Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
TABLES, PATIENT and His Care, NCP
Hochgeladen von
ZNEROL0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
54 Ansichten33 SeitenThe document describes the medical management of a patient diagnosed with typhoid fever. It details the IV fluids, medications, and nursing responsibilities for the patient's care. Over two days, the patient received IV fluids including 5% Dextrose in Lactated Ringer's Injection and Normosol-M and 5% Dextrose injection to rehydrate the body and provide electrolytes and calories. Medications administered included Paracetamol for fever relief, Ciprofloxacin and Ceftriaxone as antibiotics, Omeprazole to decrease gastric irritation, and Hydrocortisone. The patient responded well to all treatments without any adverse reactions.
Originalbeschreibung:
Case studyCase study
Case studyCase study
Case studyCase study
Case studyCase study
Case studyCase studyCase studyCase study
Case study
Case study
Originaltitel
TABLES, PATIENT and his care, NCP.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document describes the medical management of a patient diagnosed with typhoid fever. It details the IV fluids, medications, and nursing responsibilities for the patient's care. Over two days, the patient received IV fluids including 5% Dextrose in Lactated Ringer's Injection and Normosol-M and 5% Dextrose injection to rehydrate the body and provide electrolytes and calories. Medications administered included Paracetamol for fever relief, Ciprofloxacin and Ceftriaxone as antibiotics, Omeprazole to decrease gastric irritation, and Hydrocortisone. The patient responded well to all treatments without any adverse reactions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
54 Ansichten33 SeitenTABLES, PATIENT and His Care, NCP
Hochgeladen von
ZNEROLThe document describes the medical management of a patient diagnosed with typhoid fever. It details the IV fluids, medications, and nursing responsibilities for the patient's care. Over two days, the patient received IV fluids including 5% Dextrose in Lactated Ringer's Injection and Normosol-M and 5% Dextrose injection to rehydrate the body and provide electrolytes and calories. Medications administered included Paracetamol for fever relief, Ciprofloxacin and Ceftriaxone as antibiotics, Omeprazole to decrease gastric irritation, and Hydrocortisone. The patient responded well to all treatments without any adverse reactions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 33
I.
PATIENT AND HIS CARE
A. MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
Medical
Management
General Description Indications DATE
Ordered/
Performed
Clients
Response
IVF #1 D5LRS
1L x 8
IVF #2 D5NM
1L x 8
5% Dextrose in
Lactated Ringer's
Injection provides
electrolytes and
calories, and is a
source of water for
hydration. It is
capable of inducing
diuresis depending on
the clinical condition
of the patient. This
solution also contains
lactate which
produces a metabolic
alkalinizing effect.
Sodium, the major
cation of the
extracellular fluid,
functions primarily in
the control of water
distribution, fluid
balance and osmotic
pressure of body
fluids.
Normosol-M and 5%
Dextrose injection is
nonpyrogenic and is a
It is
indicated
for restoring
electrolytes
and
replacing
fluids in the
body
especially in
the case of
the patient
who has
had
dehydration
from
Typhoid
Fever.
It also serves
as a route
for
medication.
It serves as a
01/23/14
01/24/14
Client
manifested
no adverse
reactions to
the
treatment,
but it
helped by
rehydrating
the body
and
providing
electrolytes
and
calories.
Client
manifested
no adverse
reactions to
nutrient replenisher. It
provides water and
electrolytes (with
dextrose as a readily
available source of
carbohydrate) for
maintenance of daily
fluid and electrolyte
requirements, plus
minimal carbohydrate
calories. The
electrolyte
composition
approaches that of
the principal ions of
normal plasma
(extracellular fluid).
maintenanc
e of daily
fluid and
electrolyte
levels for the
patient. The
dextrose
(sugar)
restores
glucose
levels and
provides
minimal
carbohydrat
e calories
the
treatment,
but it
helped by
rehydrating
the body
and
providing
electrolytes
and calories
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES:
Before the Procedure
Check the doctors order regarding to what type of IVF to be used and also
its volume and rate.
Explain the procedure to the patient.
Gather all materials needed for the insertion of IVF to save time and not to
waste time for looking for other materials.
Wash hands before and after the procedure to prevent contamination from
insertion site.
During the Procedure
Place patient in a comfortable position to facilitate easy insertion of IV line
and to decrease patients fear about the procedure.
Make sure that we give the proper IV fluid and drop rate accurately
because patient may experience fluid overload or dehydration.
Check for its patency by observing the backflow of blood upon insertion.
After the Procedure
Press the site where the needle was inserted and secure it with micropore.
Check the site of hand where the needle is inserted if bulging is not visible. If
so, reinsertion is to be undertaken.
Advice patient to avoid scratching the site less movement of the hand
where the needle was inserted to keep it in place.
