Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
SJ 1
Hochgeladen von
ray72roOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SJ 1
Hochgeladen von
ray72roCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sanjiao Channel
1
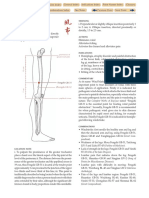
GUANCHONG SJ-1
Rushing Pass
Jing-Well and Metal point of the Sanjiao channel
LOCATION
On the dorsal aspect of the ring finger, at the junction of
lines drawn along the ulnar border of the nail and the base
of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the
nail.
NEEDLING
Perpendicular or oblique insertion directed proximally
0.1 to 0.2 cun, or prick to bleed.
ACTIONS
Clears upper jiao heat
Benefits the ears and tongue
Activates the channel and alleviates pain
INDICATIONS
Tinnitus, deafness, earache, stiff tongue, curled
tongue, pain at the root of the tongue, cracked
tongue, dryness of the mouth, dry lips, bitter taste in
the mouth, headache, wind dizziness and headache,
redness of the eyes, superficial visual obstruction,
throat painful obstruction, pain of the submandibu-
lar region, dark complexion.
Febrile disease, congested heat of the Sanjiao, con-
gested heat of the upper jiao, heat in the body like
fire, fever, fever with absence of sweating, chills and
fever, fever with agitation, oppression of the Heart
with absence of sweating, Heart pain.
Sudden turmoil disorder, vomiting of sour fluid, no
pleasure in eating.
Pain of the elbow and shoulder, pain of the shoulder
and back with inability to turn and look backwards.
COMMENTARY
As the jing-well point, Guanchong SJ-1 is the terminal
point of the Sanjiao channel, and in common with the
other jing-well points has its most powerful influence on
the opposite end of the channel. The primary action of
Guanchong SJ-1 is in clearing heat affecting the upper jiao,
and as a jing-well point it is mainly used for acute symp-
toms. This action is reflected in two main ways: i. clearing
heat from the channel, and ii. treating febrile diseases of
external origin.
The Song of the Jade Dragon recommends Guanchong
SJ-1 for 'congested Sanjiao heat in the upper jiao' and says
bleeding this point will remove toxic blood. The upper
portion of the Sanjiao channel originates in the chest and
ascends via the neck to the ear, temple, inferior aspect of
the eye and outer canthus. If exterior heat (primarily
wind-heat) or interior heat (mainly Liver heat which
transmits to the foot shaoyang Gall Bladder channel and
thence to the hand shaoyang Sanjiao channel) obstruct the
Sanjiao channel there may be tinnitus, deafness, earache,
headache, dizziness, redness of the eyes, throat painful
obstruction etc. The Sanjiao sinew channel ascends to the
root of the tongue and Guanchong SJ-1 has a special
affinity for this area. It is indicated for stiff tongue (usually
due to heat injuring body fluids), curled tongue (usually
due to excess or deficiency fire of the Heart) and cracked
tongue (usually due to heat scorching body fluids), as well
as pain at the root of the tongue.
There are three main systems for differentiating fevers
in the corpus of Chinese medicine: i. according to the six
channels, ii. according to the four levels, and iii. according
to the sanjiao (three jiao). The sanjiao theory divides the
body into three portions, the upper, middle and lower
jiao. According to this method of differentiating fevers
(developed by Wu Ju-tong in the Systematic Differentiation
of Warm Diseases) the upper jiao corresponds to the Lung
and Pericardium. The Warp and Woof of Warm Febrile
Diseases explains When a warm pathogen attacks the
upper body, first it invades the Lung; it is then transmitted
to the Pericardium. As far as exterior pathogenic heat
attacking the Lung is concerned, this corresponds to the
taiyang channel stage and the defensive level in the
Guanchong SJ-1
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Lung
L. Intestine
Stomach
Spleen
Heart
S. Intestine
Bladder
Kidney
Pericardium
Sanjiao
Gall Bladder
Liver
Conception
Governing
Extra Points
See Notes
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Sanjiao Channel 2
differentiations according to the six channels and the four
levels respectively, and is the most exterior and superfi-
cial stage of fever, manifesting with chills and fever,
headache, sore throat, and redness of the eyes. If exterior
pathogenic heat penetrates deeper to attack the Pericar-
dium, the heat condenses the body fluids to form phlegm.
Phlegm-heat then obstructs the Pericardium and disturbs
the spirit, giving rise to such symptoms as high fever with
agitation, Heart pain, dry mouth with a bitter taste, and
stiff or curled tongue. Since Guanchong SJ-1 is able to
dispel pathogenic heat and wind-heat from the upper jiao
as a whole and from its interiorly-exteriorly coupled
Pericardium channel in particular, it is therefore able to
treat both these patterns.
