Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ball Mill Testingjune99
Hochgeladen von
Shakil Ahmad83%(6)83% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (6 Abstimmungen)
655 Ansichten29 SeitenBALL MILL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenBALL MILL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
83%(6)83% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (6 Abstimmungen)
655 Ansichten29 SeitenBall Mill Testingjune99
Hochgeladen von
Shakil AhmadBALL MILL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 29
Ball Mill Testing
Cement / Raw Mills
D.Baird /Sean Haseldine
OBJECTIVES
To Establish Actual Performance Criteria
To Identify the Problem Areas
To resolve the Problems and Optimise the mill
Product Residues (Raw Meal)
Surface Area (Blaine / L+N)
Feed Quality Clinker / Gypsum ratio
Clinker chemistry
C3S / C2S
Feed size
Monitoring mill operation
Establish the facts
Mill Throughput Tonnes /h
Power Used kWh - Mill + Ancillaries
Temperature Degrees C
Air Flow Kg air /Kg cement
Water injection % on Feed rate
Motor power
Cos from the motor nameplate
normally 0.85 - 0.9
Where V = Applied voltage
I = Motor current
Cos = Motor power factor
3 = 1.732
W = x V x I x Cos
3
Effect of Gypsum, Limestone + Pozzolan
On mill performance
1% SO3 = m2/kg Surface Area
1% Gypsum = Production
1% Gypsum = m2/kg Surface Area
1% Limestone = % B.C.I Grindability
1% Pozzolan = to % B.C.I.
Grindability
+30
+5%
+12
-2.5
-0.4
-0.67
Relationship between power consumption and
Chemistry for two closed circuit mills
No 2 Mill SRC
N1 Mill (OPC)
N1 Mill (OPC)
N2 Mill (SRC)
Mill Only Kwh/t
L.S.F.
L
S
F
C
2
S
C
3
S
32.5 33.0 33.5
C
3
S
C
2
S
C
3
S
C
2
S
Mills under
Automatic
Total Feed
Control
Chemical effects
on mill
performance
Max. T.P.H.
t.p.h.
Kwh/T
1986 1987
C2S
C3S
Min C2S
Max. C3S
Lowest cement
grindability
Highest mill output
Grindability
Axial Testing
Procedure
1. OBSERVE STABLE MILL OPERATION BEFORE THE TEST.
MEASURE POWER CONSUMPTION AND PRODUCTION.
TAKE SAMPLES OF FEED AND PRODUCT.
TAKE SEPARATOR AND MILL CIRCUIT SAMPLES
2.- STOP BOTH MILL AND FEED SIMULTANEOUSLY.
3.- TAKE AXIAL SAMPLES (ALONG THE LENGTH OF THE MILL)
4.- DETERMINE FINENESS OF THE SAMPLES
FOR EXAMPLE RESIDUES AT 2.36 mm, 1.18 mm, 300 mic. 90 mic, 45 mic.
- CAN CALCULATE SURFACE AREA IF REQUIRED
5.- MEASURE - VOLUME LOAD = CALCULATE CHARGE WEIGHT
6. - CALCULATE POWER USED
NETT kW = 0.2846 x D x A x W x N
7. - PLOT THE AXIAL GRAPH.
Taking axial samples
Sample below the
surface of the material
and media
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
Measure the height
above charge in each
chamber H1 +H2
H2
H1
Material Flow
%
V
o
l
u
m
e
l
o
a
d
RATIO H/D
Ball mill volume load =estimation
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0.50 0.55 0.60 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85
H=HEIGHT ABOVE
CHARGE
D= INTERNAL DIA.