Instruct patient and significant others to inform the nurse on duty if bulging of
the site is visible, if there is back flow of blood of if IVF is not infusing well.
Observe the IV site at least every hour for signs of infiltration or other
complications fluid or electrolyte overload and air embolism.
IVF regulation should be checked and monitored upon receiving patient.
Always check the doctors order for new orders regarding the IVF
supplement of the patient.
Always check if the IVF is infusing well and intact.
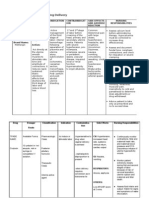
B. PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT
Generic
Name
(brand
name)
Mechanism
of Action
Date
Ordered/
Administe
red
Indications
Contraind
ications
Clients
Response
to
Treatment
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
PARACETAM
OL
(biogesic)
Adult: PO 500
mg/tab q4
RTC/
PRN(T>37.5)
ANTIPYRETIC,
ANALGESICS
(NON-
OPIOID)
Decreases
fever by a
hypothalami
c effect
leading to
sweating
and
vasodilation.
Inhibits
pyrogen
effect on
the
hypothalami
c-heat-
regulating
centers
01-23-14 For
temporary
relief of pain
and
discomfort
from
headache
and fever.
For relieving
fever.
.
Hypersens
itivity to
paraceta
mol
The patient
didnt
manifest
any
allergic
reaction to
Paracetam
ol. The
fever
subsided
from 38.6
to 37.3
degrees
Celsius
Before the administration of drug
Check for medical order
Determine if patient is allergic to
the drug
Explain the procedure and
reasons for giving the drug, to
gain patient cooperation
Explain possible side effects
During drug administration
Maintain aseptic technique
Check medication, right route,
dosage, storage, etc
Stay with the patient while she
takes in the drug
Do not exceed the
recommended dosage
Inhibits CNS
prostaglandi
n synthesis.
After the administration of drug
Monitor any untoward effects of
the drug
Instruct SOs to report to the
attending nurse if any unusual
effects occur
Provide comfort for the patient.
Report and record as
appropriate.
Generic
Name
(brand
name)
Mechanism
of Action
Date
Ordered/
Administe
red
Indications
Contraindications
Clients
Response to
Treatment
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
CIPROFLOXA
CIN
(ciprobay xr)
Adult: PO
1gm/tab
B.I.D
ANTI-
BACTERIAL
Bactericidal;
interferes
with the
DNA
replication
in
susceptible
bacteria
preventing
cell
reproductio
n.
01-23-14 For Gram-
negative
bacteria like
Salmonella
typhi
Hypersensitivity. Not
to be used
concurrently with
tizanidine. Avoid
exposure to strong
sunlight or sunlamps
during treatment.
The patient
didnt
manifest
any allergic
reaction to
ciprofloxaci
n
Before the administration
of drug
Check for medical
order
Determine if patient is
allergic to the drug
Explain the procedure
and reasons for giving
the drug, to gain
patient cooperation
Explain possible side
effects
During drug administration
Maintain aseptic
technique
Check medication,
right route, dosage,
storage, etc
Stay with the patient
while she takes in the
drug
Do not exceed the
recommended
dosage
After the administration of
drug
Monitor any untoward
effects of the drug
Instruct SOs to report
to the attending nurse
if any unusual effects
occur.
Report and record as
appropriate.
Generic
Name
(brand
name)
Mechanism
of Action
Date
Ordered/
Administe
red
Indications
Contraindications
Clients
Response to
Treatment
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
CEFTRIAXONE
(xtenda)
Adult: IV inf.
ST(-) 1gm q8
ANTIBACTERI
AL
Inhibits
bacterial
cell wall
synthesis,
rendering
cell wall
osmotically
unstable
leading to
cell death.
01-23-14 Typhoid
fevers
causative
agent is
Salmonella,
a gram-
negative
bacilli, this
medication
inhibits this
bacteria to
multiply by
inhibiting
cell wall
synthesis.
Contraindicated in
patients with known
allergy to the
cephalosporin class
of antibiotics.
The patient
didnt
manifest
any allergic
reaction to
ceftriaxone.
Before the administration
of drug
Check for medical
order
Determine if patient is
allergic to the drug
Explain the procedure
and reasons for giving
the drug, to gain
patient cooperation
Explain possible side
effects
During drug administration
Maintain aseptic
technique
Check medication,
right route, dosage,
storage, etc
Stay with the patient
while she takes in the
drug
Do not exceed the
recommended
dosage
After the administration of
drug
Monitor any untoward
effects of the drug
Instruct SOs to report
to the attending nurse
if any unusual effects
occur.
Report and record as
appropriate.
