Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Design For Static Load: Design of Machine Elements Module-I
Hochgeladen von
nikhilasoknOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Design For Static Load: Design of Machine Elements Module-I
Hochgeladen von
nikhilasoknCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 1
Design for Static Load
A static load is defined as a force which is gradually applied to a mechanical component
and which does not change its magnitude or direction with respect to time.
Engineering materials are classified into two groupsductile and brittle materials. A
ductile material is one which has a relatively large tensile strain before fracture takes place. On
the other hand, a brittle material has a relatively small tensile strain before fracture. Structural
steels and aluminium are ductile materials, while cast iron is an example of a brittle material.
A mechanical component may fail, that is, may be unable to perform its function
satisfactorily, as a result of any one of the following three modes of failure,
(i) Failure by elastic deflection
(ii) Failure by general yielding
(iii) Failure by fracture.
While designing a component, it is necessary to provide sufficient reserve strength in case of an
accident. This is achieved by taking a suitable factor of safety (n).
The factor of safety is defined as
The allowable stress is the stress value, which is used in design to determine the
dimensions of the component. It is considered as a stress, which the designer expects will not be
exceeded under normal operating conditions.
Yield strength in shear is 50% of the yield strength in tension.
Ie:
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 2
Problems
1. A cast iron link, as shown in Fig. is required to transmit a steady tensile load of 45 kN. Find
the tensile stress induced in the link material at sections A-A and B-B.
Given Data:
Tensile stress induced at section A-A
Tensile stress induced at section B-B
--------------------------------(2-1)
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 3
2. A hydraulic press exerts a total load of 3.5 MN. This load is carried by two steel rods,
supporting the upper head of the press. If the safe stress is 85 MPa and E = 210 kN/mm2,
find : 1. diameter of the rods, and 2. extension in each rod in a length of 2.5 m.
Given Data:
1. Diameter of the rods
2. Extension in each rod
--------------------------------(2-1)
--------------------------------(2-2)
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 4
3. A pump lever rocking shaft is shown in Fig. The pump lever exerts forces of 25 kN and 35
kN concentrated at 150 mm and 200 mm from the left and right hand bearing respectively.
Find the diameter of the central portion of the shaft, if the stress is not to exceed 100 MPa.
Given Data:
Note: Equations for moment of inertia I, for various cross sections, are given in table 2.7
--------------------------------(2-91)
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 5
4. A beam of uniform rectangular cross-section is fixed at one end and carries an electric motor
weighing 400 N at a distance of 300 mm from the fixed end. The maximum bending stress in
the beam is 40 MPa. Find the width and depth of the beam, if depth is twice that of width.
Given Data:
5. A wall rack, used to store round steel bars, consists of two I-section cantilever beams fixed
in the wall. The bars are stacked in triangular fashion as shown in figure. The total weight of
the bars is 75kN. The permissible bending stress for cantilevers is 165N/mm2.
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 6
Note: Standard beam sections can be selected from table 24.31
Given Data:
6. An offset link subjected to a force of 25kN is shown in figure. It is made of grey cast iron
FG300 and the factor of safety is 3. Determine the dimensions of the cross-section of the
link.
Note: Material properties for F300 is given in table 1-4
Given Data:
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 7
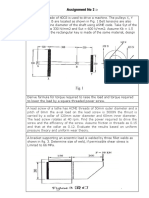
7. A steel shaft 35 mm in diameter and 1.2 m long held rigidly at one end has a hand wheel 500
mm in diameter keyed to the other end. The modulus of rigidity of steel is 80 GPa.
a. What load applied to tangent to the rim of the wheel produce a torsional shear of
60 MPa?
b. How many degrees will the wheel turn when this load is applied?
Given Data:
--------------------------------(2-99)
--------------------------------(2-86)
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 8
8. A shaft is transmitting 97.5 kW at 180 r.p.m. If the allowable shear stress in the material is 60
MPa, find the suitable diameter for the shaft. The shaft is not to twist more that 1 in a length
of 3 metres. Take C = 80 GPa.
Given Data:
1. Considering strength of the shaft
--------------------------------(2-88)
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 9
2. Considering stiffness of the shaft
9. A hollow shaft is required to transmit 600 kW at 110 r.p.m., the maximum torque being 20%
greater than the mean. The shear stress is not to exceed 63 MPa and twist in a length of 3
metres not to exceed 1.4 degrees. Find the external diameter of the shaft, if the internal
diameter to the external diameter is 3/8. Take modulus of rigidity as 84 GPa.