H
VOLUME LOAD FORMULA
VOLUME LOAD FORMULA
% Volume Load =
400/PI*((0.25*Cos(2*(H/D-0.5)))
-((H/D-0.5)*((H/D-(H/D)^2)^0.5)))
H = HEIGHT ABOVE CHARGE (M)
D = MILL INTERNAL DIAMETER INSIDE LINING (M)
Changes in apparent volume load
due to charge expansion
H1 = Height above charge -Mill Crash Stop
Apparent Charge density Case %Volume load
t/m3
3.91 H1 Crash Stop 38%
H 1
H 2
H2 = Height above charge - Mill Run Out
4.50
H2 Without Material
33%
Charge Expansion 5%
Mill power calculation
- DAWN Formula
NETT KW = 0.2846
DAWN
Where
D
= Internal Diameter of Mill
A
= 1.073 - J
(Where J = Fractional Volume Load i.e. if VL = 30% then J = 0.3)
W = Charge weight in Tonnes
N
= Mill speed in RPM
Net and Gross mill power
Normal values for the ratio Net/Gross power
0.90 Normally for old and inefficient mills
0.92 Polysius Combiflex Drive
0.93 Girth gear driven mill
0.94 -0.95 Modern central drive mill
Unexpected values
0.88 High power losses possibly due to mill
chambers running empty.
0.97 - 1.00 Low power losses possibly due to charge
expansion and/or build up of clinker nibs.
If unexpected values occur : review the mill data
Target levels for material fineness
before the intermediate diaphragm
Sieve size % Cumulative
Residue
2.36 mm 1 %
1.18 mm 6 %
300 um 20%
Basis - sieve about 0.5 - 1 Kg of material if
there are clinker nibs present.
Axial samples can help identify the problem
% Retained
on the sieve
Inlet
Outlet
chamber 1
chamber 2
100
0
Coarse accumulation due
to nibs leaving chamber 1.
45 mic
2.36mm
2.36mm
300 mic
Targets for cement
mills with 6-8mm slots
Sample fineness here
Expect 20% max + 300 mic
1% + 2.36 mm (4% max)
Low reduction in 45 micron sieve residue
due to media coating and charge cushioning
with chamber overfilling.
Badly worn or incorrect gradings with
backmixing can have the same effect.
Coarse material accumulation
% Retained v.s.Position
C em en t M ill E xam p le
0.00
10.00
20.00
30.00
40.00
50.00
60.00
70.00
80.00
90.00
100.00
1a 1b 1c 2a 2b 2c 3a 3b 3c 3d 3e 3f
P osition A long M ill
%
R
e
t
a
i
n
e
d
19,000
9500
6700
2360
1180
600
300
150
90
+ 45
SSA v.s Position
P lot of SSA (m 2/kg) V .s. position along m ill
0.00
100.00
200.00
300.00
400.00
1a 1b 1c 2a 2b 2c 3a 3b 3c 3d 3e 3f
P osition
S
S
A
(
m
2
/
k
g
)
S S A
INSPECTION POINTS
LINING PLATES
WATER INJECTION
AIR OUTLET
PRODUCT
DIAPHRAGMS
GRINDING
MEDIA
FRESH AIR INLET
SEALS
(SIZES - SAMPLES -CONDITION)
(SLOT SIZES - AVAILABLE SLOT AREA
- VENTILATION GRID)
Sampling closed circuit mills
Fresh Feed
Separator rejects
Mill Product
(Separator feed)
Separator
Fines
Finished Product
Filter Product
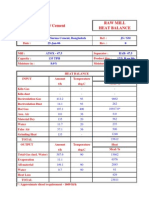
CEMENT MILL - AIR FLOW TESTS
MEASURED AIRFLOW
= 200 m/min
TEMP 50 C
MILL EXIT = 115C
TO ELEVATOR
TOTAL FREE VOLUME
ABOVE CHARGE = 40 m
APPARENT AIR CHANGES/MIN = 200 = 5
40
(TARGET 2 - 3 OPEN CIRCUIT 5 - 7 CLOSED CIRCUIT)
( 0.25 0.4 KG AIR/KG CEMENT )
COLD AIR
20C
FRESH FEED AND
SEPARATOR REJECTS
FALSE AIR
INLEAK
ACTUAL -
FROM HEAT AND MASS BALANCE
= 1 5
AIR CHANGES !!!!!