Generic
Name
(brand
name)
Mechanism
of Action
Date
Ordered/
Administe
red
Indications
Contraindications
Clients
Response to
Treatment
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
OMEPRAZOLE
(risek)
Adult: PO
40mg/cap HS
PROTON
PUMP
INHIBITOR
Gastric-acid
pump
inhibitor;
suppresses
gastric acid
secretion at
the
secretory
surface of
the gastric
parietal
cells; blocks
the final
step of acid
production.
01-23-14 To decrease
further
irritation of
the gastric
mucosal
lining.
Contraindicated in
patients with known
hypersensitivity to
substituted
benzimidazoles or
to any component
in the formulation.
The patient
didnt
manifest
any allergic
reaction to
Omeprazole
. Verbalized
reduced
abdominal
cramps.
Before the administration
of drug
Check for medical
order
Determine if patient is
allergic to the drug
Explain the procedure
and reasons for giving
the drug, to gain
patient cooperation
Explain possible side
effects
During drug administration
Give before food,
preferably breakfast;
capsules must be
swallowed whole
Maintain aseptic
technique
Stay with the patient
while she takes in the
drug
Do not exceed the
recommended
dosage
After the administration of
drug
Monitor urinalysis for
hematuria and
proteinuria. Periodic
liver function tests with
prolonged use.
Advise patient to
report any changes in
urinary elimination such
as pain or discomfort
associated with
urination, or blood in
urine.
Instruct SOs to report
to the attending nurse
if any unusual effects
occur
Provide comfort for the
patient.
Report and record as
appropriate.
Generic
Name
(brand
name)
Mechanism
of Action
Date
Ordered/
Administe
red
Indications
Contraindications
Clients
Response to
Treatment
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
HYDROCORTI
SONE
(solu-cortef)
Adult: IV
100mg q6 x 3
doses
STEROID
Hydrocortiso
ne is a short-
acting
synthetic
steroid with
both
glucocortic
oid and
mineralocort
icoid
properties
that affect
nearly all
systems of
the body. By
inhibiting
the
formation,
storage and
01-23-14 Hydrocortiso
ne is used to
reduce
inflammatio
n. It reduces
swelling.
Contraindicated in
patients with known
hypersensitivity to
substituted
benzimidazoles or
to any component
in the formulation.
The patient
didnt
manifest
any allergic
reaction to
Hydrocortiso
ne.
Before the administration
of drug
Assess for
contraindications.
Assess body weight, skin
color, V/S, urinalysis,
serum electrolytes, X-
rays, CBC.
Arrange for increased
dosage when patient is
subject to unusual
stress.
Observe the rights of
drug administration.
During drug administration
Give daily before 9am to
mimic normal peak
diurnal corticosteroid
levels.
Space multiple doses
evenly throughout the
day.
Use minimal doses for
minimal duration to
release of
histamine
from mast
cells, it
reduces the
effects of an
allergic
response. It
also
increases
the bodys
response to
circulating
catecholam
ines.
minimize adverse effects.
Do not give IM injections if
patient has
thrombocytopenic
purpura.
Taper doses when
discontinuing high-dose or
long-term therapy.
After the administration of
drug
Monitor client for at least
30minutes.
Educate client on the side
effects of the medication
and what to expect.
Instruct client to report
pain at injection site.
Instruct client to take
drug exactly as
prescribed.
Dispose of used materials
properly.
Document that drug has
been given
C. DIET
Type of
Activity
General
Description
Indications/
Purpose
Date
Ordered/
Performed
Examples of
food
Clients
Response
Soft Diet A diet that is
soft in texture,
low in
residue, easily
digested,
and well
tolerated. It
provides the
essential
nutrients in
the form of
liquids and
semisolid
foods.
A soft diet
food can
easily be
digested by
the body. As
the digestive
system of the
patient
becomes
weak during
typhoid, the
typhoid
remedies do
not
recommend
a patient to
eat any food
that may be
high in tough
fibers.
01/23/14 Soup,
eggs,
yoghurt,
breads,
cereals,
mashed
potato,
oatmeal
The patient
complied to the
given diet.
SOFT DIET
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES BEFORE, DURING, AND AFTER
Before the Procedure
Check the doctors order.
Check the right client.
Be sure that the diet is properly instructed.
Explain the reason for type of diet
During the Procedure
Monitor if the client complies with the given diet.
Be sure patient is taking or eating food he/she can tolerate
After the Procedure
Assess for patients condition; how he responded to the diet.
A. ACTIVITY and EXERCISE
Type of
Activity
General
Description
Indications/
Purpose
Date
Ordered/
Performed
Clients Response
Bed Rest
with
Bathroom
Privilege
with
assistance
It is a
restriction of a
patient's
activities,
either partially
or completely
, but
permitted to
use the
One of the
symptoms of
Typhoid Fever is
dehydration and
weakness.