It is interesting to note that in general, points of the
Sanjiao channel treat fevers at the defensive and qi levels
and the Lung pattern, whilst points of the Pericardium
channel treat the nutritive and blood levels and the Pericar-
dium pattern (see Discussion). Since the defensive level, qi
level and Lung patterns are relatively more superficial and
yang, this reflects the interior-exterior relationship of this
yin-yang pair of channels. As the jing-well point of the
Sanjiao channel where the qi of the Pericardium enters the
Sanjiao, however, Guanchong SJ-1 is ideally suited to
treat both the Lung and Pericardium patterns.
Guanchong SJ-1 is indicated in two other conditions.
Firstly, acute disharmony of the Stomach and intestines
manifesting as sudden turmoil disorder, vomiting of sour
fluid and loss of appetite, reflecting the interior pathway
of the Sanjiao primary channel to the middle and lower
jiao. Secondly, it appears in a number of classical combi-
nations for the treatment of wasting and thirsting disorder,
reflecting its ability to clear heat and moisten dryness of
the mouth and lips.
COMBINATIONS
Deafness: Guanchong SJ-1 and Zuqiaoyin GB-44
(Spiritual Pivot).
Tinnitus and deafness: Guanchong SJ-1, Xiaguan
ST-7, Yangxi L.I.-5, Yemen SJ-2 and Yanggu SI-5 (Sys-
tematic Classic).
Ear pain, deafness and tinnitus: Guanchong SJ-1,
Yemen SJ-2, Zhongzhu SJ-3, Tianchuang SI-16 and
Yangxi L.I.-5, (Thousand Ducat Formulas).
Wind dizziness and headache: Guanchong SJ-1,
Kunlun BL-60, Tianyou SJ-16, Fengmen BL-12 and
Guanyuan REN-4 (Thousand Ducat Formulas).
Throat painful obstruction, curled tongue and dry
mouth: Guanchong SJ-1, Zuqiaoyin GB-44 and
Shaoze SI-1 (Thousand Ducat Formulas).
Flaccid tongue with inability to speak: Guanchong
SJ-1 and Yamen DU-15 (One Hundred Patterns).
Wasting and thirsting disorder with great desire to
drink: Guanchong SJ-1, Chengjiang REN-24, Rangu
KID-2 and Yishe BL-49 (Thousand Ducat Formulas).
Heat sensation of the shoulder with inability to turn
the head: Guanchong SJ-1, Jianzhen SI-9 and Jianyu
L.I.-15 (Thousand Ducat Formulas).
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Lung
L. Intestine
Stomach
Spleen
Heart
S. Intestine
Bladder
Kidney
Pericardium
Sanjiao
Gall Bladder
Liver
Conception
Governing
Extra Points
See Notes
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Vaccination Curse 00 Pee BDokument344 SeitenVaccination Curse 00 Pee BLeona King100% (4)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Yi Notes PDFDokument19 SeitenYi Notes PDFEe6803100% (1)
- 5th Grade Basic Skills Reading Comprehension and Skills PDFDokument49 Seiten5th Grade Basic Skills Reading Comprehension and Skills PDFAugusto Castellano100% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Emotions Essential Oils 6th EnlightenDokument271 SeitenEmotions Essential Oils 6th Enlightenray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Unisystem PiratesDokument8 SeitenUnisystem PiratesAnime300100% (1)
- A Dark Brown Dog by Stephen CraneDokument13 SeitenA Dark Brown Dog by Stephen CraneDayangFauziah Bt AwangAhetNoch keine Bewertungen
- FourSacredSeasons EbookDokument19 SeitenFourSacredSeasons EbookLouis Lee Hires100% (3)
- Gui NotesDokument18 SeitenGui Notesffmbdrng100% (8)
- Zuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The FootDokument2 SeitenZuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The Footray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yang Earth Joye Yap PDFDokument18 SeitenYang Earth Joye Yap PDFSerenity Serenity100% (3)
- Three Faces of Hecate - Ritual PDFDokument3 SeitenThree Faces of Hecate - Ritual PDFEric TuckerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pest ControlDokument2 SeitenPest ControlmaxkerandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BaZi - Notes On Yang Metal, GengDokument18 SeitenBaZi - Notes On Yang Metal, GengMoses YeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zak's Class SystemDokument115 SeitenZak's Class SystemGeorge Quail100% (2)
- Introduction To Thai Foot MassageDokument2 SeitenIntroduction To Thai Foot MassageinnasulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Spinal KriyaDokument2 SeitenBasic Spinal KriyaGabriel C100% (3)
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDokument2 SeitenNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeGabriel Tolentino70% (10)
- Jiang Notes PDFDokument19 SeitenJiang Notes PDFffmbdrngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Da Liu Ren: Hour Day Month Year SpiritsDokument2 SeitenDa Liu Ren: Hour Day Month Year Spiritsray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dog Training Methods ReviewDokument48 SeitenDog Training Methods Reviewnagorelasfuentes100% (1)
