Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Core Barrel Components Explained Under 40 Characters
Hochgeladen von
mmohsinaliawanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Core Barrel Components Explained Under 40 Characters
Hochgeladen von
mmohsinaliawanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Coring:
Coring is the removal of sample formation material from a wellbore. To the extent
possible, core samples are taken in an undamaged, physically unaltered state.
The Purpose of Coring:
Laboratory measurements performed on core samples recovered from hydrocarbon
reservoirs furnish reservoir descriptive data available from no other source. Well
logs, including the new generation NMR tools, play a very important role in reservoir
identification and characterization. However, the reservoir core material itself will
provide the most accurate information available to geologists, engineers, and
petrophysicists. In addition, core material is needed to calibrate well logs.
Evaluation data gained from core samples fall into three general categories:
geological, completion, and engineering.
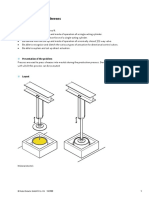
Core Barrel Components:
Outer Barrel:
Outer, thick-walled barrel which attaches to core bit on one end and drill string on
the other. The outer barrel encloses inner core barrel components. The O.D. of the
outer barrel is always less than the hole size to allow for fishing operations.
Inner Barrel:
Receiver for core column being cut by core bit. Inner barrels are generally made of
thin walled steel. Aluminum and Fiberglass inner barrels are now commonly used as
the standard and preferred method to containerize the core. Both aluminum and
fiberglass are disposable. Inner barrel containerize the core, protecting the core from
fluid contamination and erosion.
Inner Tube:
PVC, aluminum and fiberglass inserts or inner tubes are used for the steel inner
barrel. Inner tubes containerize core samples and generally are disposable.
Core Head or Core bit:
Hollow drill bit at end of core barrel designed to cut the rock. The center part of the
bit forms a column of rock to become a core. Core bits are application-specific with
a cutting structure of choice, i.e., natural diamond, synthetic diamond, or
polycrystalline diamond compact cutters.
Outer Barrel Stabilizers:
Segments of outer barrel, generally 3 feet in length and constructed with hardened
ribs, keep core barrel centered in well bore. OD of stabilizer ribs is larger than that
of outer barrel and equal to hole size.
Top Sub:
Top part of the HT core barrel that connects to the drill string. High torque core
barrels (HT series & Core Master) have been designed and standardized with a top
sub, leaving the safety joint as an option only.
Swivel Assembly:
A section of inner barrel that connects inner barrel to safety joint or top sub.
Bearings allow outer barrel to rotate about inner barrel without turning the inner
barrel. Swivel consists of thrust bearing, Inner tube plug and pressure relief plug.
Drop Ball:
A steel ball dropped from the surface through the drill string. The ball is dropped to
initiate coring, which is conducted without drilling fluid flow through inner barrel.
Seating action of the ball forces fluid flow through the annulus space between outer
and inner core barrels.
Core Catcher:
A device configured inside a shoe assembly located at the bottom end of the inner
barrel assembly. Its function is to grab and break the core at the bottom prior to
retrieving the core. The core catcher goes into the coregard shoe and sits in the
coregard shoe which is tapered to enable the catcher to grip the core.
Lower or Coregard Shoe:
Lower end of inner core barrel; holds core catcher and seats into throat of bit.
Upper or Top End Shoe:
Extension connecting the pilot or extended pilot (Low Invasion) lower shoe to the
inner barrel. The Top End or Upper shoe screws into the coregard and onto the
inner tube.
Inner tube extension:
This Inner tube extension is used to space out the inner tubes to the outer barrel.
Long Distance Adjustment (LDA):
A device and procedure for spacing aluminum or fiberglass inner tubes to
compensate for differences in thermal expansion between steel outer barrel and
disposable inner tubes.LDA consists of Slick housing, stabilizer and top sub.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Jar Placement Best PracticesDokument2 SeitenJar Placement Best PracticesmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 101-Zebra ManDokument51 Seiten101-Zebra Manapi-3728275Noch keine Bewertungen
- 28-01-20 RIH With Motor AssemblyDokument1 Seite28-01-20 RIH With Motor AssemblymmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Distance Learning Exam Confidentiality AgreementDokument1 SeiteOnline Distance Learning Exam Confidentiality AgreementmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlugDokument1 SeitePlugmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of CPD Courses 2014Dokument4 SeitenList of CPD Courses 2014mmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV MohsinDokument1 SeiteCV MohsinmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling Jar PlacementDokument3 SeitenDrilling Jar PlacementmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employment Form PPLDokument4 SeitenEmployment Form PPLmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hamood Ur Rehman CommissionDokument68 SeitenHamood Ur Rehman CommissionrahehaqguestsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dupont AccidentDokument1 SeiteDupont AccidentmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Survey System (ESS) Tool Records Downhole Inclination and AzimuthDokument1 SeiteElectronic Survey System (ESS) Tool Records Downhole Inclination and AzimuthmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDCA For Health & Safety Managment in Wood Cutting CompanyDokument17 SeitenPDCA For Health & Safety Managment in Wood Cutting CompanymmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Country TagDokument43 SeitenCountry TagmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Phantom of The OperaDokument277 SeitenThe Phantom of The OperaJennibethNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionDokument33 SeitenPDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBM TestDokument4 SeitenOBM Testmmohsinaliawan0% (1)