Therefore, patient
must be assisted
in using the
bathroom to
01/23/14 Patient complied
to the prescribed
activity. It
provided
assistance to ease
the effort in using
the bathroom by
saving energy and
preventing
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Educate client regarding his activity
Assisting client to his bathroom privileges
Explain the purpose of restrictions in activity and position in bed as ordered.
Assist the patient to maintain the prescribed position.
Encourage the patient to adhere to ordered activity.
Accomplish necessary documentation of patients reaction to the ordered activity restrictions.
bathroom
with
assistance.
prevent any
injury.
exhaustion.
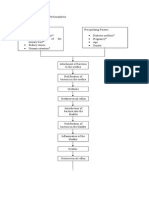
II. NURSING CARE PLANS
NURSING PROBLEM: Hyperthermia related to infection of systemic effects of endotoxins and bacterial products of
salmonella typhi
CUES
NURSING
DIAGNOSIS
SCIENTIFIC
EXPLANATION
OBJECTIVES
NURSING
INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Subjective:
Halos 2 weeks
nakong
nilalagnat as
verbalized by the
patient
Objective:
Restlessness
Malaise
Headache
Warm to
touch
Elavated
WBC (14.6)
Typhidot
(presence
Hyperthermia
related to
infection of
systemic
effects of
endotoxins
and
bacterial
products of
salmonella
typhi.
Body
temperature
elevated above
normal level
that is usually
caused by
several factors
related to
illness. As
inoculation
occurs, prolifera
tion of bacteria
follows and
multiplication
occurs. Once
the bacteria
starts to grow in
number, it will
After 4 hours
of nursing
intervention
client will be
able to
maintain
core
temperature
within normal
range as
evidenced
by:
Body
temperatu
re
reduced
lowered to
38.6C to
Monitor patient
temperature
degree and
patterns.
Observe for
shaking chills
and profuse
diaphoresis
Provide tepid
sponge baths
Fever
pattern
may aids in
diagnosing
underlying
disease.
Chills often
precede
during high
temperatur
e and in
presence
of
generalize
d infection.
May help
Goal met
After 4 hours of
nursing
intervention
goals and
objectives was
met as
evidenced by
body
temperature of
37.3C
of IgM)
V/S taken
are as
follows:
T = 38.6 C
RR = 22
PR = 92
BP = 90/60
soon reach
it pathogenic
level that will
result
into pyrexia or
fever as a
defense
mechanism of
the body.
37.5C. and avoid the
use of ice water
and alcohol.
Remove excess
clothing and
covers
Maintain bed
rest or minimize
movement.
reduce
fever. Use
of ice
water and
alcohol
may cause
chills and
can
elevate
temperatur
e
This
decreases
warmth
and
increases
evaporativ
e cooling
To reduce
metabolic
NURSING PROBLEM: Acute Pain R/T irritation of intestinal mucosa AEB facial grimace, guarding position, restlessness, and
Encourage
client to
increase fluid
intake.
INDEPENDENT:
Administer
Paracetamol as
prescribed by
the physician ,
utilizing 10Rs in
giving
medication.
demands
of oxygen
consumpti
on.
If patient is
dehydrate
d or
diaphoretic
, fluid loss
contributes
to fever.
Antipyretics
acts on the
hypothala
mus,
reducing
hypertherm
ia.
7/10 pain scale secondary to Typhoid Fever
ASSESSMENT
NURSING
DIAGNOSIS
SCIENTIFIC
EXPLANATION
OBJECTIVES INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective Cues:
Masakit tiyan
ko.
Objective Cues:
(+) facial
grimace
(+)
guarding
position
(+)
restlessnes
s
7/10 Pain
Scale
V/S taken are
as follows:
Acute Pain
R/T irritation
of intestinal
mucosa AEB
facial
grimace,
guarding
position,
restlessness,
and 7/10
pain scale
secondary to
Typhoid Fever
Once the
Salmonella
typhi that
causes typhoid
fever is
consumed, it
travels initially
through the
digestive
system.
Therefore,
causing
irritation that will
eventually
trigger diarrhea
or constipation,
weight loss, and
abdominal
pain.
Short Term:
After 4 hours
of nursing
interventions,
the patient
will verbalize
relief from
pain.
Long Term:
After 24 hours
of nursing
intervention,
the patient
will show
signs of
comfort and
will be able
to rest and
Assess the
level of pain,
location,
duration,
intensity and
characteristic
s of pain.
Give warm
compresses
on the area
of pain.
Provide a
quiet
environment
Changes in
the
characteristi
cs of the
pain may
indicate the
spread of
disease or
any
complicatio
n.
Warm can
help ease
the pain.
Promotes
Goal met
After 4 hours of
nursing
interventions, the
patient
verbalized
reduced pain
from pain scale
of 7 to 5/10.
Reported relief
from and have
rested and slept
comfortably.