MEASURED AIRFLOW
= 200 m/min
TEMP 50 C
FRESH FEED AND
SEPARATOR REJECTS
COLD AIR
20C
30% OF TOTAL
AIRFLOW
COLD AIR
20C MILL EXIT = 115C
TOTAL FREE VOLUME
ABOVE CHARGE = 40 m
APPARENT AIR CHANGES/MIN = 200 = 5
40
(TARGET 2 - 3 OPEN CIRCUIT 5 - 7 CLOSED CIRCUIT)
( 0.25 0.4 KG AIR/KG CEMENT )
TO ELEVATOR
CEMENT MILL - AIR FLOW TESTS
MILL TESTING EXAMPLE
or
Your Time To Think
A Closed Circuit Cement Mill has
recently been overhauled with
new internals.
Output is up by 15% and you are
promoted to Works Director.
After 6 months, output drops by
25%.
What will YOU do to avoid being
demoted to Tea Boy?
Your Boss hears about
the 20% drop in output !
Checklist-Look for Changes in:-
Cement Grindability, chemistry, SO3,
Free lime, C2S, C3S, Gypsum, MAC %.
Mill Absorbed Power, Kw per chamber.
Mill Internals Inspection, Media size
grading, Liners -type/condition,
Diaphragm slot sizes/areas + % blockage.
Powder levels, degree of coating, charge
expansion.
Cement-Residue, SSA, SO3, R-R Slope.
Mill Ventilation flow at mill inlet and
filter, Inleaking air, Water Injection rates.
Ancillary plant limitations, B/Elevator etc.
Separator inspection, Efficiency, Bypass.
MILL AXIAL SAMPLING TEST AND FULL
INTERNAL INSPECTION
Worn diaphragm
Media Blockage
1st Chamber
Lining
Worn Chamber Lining
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ball Mill OptimizationDokument82 SeitenBall Mill OptimizationRashek_119588% (16)
- Ball Mill - Operation, Inspection & OptimizationDokument38 SeitenBall Mill - Operation, Inspection & OptimizationMadang Wijaya100% (2)
- Process Train Ball MillDokument28 SeitenProcess Train Ball MillvvijaybhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grinding Course: Ball Charge Design MethodsDokument12 SeitenGrinding Course: Ball Charge Design MethodsVishnu Vardhan . C100% (12)
- Ball Mill Audit and OptimizationDokument82 SeitenBall Mill Audit and Optimizationanrulo100% (4)
- VP - 10 - Ball Cement Mill Monitoring, Inspection & EvaluationDokument41 SeitenVP - 10 - Ball Cement Mill Monitoring, Inspection & Evaluationrecai91% (11)
- OSepaseparator 1Dokument6 SeitenOSepaseparator 1Slobodan StrainovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kiln Process and Operation Training - TRR - NEWDokument97 SeitenKiln Process and Operation Training - TRR - NEWDIAGNE100% (4)
- Loesche Round Table VICAT PDFDokument20 SeitenLoesche Round Table VICAT PDFrecaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement Cooler ProcessDokument57 SeitenCement Cooler Processniteshvtank100% (2)
- Day 1 - 5 - BALL Mill Internals - MBu PDFDokument80 SeitenDay 1 - 5 - BALL Mill Internals - MBu PDFTELEGBIASIA100% (3)
- Vega LinersDokument80 SeitenVega LinersAnonymous knICax100% (2)
- Mill Ventilation MeasurementDokument5 SeitenMill Ventilation MeasurementBùi Hắc HảiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization of Vertical Raw Mill OperationDokument32 SeitenOptimization of Vertical Raw Mill OperationNael93% (40)
- Vertical Mill CalculationsDokument11 SeitenVertical Mill Calculationsrecai100% (6)
- Newly Developed 0-Sepa Air Separator Provides Sharp Particle ClassificationDokument7 SeitenNewly Developed 0-Sepa Air Separator Provides Sharp Particle ClassificationTomas Masquimillan Peñailillo100% (1)
- 03 Ball MillsDokument71 Seiten03 Ball Millsranaravikiran100% (5)
- Mill Testing Optimisation and TargetingDokument134 SeitenMill Testing Optimisation and TargetingArtemMirra90% (10)
- Vertical Roller Mill Operation and OptimizationDokument49 SeitenVertical Roller Mill Operation and OptimizationMKPashaPasha100% (4)
- Report On Cement MillDokument9 SeitenReport On Cement MillYounas Khan100% (1)
- Cement Chapter 4Dokument11 SeitenCement Chapter 4shani5573100% (2)
- Clinker FormationDokument120 SeitenClinker FormationDragos PlaesuNoch keine Bewertungen
- VRM Heat and Mass BalanceDokument1 SeiteVRM Heat and Mass BalanceRajeshRockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement Kiln Operation Hand BookDokument12 SeitenCement Kiln Operation Hand BookAmit Pandey100% (2)