Given Data:
1. Considering strength of the shaft
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 10
3. Considering stiffness of the shaft
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 11
Theories of failure
The maximum normal stress
theory (Rankines theory)
(Used for brittle materials)
5.29
The maximum shear stress
theory (Guests Theory)
(Used for ductile materials)
5.30
The shear energy theory
(Hencky-Von mises theory)
(Used for ductile materials)
5.31
The maximum strain theory
(Saint Venants theory)
5.32
10. A cylindrical shaft made of steel of yield strength 700 MPa is subjected to static loads
consisting of bending moment 10 kN-m and a torsional moment 30 kN-m. Determine the
diameter of the shaft using two different theories of failure, and assuming a factor of safety
of 2. Take E = 210 GPa and poisson's ratio = 0.25.
Given Data:
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 12
11. A mild steel shaft of 50 mm diameter is subjected to a bending moment of 2000 N-m and a
torque T. If the yield point of the steel in tension is 200 MPa, find the maximum value of this
torque without causing yielding of the shaft according to 1. the maximum principal stress; 2.
The maximum shear stress; and 3. the maximum distortion strain energy theory of yielding.
Design of Machine Elements
Module-I
[ T y p e t h e c o m p a n y a d d r e s s ]
Page 13
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- DMM 1 Assignment Questions FinalDokument2 SeitenDMM 1 Assignment Questions FinalSrimanthula SrikanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB Unit-1,2Dokument5 SeitenQB Unit-1,2Agranshu BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME Question Bank Unit (1 2)Dokument5 SeitenDME Question Bank Unit (1 2)PrathamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment MD IDokument7 SeitenAssignment MD Iprajitsen damleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design I - ME501 - Sup 011Dokument2 SeitenMachine Design I - ME501 - Sup 011Saurav JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- MECH 344 - Final Exam (Winter 2021)Dokument4 SeitenMECH 344 - Final Exam (Winter 2021)Puneet Rudhar100% (1)
- Dome 6TH Sem. SP - 09Dokument7 SeitenDome 6TH Sem. SP - 09neelesh singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 Fluctuating LoadDokument3 SeitenAssignment 2 Fluctuating Loadabhishek chaurasiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Termpaper-Strength Analysis of Screw Jack-Mechanics of SolidsDokument21 SeitenTermpaper-Strength Analysis of Screw Jack-Mechanics of SolidsOmkar Kumar JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machine Elements IDokument8 SeitenDesign of Machine Elements Imesab100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01Dokument10 SeitenMachine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01The AIRS CreationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 PDFDokument2 SeitenAssignment 1 PDFvishal kabdwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me2303 - Design of Machine ElementsDokument14 SeitenMe2303 - Design of Machine ElementsGowtham RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- R7310305 Design of Machine Members - IDokument1 SeiteR7310305 Design of Machine Members - IsivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME-1: Design of Mechanical ElementsDokument2 SeitenDME-1: Design of Mechanical ElementsSantolashNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionsDokument11 SeitenQuestionsSundara MoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDokument6 Seiten4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- Design of Machine Members - IDokument8 SeitenDesign of Machine Members - IPradeepkumarKatgiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No-01 MEPC-301Dokument6 SeitenAssignment No-01 MEPC-301SANDEEP BUDANIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Assign I MD IDokument3 SeitenAssign I MD IAtharva KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech-V-Design of Machine Elements I (10me52) - AssignmentDokument10 SeitenMech-V-Design of Machine Elements I (10me52) - AssignmentArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine DesignDokument3 SeitenMachine DesignSantosh Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machine ElementDokument11 SeitenDesign of Machine ElementVenkat RajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dme I Mock Test Question BankDokument5 SeitenDme I Mock Test Question BankRushikesh SwamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTP 5Dokument4 SeitenMTP 5tinku singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 2sonawanepmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- LabManual MDID2016 2016 02 24 16 29 36Dokument23 SeitenLabManual MDID2016 2016 02 24 16 29 36Rajat MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A03504 Design of Machine Elements 21Dokument8 Seiten9A03504 Design of Machine Elements 21slv_prasaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machine Members-II Feb 2022Dokument3 SeitenDesign of Machine Members-II Feb 2022Anand KedhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code: 13A03505: (Mechanical Engineering)Dokument2 SeitenCode: 13A03505: (Mechanical Engineering)MrHEMAMAHEHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design Answer KeyDokument16 SeitenMachine Design Answer KeyK.KESAVARAJ HICET STAFF MCTSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rr312404 Design of Machine ElementsDokument9 SeitenRr312404 Design of Machine ElementsSrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dmm1 Mar2007Dokument8 SeitenDmm1 Mar2007prk74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Previous Exam QuestionsDokument8 SeitenPrevious Exam QuestionssallyreffatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 1Pawan Kumar GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 02Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 02adhnan_rasheed0% (1)