T = 38.6 C
RR = 22
PR = 92
BP = 90/60
sleep.
and reduce
stressful
stimuli.
Place in
position of
comfort.
Provide
diversional
activities,
and
relaxation
technique
Administered
Omeprazole
as prescribed
by the
rest that
may
alleviate the
pain
May lessen
associated
discomfort
Helps with
pain
manageme
nt by
redirecting
attention to
such
activities.
Omeprazole
physician is a proton
pump
inhibitor
which
decreases
acid
secretion to
prevent
further
irritation of
mucosa
which
contributes
to the
abdominal
pain.
NURSING PROBLEM: Activity Intolerance r/t muscle weakness
CUES
NURSING
DIAGNOSIS
SCIENTIFIC
EXPLANATION
OBJECTIVES
NURSING
INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Subjective:
Masaki tang
mga
kasukasuhan
ko,
nahihirapan
ako
gumalaw as
verbalized by
patient.
Objective:
Febrile
(38.6)
body
weakness
restlessnes
s
increased
RR (22
Activity
Intolerance
r/t muscle
weakness
Activity
Intolerance is
insufficient
physiological or
psychological
energy, poor
endure or
complete
required or
desired daily
activities.
Because of low
hct level there
will be decrease
oxygen being
delivered to the
tissues of the
body since the
hgb is responsible
for the
oxygenation of
After 2-3
hours
of nursing
interventions
and giving
health
teachings,
the patient
will be able
to :
Follow
energy
conservati
on
technique
s to lessen
fatigue
Perform
ADL as
tolerated.
Assess patients
level
of mobility.
Assess ability to
stand and
move about
and the
degree
of assistance
necessary.
This aids
defining
what pati
ent is
capable
of which is
necessary
before
setting
realistic
goals.
To
determine
current
status and
needs
associate
d
with partic
ipation in
Goal met.
After 2-3 hours
of nursing
interventions the
patient was able
to perform
comfort measure
to minimize
energy
consumption like
refraining from
doing non
essential
procedures and
placing
frequently used
items within
reach.
cpm)
low hgb
count
(11.9g/L)
fatigue
prefers to
lie down
on bed
tissue. As a
compensatory
mechanism, the
body will
increase its
demand of
oxygen by
increasing
respiratory rate of
the patient
which results then
to fatigue.
Because of this
there will be fast
consumption of
ATP leading to
weaker
contractions thus
causing muscle
weakness and if
the patient has
muscle weakness
there will be
Provided
adequate rest
periods,
especially
before meals,
other ADLs,
and
ambulation.
Instruct patient
to eat nutritious
foods and
drink adequate
fluid intake.
Teach comfort
measure to
needs
or desired
activities.
Rest
between
activities p
rovides
time
energy
conservati
on and
recovery.
Promotes
well-being
and
maximizes
energy
production.
This
distributes
activity
intolerance.
conserve
energy by: 1.)
Changing
position
frequently; 2.)
Placing
frequently used
items within
reach; 3)
Bedside
commode
Instruct patient
to promote /
have
ambulation
and reposition
as necessary.
work to
the
different
muscles to
avoid
fatigue
To prevent
skin
breakdow
n and
maximizes
energy
productio
n.
NURSING PROBLEM: Risk for Imbalance Nutrition: Less than body requirements r/t loss of appetite and altered absorption
of nutrients
CUES
NURSING
DIAGNOSIS
SCIENTIFIC
EXPLANATION
OBJECTIVES
NURSING
INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Subjective:
Minsan wala
ako gang
kumain kasi
masyadong
masakit as
verbalized by
patient.
Objective:
Poor skin
turgor
body
weakness
Pale
conjunctiv
a
Diaphoreti
c
Risk for
Imbalance
Nutrition: Less
than body
requirements
r/t loss of
appetite and
altered
absorption of
nutrients
Lack of appetite
is a common
symptom of
many diseases.
Brief periods of
anorexia are life
threatening but
can cause
temporary
nutrition.
Prolonged
anorexia may
lead to serious
consequences
such as
malnutrition.
During reduced
food
consumption,
people use up
their stored
glycogen which
provides energy
After 2 hours
of nursing
interventions
the patient
will be able
to:
Maintain
hydration
status
State
importanc
e of meal
intake to
meet
metabolic
needs
Have
adequate
amount of
food
intake
Assess appetite
changes.
Frequency and
amount of
food intake
Ask SO to
provide
companionship
during meal
Indicates
health
status and
effect of
illness
which
require an
increased
nutritional
needs and
appetite
affected
by illness
Attention
to the
social
aspects of
eating is
important
in both
hospital
and home
Goal met.
After 2 hours
of nursing
interventions the
patient was able
to verbalized
understanding of
the importance
of food intake to
sustain the
nutrients of the
body and for
faster recovery.
through
glycgenolysis.