- ChemicalsDokument2 SeitenChemicalsmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specification of Sections of Well HeadDokument1 SeiteSpecification of Sections of Well HeadmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBM TestDokument4 SeitenOBM Testmmohsinaliawan0% (1)
- Cement CalcDokument6 SeitenCement Calcmmohsinaliawan100% (1)
- DST Surface EquipmentDokument4 SeitenDST Surface Equipmentmmohsinaliawan100% (2)
- Oil Based Mud or Fluids (OBM)Dokument7 SeitenOil Based Mud or Fluids (OBM)mmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formation Integrity Test (FIT) and Leak Off Test (LOT)Dokument1 SeiteFormation Integrity Test (FIT) and Leak Off Test (LOT)mmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Headassembly: Section A or Casing Head Housing (CHH)Dokument3 SeitenWell Headassembly: Section A or Casing Head Housing (CHH)mmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBM TestDokument4 SeitenOBM Testmmohsinaliawan0% (1)
- Solid Control EquipmentDokument8 SeitenSolid Control EquipmentmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accumulator or Koomey UnitDokument3 SeitenAccumulator or Koomey Unitmmohsinaliawan100% (3)
- Cutting Drilling Fluid Recovery System Recovers Expensive OBMDokument1 SeiteCutting Drilling Fluid Recovery System Recovers Expensive OBMmmohsinaliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Adi Automotive Sensor Solutions - enDokument6 SeitenAdi Automotive Sensor Solutions - enservice autoNoch keine Bewertungen
- StudenttextDokument15 SeitenStudenttextapi-195130729Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of The Concha Type Microtia and Their New Suitable Tratment Strategies Without Autogenous Costal Cartilage GraftingDokument7 SeitenClassification of The Concha Type Microtia and Their New Suitable Tratment Strategies Without Autogenous Costal Cartilage Graftingromina paz morales camposNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1: Pressing Cheeses: Cheese ProductionDokument8 SeitenExercise 1: Pressing Cheeses: Cheese ProductionAhmed HusseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cocoa Fermentation ManualDokument18 SeitenCocoa Fermentation ManualJimena Rios100% (1)
- Solution of Problem Set 1 For Purity Hydrocarbon Data PDFDokument4 SeitenSolution of Problem Set 1 For Purity Hydrocarbon Data PDFDrumil TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unisonic Technologies Co., LTD: 8-Channel Analog Multiplexers/DemultiplexersDokument7 SeitenUnisonic Technologies Co., LTD: 8-Channel Analog Multiplexers/DemultiplexersNaresh KsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.rolling Disc SolutionDokument12 Seiten11.rolling Disc SolutionAlimin AnniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Lennard Jones PotentialDokument6 SeitenChapter 5 Lennard Jones PotentialMuhamad RayhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Hawk 4000 PDFDokument158 SeitenManual Hawk 4000 PDFNebur MtzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redirection & PipingDokument16 SeitenRedirection & PipingPraveen PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dell Emc Data Domain Dd3300 Faq: Frequently Asked QuestionsDokument14 SeitenDell Emc Data Domain Dd3300 Faq: Frequently Asked QuestionseriquewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Handbook Ripping Cat Selection Techniques Applications Production CompatibilityDokument32 SeitenManual Handbook Ripping Cat Selection Techniques Applications Production CompatibilityPoPandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vikramraju Updated Excel (EXCEL GOODIES)Dokument40 SeitenVikramraju Updated Excel (EXCEL GOODIES)vikramrajuu0% (1)
- Grand Vitara 2012 2013Dokument193 SeitenGrand Vitara 2012 2013Favio Alejandro Herrera ZapataNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT407 Knowledge EngineeringDokument2 SeitenIT407 Knowledge EngineeringVidya ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Poynting OMNI A0098 BrochureDokument2 SeitenPoynting OMNI A0098 BrochurekaminareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roll Handling Data Form: Company DetailsDokument1 SeiteRoll Handling Data Form: Company DetailsAlfredo MinchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRINELL BH3000 - WilsonHardnessDokument2 SeitenBRINELL BH3000 - WilsonHardnessKhoa Bui AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion QuestionsDokument45 SeitenDiscussion QuestionsSriRahayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A e Regulator GuideDokument1 SeiteA e Regulator Guidenasser4858Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rex - O. Ed. Wagner - W-Waves - BiocommDokument13 SeitenRex - O. Ed. Wagner - W-Waves - BiocommLeon BlažinovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECI Symposium Proceedings Optimizes Fouling Mitigation DesignDokument6 SeitenECI Symposium Proceedings Optimizes Fouling Mitigation DesignJoseAndresCarreñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jennings 1978Dokument9 SeitenJennings 1978Jacob Luttrell100% (1)
- Ivy Bridge PDFDokument25 SeitenIvy Bridge PDFDương Tấn QuốcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Make Your Own Eye Chart!: Interpreting The TableDokument2 SeitenMake Your Own Eye Chart!: Interpreting The TableneuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laminar Flow Reactor ProblemDokument6 SeitenLaminar Flow Reactor ProblemAileen Banua Añonuevo100% (1)
- Software Test MetricsDokument8 SeitenSoftware Test MetricscmarrivadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqa MM1B W QP Jun07Dokument8 SeitenAqa MM1B W QP Jun07Annan_Faridi_517Noch keine Bewertungen
- QST HamClockDokument3 SeitenQST HamClockCPC PHCNoch keine Bewertungen