- Esthetic Rehabilitation of A Severely Worn Dentition With MIPPDokument22 SeitenEsthetic Rehabilitation of A Severely Worn Dentition With MIPPKarla Margine PérezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructions Ffmpeg MacDokument3 SeitenInstructions Ffmpeg Macray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLR 2021 04 18 14 00Dokument3 SeitenDLR 2021 04 18 14 00ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLR 2021 04 18 08 00Dokument3 SeitenDLR 2021 04 18 08 00ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLR 2021 04 18 10 00Dokument3 SeitenDLR 2021 04 18 10 00ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructions Ffmpeg WinDokument3 SeitenInstructions Ffmpeg Winray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLR 2021 04 18 02 00Dokument3 SeitenDLR 2021 04 18 02 00ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLR 2021 04 18 06 00Dokument3 SeitenDLR 2021 04 18 06 00ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes: Gall Bladder ChannelDokument1 SeiteNotes: Gall Bladder Channelray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zhongdu Gb-32: Middle DitchDokument1 SeiteZhongdu Gb-32: Middle Ditchray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gall Bladder Channel of Foot ShaoyangDokument6 SeitenThe Gall Bladder Channel of Foot Shaoyangray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guangming Gb-37: Bright LightDokument2 SeitenGuangming Gb-37: Bright Lightray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- GB 34Dokument3 SeitenGB 34ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- GB 36Dokument1 SeiteGB 36ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zulinqi Gb-41: Foot Governor of TearsDokument2 SeitenZulinqi Gb-41: Foot Governor of Tearsray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- GB 39Dokument2 SeitenGB 39ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yangjiao Gb-35: Gall Bladder Channel 1Dokument1 SeiteYangjiao Gb-35: Gall Bladder Channel 1ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- GB 30Dokument2 SeitenGB 30ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- GB 31Dokument2 SeitenGB 31ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- GB 38 PDFDokument2 SeitenGB 38 PDFray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Juliao Gb-29: Stationary CreviceDokument1 SeiteJuliao Gb-29: Stationary Creviceray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toulinqi Gb-15: Gall Bladder Channel 1Dokument1 SeiteToulinqi Gb-15: Gall Bladder Channel 1ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Support For WSU Researcher Dr. RobbinsDokument12 SeitenSupport For WSU Researcher Dr. RobbinsKaitlin RiordanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gender in English and ArabicDokument20 SeitenGender in English and ArabicKhawla Adnan100% (1)
- Vem007 Sas01Dokument8 SeitenVem007 Sas01wgyk54ypkmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broiler Rearing CIG Training ManualDokument31 SeitenBroiler Rearing CIG Training ManualAL MAMUN BIN SALIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.2 RT Summarizing PracticeDokument5 Seiten6.2 RT Summarizing PracticeMoulay Mohamed (Student) Bouabd ElliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laxative and Purgative HerbsDokument2 SeitenLaxative and Purgative HerbsqueencelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slideshow 3rd Grade Species - Western BluebirdDokument24 SeitenSlideshow 3rd Grade Species - Western Bluebirdapi-553036288Noch keine Bewertungen
- Product Catalogue 2010Dokument112 SeitenProduct Catalogue 2010Dennis NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Proposal For GrantDokument8 SeitenSample Proposal For GrantRomee SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Form For NimDokument1 SeiteMedical Form For NimvishalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rehab Neglected HorseDokument15 SeitenRehab Neglected HorseABNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black Caviar Blog 10Dokument2 SeitenBlack Caviar Blog 10bruce6526Noch keine Bewertungen
- Paket 1 Un Bahasa Inggris 18-19Dokument81 SeitenPaket 1 Un Bahasa Inggris 18-19Rafirli Yuspa Al HafizNoch keine Bewertungen
- WF 2Dokument4 SeitenWF 2Mario TrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zebra Puzzle GuideDokument3 SeitenZebra Puzzle GuideLightFinderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain Training Dogs (Develops Your Dog's "Hidden Intelligence")Dokument16 SeitenBrain Training Dogs (Develops Your Dog's "Hidden Intelligence")JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dossier 2nd Grade Unit1-4Dokument34 SeitenDossier 2nd Grade Unit1-4Paolita RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- การเคลื่อนที่ของสิ่งมีชีวิตDokument1 Seiteการเคลื่อนที่ของสิ่งมีชีวิตธีรนัย เสารางทอยNoch keine Bewertungen