Prolonged
reduced food
consumption
may minimize or
consume all
stored glycogen
thus improper
diet occurs.
Suggested
liquid drinks for
supplemental
nutrition
Instruct patient
to eat nutritious
foods high in
calories and
protein that will
promote
weight gain.
setting
Such
suppleme
nts can be
used to
increase
calories
and
proteins
without
interfering
voluntary
food
intake.
Maintains
and
promotes
health
status
Explain to
patient that
nutritional
needs during
the course of
illness also
increase so it is
imperative to
take in food.
Advised
patient to take
small frequent
feedings
Administered
intravenous
fluid D5NM 1L
To aid in
the
understadi
ng of
patient of
the
importanc
e of
nutrition
for faster
recovery
To
increase
energy
levels at
regular
intervals
To
maintain
hydration
status of
the
patient
NURSING PROBLEM: Deficient Fluid volume related to diarrhea.
ASSESSMENT
NURSING
DIAGNOSIS
SCIENTIFIC
EXPLANATION
PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective
Cues:
Nauuhaw
ako lagi
prang
nanunuyo
ang
lalamunan
ko.
Objective
Cues:
o Dry
mucous
membran
e
o Dry skin
and lips.
o Pale
Conjuncti
va.
Risk for
deficient
Fluid
volume
related to
excessive
fluid loss
through
frequent
passage of
stools
When there is
insufficient fluid
intake, and
excessive fluid loss
from and diarrhea
it indicates
imbalance in fluid
volume in which
the body cant
compensate by an
adequate intake of
water. Decreased
volume in the
intravascular
compartment is
called
hypovolemia.
Since water moves
freely between the
compartments,
extracellular fluid
deficit causes
After 2-4 hours
of nursing
intervention,
the client will:
o Learn ways
on how to
keep body
hydrated
o Comply with
the
prescribed
soft diet
o Demonstrate
clinical signs
of adequate
hydration
o Assess and
document
amount,
color and
characteristi
cs of vomitus
and
diarrhea.
o Assess skin
turgor and
oral mucous
membrane;
o Provide for
changes in
dietary
intake
o Increase oral
fluids
o Determine
Fluid
replaceme
nt.
o To
evaluate
changes
as related
to fluid
status.
o To avoid
foods that
precipitate
diarrhea
o To replace
fluid loss
After 4 hours of
nursing
intervention the
client was able to:
o Maintain
normal
hydration as
evidenced
by moist skin
o Comply with
the given
diet
o Increase
fluid intake
o Frequent
Diarrhea
3-5x a
day
intracellular fluid
deficit (cellular
dehydration),which
leaves the cells
without adequate
water to carry on
normal function.
o Recommend
products
such as
normal
fibers, plain
yoghurt
o Restrict solid
food intake
as indicated
o Assess
presence of
postural
hypotension,
tachycardia,
o To restore
normal
flora of
bowel
o To allow
bowel to
rest and
reduce
intestinal
workload
o To watch
out
warning
signs of
dehydratio
n
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenDrug StudyZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenDrug StudyDanica de LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5th Draft DrugsDokument7 Seiten5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beta Karoten: (BAY Ta KARE Oh Teen)Dokument9 SeitenBeta Karoten: (BAY Ta KARE Oh Teen)Nisa'ul KhoiriyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument16 SeitenCase StudyRaidis PangilinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUGS sTUDY W6 2013Dokument5 SeitenDRUGS sTUDY W6 2013Jerald S. OlaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study DMDokument5 SeitenDrug Study DMKimsha ConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugStudy SedinioDokument4 SeitenDrugStudy Sediniociela00034Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study EditedDokument5 SeitenDrug Study EditedfabtaciousVeelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHH Drug Study Week 2Dokument25 SeitenCHH Drug Study Week 2maryxtine24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Piddig. Yuan Marcos - Dela Cruz Angela Corine, UDokument15 SeitenPiddig. Yuan Marcos - Dela Cruz Angela Corine, UAngela CorineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Met Her GineDokument6 SeitenMet Her GineLeofe CorregidorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboDokument7 SeitenNursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboAlexa Abidin Oldenborg100% (8)
- Drugs ReviewerDokument3 SeitenDrugs ReviewerArt russelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs StudyDokument7 SeitenDrugs Studymcmac24Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Drug StudyDokument11 Seiten9 Drug StudyJessa Mae Mauricio CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nov6 Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenNov6 Drug Studyciela00034Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nurses' Duties and Responsibilities: "Pharmacology: Calculation of Rates and Dosage of Drugs"Dokument10 SeitenNurses' Duties and Responsibilities: "Pharmacology: Calculation of Rates and Dosage of Drugs"Sj EclipseNoch keine Bewertungen
- FurosemideDokument1 SeiteFurosemideCassie100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDokument4 SeitenAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeBianca WelchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sepsis PharmacologyDokument9 SeitenSepsis PharmacologyAlex MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenRani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyIv'z TandocNoch keine Bewertungen