- 21751-6838-Principles of Machine DesignDokument8 Seiten21751-6838-Principles of Machine DesignMacasaet Al-awnNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME2303Dokument5 SeitenME2303balameckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dme Model Key 2019Dokument25 SeitenDme Model Key 2019Siva RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment QuestionDokument15 SeitenAssignment QuestionPratik WalimbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment MD IIDokument6 SeitenAssignment MD IIRupali PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - 1: Case Study Taking Into Account The Force Analysis, Stress Calculations, TheoriesDokument4 SeitenAssignment - 1: Case Study Taking Into Account The Force Analysis, Stress Calculations, TheoriesVinay DograNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Fabrication of Motorized Screw JackDokument8 SeitenDesign and Fabrication of Motorized Screw Jackvarma100% (1)
- Snist Dom Previous PaperDokument9 SeitenSnist Dom Previous PaperKapil Siddhant DevulapalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dmm1 Mar2006Dokument8 SeitenDmm1 Mar2006prk74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machine Element ProblemsDokument2 SeitenDesign of Machine Element Problemsmaxpayne5550% (1)
- Assignment 1Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 1Pawan Kumar GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME Model QuesDokument3 SeitenDME Model QuesSiva RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME QB All UnitsDokument11 SeitenDME QB All UnitsPrakash ThangavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSD Assignment 2016Dokument4 SeitenMSD Assignment 2016Dev ubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME6503 DME Question PapersDokument27 SeitenME6503 DME Question PapersSaravanan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME2303-Design of Machine ElementsDokument17 SeitenME2303-Design of Machine ElementsSith AnanthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design Elements and AssembliesVon EverandMachine Design Elements and AssembliesBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignVon EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Small Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsVon EverandSmall Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationVon EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionVon EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and Analysis of Car WheelDokument8 SeitenModeling and Analysis of Car WheelAnonymous CUPykm6DZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyp PDFDokument4 SeitenHyp PDFHarsh VardhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 231 Computer Aided Machine DrawingDokument2 SeitenME 231 Computer Aided Machine DrawingsudheeshrsNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS7015 MRF-132DGMRFluid PDFDokument2 SeitenDS7015 MRF-132DGMRFluid PDFSimoes JBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkaline HydrolysisDokument28 SeitenAlkaline Hydrolysissiamak77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Radial Rotating Detonation Engine Driven Bleed Air TurbineDokument9 SeitenRadial Rotating Detonation Engine Driven Bleed Air TurbinenikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimizing The Shape of A Bumper Beam Section Considering Pedestrian ProtectionDokument6 SeitenOptimizing The Shape of A Bumper Beam Section Considering Pedestrian ProtectionnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Stress Evaluation and Analysis in FRP CompositesDokument6 SeitenMicro Stress Evaluation and Analysis in FRP CompositesnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule - STTP Series IIDokument1 SeiteSchedule - STTP Series IInikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule - STTP Series IIDokument1 SeiteSchedule - STTP Series IInikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS7015 MRF-132DGMRFluid PDFDokument2 SeitenDS7015 MRF-132DGMRFluid PDFSimoes JBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Not 0072020 1542020Dokument5 SeitenNot 0072020 1542020achukplyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 584733main - Wings ch4g pgs270 285 PDFDokument16 Seiten584733main - Wings ch4g pgs270 285 PDFnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Pages: 1 Scms School of Engineering and TechnologyDokument1 SeiteTotal Pages: 1 Scms School of Engineering and TechnologynikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- FDP - Aero@TKMCEDokument2 SeitenFDP - Aero@TKMCEnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- QP ScrutinyDokument1 SeiteQP ScrutinynikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordinate Conjunctions and Punctuation ChartDokument1 SeiteCoordinate Conjunctions and Punctuation ChartArman AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of PARTICIPATION: Nikhil Asok NDokument1 SeiteCertificate of PARTICIPATION: Nikhil Asok NnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me304 QPDokument4 SeitenMe304 QPnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Examination Eligibility