- Ball Mill PresentationDokument34 SeitenBall Mill PresentationISLAM I. Fekry100% (18)
- Grinding and Classifying Technology For Slag: Replacement Factors DryingDokument6 SeitenGrinding and Classifying Technology For Slag: Replacement Factors DryingGerman Gabriel Anaya Vega100% (1)
- 11.30 DR Stefan Seemann, KHD Humboldt Wedag GMBHDokument15 Seiten11.30 DR Stefan Seemann, KHD Humboldt Wedag GMBHMohd AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final - (Stefan Tuberg) Fundamentals of Mill Operation and ControlDokument46 SeitenFinal - (Stefan Tuberg) Fundamentals of Mill Operation and ControlRaúl Marcelo Veloz100% (1)
- MPS Vertical Roller Mills for Slag GrindingDokument4 SeitenMPS Vertical Roller Mills for Slag Grindinglijosh_rexy1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ball Mill Checking (Compatibility Mode)Dokument33 SeitenBall Mill Checking (Compatibility Mode)Nael100% (9)
- Ball Mill Inspection FinDokument77 SeitenBall Mill Inspection FinTamer Fathy75% (4)
- Raw Mill Heat BalanceDokument1 SeiteRaw Mill Heat BalanceElwathig Bakhiet100% (1)
- O-Sepa 750 enDokument29 SeitenO-Sepa 750 enEmanuel Widodo50% (2)
- Ball Mill CalculationsDokument12 SeitenBall Mill Calculationsvvijaybhan80% (15)
- Diagnostic Study For Cement Mill OptimizationDokument9 SeitenDiagnostic Study For Cement Mill OptimizationHilmy MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multifuel Rotary Kiln Burner: Presented At: "1 Burner Day" 18 February 2004"Dokument38 SeitenMultifuel Rotary Kiln Burner: Presented At: "1 Burner Day" 18 February 2004"mustafNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 VRM PregrinderDokument22 Seiten07 VRM PregrinderVishnu Vardhan . C100% (9)
- Clinker Coolers PDFDokument22 SeitenClinker Coolers PDFAhmed AwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refractory failure at nose ring and cooling zoneDokument69 SeitenRefractory failure at nose ring and cooling zonezementhead100% (3)
- Process Guidelines for Cement Production OptimizationDokument20 SeitenProcess Guidelines for Cement Production OptimizationMKPashaPasha100% (4)
- Grinding Systems Operation Principles and Advances in Grinding SystemDokument58 SeitenGrinding Systems Operation Principles and Advances in Grinding SystemDinesh100% (3)
- Vertical Mill CalculationsDokument12 SeitenVertical Mill CalculationsAbhijeet Jhankal100% (1)
- VRM Operation and OptimizationDokument39 SeitenVRM Operation and OptimizationrecaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Cement Formulae PDFDokument163 SeitenAll Cement Formulae PDFGanapathy SubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Ball Mill GrindingDokument78 Seiten3 - Ball Mill GrindingMega Purnama Zainal91% (11)
- Finish Grinding by Roller PressDokument3 SeitenFinish Grinding by Roller PressManish Verma100% (3)
- Rotary Kilns: Transport Phenomena and Transport ProcessesVon EverandRotary Kilns: Transport Phenomena and Transport ProcessesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Advanced Pulverized Coal Injection Technology and Blast Furnace OperationVon EverandAdvanced Pulverized Coal Injection Technology and Blast Furnace OperationK. IshiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combustion of Pulverised Coal in a Mixture of Oxygen and Recycled Flue GasVon EverandCombustion of Pulverised Coal in a Mixture of Oxygen and Recycled Flue GasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ball Mill Testing and OptimizationDokument29 SeitenBall Mill Testing and OptimizationdeepakNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 MillingDokument21 Seiten04 MillingMKPashaPasha100% (1)
- Grooved Rubber Sole Plate SpecificationDokument30 SeitenGrooved Rubber Sole Plate Specificationgotosud100% (1)
- Factors Influencing The Grinding EfficiencyDokument27 SeitenFactors Influencing The Grinding Efficiencynoelbaba71100% (1)
- Lab Report On CBR Compaction TestDokument7 SeitenLab Report On CBR Compaction Testemmanuel biodunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polycom Process-CalculationDokument42 SeitenPolycom Process-Calculationdarkcorsair100% (4)