- AminosterilDokument6 SeitenAminosterilAngelito LeritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study 2Dokument7 SeitenDrug Study 2Jediale CarcelerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument12 SeitenDrug StudyMaricris Tubig LeritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument13 SeitenDrug StudyGi Ey ElNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endoscopic Retrograde CholangiopancreatographyDokument5 SeitenEndoscopic Retrograde CholangiopancreatographyEllyza EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9% Sodium Chloride Solution MSDSDokument14 Seiten9% Sodium Chloride Solution MSDSbidangNoch keine Bewertungen
- MetoclopramideDokument2 SeitenMetoclopramidehoneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibDokument4 SeitenTramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibEric de JulianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8copd DrugtabncpDokument18 Seiten8copd DrugtabncpMaristelaMolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Drugs StudyDokument13 SeitenComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Study Pedia PDFDokument8 SeitenDrugs Study Pedia PDFmark angeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument14 SeitenDrug StudyKatrina EstoconingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeDokument2 SeitenDrug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeApol PenNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP HyperthermiaDokument6 SeitenNCP HyperthermiaGrax DeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ranitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenRanitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug StudyMarco MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mefenamic AcidDokument3 SeitenMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study OR AreaDokument7 SeitenDrug Study OR AreaVal FielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 Item Pharmacology ExamDokument17 Seiten50 Item Pharmacology ExamZaphanta Rhea P. BangaoetNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRug StudyDokument6 SeitenDRug StudyRochell Torres ArtatesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - Feb 16Dokument9 SeitenDrug Study - Feb 16ciela00034Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study For Hepatic ABCESSDokument3 SeitenDrug Study For Hepatic ABCESSEric EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adpie: Assessment: History and ExaminationDokument56 SeitenAdpie: Assessment: History and ExaminationRaRa LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument17 SeitenDrug StudyKrishelle Kate PannigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Scenario Drug Study - VicenteDokument4 SeitenCase Scenario Drug Study - VicenteLouraine VicenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study ProjectDokument7 SeitenDrug Study ProjectMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Drug Study Clindamycin, Ipatropium BromideDokument8 SeitenDrug Study Clindamycin, Ipatropium Bromidepaupaulala100% (2)
- Drusadg Study For Paracetamol Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexDokument3 SeitenDrusadg Study For Paracetamol Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexzerpthederpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intramuscular InjectionDokument6 SeitenIntramuscular Injectionkiran mahalNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB Ward DrugDokument6 SeitenTB Ward DrugDiana Laura LeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB Drug StudyDokument19 SeitenOB Drug StudyKismet Summons100% (8)
- V. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationDokument23 SeitenV. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationAvigael Gabriel AvilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Management To ConclusionDokument88 SeitenMedical Management To ConclusionRomelle Jane M. VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExamDokument7 SeitenExamRhabdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!Von EverandNCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesVon EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Molecular Pathophysiology of StrokeDokument10 SeitenMolecular Pathophysiology of StrokeKahubbi Fatimah Wa'aliyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Interrelationship Between Income, Health and Employment StatusDokument9 SeitenThe Interrelationship Between Income, Health and Employment StatusZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barrter SyndromeDokument7 SeitenBarrter SyndromeZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patofisiologi StrkeDokument14 SeitenPatofisiologi StrkeTeuku ILza Nanta SatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostics and Laboratory Procedures CvaDokument6 SeitenDiagnostics and Laboratory Procedures CvaZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- CesDokument114 SeitenCesZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care Nurses' Perceptions of Workplace Empowerment, Magnet Hospital Traits and Mental HealthDokument6 SeitenCritical Care Nurses' Perceptions of Workplace Empowerment, Magnet Hospital Traits and Mental HealthZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accredited OFW Clinics - Jul 2014Dokument5 SeitenAccredited OFW Clinics - Jul 2014ZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pyelonephritis: University of La Salette College of Nursing Santiago CityDokument22 SeitenAcute Pyelonephritis: University of La Salette College of Nursing Santiago CityZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument101 SeitenCase Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseZNEROL100% (6)
- PyelonephritisDokument2 SeitenPyelonephritisZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument101 SeitenCase Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseZNEROL100% (6)
