. This includes
establishing strong quality management systems, obtaining appropriate quality raw materials,
establishing robust operating procedures, detecting and investigating product quality deviations,
and maintaining reliable testing laboratories. This formal system of controls at a pharmaceutical
company, if adequately put into practice, helps to prevent instances of contamination, mix-ups,
deviations, failures, and errors. This assures that drug products meet their quality standards.
The cGMP requirements were established to be flexible in order to allow each manufacturer to
decide individually how to best implement the necessary controls by using scientifically sound
design, processing methods, and testing procedures. The flexibility in these regulations allows
companies to use modern technologies and innovative approaches to achieve higher quality
through continual improvement.
Why are cGMPs so important?
A consumer usually cannot detect (through smell, touch, or sight) that a drug product is safe or if
it will work. While cGMPs require testing, testing alone is not adequate to ensure quality. In
most instances testing is done on a small sample of a batch (for example, a drug manufacturer
may test 100 tablets from a batch that contains 2 million tablets), so that most of the batch can be
used for patients rather than destroyed by testing. Therefore, it is important that drugs are
manufactured under conditions and practices required by the cGMP regulations to assure that
quality is built into the design and manufacturing process at every step. Facilities that are in
good condition, equipment that is properly maintained and calibrated, employees who are
qualified and fully trained, and processes that are reliable and reproducible, are a few examples
of how cGMP requirements help to assure the safety and efficacy of drug products.
If a manufacturer is not following cGMPs, are drug products safe for use?
If a company is not complying with cGMP regulations, any drug it makes is considered
adulterated under the law. This kind of adulteration means that the drug was not
manufactured under conditions that comply with cGMP. It does not mean that there is
necessarily something wrong with the drug.
For consumers currently taking medicines from a company that was not following cGMPs, FDA
usually advises these consumers not to interrupt their drug therapy, which could have serious
implications for their health. Consumers should seek advice from their health care professionals
before stopping or changing medications. Regulatory actions against companies with poor
cGMPs are taken as a preventive measure because the manufacturing processes do not meet
FDAs regulatory standards. By focusing on the procedures and processes used to make these
drugs, FDA is working to ensure that drugs meet their quality standards and are safe and
effective. The impact of cGMP violations depends on the nature of those violations and on the
specific drugs involved. A drug manufactured in violation of cGMP may still meet its labeled
specifications, and the risk that the drug is unsafe or ineffective could be minimal. Thus, FDAs
advice will be specific to the circumstances, and health care professionals are best able to
balance risks and benefits and make the right decision for their patients.
How would a new drug company learn about cGMPs and about FDAs expectations on complying with
them?
FDA publishes regulations and guidance documents for industry in the Federal Register. This is how the
federal government notifies the public of what we are doing and how we do it. FDAs website,
www.fda.gov also contains links to the cGMP regulations, guidance documents, and various resources to
help drug companies comply with the law. FDA also conducts extensive public outreach through
presentations at national and international meetings and conferences, to discuss and explain the cGMP
requirements, the latest policies, and the Agencys expectations. Guidance on the cGMP regulations
can also be obtained through FDAs Small Business Representatives that are located throughout the
country, through FDA District Offices, and from the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Office of
Compliance, Division of Manufacturing and Product Quality.
-
-
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- BSBITU314 Assessment Workbook FIllableDokument51 SeitenBSBITU314 Assessment Workbook FIllableAryan SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 04Dokument19 SeitenCH 04Charmaine Bernados BrucalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry 1Dokument265 SeitenOrganic Chemistry 1Israk Mustakim IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asterisk NowDokument82 SeitenAsterisk Nowkambojk100% (1)
- Importance of Communications 05sept2023Dokument14 SeitenImportance of Communications 05sept2023Sajib BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Focus Edition From GC: Phosphate Bonded Investments For C&B TechniquesDokument35 SeitenFocus Edition From GC: Phosphate Bonded Investments For C&B TechniquesAlexis De Jesus FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- JFC 180BBDokument2 SeitenJFC 180BBnazmulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle Grinder Gws 7 100 06013880f0Dokument128 SeitenAngle Grinder Gws 7 100 06013880f0Kartik ParmeshwaranNoch keine Bewertungen
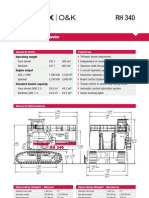
- Hydraulic Mining ExcavatorDokument8 SeitenHydraulic Mining Excavatorasditia_07100% (1)
- Dakua Makadre PresentationDokument12 SeitenDakua Makadre PresentationEli Briggs100% (1)
- Ajmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalDokument45 SeitenAjmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalNikita KadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To BiogasDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To BiogasLouis EldertardNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS8CHP EletricalDokument52 SeitenCS8CHP EletricalCristian ricardo russoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Geoelectric Method For GroundwaterDokument11 SeitenApplication of Geoelectric Method For GroundwaterMunther DhahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epreuve Anglais EG@2022Dokument12 SeitenEpreuve Anglais EG@2022Tresor SokoudjouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data StructuresDokument4 SeitenData StructuresBenjB1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus PDFDokument3 SeitenSyllabus PDFBibin Raj B SNoch keine Bewertungen
- TraceDokument5 SeitenTraceNorma TellezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Repair Manual (2017)Dokument59 SeitenConcrete Repair Manual (2017)Fernando EscriváNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - Basic ProbabilityDokument37 SeitenChapter 4 - Basic Probabilitynadya shafirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Letter To Hon. Nitin Gadkari On Pothole Problem On National and Other Highways in IndiaDokument3 SeitenOpen Letter To Hon. Nitin Gadkari On Pothole Problem On National and Other Highways in IndiaProf. Prithvi Singh KandhalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar - Strengths and WeaknessesDokument5 SeitenComparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar - Strengths and WeaknessesMostafa AbdelrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 82686b - LOAD SHARING MODULEDokument2 Seiten82686b - LOAD SHARING MODULENguyễn Đình ĐứcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transportasi Distribusi MigasDokument25 SeitenTransportasi Distribusi MigasDian Permatasari100% (1)
- Feed-Pump Hydraulic Performance and Design Improvement, Phase I: J2esearch Program DesignDokument201 SeitenFeed-Pump Hydraulic Performance and Design Improvement, Phase I: J2esearch Program DesignJonasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arduino Uno CNC ShieldDokument11 SeitenArduino Uno CNC ShieldMărian IoanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 W-2 Gross Wages CityDokument16 Seiten2016 W-2 Gross Wages CityportsmouthheraldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Back Propagation Neural NetworkDokument10 SeitenBack Propagation Neural NetworkAhmad Bisyrul HafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Эквивалентная Схема Мотра Теслы с Thomas2020Dokument7 SeitenЭквивалентная Схема Мотра Теслы с Thomas2020Алексей ЯмаNoch keine Bewertungen
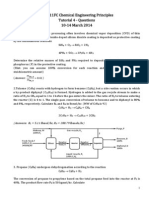
- CN1111 Tutorial 4 QuestionDokument3 SeitenCN1111 Tutorial 4 Questionthenewperson0% (1)