- Size ReductionDokument12 SeitenSize ReductionJohn Paul RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Excavators 3Dokument68 Seiten05 Excavators 3Mohammed FaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Mix Calculation Grade 30NDokument6 SeitenDesign Mix Calculation Grade 30NikhwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ball Mill OptimizationDokument7 SeitenBall Mill OptimizationWael Fanous100% (1)
- University of Health Sciences, Lahore. MBBS Session 2020-2021Dokument3 SeitenUniversity of Health Sciences, Lahore. MBBS Session 2020-2021Shakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICR MG Brick Shelf Life Article PDFDokument4 SeitenICR MG Brick Shelf Life Article PDFMuhammadShoaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equity Trading PackagesDokument1 SeiteEquity Trading PackagesShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dissertation, Final SubmissionDokument146 SeitenDissertation, Final SubmissionjenifferrayenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Raw Milling and BlendingDokument6 Seiten3 Raw Milling and BlendingDianSwaraPiliangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equity Trading PackagesDokument1 SeiteEquity Trading PackagesShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super AsiaDokument2 SeitenSuper AsiaShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taseer MustafaDokument1 SeiteTaseer MustafaShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grinding Theory SentDokument27 SeitenGrinding Theory SentShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- BangistanDokument1 SeiteBangistanShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- AfridiDokument2 SeitenAfridiShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRINDING MillDokument5 SeitenGRINDING MillShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kiln RefractoryDokument23 SeitenKiln Refractorymahreza189100% (1)
- Cement Quality Enhancement With Multi Channel Burner in Kiln-DepartmentDokument10 SeitenCement Quality Enhancement With Multi Channel Burner in Kiln-DepartmentShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure APMF 2007 PDFDokument275 SeitenPressure APMF 2007 PDFShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Underprocess PDFDokument12 SeitenUnderprocess PDFShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Ball MillDokument23 SeitenNew Ball MillShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- SKF RemeniceDokument91 SeitenSKF RemeniceSeherzada Kadric-RibicNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Cement Article August 2013-Data PDFDokument4 SeitenWorld Cement Article August 2013-Data PDFShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kiln RefractoryDokument23 SeitenKiln Refractorymahreza189100% (1)
- Optimum efficiency range for separator performanceDokument3 SeitenOptimum efficiency range for separator performanceShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Kiln ProcessDokument79 Seiten1 Kiln ProcessFedi ChennaouiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Points Friction Torque LimitersDokument2 SeitenTechnical Points Friction Torque LimitersShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinker Formation PDFDokument120 SeitenClinker Formation PDFShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC Math 2nd RegDokument25 SeitenMSC Math 2nd RegShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nox Sox ClinkerDokument21 SeitenNox Sox ClinkerShakil Ahmad100% (2)