ReportDokument7 SeitenStudent Examination Eligibility ReportnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate For NIKHIL ASOK N For - Link For CertificateDokument1 SeiteCertificate For NIKHIL ASOK N For - Link For CertificatenikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Civil & Mechanical-2019-Syllabus-Ktustudents - in PDFDokument13 SeitenBasic Civil & Mechanical-2019-Syllabus-Ktustudents - in PDFAjeshSomanPulladNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of PARTICIPATION: Nikhil Asok NDokument1 SeiteCertificate of PARTICIPATION: Nikhil Asok NnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACT EDRMedeso Mesh Settings V170.3Dokument44 SeitenACT EDRMedeso Mesh Settings V170.3JORGE FREJA MACIASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus For S1 and S2 KTUmodified15.06.2016Dokument71 SeitenSyllabus For S1 and S2 KTUmodified15.06.2016sreedeepuNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.tech (Evening) Curriculum MEDokument8 SeitenB.tech (Evening) Curriculum MEnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me304 SchemeDokument4 SeitenMe304 SchemenikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rult SCMDokument34 SeitenRult SCMnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me206 - Ak PDFDokument4 SeitenMe206 - Ak PDFnikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me304 SchemeDokument4 SeitenMe304 SchemenikhilasoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semester 1 Assessment 2009 436-431 Mechanics 4 Unit2 DynamicsDokument4 SeitenSemester 1 Assessment 2009 436-431 Mechanics 4 Unit2 DynamicsSon TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Induction Cookers WorkDokument2 SeitenHow Induction Cookers WorkKryzler Kaye100% (1)
- Changes Around Us Science - Class-ViDokument28 SeitenChanges Around Us Science - Class-ViAmit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Applied Dynamics Revised PrintingDokument1 SeiteFundamentals of Applied Dynamics Revised PrintingMochamad Safarudin0% (3)
- Physics Chapter 11Dokument18 SeitenPhysics Chapter 11cryptachrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Final Notes UsydDokument5 SeitenChem Final Notes UsydRobs0% (1)
- Transducers Instrumentation: Second EditionDokument11 SeitenTransducers Instrumentation: Second EditionkrlalitNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Circuits PDFDokument34 SeitenE Circuits PDFFishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dino Tego Cera and Rano SetsDokument2 SeitenDino Tego Cera and Rano Setsthanh nhan dinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Planar Laser-Induced FlourescenceDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To Planar Laser-Induced FlourescencegaccioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friedmann Equations: Assumptions Equations Density Parameter Useful SolutionsDokument8 SeitenFriedmann Equations: Assumptions Equations Density Parameter Useful SolutionsEdwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 1: Different Forms of EM WavesDokument25 SeitenScience: Quarter 2 - Module 1: Different Forms of EM WavesMercy Mangaoil100% (3)
- Analysis of Stripline-Fed Slot-Coupled Patch Antennas With Vias For Parallel-Plate Mode SuppressionDokument8 SeitenAnalysis of Stripline-Fed Slot-Coupled Patch Antennas With Vias For Parallel-Plate Mode SuppressionnaranjitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CGPISL Arrester Presentation HVPNDokument88 SeitenCGPISL Arrester Presentation HVPNAnonymous 42LkomNoch keine Bewertungen
- IpcDokument3 SeitenIpcJigna PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIM Metrology SchoolDokument56 SeitenSIM Metrology SchoolDaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- AstronomyDokument1 SeiteAstronomyHITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science 1978 Rao 271 82Dokument13 SeitenJournal of Mechanical Engineering Science 1978 Rao 271 82mehtabpathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium Worksheet 2Dokument9 SeitenEquilibrium Worksheet 2haileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production of High Porosity Metal Foams Using E 2012 Materials Science and EDokument6 SeitenProduction of High Porosity Metal Foams Using E 2012 Materials Science and Ejmaurício_161194Noch keine Bewertungen
- Study On The Semiconducting PropertiesDokument155 SeitenStudy On The Semiconducting Propertiespadidela swarochishraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 267: Advanced Thermodynamics I: Thermodynamic RelationsDokument73 SeitenME 267: Advanced Thermodynamics I: Thermodynamic Relationsluzviminda ramosNoch keine Bewertungen
- SurgeProtectionforACMachinery PrintDokument8 SeitenSurgeProtectionforACMachinery PrintAldy R OpccNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.6 Scope of Physical ScienceDokument9 Seiten1.6 Scope of Physical ScienceJulius Macaballug100% (1)
- ME 121: Engineering MechanicsDokument45 SeitenME 121: Engineering MechanicsMuhammad FahadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of Electronic MaterialsDokument359 SeitenChemistry of Electronic MaterialsAna TomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 106資優特訓班Dokument96 Seiten106資優特訓班utaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light and Architectural Lighting SystemsDokument17 SeitenLight and Architectural Lighting SystemsCrystal Kaye CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Frequency For The Operating CaseDokument1 SeiteNatural Frequency For The Operating CaseHajaMideenNoch keine Bewertungen