- Accredited OFW Clinics - Jul 2014Dokument5 SeitenAccredited OFW Clinics - Jul 2014ZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accredited OFW Clinics - Jul 2014Dokument5 SeitenAccredited OFW Clinics - Jul 2014ZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Surgery WardDokument6 SeitenNCP Surgery WardZNEROL100% (2)
- HIRSCHSPRUNGDokument77 SeitenHIRSCHSPRUNGZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Patho) PTB COPDDokument1 Seite(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Contents RevisedDokument2 SeitenTable of Contents RevisedZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iv. Pathophysiology 1. Schematic Diagram Book Based Pathophysiology: Precipitating/Modifiable Factors Non Modifiable / Predisposing FactorsDokument2 SeitenIv. Pathophysiology 1. Schematic Diagram Book Based Pathophysiology: Precipitating/Modifiable Factors Non Modifiable / Predisposing Factorsikemas67% (6)
- Table of Contents RevisedDokument2 SeitenTable of Contents RevisedZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- HirschzxcxzcDokument2 SeitenHirschzxcxzcZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- JHHJHDokument6 SeitenJHHJHZNEROLNoch keine Bewertungen
- HyperthyroidismDokument73 SeitenHyperthyroidismZNEROL100% (1)
- Leta-Leta CaveDokument5 SeitenLeta-Leta CaveToniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigeration Engineer Quick ReferenceDokument2 SeitenRefrigeration Engineer Quick ReferenceventilationNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Science To God by Peter RussellDokument6 SeitenFrom Science To God by Peter RussellFilho adulto pais alcolatrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metageographies of Coastal Management: Negotiating Spaces of Nature and Culture at The Wadden SeaDokument8 SeitenMetageographies of Coastal Management: Negotiating Spaces of Nature and Culture at The Wadden Seadwi kurniawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nammiaca 000032Dokument5.323 SeitenNammiaca 000032gangadhark196Noch keine Bewertungen
- FREEWAT Vol0 v.1.1.2Dokument159 SeitenFREEWAT Vol0 v.1.1.2Jonathan QuirozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding Research Council: BulletinDokument28 SeitenWelding Research Council: BulletinRogerio Tropia GranjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column c4 From 3rd FloorDokument1 SeiteColumn c4 From 3rd Floor1man1bookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Output Process Input: Conceptual FrameworkDokument4 SeitenOutput Process Input: Conceptual FrameworkCHRISTINE DIZON SALVADORNoch keine Bewertungen
- JCHT35K9 EngDokument5 SeitenJCHT35K9 EngRodica PuscauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collage Lab PDFDokument145 SeitenCollage Lab PDFmaa siddhi92% (12)
- Ge Druck PTX 7535Dokument2 SeitenGe Druck PTX 7535ICSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Mosquito Larvicidal Effects of (Bitter Gourd) Extracts As NanopowderDokument3 SeitenStudy of Mosquito Larvicidal Effects of (Bitter Gourd) Extracts As NanopowderAnonymous AkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc 2019-2020Dokument95 SeitenArc 2019-2020AEN HTM DD1 HTM DD1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Airbus A319-A320-A321 - Quick Reference HandbookDokument113 SeitenAirbus A319-A320-A321 - Quick Reference Handbookrafaelldalpra100% (9)
- Art1 2Dokument24 SeitenArt1 2Peter Paul Rebucan PerudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Acetylation Method On Characterization of Cellulose Acetate Based Sago "Hampas"Dokument18 SeitenEffect of Acetylation Method On Characterization of Cellulose Acetate Based Sago "Hampas"myrraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EET - Formulas - Christmas TermDokument3 SeitenEET - Formulas - Christmas TermJMDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icpc11 - Thermodynamics and Fluid MechanicsDokument22 SeitenIcpc11 - Thermodynamics and Fluid MechanicsAPARNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Arlypon VPCDokument1 SeitePresent Arlypon VPCErcan Ateş100% (1)
- CADS Revit Scia Engineer Link Best PracticesDokument32 SeitenCADS Revit Scia Engineer Link Best PracticestrevorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calabano Clinical Bacteriology Exercise 1Dokument5 SeitenCalabano Clinical Bacteriology Exercise 1MarkJasperCalabanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- InTech-Batteries Charging Systems For Electric and Plug in Hybrid Electric VehiclesDokument20 SeitenInTech-Batteries Charging Systems For Electric and Plug in Hybrid Electric VehiclesM VetriselviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2606 PDFDokument6 Seiten2606 PDFzainab jehangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mercedez-Benz: The Best or NothingDokument7 SeitenMercedez-Benz: The Best or NothingEstefania RenzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diablo Watch Newsletter, FALL 2009 Save Mount DiabloDokument16 SeitenDiablo Watch Newsletter, FALL 2009 Save Mount DiabloIoannqisHatzopoulosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016Dokument3 Seiten1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016api-292307509Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indigo Airlines - Final ReportDokument22 SeitenIndigo Airlines - Final Reportanand_lihinarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of MaterialsDokument11 SeitenMechanics of MaterialsPeter MwangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVR Brosure Basler Decs 100Dokument2 SeitenAVR Brosure Basler Decs 100NikolayNoch keine Bewertungen