- MSC Maths CourseOutlineDokument36 SeitenMSC Maths CourseOutlineShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.S. Engineering Technology: EligibilityDokument2 SeitenB.S. Engineering Technology: EligibilityDhirendra Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- BoilerDokument237 SeitenBoilerShakil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Job Specific Safety PPE Used On Site.Dokument2 SeitenList of Job Specific Safety PPE Used On Site.Aejaz MujawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC72D MK2 Genset Controller User Manual V1.5Dokument61 SeitenDC72D MK2 Genset Controller User Manual V1.5Cristobal AvecillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCT 4410 Taxation Salaries tax (Part II) Key areasDokument40 SeitenACCT 4410 Taxation Salaries tax (Part II) Key areasElaine LingxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anabolic Steroids Are Easily PurchasedDokument14 SeitenAnabolic Steroids Are Easily Purchasedfaqed ilzakira100% (2)
- Clean Room Laboratory ReportDokument6 SeitenClean Room Laboratory ReportHaider IftikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antox Pickling Paste MSDSDokument10 SeitenAntox Pickling Paste MSDSKrishna Vacha0% (1)
- Full Test 14 (Key) PDFDokument4 SeitenFull Test 14 (Key) PDFhoang lichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Clearance CertificateDokument4 SeitenEnvironmental Clearance CertificateAra Jane T. PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Organic Questions Q1Dokument5 SeitenUnit 1 Organic Questions Q1Hadeel DossaNoch keine Bewertungen
- We Get Results!: Spring FlingDokument35 SeitenWe Get Results!: Spring FlingThe WorldNoch keine Bewertungen
- SF 9 - ES Learners Progress Report CardDokument3 SeitenSF 9 - ES Learners Progress Report Cardroxanne50% (2)
- Typhoid FeverDokument9 SeitenTyphoid FeverAli Al.JuffairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AZIZ Ur RehmanDokument3 SeitenAZIZ Ur Rehmantop writerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marital Rape in IndiaDokument8 SeitenMarital Rape in IndiaSHUBHANK SUMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Industrial DisputesDokument12 SeitenTypes of Industrial DisputesAntony MwangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PreparationDokument2 SeitenPreparationmghaffarzadehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Leadership and Management in Nursing 4th Edition Mary Ellen Grohar MurrayDokument36 SeitenTest Bank For Leadership and Management in Nursing 4th Edition Mary Ellen Grohar Murraywitchingmazybs7k7100% (39)
- Litreature On Automatic Dipper Circuit For Vehicle-2Dokument10 SeitenLitreature On Automatic Dipper Circuit For Vehicle-2Rushikesh TajneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Analysis of Mineral Constituents of Ethanol Leaf and SeedDokument9 SeitenComparative Analysis of Mineral Constituents of Ethanol Leaf and SeedKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABS and Air Conditioner Wiring DiagramDokument207 SeitenABS and Air Conditioner Wiring Diagramservice_00783% (30)
- 360 Joints PDFDokument9 Seiten360 Joints PDFelimz0100% (1)
- Lappasieugd - 01 12 2022 - 31 12 2022Dokument224 SeitenLappasieugd - 01 12 2022 - 31 12 2022Sri AriatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trilead bis(carbonate) dihydroxide identified as SVHC due to reproductive toxicityDokument7 SeitenTrilead bis(carbonate) dihydroxide identified as SVHC due to reproductive toxicityCekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- TN EpasssDokument2 SeitenTN EpasssStephenrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iesc101 PDFDokument13 SeitenIesc101 PDFBhaskar Sharma0% (1)
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1Dokument6 SeitenDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1AnatasukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Dukan Diet by Dr. Pierre Dukan - ExcerptDokument8 SeitenThe Dukan Diet by Dr. Pierre Dukan - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group15% (20)
- Performance Task MidTerm Second Sem. AY 2022 2023Dokument2 SeitenPerformance Task MidTerm Second Sem. AY 2022 2023KZpathryn Jemimench AleurevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schematic 1280 - So Do Nokia 1 PDFDokument18 SeitenSchematic 1280 - So Do Nokia 1 PDFanh3saigon0% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0016706105000467 MainDokument12 Seiten1 s2.0 S0016706105000467 MainLeonardo JaimesNoch keine Bewertungen